HM-SpringCloud微服务系列9.3.2【实践:TCC模式、SAGA模式】
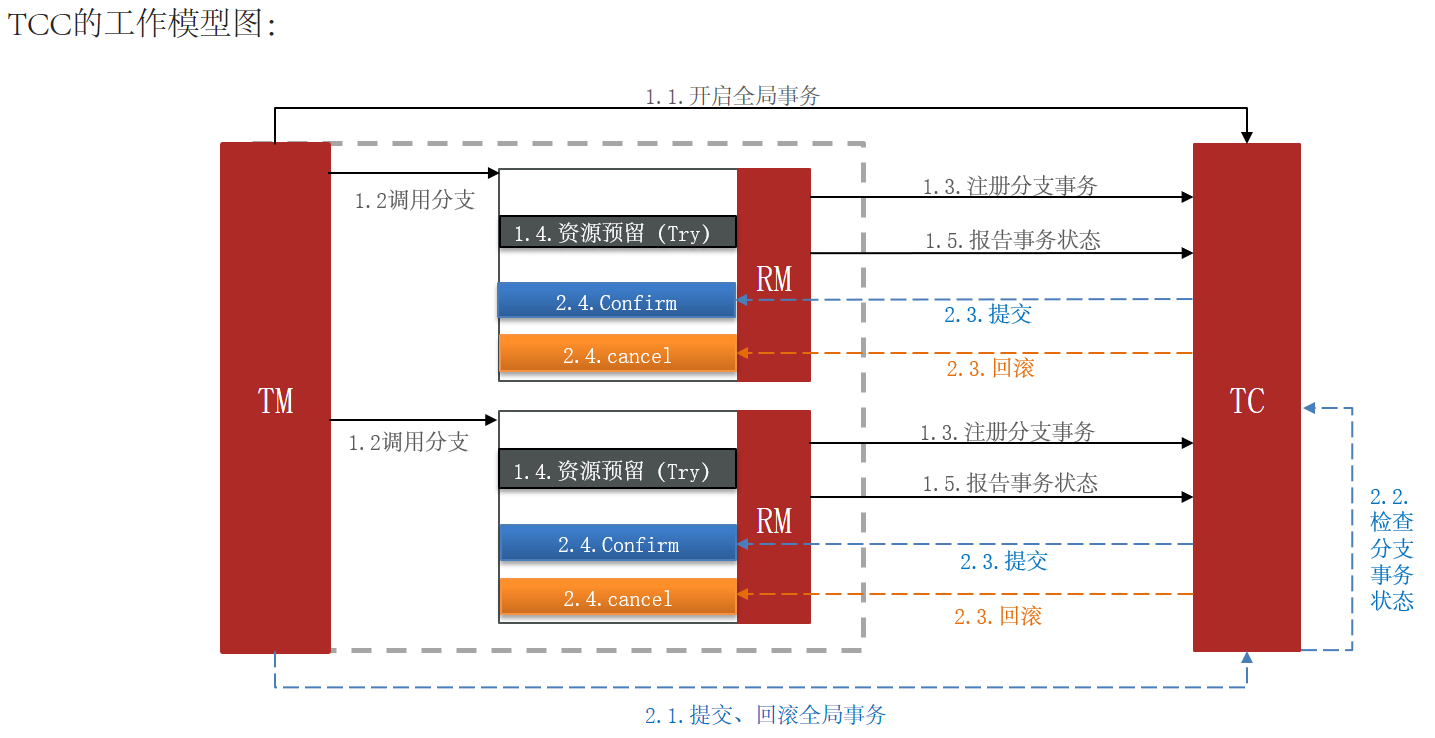
3. TCC模式
3.1 原理
TCC模式与AT模式非常相似,每阶段都是独立事务,不同的是TCC通过人工编码来实现数据恢复。需要实现三个方法:
- Try:资源的检测和预留;
- Confirm:完成资源操作业务;要求 Try 成功 Confirm 一定要能成功。
- Cancel:预留资源释放,可以理解为try的反向操作。
举例,一个扣减用户余额的业务。假设账户A原来余额是100,需要余额扣减30元。




3.2 TCC的优缺点
- TCC模式的每个阶段是做什么的?
- Try:资源检查和预留
- Confirm:业务执行和提交
- Cancel:预留资源的释放
- TCC的优点是什么?
- 一阶段完成直接提交事务,释放数据库资源,性能好
- 相比AT模型,无需生成快照,无需使用全局锁,性能最强
- 不依赖数据库事务,而是依赖补偿操作,可以用于非事务型数据库(比如可以将非事务的redis做成TCC模式的分布式事务)
- TCC的缺点是什么?
- 有代码侵入,需要人为编写try、Confirm和Cancel接口,太麻烦
- 软状态,事务是最终一致
- 需要考虑Confirm和Cancel的失败情况,做好幂等处理(即考虑好接口健壮性)
3.2 利用TCC实现分布式事务
3.2.1 案例说明

幂等性:对于某接口,调用1次和调用多次的效果是一致的,不会因为重复调用而出问题
3.2.2 TCC的问题:空回滚和业务悬挂
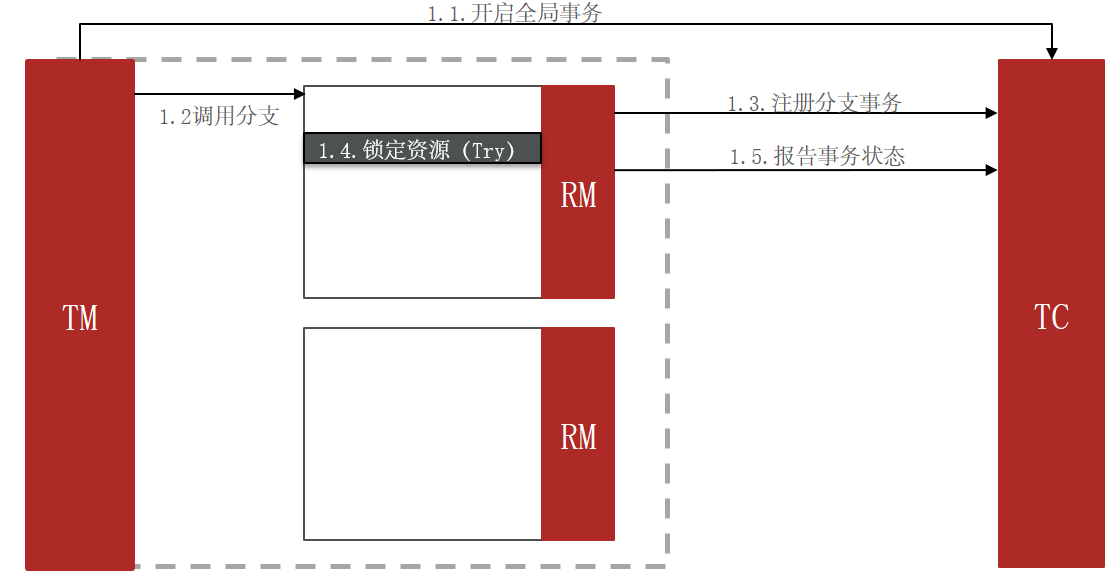
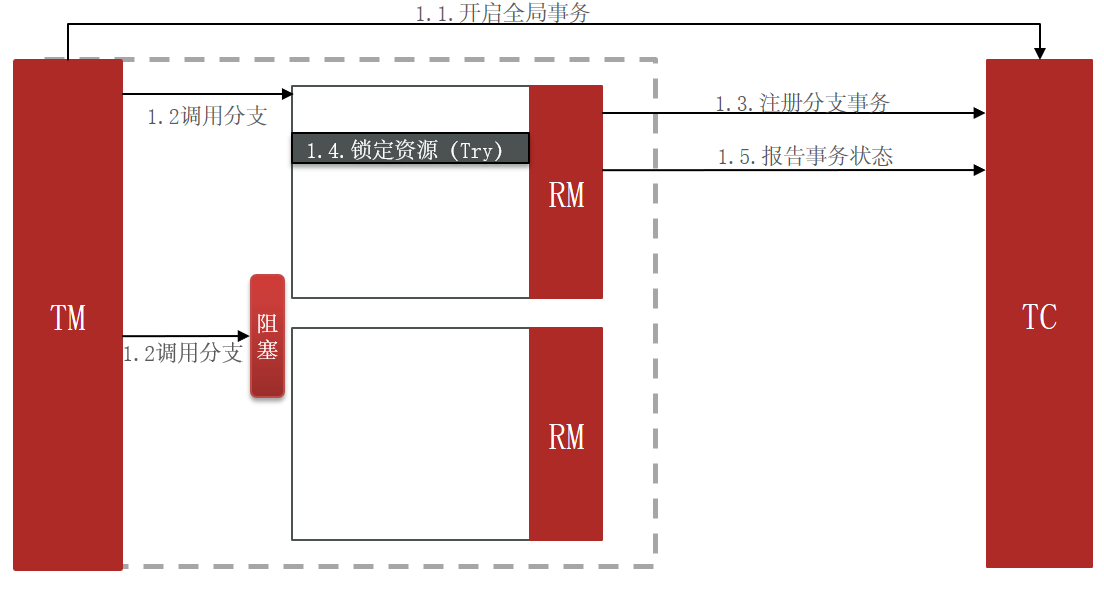
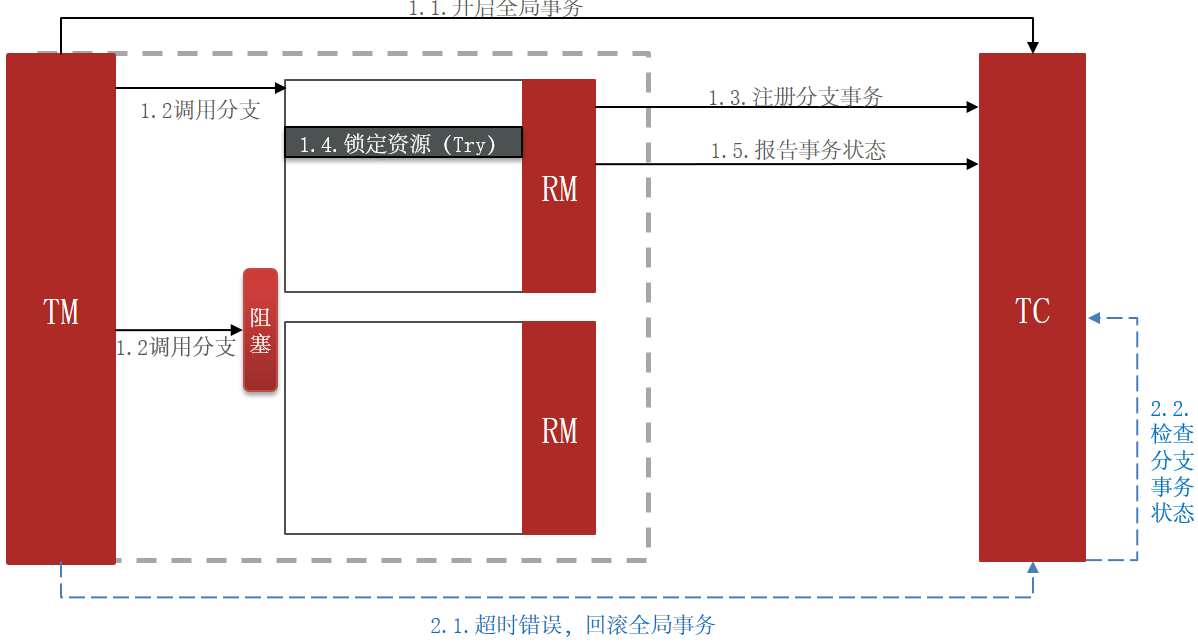
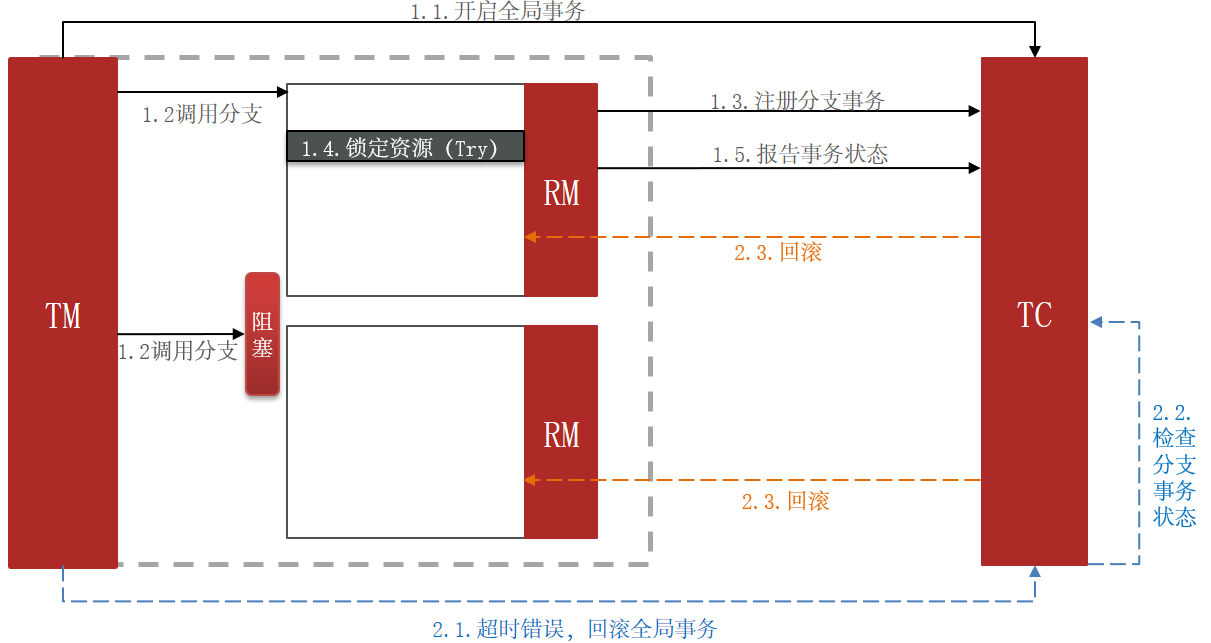
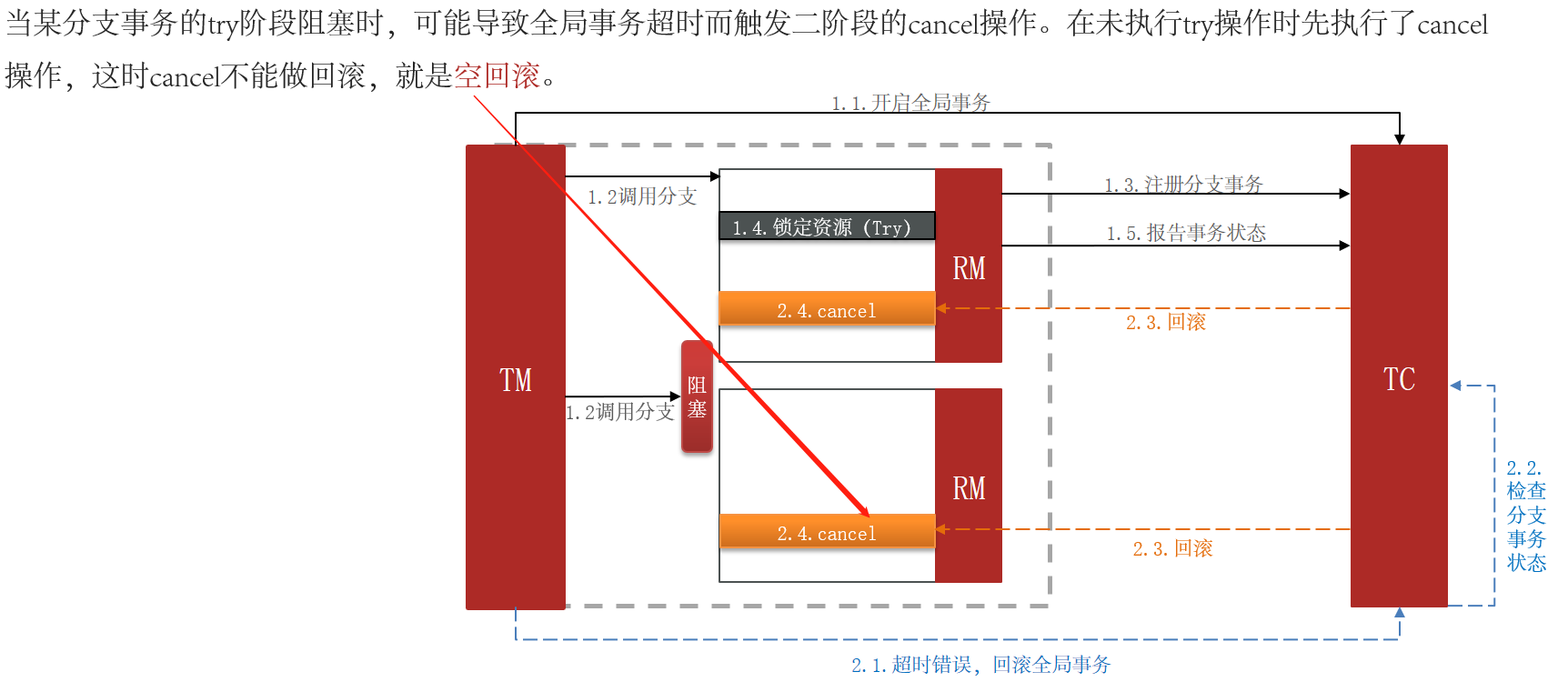
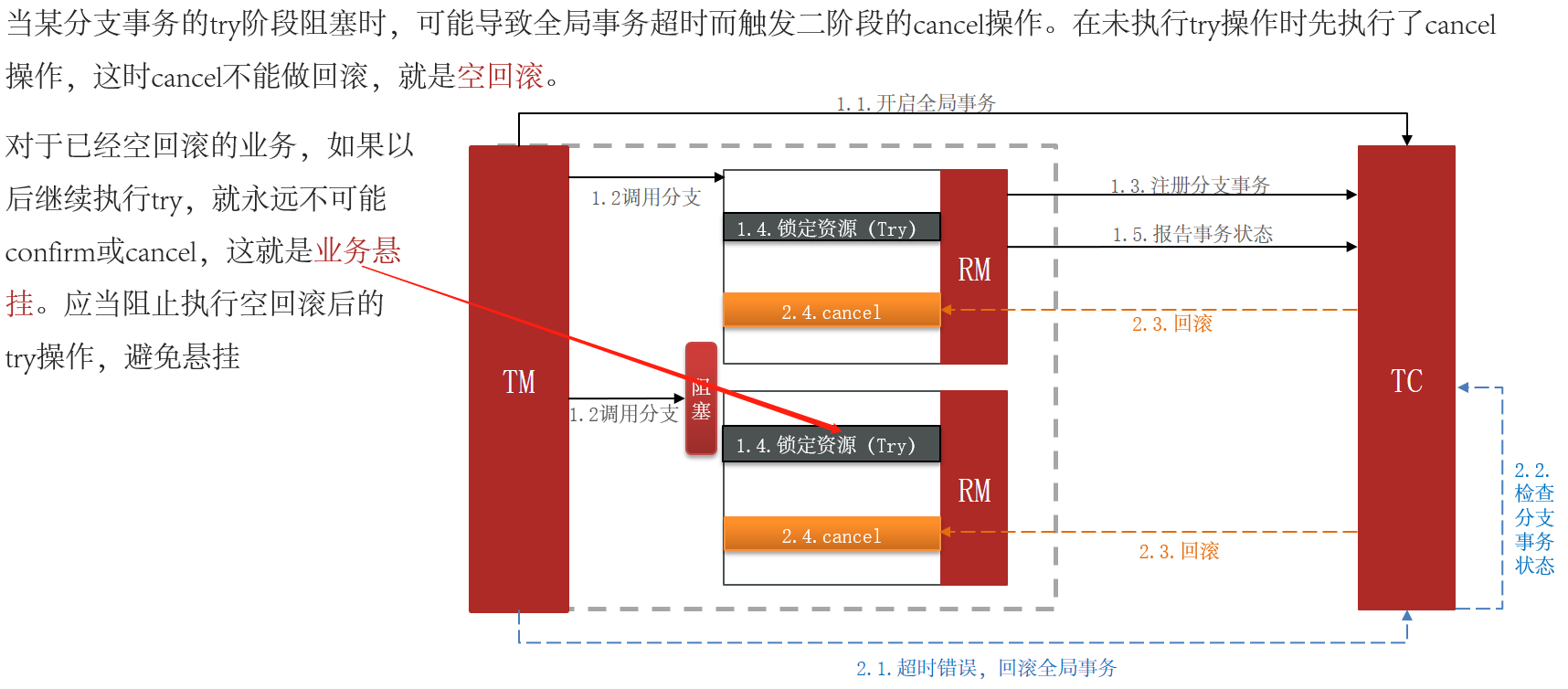
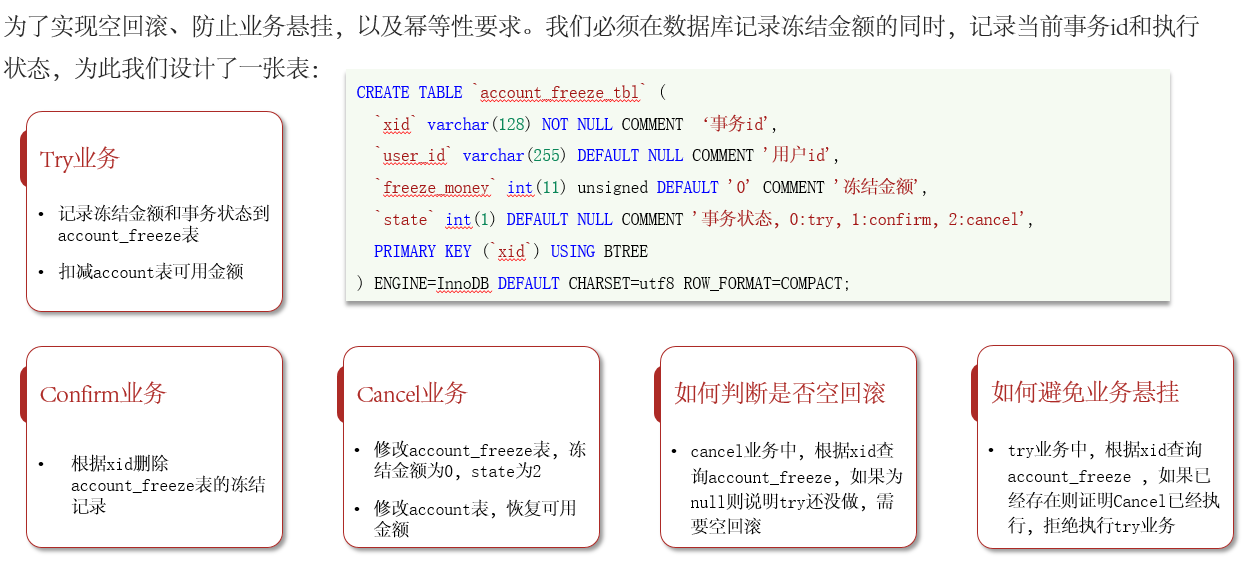
3.2.3 实现TCC模式
一、案例业务分析
二、声明TCC接口

三、实现
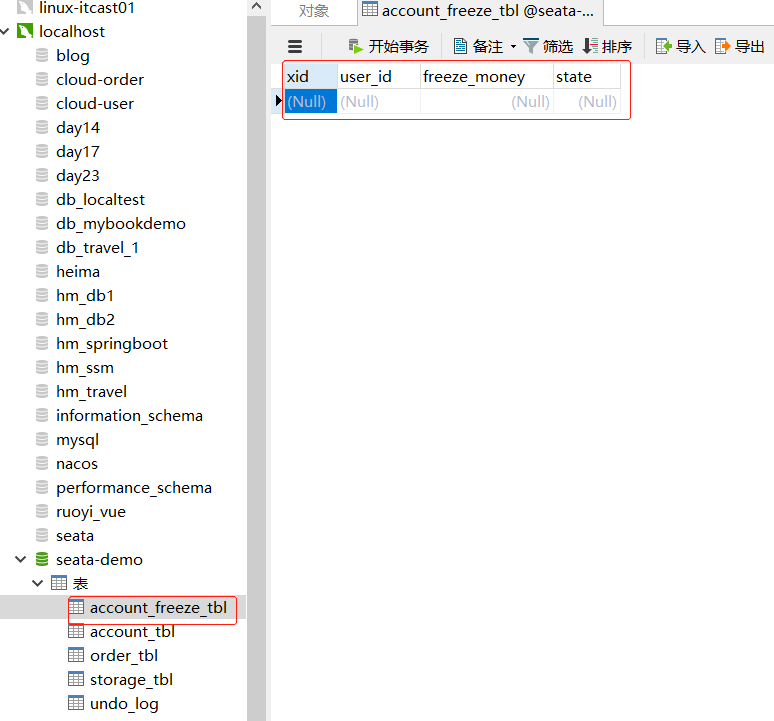
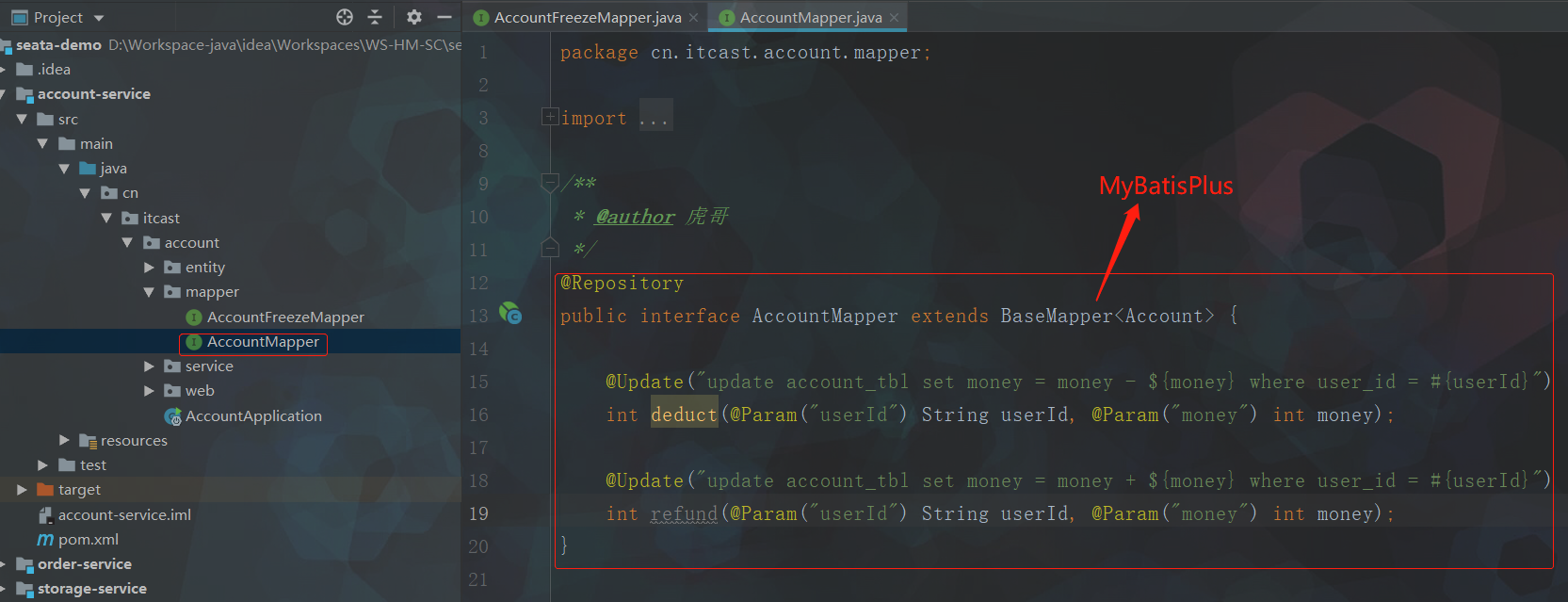
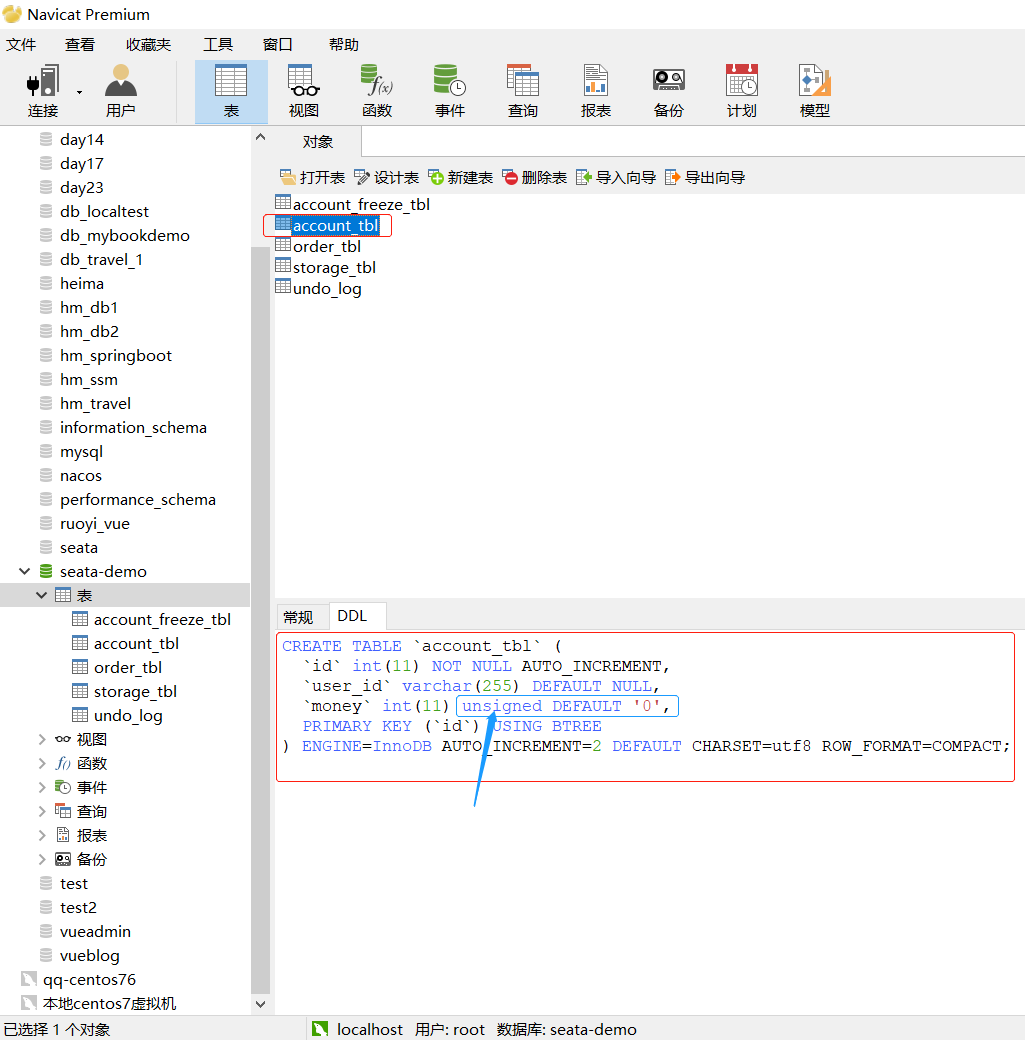
此处可以看到账户表在设计之处就将money字段设置为无符号格式,默认为0,即不可能有负数(如果扣减过程中将其扣为了负数,再回直接报错,事务自动回滚)。
所以下面业务代码中可以省略余额判断,直接尝试扣减可用余额,因为如果扣减过程中发现余额不足则会直接报错,不会执行之后的逻辑;余额充足时才会执行之后逻辑。
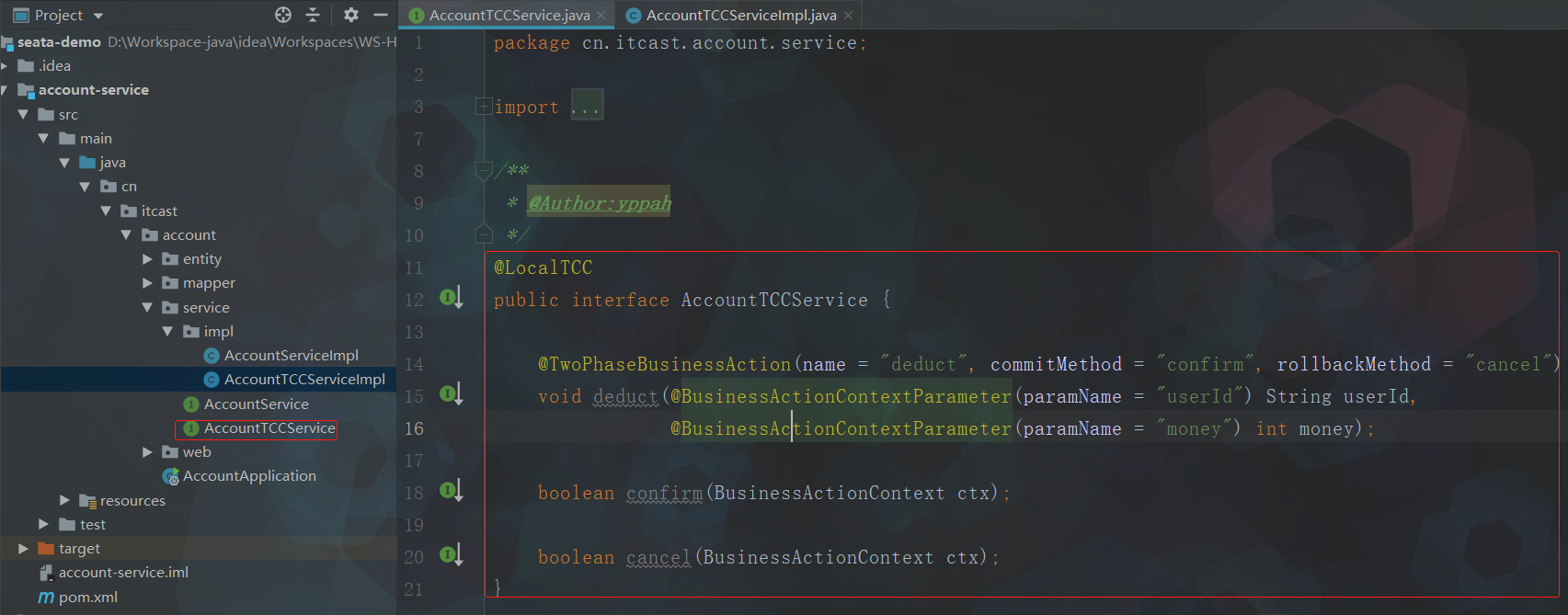
点击查看代码
package cn.itcast.account.service;
import io.seata.rm.tcc.api.BusinessActionContext;
import io.seata.rm.tcc.api.BusinessActionContextParameter;
import io.seata.rm.tcc.api.LocalTCC;
import io.seata.rm.tcc.api.TwoPhaseBusinessAction;
/**
* @Author:yppah
*/
@LocalTCC
public interface AccountTCCService {
@TwoPhaseBusinessAction(name = "deduct", commitMethod = "confirm", rollbackMethod = "cancel")
void deduct(@BusinessActionContextParameter(paramName = "userId") String userId,
@BusinessActionContextParameter(paramName = "money") int money);
boolean confirm(BusinessActionContext ctx);
boolean cancel(BusinessActionContext ctx);
}
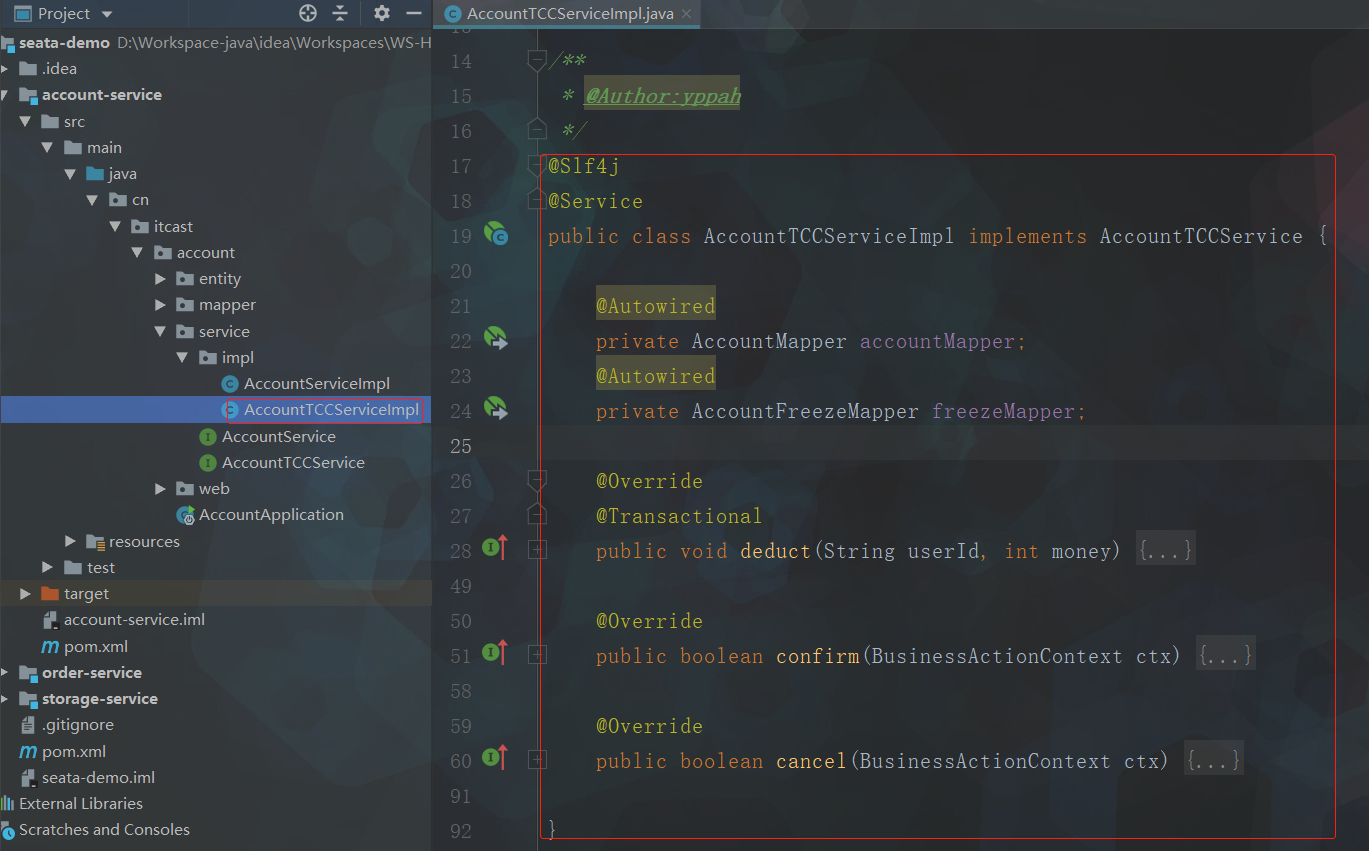
点击查看代码
package cn.itcast.account.service.impl;
import cn.itcast.account.entity.AccountFreeze;
import cn.itcast.account.mapper.AccountFreezeMapper;
import cn.itcast.account.mapper.AccountMapper;
import cn.itcast.account.service.AccountTCCService;
import io.seata.core.context.RootContext;
import io.seata.rm.tcc.api.BusinessActionContext;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
/**
* @Author:yppah
*/
@Slf4j
@Service
public class AccountTCCServiceImpl implements AccountTCCService {
@Autowired
private AccountMapper accountMapper;
@Autowired
private AccountFreezeMapper freezeMapper;
/*@Override
@Transactional
public void deduct(String userId, int money) {
// 0. 获取事务id
String xid = RootContext.getXID();
// 1. 扣减可用余额
accountMapper.deduct(userId, money); // 此处异常时会通过@Transactional触发事务回滚,不会执行下面逻辑
// 2. 记录冻结金额和事务状态
AccountFreeze freeze = new AccountFreeze();
freeze.setUserId(userId);
freeze.setFreezeMoney(money);
freeze.setState(AccountFreeze.State.TRY);
freeze.setXid(xid);
freezeMapper.insert(freeze);
}*/
@Override
@Transactional
public void deduct(String userId, int money) {
// 0. 获取事务id
String xid = RootContext.getXID();
// 避免业务悬挂:判断freeze中是否有冻结记录
AccountFreeze oldFreeze = freezeMapper.selectById(xid);
if (oldFreeze != null) {
// 若有,则一定是执行过CANCEL,要拒绝业务
return;
}
// 1. 扣减可用余额
accountMapper.deduct(userId, money); // 此处异常时会通过@Transactional触发事务回滚,不会执行下面逻辑
// 2. 记录冻结金额和事务状态
AccountFreeze freeze = new AccountFreeze();
freeze.setUserId(userId);
freeze.setFreezeMoney(money);
freeze.setState(AccountFreeze.State.TRY);
freeze.setXid(xid);
freezeMapper.insert(freeze);
}
@Override
public boolean confirm(BusinessActionContext ctx) { // ctx:上下文
// 1. 获取事务id
String xid = ctx.getXid();
// 2. 根据id删除冻结记录
int count = freezeMapper.deleteById(xid);
return count==1;
}
@Override
public boolean cancel(BusinessActionContext ctx) {
// 0. 查询冻结记录
String xid = ctx.getXid();
String userId = ctx.getActionContext("userId").toString();
AccountFreeze freeze = freezeMapper.selectById(xid);
// [1] 空回滚判断:判断freeze是否为null
if (freeze == null) {
// 为null证明try没执行,需要空回滚
freeze = new AccountFreeze();
freeze.setXid(xid);
freeze.setUserId(userId);
freeze.setState(AccountFreeze.State.CANCEL);
freeze.setFreezeMoney(0);
freezeMapper.insert(freeze);
return true;
}
// [2] 幂等判断
if (freeze.getState() == AccountFreeze.State.CANCEL) {
// 已经处理过一次CANCEL了,无需重复处理
return true;
}
// 1. 恢复可用余额
accountMapper.refund(freeze.getUserId(), freeze.getFreezeMoney());
// 2. 将冻结金额清零+状态改为CANCEL
freeze.setFreezeMoney(0);
freeze.setState(AccountFreeze.State.CANCEL);
int count = freezeMapper.updateById(freeze);
return count==1;
}
/*@Override
public boolean cancel(BusinessActionContext ctx) {
// 0. 查询冻结记录
AccountFreeze freeze = freezeMapper.selectById(ctx.getXid());
// 1. 恢复可用余额
accountMapper.refund(freeze.getUserId(), freeze.getFreezeMoney());
// 2. 将冻结金额清零+状态改为CANCEL
freeze.setFreezeMoney(0);
freeze.setState(AccountFreeze.State.CANCEL);
int count = freezeMapper.updateById(freeze);
return count==1;
}*/
}
重启account服务,进行测试
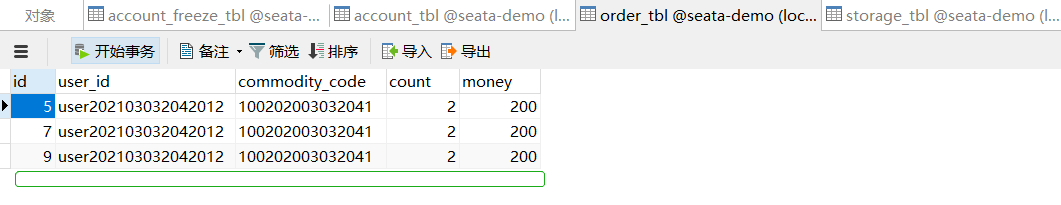
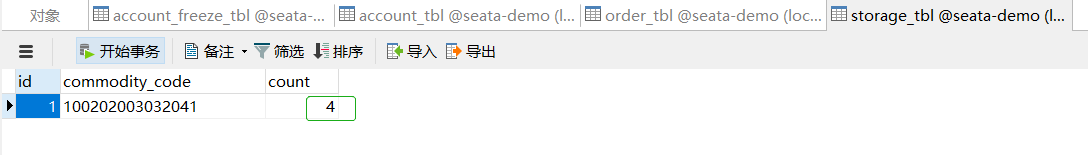
先查看一下原数据库情况
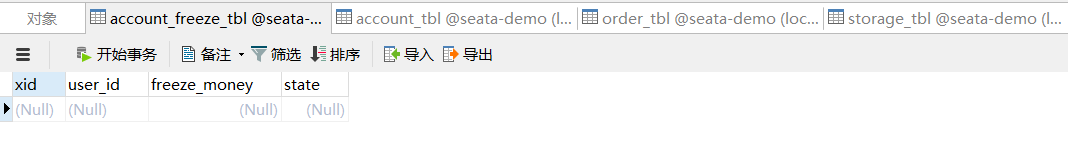
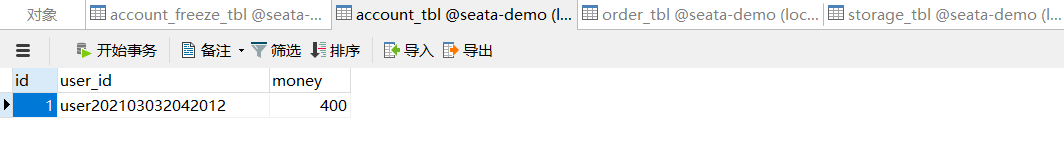
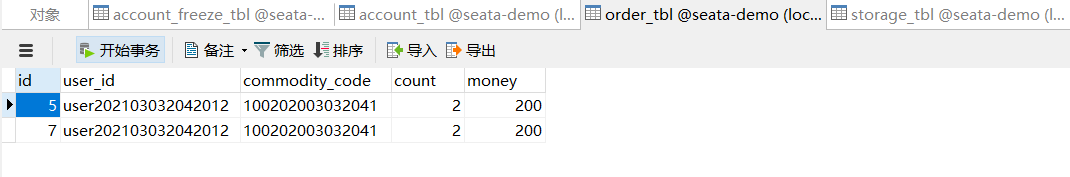
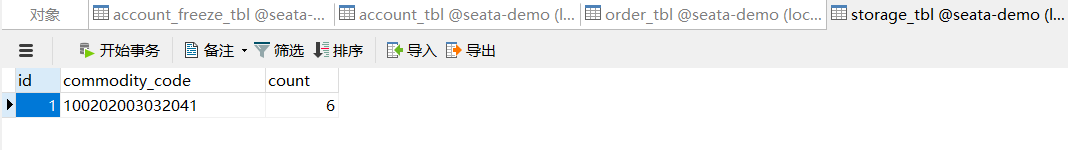
正常请求
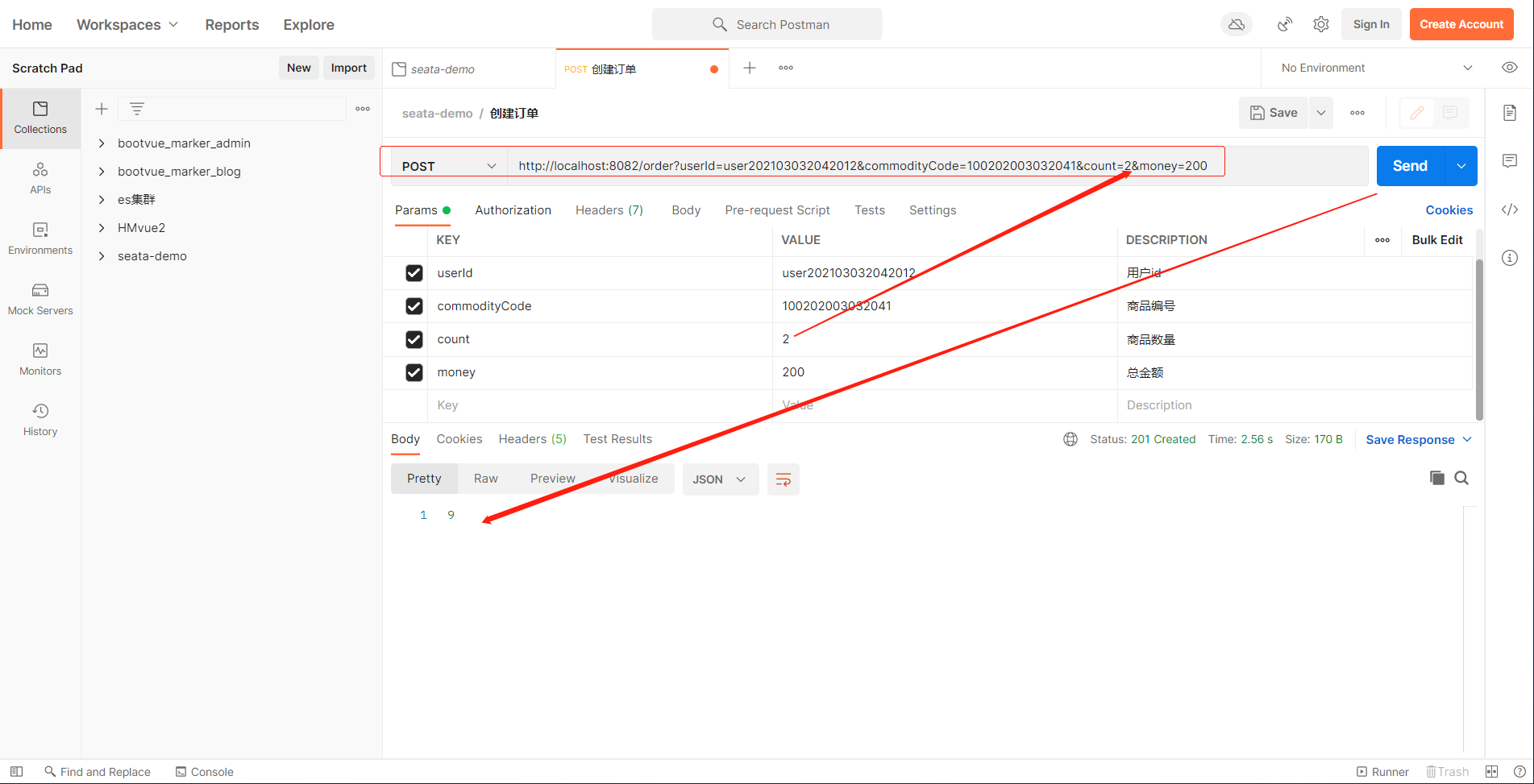
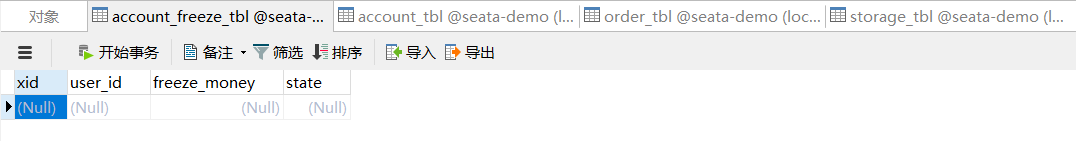
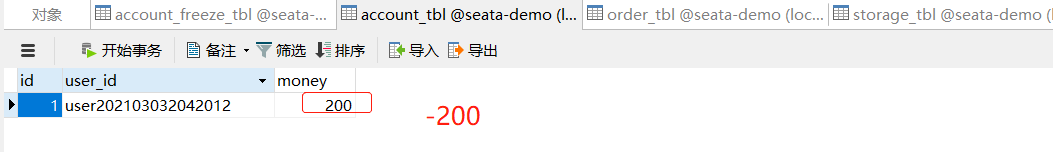
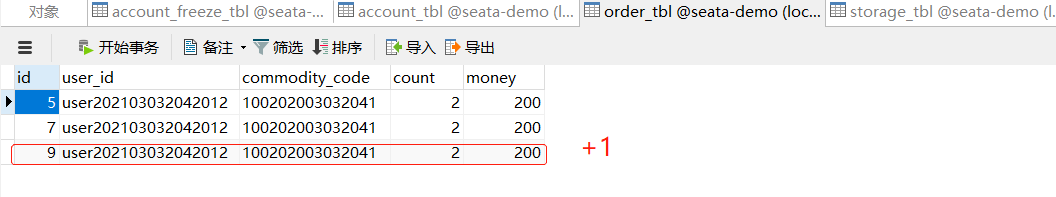
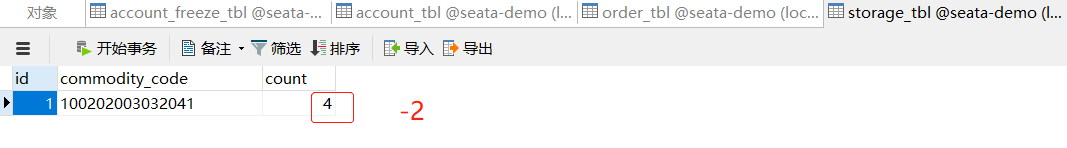
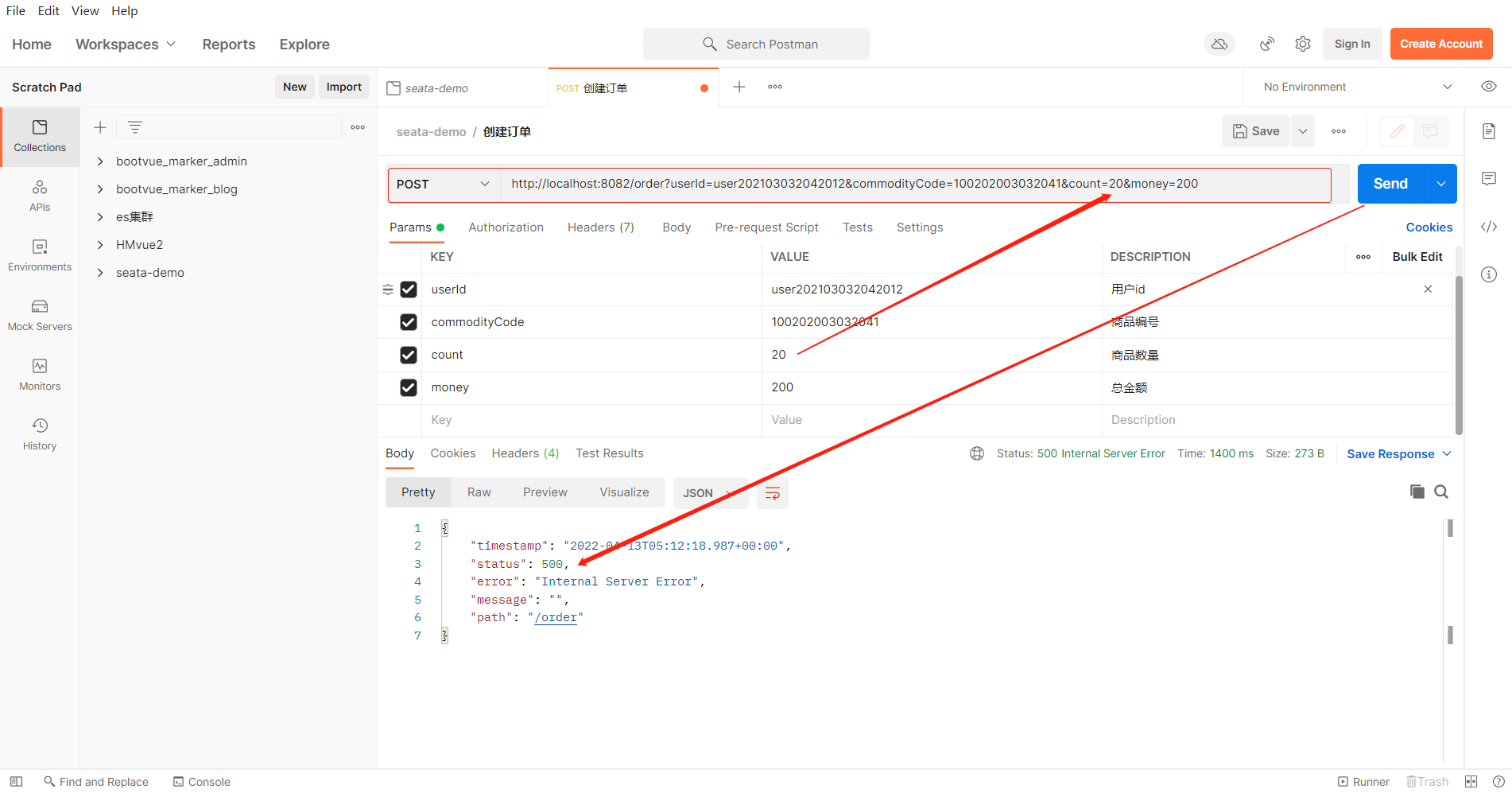
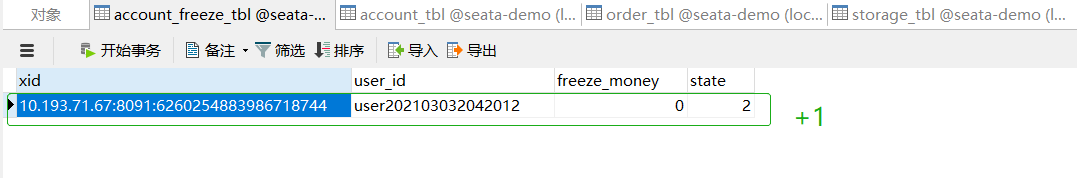
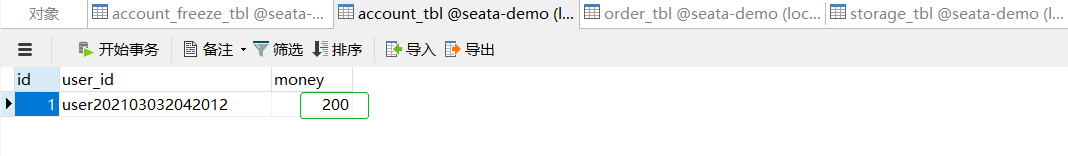
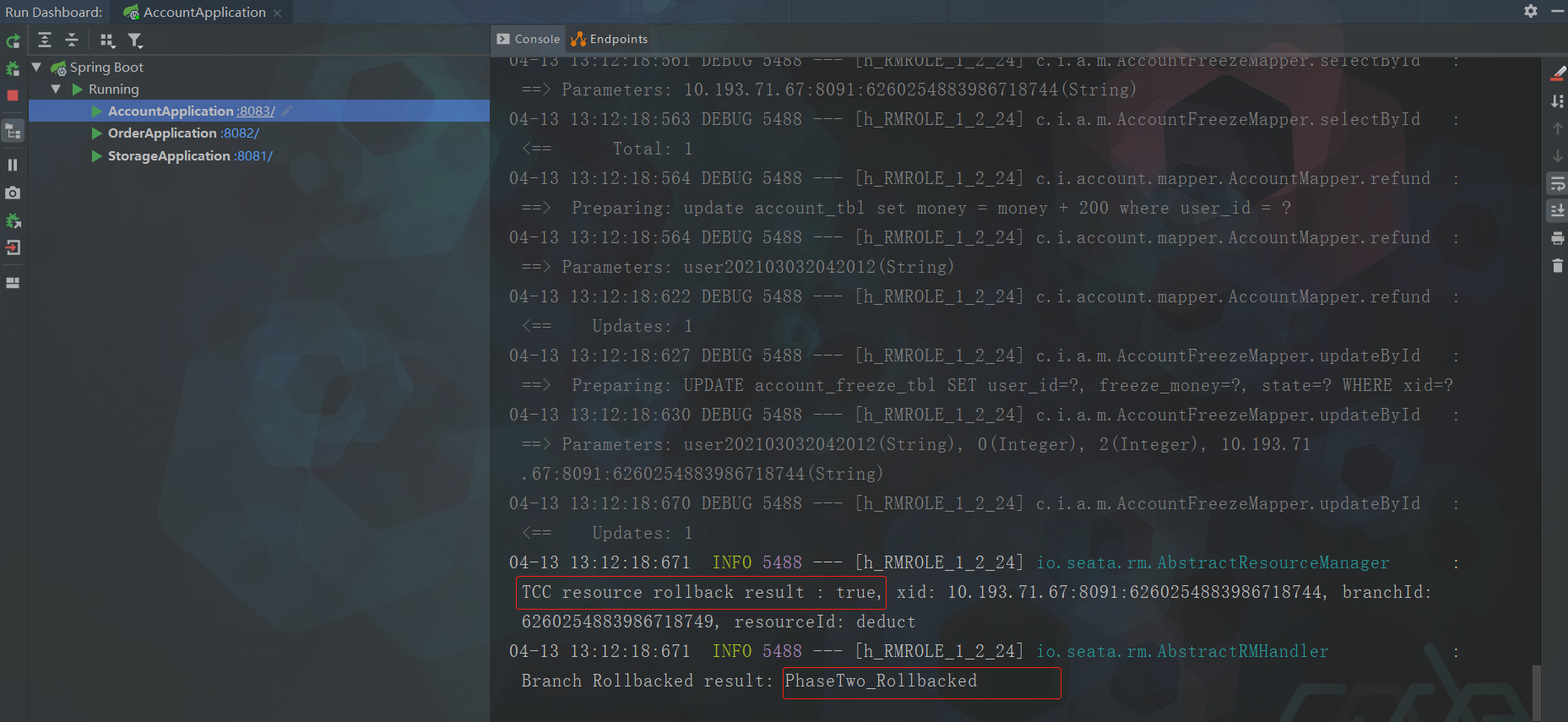
异常请求
4. SAGA模式
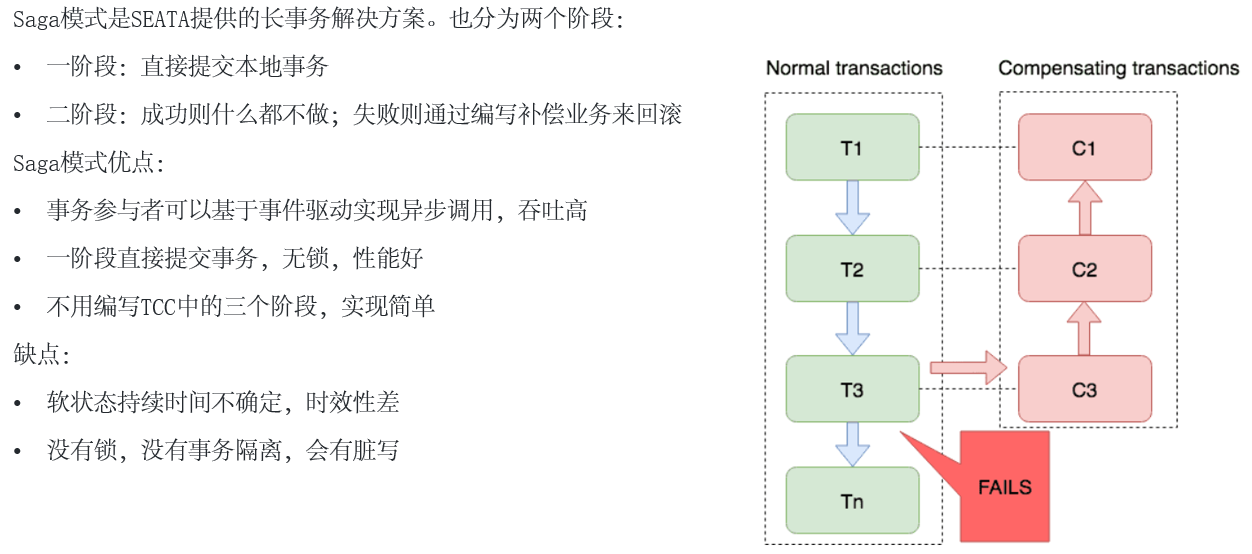
不常用,未演示实现
5. 四种模式对比
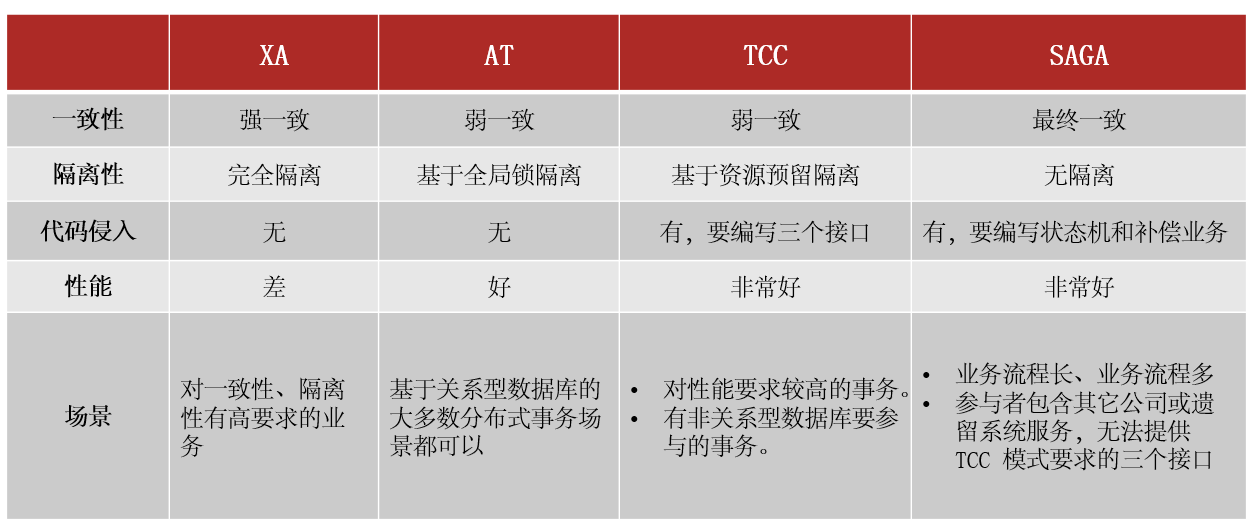
分类:
微服务
标签:
SpringCloud



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· Docker 太简单,K8s 太复杂?w7panel 让容器管理更轻松!