nowcoder-oj【面试高频TOP榜单-中等难度(1)5道】
1、NC140 排序

import java.util.*; public class Solution { /** * 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可 * 将给定数组排序 * @param arr int整型一维数组 待排序的数组 * @return int整型一维数组 */ public int[] MySort (int[] arr) { // write code here } }
实现
/* import java.util.*; public class Solution { public int[] MySort (int[] arr) { //冒泡(1/5 组用例通过,超时) for(int i=0; i<arr.length-1; i++){ for(int j=0; j<arr.length-i-1; j++){ if(arr[j] > arr[j+1]){ int temp = arr[j]; arr[j] = arr[j+1]; arr[j+1] = temp; } } } return arr; } } */ /* import java.util.*; public class Solution { public int[] MySort (int[] arr) { //冒泡改进(1/5 组用例通过,超时) for(int i=0; i<arr.length-1; i++){ int flag = 0; //通过符号位减少无谓的比较,若有序则直接退出循环 for(int j=0; j<arr.length-i-1; j++){ if(arr[j] > arr[j+1]){ int temp = arr[j]; arr[j] = arr[j+1]; arr[j+1] = temp; flag = 1; } } if(flag == 0){ break; } } return arr; } } */ /* import java.util.*; public class Solution { public int[] MySort (int[] arr) { //选择排序(1/5 组用例通过,超时) for(int i=0; i<arr.length-1; i++){ int minIndex = i; //假设当前数为最小的,记录其下标 for(int j=i+1; j<arr.length; j++){ if(arr[minIndex] > arr[j]){ minIndex = j; } } if(i != minIndex){ int temp = arr[i]; arr[i] = arr[minIndex]; arr[minIndex] = temp; } } return arr; } } */ import java.util.*; public class Solution { public int[] MySort (int[] arr) { //插入排序(1/5 组用例通过,超时) if(arr==null || arr.length<2){ return arr; } for(int i=0; i<arr.length; i++){ //外层循环控制总数量 for(int j=i; j>0; j--){ //内层循环一次减少,并提出结果 if(arr[j] < arr[j-1]){ int temp = arr[j];; arr[j] = arr[j-1]; arr[j-1] = temp; }else{ break; } } } return arr; } } //以上排序算法(冒泡、选择、插入)中都包含两层循环,所以O(N^2),不符合题目要求 //O(nlogn):堆、归并、快速
参考
【数据结构和算法】十几种排序算法,图文详解_牛客博客 (nowcoder.net)

//快速排序 import java.util.*; public class Solution { public int[] MySort(int[] arr) { quickSort(arr, 0, arr.length - 1); return arr; } private void quickSort(int[] array, int start, int end) { if (start < end) { int key = array[start];//用待排数组的第一个作为中枢 int i = start; for (int j = start + 1; j <= end; j++) { if (key > array[j]) { swap(array, j, ++i); } } array[start] = array[i];//先挪,然后再把中枢放到指定位置 array[i] = key; quickSort(array, start, i - 1); quickSort(array, i + 1, end); } } //交换两个数的值 public void swap(int[] A, int i, int j) { if (i != j) { A[i] ^= A[j]; A[j] ^= A[i]; A[i] ^= A[j]; } } }

//归并排序 import java.util.*; public class Solution { public int[] MySort(int[] arr) { int i = 1; while (i < arr.length) { //原理很简单,就是先两个两个合并,然后4个,然后8个…… for (int j = 0; j + i < arr.length; j += 2 * i) { merge(arr, j, j + i - 1, Math.min(j + 2 * i - 1, arr.length - 1)); } i = i << 1; } return arr; } private void merge(int[] data, int left, int center, int right) { int length = right - left + 1; int[] tmp = new int[length]; int tempIndex = 0; //_left是前半部分开始的位置,_right是后半部分开始的位置 int _left = left; int _right = center + 1; while (_left <= center && _right <= right) { if (data[_left] <= data[_right]) { tmp[tempIndex++] = data[_left++]; } else { tmp[tempIndex++] = data[_right++]; } } while (_right <= right) { tmp[tempIndex++] = data[_right++]; } while (_left <= center) { tmp[tempIndex++] = data[_left++]; } tempIndex = 0; while (tempIndex < length) { data[left + tempIndex] = tmp[tempIndex++]; } } }

//堆排序 import java.util.*; public class Solution { public int[] MySort(int[] arr) { int length = arr.length; buildMaxHeap(arr, length); for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) { swap(arr, 0, length - 1 - i); maxHeapfy(arr, 0, length - i - 1); } return arr; } private void maxHeapfy(int[] arr, int i, int heapSize) { int left = i * 2 + 1; int right = i * 2 + 2; int largest = i; if (left < heapSize && arr[left] > arr[largest]) { largest = left; } if (right < heapSize && arr[right] > arr[largest]) { largest = right; } if (largest != i) {//把最大值给父节点 swap(arr, largest, i); maxHeapfy(arr, largest, heapSize); } } private void buildMaxHeap(int[] array, int heapSize) { //从最后一个非叶子节点开始循环 for (int i = (heapSize - 2) >> 1; i >= 0; i--) { maxHeapfy(array, i, heapSize); } } public void swap(int[] A, int i, int j) { if (i != j) { A[i] ^= A[j]; A[j] ^= A[i]; A[i] ^= A[j]; } } }
2、NC93 设计LRU缓存结构


import java.util.*; public class Solution { /** * lru design * @param operators int整型二维数组 the ops * @param k int整型 the k * @return int整型一维数组 */ public int[] LRU (int[][] operators, int k) { // write code here } }
参考1

import java.util.*; public class Solution { /** * lru design * @param operators int整型二维数组 the ops * @param k int整型 the k * @return int整型一维数组 */ public int[] LRU (int[][] operators, int k) { // write code here Map<Integer, Integer> map = new LinkedHashMap<>(); List<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>(); for (int[] operator : operators) { int key = operator[1]; switch(operator[0]) { case 1: int value = operator[2]; if (map.size() < k) { map.put(key, value); } else { Iterator it = map.keySet().iterator(); map.remove(it.next()); map.put(key, value); } break; case 2: if (map.containsKey(key)) { int val = map.get(key); list.add(val); map.remove(key); map.put(key, val); } else { list.add(-1); } break; default: } } int[] res = new int[list.size()]; int i = 0; for (int val : list) { res[i++] = val; } return res; } }
参考2

import java.util.*; public class Solution { private Map<Integer, Node> map = new HashMap<>(); private Node head = new Node(-1,-1); private Node tail = new Node(-1,-1); private int k; public int[] LRU (int[][] operators, int k) { this.k = k; head.next = tail; tail.prev = head; int len = (int)Arrays.stream(operators).filter(x -> x[0] == 2).count(); int[] res = new int[len]; for(int i = 0, j = 0; i < operators.length; i++) { if(operators[i][0] == 1) { set(operators[i][1], operators[i][2]); } else { res[j++] = get(operators[i][1]); } } return res; } private void set(int key, int val) { if(get(key) > -1) { map.get(k).val = val; } else { if(map.size() == k) { int rk = tail.prev.key; tail.prev.prev.next = tail; tail.prev = tail.prev.prev; map.remove(rk); } Node node = new Node(key, val); map.put(key, node); moveToHead(node); } } private int get(int key) { if(map.containsKey(key)) { Node node = map.get(key); node.prev.next = node.next; node.next.prev = node.prev; moveToHead(node); return node.val; } return -1; } private void moveToHead(Node node) { node.next = head.next; head.next.prev = node; head.next = node; node.prev = head; } static class Node{ int key, val; Node prev, next; public Node(int key, int val) { this.key = key; this.val = val; } } }
3、NC45 实现二叉树先序,中序和后序遍历
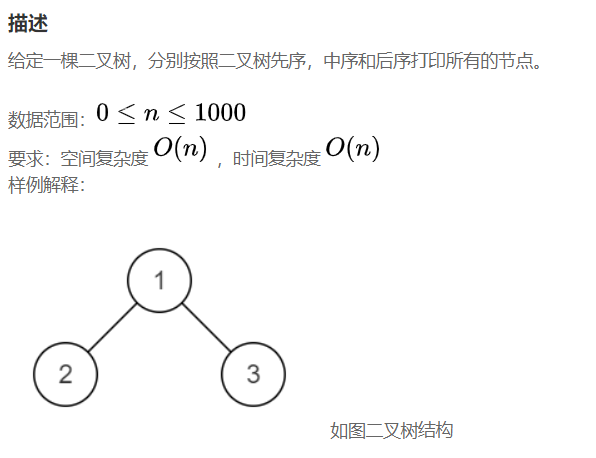
import java.util.*; /* * public class TreeNode { * int val = 0; * TreeNode left = null; * TreeNode right = null; * } */ public class Solution { /** * * @param root TreeNode类 the root of binary tree * @return int整型二维数组 */ public int[][] threeOrders (TreeNode root) { // write code here } }
参考1
Java-LeetCode94&144&145. 二叉树的三种遍历-递归 | 迭代_牛客博客 (nowcoder.net)
参考2
import java.util.*; /* * public class TreeNode { * int val = 0; * TreeNode left = null; * TreeNode right = null; * } */ public class Solution { /** * * @param root TreeNode类 the root of binary tree * @return int整型二维数组 */ public int[][] threeOrders (TreeNode root) { // write code here List<Integer>list=new ArrayList<>(); preOrder(root,list); int len=list.size(); int[][]res=new int[3][len]; fill(res,list,0); list.clear(); inOrder(root,list); fill(res,list,1); list.clear(); postOrder(root,list); fill(res,list,2); return res; } public void preOrder(TreeNode root,List<Integer>list){ if(root==null){ return ; } list.add(root.val); preOrder(root.left,list); preOrder(root.right,list); } public void inOrder(TreeNode root,List<Integer>list){ if(root == null){ return ; } inOrder(root.left,list); list.add(root.val); inOrder(root.right,list); } public void postOrder(TreeNode root,List<Integer>list){ if(root == null){ return ; } postOrder(root.left,list); postOrder(root.right,list); list.add(root.val); } public void fill(int[][]res,List<Integer>list,int j){ for(int i=0;i<list.size();i++){ res[j][i]=list.get(i); } } }
参考3
import java.util.*; /* * public class TreeNode { * int val = 0; * TreeNode left = null; * TreeNode right = null; * } */ public class Solution { /** * * @param root TreeNode类 the root of binary tree * @return int整型二维数组 */ public int[][] threeOrders (TreeNode root) { // write code here List<Integer>list=new ArrayList<>(); preOrder(root,list); int len=list.size(); int[][]res=new int[3][len]; fill(res,list,0); list.clear(); inOrder(root,list); fill(res,list,1); list.clear(); postOrder(root,list); fill(res,list,2); return res; } public void preOrder(TreeNode root,List<Integer>list){ if(root==null){ return ; } list.add(root.val); preOrder(root.left,list); preOrder(root.right,list); } public void inOrder(TreeNode root,List<Integer>list){ if(root == null){ return ; } inOrder(root.left,list); list.add(root.val); inOrder(root.right,list); } public void postOrder(TreeNode root,List<Integer>list){ if(root == null){ return ; } postOrder(root.left,list); postOrder(root.right,list); list.add(root.val); } public void fill(int[][]res,List<Integer>list,int j){ for(int i=0;i<list.size();i++){ res[j][i]=list.get(i); } } }
4、NC119 最小的K个数


import java.util.ArrayList; public class Solution { public ArrayList<Integer> GetLeastNumbers_Solution(int [] input, int k) { } }
实现
import java.util.ArrayList; public class Solution { public ArrayList<Integer> GetLeastNumbers_Solution(int [] input, int k) { ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); if(k <=0){ return list; } quickSort(input, 0, input.length-1); //快速排序(升序) for(int i=0; i<k; i++){ list.add(input[i]); } return list; } private void quickSort(int[] array, int start, int end) { if (start < end) { int key = array[start];//用待排数组的第一个作为中枢 int i = start; for (int j = start + 1; j <= end; j++) { if (key > array[j]) { swap(array, j, ++i); } } array[start] = array[i];//先挪,然后再把中枢放到指定位置 array[i] = key; quickSort(array, start, i - 1); quickSort(array, i + 1, end); } } //交换两个数的值 public void swap(int[] A, int i, int j) { if (i != j) { A[i] ^= A[j]; A[j] ^= A[i]; A[i] ^= A[j]; } } }
参考
【数据结构和算法】4种实现方式,排序,最大堆,TreeMap,快排_牛客博客 (nowcoder.net)

import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; public class Solution { public ArrayList<Integer> GetLeastNumbers_Solution(int[] input, int k) { ArrayList<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>(k); //根据题意要求,如果K>数组的长度,返回一个空的数组 if (k > input.length) return res; //先排序,然后选择前k个即可 Arrays.sort(input); for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i) { res.add(input[i]); } return res; } }



5、NC15 求二叉树的层序遍历

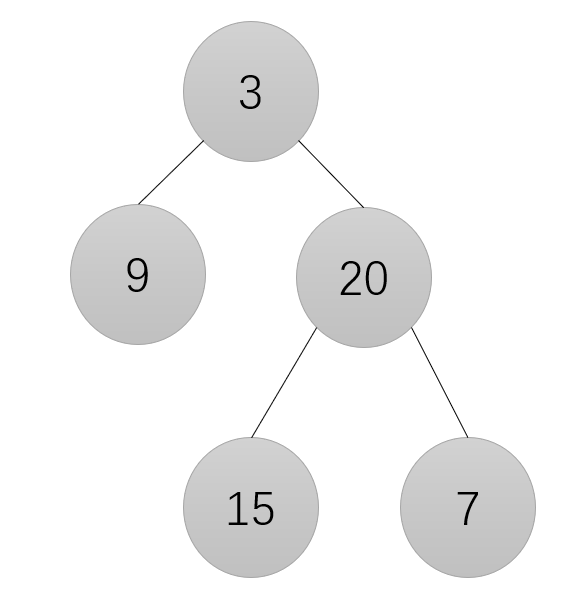

import java.util.*; /* * public class TreeNode { * int val = 0; * TreeNode left = null; * TreeNode right = null; * } */ public class Solution { /** * * @param root TreeNode类 * @return int整型ArrayList<ArrayList<>> */ public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> levelOrder (TreeNode root) { // write code here } }
参考1

import java.util.*; public class Solution { public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> levelOrder (TreeNode root) { ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>(); if (root == null) { return result; } // 队列,用于存储元素 Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>(); // 根节点先入队 queue.offer(root); // 当队列不为空的时候 while(!queue.isEmpty()) { // 队列的大小就是这一层的元素数量 int size = queue.size(); ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); // 开始遍历这一层的所有元素 for (int i = 0; i < size; i ++) { TreeNode node = queue.poll(); // 如果左节点不为空,则入队,作为下一层来遍历 if(node.left != null) { queue.offer(node.left); } // 同上 if (node.right != null) { queue.offer(node.right); } // 存储一层的节点 list.add(node.val); } // 将一层所有的节点汇入到总的结果集中 result.add(list); } return result; } }
参考2

import java.util.*; public class Solution { ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> levelOrder; public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> levelOrder (TreeNode root) { levelOrder=new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>(); if(root==null)return levelOrder; LinkedList<TreeNode>queue=new LinkedList<>(); int now=1,next=0; queue.add(root); while(!queue.isEmpty()){ ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); while(now>=1){ TreeNode node = queue.poll(); list.add(node.val); now--; if(node.left!=null){ queue.add(node.left); next++; } if(node.right!=null){ queue.add(node.right); next++; } } now=next; next=0; levelOrder.add(list); } return levelOrder; } }
标签:
Online Judge





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· Docker 太简单,K8s 太复杂?w7panel 让容器管理更轻松!