注解与反射
注解与反射
1. 注解
1.1 内置注解
@SuppressWarnings("all") String name;
1.2 元注解
-
负责解释其他注解
-
@Target:表示注解可以用在哪些地方(class,method...)
-
@Retention:表示注解在什么地方有效。
runtime>class>sources
-
@Documented:表示是否将我们的注解生成在javadoc中
-
@Inherited:表示子类可以继承父类
package demo01; import java.lang.annotation.*; //元注解 public class AnnotationDemo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { } @MyAnnotation public void test(){ } } //定义注解 @Target(value = {ElementType.METHOD,ElementType.TYPE}) @Retention(value = RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Inherited @interface MyAnnotation{ }
1.3 自定义注解
package demo01; import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; import java.lang.annotation.Target; public class AnnotationDemo02 { //@MyAnnotation2(name = "quinn") @MyAnnotation2() public void test(){ } @MyAnnotation3("quinn") public void test2(){ } } @Target({ElementType.TYPE,ElementType.METHOD}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @interface MyAnnotation2{ //注解的参数:参数类型 + 参数名() //String name(); String name() default ""; int age() default 0; int id() default -1;//-1代表不存在 String[] school() default {"清华大学"}; } @Target({ElementType.TYPE,ElementType.METHOD}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @interface MyAnnotation3{ //一个值可以用value命名 String value(); }
2. 反射
2.1 概述
-
动态语言:可以改变类的结构
静态语言:运行时结构不可改变
-
正常方式:引入需要的包类名称 -->通过new实例化 -->取得实例化对象
反射方式:实例化对象 -->getClass()方法 -->得到完整的包类信息
-
优点:可以实现动态创建对象,体现很大的灵活性
缺点:对性能有影响
2.2 获得反射对象
package reflection.demo01; public class ReflectionDemo01 { public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException { //通过反射获取类的class对象 Class c1 = Class.forName("reflection.demo01.Student"); System.out.println(c1); //一个类在内存中只有一个class对象 //一个类被加载之后,类的整个结构都会被封装在class对象中 Class c2 = Class.forName("reflection.demo01.Student"); Class c3 = Class.forName("reflection.demo01.Student"); Class c4 = Class.forName("reflection.demo01.Student"); System.out.println(c2.hashCode()); System.out.println(c3.hashCode()); System.out.println(c4.hashCode()); } } //实体类:pojo,entity class Student{ private int id; private int sge; private String name; public Student() { } public Student(int id, int sge, String name) { this.id = id; this.sge = sge; this.name = name; } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public int getSge() { return sge; } public void setSge(int sge) { this.sge = sge; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } @Override public String toString() { return "Student{" + "id=" + id + ", sge=" + sge + ", name='" + name + '\'' + '}'; } }
2.3 得到Class类的方法
package reflection.demo01; public class ReflectionDemo02 { public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException { Person student = new Student(); System.out.println("这个是:"+student.name); //1. 通过对象获得 Class c1 = student.getClass(); System.out.println(c1.hashCode()); //2. forName() Class c2 = Class.forName("reflection.demo01.Student"); System.out.println(c2.hashCode()); //3. 通过类名.class获得 Class c3 = Student.class; System.out.println(c3.hashCode()); //4. 通过包装类的TYPE属性获得 Class c4 = Integer.TYPE; System.out.println(c4.hashCode()); //获得父类类型 Class c5 = c1.getSuperclass(); System.out.println(c5.hashCode()); } } class Person{ String name; public Person() { } public Person(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } @Override public String toString() { return "Person{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + '}'; } } class Student extends Person{ public Student() { this.name = "学生"; } } class Teacher extends Person{ public Teacher() { this.name = "老师"; } }
2.4 类加载内存分析
package reflection.demo02; public class Test01 { public static void main(String[] args) { A a = new A(); System.out.println(a.m); } } class A{ static { System.out.println("这是A类静态代码块"); m = 300; } static int m = 100; public A(){ System.out.println("A类无参构造初始化"); } }
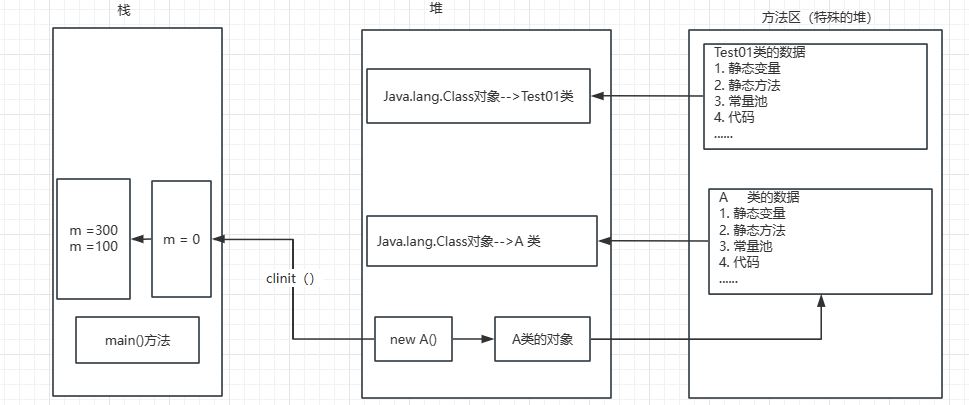
2.5 类加载器
package reflection.demo03; public class ReflectionDemo01 { public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException { //获得系统类的加载器 ClassLoader loader = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader(); System.out.println(loader); //获得系统类加载器的父类加载器-->扩展类加载器 ClassLoader parent = loader.getParent(); System.out.println(parent); //获得扩展类加载器的父类加载器-->跟加载器(c/c++) ClassLoader parent1 = parent.getParent(); System.out.println(parent1); //获得当前类的加载器 ClassLoader classLoader = Class.forName("reflection.demo03.ReflectionDemo01").getClassLoader(); System.out.println(classLoader); //jdk内置的类加载器 ClassLoader classLoader1 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getClassLoader(); System.out.println(classLoader1); } }
2.6 类的运行时结构
package reflection.demo03; import java.lang.reflect.Constructor; import java.lang.reflect.Field; import java.lang.reflect.Method; public class ReflectionDemo02 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Class c1 = Class.forName("reflection.demo01.Student1"); System.out.println(c1.getName());//获得包名+类名 System.out.println(c1.getSimpleName());//获得类名 System.out.println("=========================="); //获得类的属性 Field[] fields = c1.getFields(); for (Field field : fields) { System.out.println(field);//只能获得public属性 } fields = c1.getDeclaredFields(); for (Field field : fields) { System.out.println(field); } System.out.println("=========================="); //获得当前属性的值 Field name = c1.getDeclaredField("name"); System.out.println(name); System.out.println("=========================="); //获得类的方法 Method[] methods = c1.getMethods();//获得本类及其父类全部public方法 for (Method method : methods) { System.out.println(method); } System.out.println("=========================="); methods = c1.getDeclaredMethods();//获得本类的所有方法 for (Method method : methods) { System.out.println(method); } System.out.println("=========================="); //获得指定方法 Method getName = c1.getMethod("getName", null); Method setName = c1.getMethod("setName", String.class); System.out.println(getName); System.out.println(setName); System.out.println("=========================="); //获得指定的构造器 Constructor[] cs = c1.getConstructors(); for (Constructor c : cs) { System.out.println(c); } cs = c1.getDeclaredConstructors(); for (Constructor c : cs) { System.out.println(c); } System.out.println("=========================="); } }
2.7 动态创建对象
package reflection.demo03; import java.lang.reflect.Constructor; import java.lang.reflect.Field; import java.lang.reflect.Method; public class ReflectionDemo03 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Class c1 = Class.forName("reflection.demo03.Student1"); //通过无参构造 Student1 o = (Student1) c1.newInstance(); System.out.println(o); System.out.println("=========================="); //通过构造器创建对象 Constructor constructor = c1.getDeclaredConstructor(int.class, int.class, String.class); Student1 s2 = (Student1) constructor.newInstance(1, 12, "quinn"); System.out.println(s2); System.out.println("=========================="); //通过反射调用普通方法 Student1 s3 = (Student1) c1.newInstance(); Method setName = c1.getDeclaredMethod("setName", String.class); setName.invoke(s3,"quinn");//激活 System.out.println(s3.getName()); System.out.println("=========================="); //通过反射操作属性 Student1 s4 = (Student1) c1.newInstance(); Field name = c1.getDeclaredField("name"); //关闭安全检测检测,操作private属性 name.setAccessible(true); name.set(s4,"morita"); System.out.println(s4.getName()); } }
2.8 操作泛型
package reflection.demo03; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.lang.reflect.ParameterizedType; import java.lang.reflect.Type; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; public class ReflectionDemo04 { public void test1(Map<String,Student1> map, List<Student1> list){ System.out.println("test1"); } public Map<String,Student1> test2(){ System.out.println("test2"); return null; } public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException { Method m1 = ReflectionDemo04.class.getMethod("test1", Map.class, List.class); //获得泛型参数类型 Type[] t1 = m1.getGenericParameterTypes(); for (Type type : t1) { System.out.println("##"+type); //是否是一种参数化类型 if (type instanceof ParameterizedType){ //获得真实参数信息 Type[] types = ((ParameterizedType) type).getActualTypeArguments(); for (Type type1 : types) { System.out.println(type1); } } } System.out.println("======================"); Method m2 = ReflectionDemo04.class.getMethod("test2",null); //获得返回参数类型 Type returnType = m2.getGenericReturnType(); if (returnType instanceof ParameterizedType){ Type[] typeTemp = ((ParameterizedType) returnType).getActualTypeArguments(); for (Type type : typeTemp) { System.out.println(type); } } } }
2.9 获取注解信息
package reflection.demo03; import java.lang.annotation.*; import java.lang.reflect.Field; //反射操作注解 public class ReflectionDemo05 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Class<?> c1 = Class.forName("reflection.demo03.User"); //通过反射获得注解 Annotation[] annotations = c1.getAnnotations(); for (Annotation annotation : annotations) { System.out.println(annotation); } //获得注解value的值 TableQuinn table = c1.getAnnotation(TableQuinn.class); System.out.println(table.value()); //获得类指定的注解的值 Field field = c1.getDeclaredField("id"); FiledQuinn filedQuinn = field.getAnnotation(FiledQuinn.class); System.out.println(filedQuinn.colName()); System.out.println(filedQuinn.type()); System.out.println(filedQuinn.len()); } } @TableQuinn("db_user") class User{ @FiledQuinn(colName = "db_id",type = "int",len = 10) private int id; @FiledQuinn(colName = "db_age",type = "int",len = 10) private int age; @FiledQuinn(colName = "db_name",type = "varchar",len = 3) private String name; public User(int id, int age, String name) { this.id = id; this.age = age; this.name = name; } public User() { } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } @Override public String toString() { return "User{" + "id=" + id + ", age=" + age + ", name='" + name + '\'' + '}'; } } //类名注解 @Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @interface TableQuinn{ String value(); } //属性注解 @Target(ElementType.FIELD) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @interface FiledQuinn{ String colName(); String type(); int len(); }
本文作者:Quinn
本文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/yqquinn/p/17629410.html
版权声明:本作品采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 2.5 中国大陆许可协议进行许可。





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步