利用java8新特性,可以用简洁高效的代码来实现一些数据处理。
定义1个Apple对象:
public class Apple { private Integer id; private String name; private BigDecimal money; private Integer num; public Apple(Integer id, String name, BigDecimal money, Integer num) { this.id = id; this.name = name; this.money = money; this.num = num; } ... //省略getse和toString 方法 }
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { List<Apple> appleList = new ArrayList<>();//存放apple对象集合 get(appleList); //List 以ID分组 Map<Integer,List<Apple>> Map<Integer, List<Apple>> groupBy = appleList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Apple::getId)); System.err.println("groupBy:"+groupBy); //groupBy:{1=[Apple [id=1, name=苹果1, money=3.25, num=10], Apple [id=1, name=苹果2, money=1.35, num=20]], 2=[Apple [id=2, name=香蕉, money=2.89, num=30]], 3=[Apple [id=3, name=荔枝, money=9.99, num=40]]} /** * List -> Map * 需要注意的是: * toMap 如果集合对象有重复的key,会报错Duplicate key .... * apple1,apple12的id都为1。 * 可以用 (k1,k2)->k1 来设置,如果有重复的key,则保留key1,舍弃key2 */ Map<Integer, Apple> appleMap = appleList.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(Apple::getId, a -> a,(k1,k2)->k1)); System.out.println(appleMap.toString()); // {1=Apple [id=1, name=苹果1, money=3.25, num=10], 2=Apple [id=2, name=香蕉, money=2.89, num=30], 3=Apple [id=3, name=荔枝, money=9.99, num=40]} //过滤出符合条件的数据 List<Apple> filterList = appleList.stream().filter(a -> a.getName().equals("香蕉")).collect(Collectors.toList()); System.err.println("filterList:"+filterList); // filterList:[Apple [id=2, name=香蕉, money=2.89, num=30]] //计算 总金额 BigDecimal totalMoney = appleList.stream().map(Apple::getMoney).reduce(BigDecimal.ZERO, BigDecimal::add); System.err.println("totalMoney:"+totalMoney); // totalMoney:17.48 } public static void get(List<Apple> appleList){ Apple apple1 = new Apple(1,"苹果1",new BigDecimal("3.25"),10); Apple apple12 = new Apple(1,"苹果2",new BigDecimal("1.35"),20); Apple apple2 = new Apple(2,"香蕉",new BigDecimal("2.89"),30); Apple apple3 = new Apple(3,"荔枝",new BigDecimal("9.99"),40); appleList.add(apple1); appleList.add(apple12); appleList.add(apple2); appleList.add(apple3); } }
5、查找流中最大 最小值
Collectors.maxBy 和 Collectors.minBy 来计算流中的最大或最小值。
Optional<Dish> maxDish = Dish.menu.stream().collect(Collectors.maxBy(Comparator.comparing(Dish::getCalories))); maxDish.ifPresent(System.out::println); Optional<Dish> minDish = Dish.menu.stream().collect(Collectors.minBy(Comparator.comparing(Dish::getCalories))); minDish.ifPresent(System.out::println);
6、去重
import static java.util.Comparator.comparingLong; import static java.util.stream.Collectors.collectingAndThen; import static java.util.stream.Collectors.toCollection; // 根据id去重 // 根据id去重 List<Apple> unique = appleList.stream().collect( collectingAndThen(toCollection(() -> new TreeSet<>(comparingLong(Apple::getId))), ArrayList::new) ); System.out.println(unique); // [Apple [id=1, name=苹果1, money=3.25, num=10], Apple [id=2, name=香蕉, money=2.89, num=30], Apple [id=3, name=荔枝, money=9.99, num=40]]
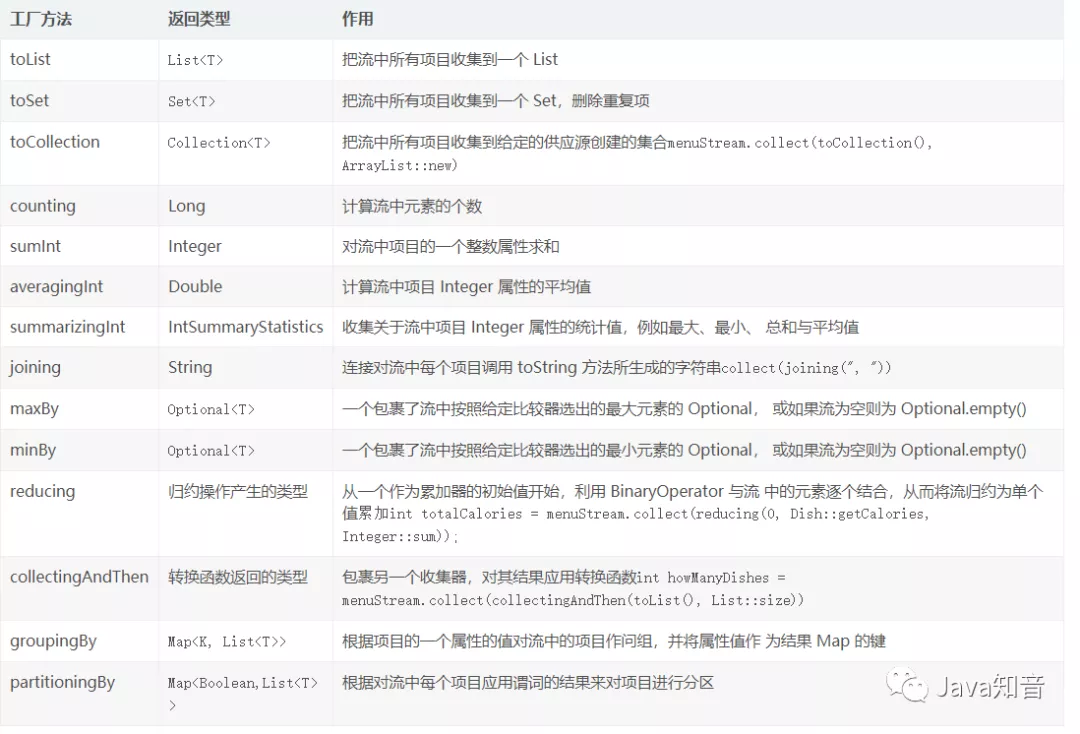
下表展示 Collectors 类的静态工厂方法。