Java8的新特性与案例解析&stream流使用场景[转]
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44107140/article/details/129721852
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_35754962/article/details/129076624
https://blog.csdn.net/The_clown/article/details/113339283
package top.irun2u.test;
import java.time.*;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Optional;
import java.util.OptionalInt;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
/**
* @Author: haifei
* @Date: 2023/9/13 16:18
*/
public class J8Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
newDateTime();
newStream();
lambdaSort();
lambdaThread();
}
public static void newDateTime() {
System.out.println(LocalDate.now());
System.out.println(LocalTime.now());
System.out.println(LocalDateTime.now());
System.out.println(Instant.now()); //时间戳
// LocalDateTime dateTime1 = LocalDateTime.of(2021, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0);
// LocalDateTime dateTime2 = LocalDateTime.now();
// Duration duration = Duration.between(dateTime1, dateTime2);
// System.out.println("时间间隔: " + duration);
//
// LocalDate date1 = LocalDate.of(2021, 1, 1);
// LocalDate date2 = LocalDate.now();
// Period period = Period.between(date1, date2);
// System.out.println("日期间隔: " + period);
}
public static void newStream() {
//1.过滤
List<String> names = Arrays.asList("Tom", "Jerry", "Alice", "Bob", "Jack");
List<String> result = names.stream().filter(name -> name.startsWith("J")).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(result); // 输出 [Jerry, Jack]
//2.映射
List<Integer> nums = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
List<Integer> squares = nums.stream().map(num -> num * num).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(squares); // 输出 [1, 4, 9, 16, 25]
//3.排序
List<String> names2 = Arrays.asList("Tom", "Jerry", "Alice", "Bob", "Jack");
List<String> result2 = names2.stream().sorted().collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(result2); // 输出 [Alice, Bob, Jack, Jerry, Tom]
//4.统计
List<Integer> nums2 = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
long count = nums2.stream().count();
int sum = nums2.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).sum();
OptionalInt max = nums2.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).max();
System.out.println("count: " + count + ", sum: " + sum + ", max: " + max.getAsInt());
// 输出 count: 5, sum: 15, max: 5
//5.匹配
List<Integer> nums3 = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
boolean allMatch = nums3.stream().allMatch(num -> num > 0);
boolean anyMatch = nums3.stream().anyMatch(num -> num > 3);
boolean noneMatch = nums3.stream().noneMatch(num -> num > 5);
System.out.println("allMatch: " + allMatch + ", anyMatch: " + anyMatch + ", noneMatch: " + noneMatch);
// 输出 allMatch: true, anyMatch: true, noneMatch: true
//6.规约
List<Integer> nums4 = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
int sum4 = nums4.stream().reduce(0, (acc, num) -> acc + num);
Optional<Integer> product = nums4.stream().reduce((acc, num) -> acc * num);
System.out.println("sum: " + sum4 + ", product: " + product.orElse(0));
// 输出 sum: 15, product: 120
}
public static void lambdaSort() {
List<Integer> numbers = Arrays.asList(3, 1, 4, 1, 5, 9, 2, 6, 5, 3, 5);
List<Integer> sortedNumbers = numbers
.stream()
.sorted((a, b) -> a.compareTo(b))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(sortedNumbers);
// [1, 1, 2, 3, 3, 4, 5, 5, 5, 6, 9]
}
public static void lambdaThread() {
Runnable task = () -> {
System.out.println("Hello, world!");
};
new Thread(task).start();
//Hello, world!
}
}
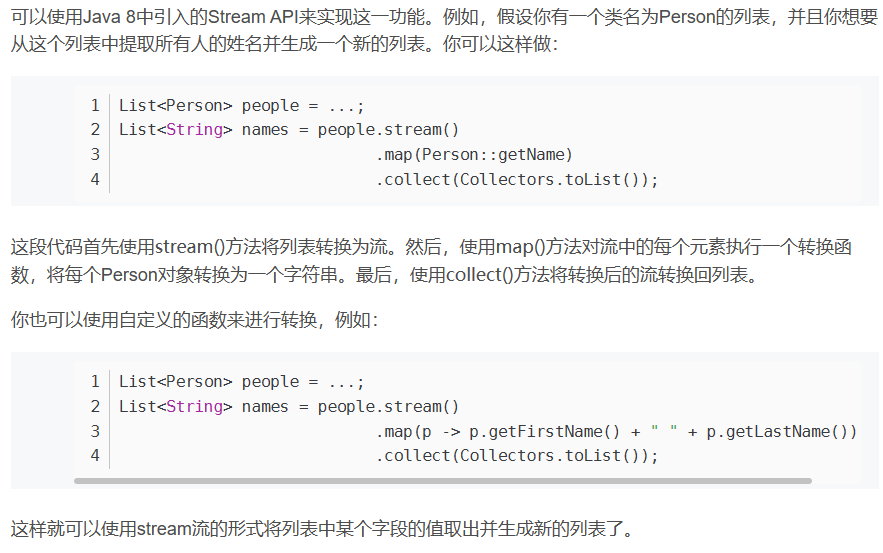
对象列表抽取属性成新的列表
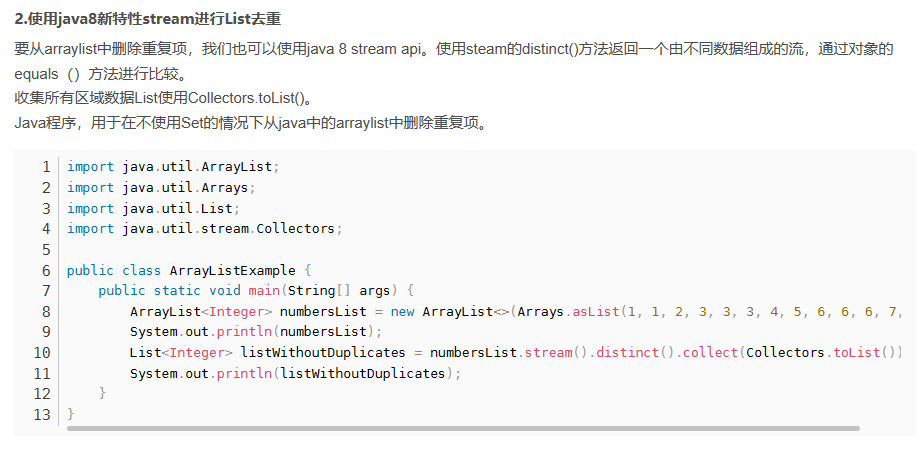
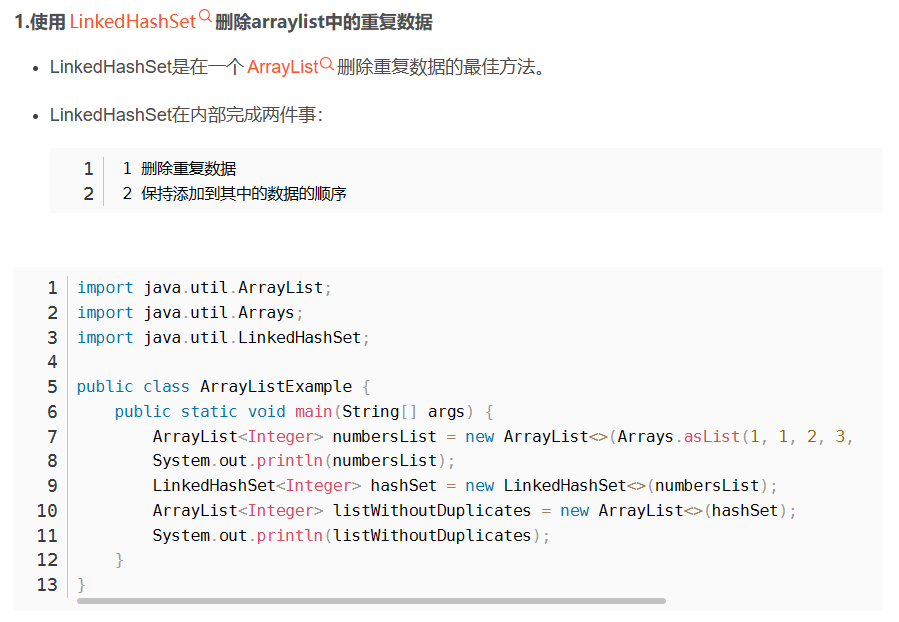
arrayList去重