#include<stdlib.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
class CPU{
public:
virtual void calculate() = 0;
};
class GPU{
public:
virtual void display() = 0;
};
class RAM{
public:
virtual void storage() = 0;
};
class PC{
private:
CPU * cpu;
GPU * gpu;
RAM * ram;
public:
PC(CPU * _cpu, GPU * _gpu, RAM * _ram){
cpu = _cpu;
gpu = _gpu;
ram = _ram;
}
void dowork(){
cpu->calculate();
gpu->display();
ram->storage();
}
~PC(){
if(cpu != NULL){
delete cpu;
cpu = NULL;
}
if(gpu != NULL){
delete gpu;
gpu = NULL;
}
if(ram != NULL){
delete ram;
ram = NULL;
}
}
};
class InterCPU : public CPU{
public:
virtual void calculate(){
cout << "inter cpu 开始计算" << endl;
}
};
class InterGPU : public GPU{
public:
virtual void display(){
cout << "inter gpu 开始显示" << endl;
}
};
class InterRAM : public RAM{
public:
virtual void storage(){
cout << "inter ram 开始存储" << endl;
}
};
class LenovoCPU : public CPU{
public:
virtual void calculate(){
cout << "Lenovo cpu 开始计算" << endl;
}
};
class LenovoGPU : public GPU{
public:
virtual void display(){
cout << "Lenovo gpu 开始显示" << endl;
}
};
class LenovoRAM : public RAM{
public:
virtual void storage(){
cout << "Lenovo ram 开始存储" << endl;
}
};
void test1(){
CPU * interCPU = new InterCPU;
GPU * interGPU = new InterGPU;
RAM * interRAM = new InterRAM;
PC * pc1 = new PC(interCPU, interGPU, interRAM);
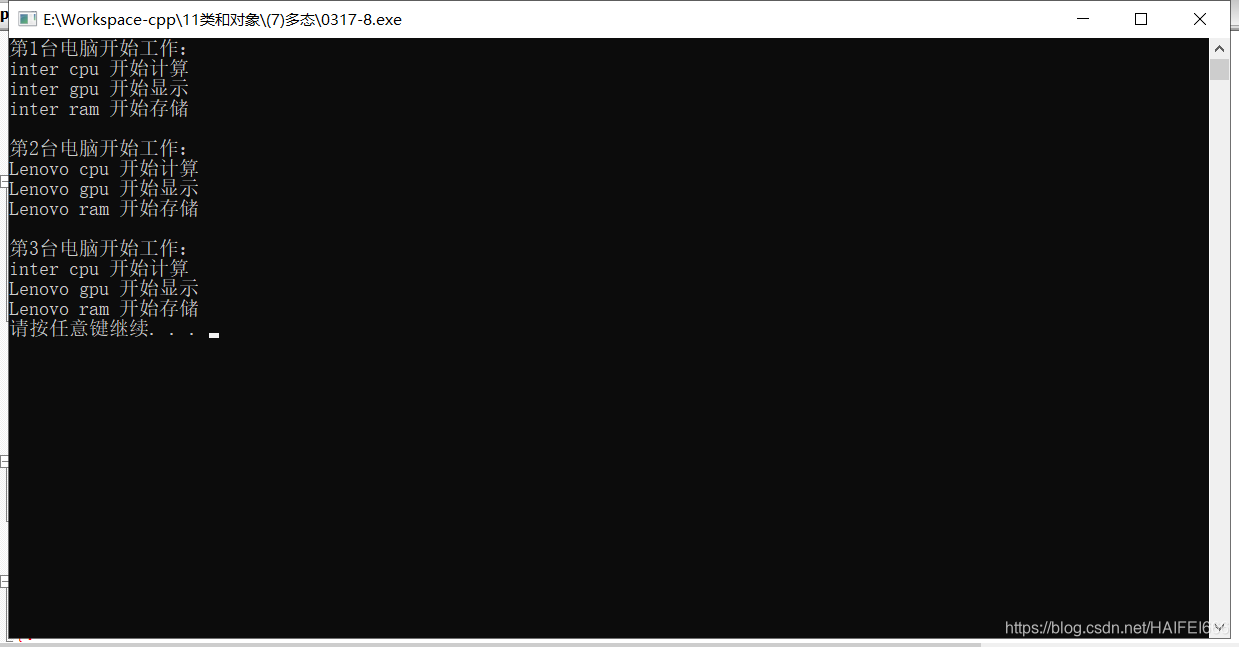
cout << "第1台电脑开始工作:" << endl;
pc1->dowork();
delete pc1;
cout << endl;
CPU * lenovoCPU = new LenovoCPU;
GPU * lenovoGPU = new LenovoGPU;
RAM * lenovoRAM = new LenovoRAM;
PC * pc2 = new PC(lenovoCPU, lenovoGPU, lenovoRAM);
cout << "第2台电脑开始工作:" << endl;
pc2->dowork();
delete pc2;
cout << endl;
PC * pc3 = new PC(new InterCPU, new LenovoGPU, new LenovoRAM);
cout << "第3台电脑开始工作:" << endl;
pc3->dowork();
delete pc3;
}
int main()
{
test1();
system("pause");
return 0;
}




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· Docker 太简单,K8s 太复杂?w7panel 让容器管理更轻松!