关于 STL 的 sort
最近两道题TLE, 把 sort 改成 stable_sort 就过了, 所以总结一下。
cplusplus.com 上没有说 stable_sort 的实现算法, stable 是稳定的意思, 也许使用的是归并排序
在大多数测试中, stable_sort 的速度快于 sort, 但内存大于 sort
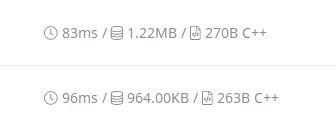
第一条 stable_sort, 第二条 sort
NOI Linux 测试 (1000万个元素排序, 仅测量排序函数所耗时间)
| 函数名称 | 数据性质 | 时间(s) |
|---|---|---|
| sort | 严格升序 | 0.729362 |
| sort | 严格降序 | 0.549648 |
| sort | [0, RAND_MAX]随机 | 1.998072 |
| sort | [0, 10]随机 | 1.352847 |
| sort | 全为1 | 1.246581 |
| stable_sort | 严格升序 | 0.505621 |
| stable_sort | 严格降序 | 0.900720 |
| stable_sort | [0, RAND_MAX]随机 | 1.706570 |
| stable_sort | [0, 10]随机 | 1.004860 |
| stable_sort | 全为1 | 0.508155 |
对于 sort 的描述
On average, linearithmic in the distance between first and last: Performs approximately \(N*\log2(N)\) (where \(N\) is this distance) comparisons of elements, and up to that many element swaps (or moves).
对于 stable_sort 的描述
If enough extra memory is available, linearithmic in the distance between first and last: Performs up to \(N*\log_2(N)\) element comparisons (where \(N\) is this distance), and up to that many element moves.
Otherwise, polyloglinear in that distance: Performs up to \(N*\log_2^2(N)\) element comparisons, and up to that many element swaps.


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号