<1>打开文件
在python,使用open函数,可以打开一个已经存在的文件,或者创建一个新文件
open(文件名,访问模式)
示例如下:
f = open('test.txt', 'w')
说明:
| 访问模式 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| r | 以只读方式打开文件。文件的指针将会放在文件的开头。这是默认模式。 |
| w | 打开一个文件只用于写入。如果该文件已存在则将其覆盖。如果该文件不存在,创建新文件。 |
| a | 打开一个文件用于追加。如果该文件已存在,文件指针将会放在文件的结尾。也就是说,新的内容将会被写入到已有内容之后。如果该文件不存在,创建新文件进行写入。 |
| rb | 以二进制格式打开一个文件用于只读。文件指针将会放在文件的开头。这是默认模式。 |
| wb | 以二进制格式打开一个文件只用于写入。如果该文件已存在则将其覆盖。如果该文件不存在,创建新文件。 |
| ab | 以二进制格式打开一个文件用于追加。如果该文件已存在,文件指针将会放在文件的结尾。也就是说,新的内容将会被写入到已有内容之后。如果该文件不存在,创建新文件进行写入。 |
| r+ | 打开一个文件用于读写。文件指针将会放在文件的开头。 |
| w+ | 打开一个文件用于读写。如果该文件已存在则将其覆盖。如果该文件不存在,创建新文件。 |
| a+ | 打开一个文件用于读写。如果该文件已存在,文件指针将会放在文件的结尾。文件打开时会是追加模式。如果该文件不存在,创建新文件用于读写。 |
| rb+ | 以二进制格式打开一个文件用于读写。文件指针将会放在文件的开头。 |
| wb+ | 以二进制格式打开一个文件用于读写。如果该文件已存在则将其覆盖。如果该文件不存在,创建新文件。 |
| ab+ | 以二进制格式打开一个文件用于追加。如果该文件已存在,文件指针将会放在文件的结尾。如果该文件不存在,创建新文件用于读写。 |
<2>关闭文件
close( )
示例如下:
# 新建一个文件,文件名为:test.txt
f = open('test.txt', 'w')
# 关闭这个文件
f.close()
文件的读写
<1>写数据(write)
使用write()可以完成向文件写入数据
demo:
f = open('test.txt', 'w')
f.write('hello world, i am here!')
f.close()
运行现象:
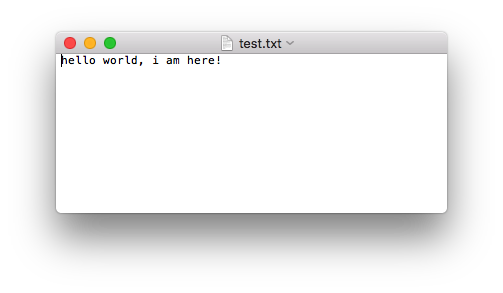
注意:
- 如果文件不存在那么创建,如果存在那么就先清空,然后写入数据
<2>读数据(read)
使用read(num)可以从文件中读取数据,num表示要从文件中读取的数据的长度(单位是字节),如果没有传入num,那么就表示读取文件中所有的数据
demo:
f = open('test.txt', 'r')
content = f.read(5)
print(content)
print("-"*30)
content = f.read()
print(content)
f.close()
运行现象:
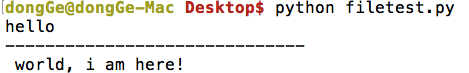
注意:
- 如果open是打开一个文件,那么可以不用谢打开的模式,即只写
open('test.txt') - 如果使用读了多次,那么后面读取的数据是从上次读完后的位置开始的
<3>读数据(readlines)
就像read没有参数时一样,readlines可以按照行的方式把整个文件中的内容进行一次性读取,并且返回的是一个列表,其中每一行的数据为一个元素
#coding=utf-8
f = open('test.txt', 'r')
content = f.readlines()
print(type(content))
i=1
for temp in content:
print("%d:%s"%(i, temp))
i+=1
f.close()
运行现象:
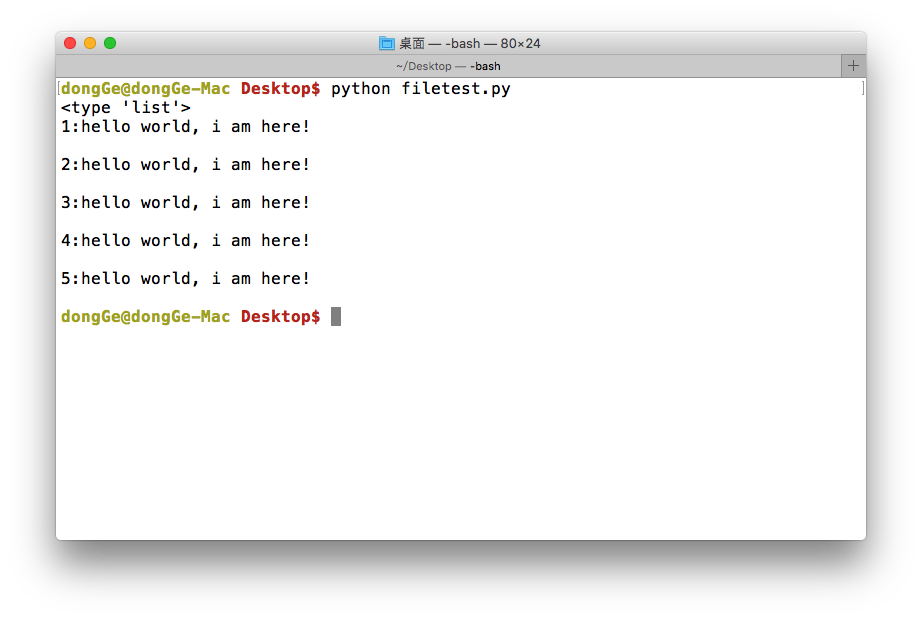
<4>读数据(readline)
#coding=utf-8
f = open('test.txt', 'r')
content = f.readline()
print("1:%s"%content)
content = f.readline()
print("2:%s"%content)
f.close()
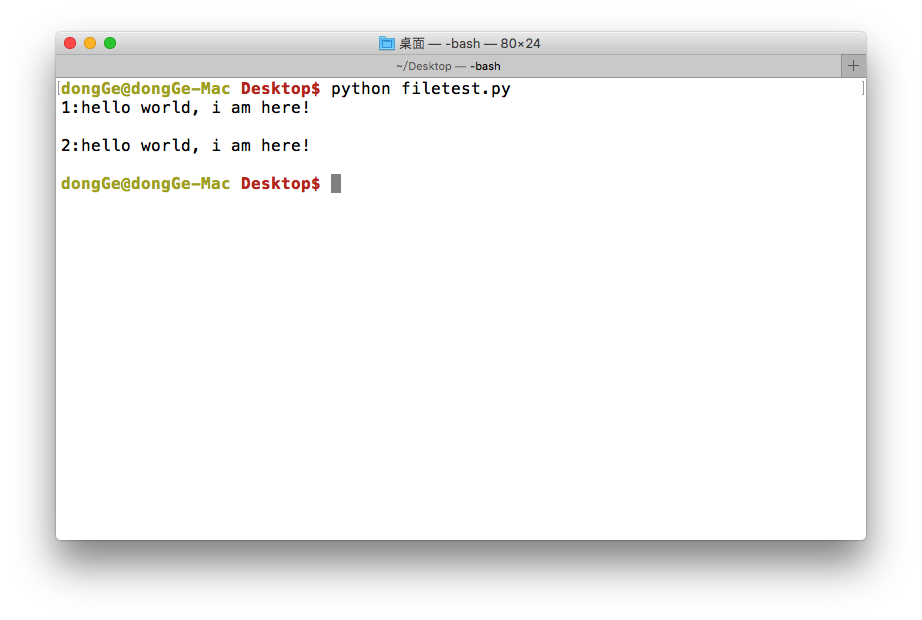
with open(file_name, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
data = f.read() # 读取整个文件
data = f.readline() # 就读取一行,并且将指针向下移动一行,可以用循环语句来完成对全文的读取。
data = f.readlines()
f = open(file_name, 'r', encoding='UTF-8')
f.read()
f.close()
with open(file_name, 'w+', encoding='utf-8') as f:
num = f.write(data)
print(num)
f = open(file_name, 'w+', encoding='utf-8')
num = f.write(data)
f.close()
5.安装行读取文件
import os
import re
import sys
import time
import pymysql
path = os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))))
sys.path.append(path)
from spider_setting import MYSQL_HOST, MYSQL_POST, MYSQL_PASSWORD, MYSQL_USER
class ReadFping(object):
def __init__(self):
self.db = pymysql.connect(host=MYSQL_HOST, port=MYSQL_POST, database="cloud_joy_monitoring", user=MYSQL_USER, password=MYSQL_PASSWORD, charset='utf8', autocommit=True)
self.cursor = self.db.cursor()
self.read_json()
def read_json(self):
for video_name in os.listdir(".//"):
if "log" in video_name:
print(video_name)
with open(".//{}".format(video_name), "rb") as f:
self._file = f
self._file.seek(0, 0)
# self._file.seek(0, 2) # 0:开始的偏移量 2:0代表从文件开头开始算起,1代表从当前位置开始算起,2代表从文件末尾算起
while True:
line = self._file.readline() # 读取整行,包括 "\n" 字符
if not line:
break
if line:
line = line.decode("utf-8")
delay = re.findall(r"(\d+\.\d+?) ms", line)[0]
data_time = time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S', time.localtime(int(re.findall(r"(\d+)\.", line)[0])))
print(delay)
insert_sql = 'insert into fping_delay(data_time, ping, name) values("{}", "{}", "{}")'.format(data_time, delay, video_name)
self.cursor.execute(insert_sql)
if __name__ == "__main__":
read_json = ReadFping()
6.获取文件夹下所有文件
import os
# 遍历所有文件夹下的文件
def walk_files(path, endpoint=None):
file_list = []
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(path):
for file in files:
file_path = os.path.join(root, file)
if file_path.endswith(endpoint):
file_list.append(file_path)
return file_list
if __name__ == '__main__':
wav_path = r"E:/07-shunwangwork/33-游戏运营/papunika/html"
text_list = walk_files(wav_path, endpoint=".html")
print(text_list)
7.yield读取大文件
def read_large_file():
with open("test.html", 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file: # test.html要都的文件
lines = []
for line in file:
lines.append(line.strip())
if len(lines) >= 10: # 每次返回多少行
yield lines
lines = []
if lines:
yield lines
for date in read_large_file():
print(date)


