1.swing基本概念与使用
1.简介:
swing是目前java不可或缺的窗口工具组,在swing尚未推出之前,要编写一个java窗口程序必须使用awt的包。
awt缺点:使用上没有弹性,例如无法任意地改变组件的外观,甚至想在一个按钮上添加团都是非常困难的
2.swing结构
利用MVC的概念衍生而出。
Model:存储组件数据的地方
View:显示组件的外观
Controller:处理用户在组件上的操作。并将改变后的数据存储到model上
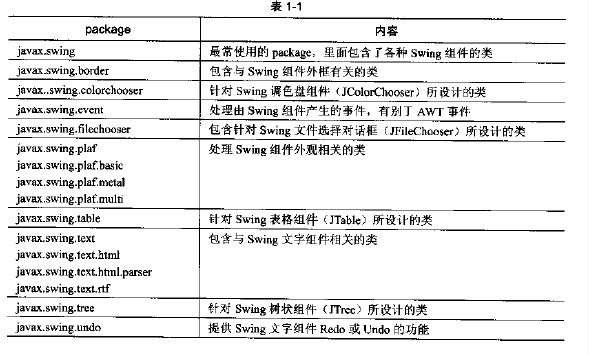
3.swing常用的package
4.java窗口演进
以前Java尚未推出Swing之前,要设计一个Java窗口程序,必须要通过AWT 组件。A W T组件虽然提供了一些构造窗口的基本需求,如文字字段(TextField)、复选框(CheckBox)-按钮(Button)、对话框(Dialog)^ 菜单(Menu)等等,但在使用上非常不方便且呆板。例如:我们无法改变按钮的形状,也无法在按钮上加上图标:于版面管理(Layout manager)的限制相当多,而对图形处理的支持也很少......................
5.swing主要包含:
1.awt组件:旧有的窗口组件包
2.swing组件:新的窗口组件包
3.accessibility API:提供一种更先进的沟通界面:语音输入货触摸式屏幕
4.java2DApi:提供更强大的图形处理函数
5.支持Drag and Drop功能:windows上开两个窗口进行复制粘贴
6.Layout Managers
1.swing中几乎所有的组件都是从JComponent衍生,也就是说所有的组件都是由纯java编写而成。
2.JFrame、JDialog、JWindow与JApplet这个四个组件统称为最上层。其余组件必须依附在这四组件上才能显示
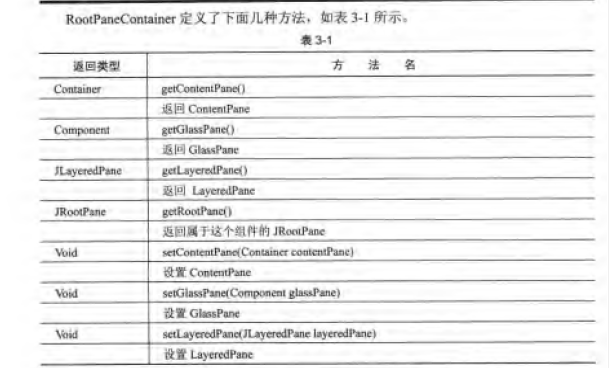
3.RootPaneContainer:
4.Layout Manager种类:
1.BorderLayout
2.FlowLayout
3.GridLayout
4.CardLayout
5.GridBagLayout
6.BoxLayout
swing中还有ScrollPaneLayout、ViewportLayout、OverlayLayout,这三个系统会自行管理,大部分情况用户不 需要知道怎么使用。
7.BorderLayout的使用
1.BorderLayout将版面分为东西南北中五个版面,可以将组件放置到这五个区域中。
2.demo
public class BorderLayoutDemo { public BorderLayoutDemo() { JFrame frame=new JFrame(); Container contentPane=frame.getContentPane(); contentPane.setLayout(new BorderLayout()); contentPane.add(new JButton("EAST"),BorderLayout.EAST); contentPane.add(new JButton("WEST"),BorderLayout.WEST); contentPane.add(new JButton("SOUTH"),BorderLayout.SOUTH); contentPane.add(new JButton("NORTH"),BorderLayout.NORTH); contentPane.add(new JLabel("CENTER",JLabel.CENTER),BorderLayout.CENTER); frame.setTitle("BorderLayout"); frame.pack(); //根据窗口里面的布局及组件的preferedSize来确定frame的最佳大小 frame.setVisible(true); frame.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() { @Override public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) { System.exit(0); } }); } public static void main(String[] args) { BorderLayoutDemo layout=new BorderLayoutDemo(); } }
8.FlowLayout的使用
1.将组件一个接着一个往右一直排列下去。若组件个数太多,无法在同一行显示时,会自动将组件往下一行排列。
2.构造函数

3.demo
public class FlowLayoutDemo { public FlowLayoutDemo() { JFrame frame=new JFrame(); Container contentPane = frame.getContentPane(); contentPane.setLayout(new FlowLayout()); contentPane.add(new JButton("first")); contentPane.add(new JButton("second")); contentPane.add(new JButton("third")); contentPane.add(new JButton("fourth")); contentPane.add(new JButton("fifth")); contentPane.add(new JButton("this id the last button")); frame.setTitle("FlowLayout"); frame.setSize(new Dimension(200, 200)); frame.setVisible(true); frame.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() { @Override public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub System.exit(0); } }); } public static void main(String[] args) { FlowLayoutDemo f=new FlowLayoutDemo(); } }
9.GridLayout
1.GridLayout比FlowLayout多了行和列的设置,也就是说要先设置GridLayout共有几行几列,然后添加进去的组件会先填完第一行再第二行
2.构造函数

3.demo
public class GridLayoutDemo { public GridLayoutDemo() { JFrame f=new JFrame(); Container contentPane= f.getContentPane(); contentPane.setLayout(new GridLayout(7, 1)); contentPane.add(new JButton("first")); contentPane.add(new JButton("first1")); contentPane.add(new JButton("first2")); contentPane.add(new JButton("first3")); contentPane.add(new JButton("first4")); contentPane.add(new JButton("first5")); contentPane.add(new JButton("first6")); f.setVisible(true); f.setTitle("GridLayout"); f.pack(); f.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() { @Override public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) { System.exit(0); } }); } public static void main(String[] args) { new GridLayoutDemo(); } }
10.CardLayout
1.如果很多卡片叠在一起,每次只能看到其中一张,但是可以任意抽出其中一张。
2.构造函数

3.demo
public class CardLayoutDemo implements ActionListener{ JPanel p1,p2,p3,p4; int i=1; JFrame f; public CardLayoutDemo() { f=new JFrame(); Container contentPane= f.getContentPane(); contentPane.setLayout(new CardLayout(2, 1)); p1 = new JPanel(); JButton button=new JButton("sss"); button.addActionListener(this); p1.add(button); contentPane.add(p1); p2 = new JPanel(); p2.setLayout(new FlowLayout()); p2.add(new JButton("1")); p2.add(new JButton("2")); p2.add(new JButton("3")); p3 = new JPanel(); p3.setLayout(new GridLayout(3, 1)); p3.add(new JButton("11")); p3.add(new JButton("22")); p3.add(new JButton("33")); contentPane.add(p3); p4 = new JPanel(); p4.setLayout(new CardLayout()); p4.add("one",p2); p4.add("two",p3); ((CardLayout)p4.getLayout()).show(p4, "one"); contentPane.add(p4); f.setTitle("CardLayoutDemo"); f.pack(); f.setVisible(true); f.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() { @Override public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub System.exit(0); } }); } public static void main(String[] args) { new CardLayoutDemo(); } @Override public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub switch (i) { case 1: ((CardLayout)p4.getLayout()).show(p4, "two"); break; case 2: ((CardLayout)p4.getLayout()).show(p4, "one"); break; } i++; if(i==3){ i=1; } f.validate();//是验证frame中的所有组件,并不会调整frame的大小. } }
11.GridBagLayout的使用
1.GridBagLayout是java中最有弹性但也是最复杂的一种版面管理器,GridBagLayout能实现其他布局不能设置组件的位置和大小
2.构造函数:GridBagLayout必须配合GridBagConstraints才能达到设置的效果

12.BoxLayout的使用
1.提供多样化的版面管理方式,只有两种排列方式:水平和垂直,使用BoxLayout提供的两个常熟X_AXIS,Y_AXIS表示水平和垂直排列。当水平组件不登高,系统会使所有的组件域最高组件登高。若将组件排在同一行,超过container宽度,不会自动换行,需要自行处理。
2.构造函数

3.Box Container构造函数

4.Box提供4种透明组件:
Glue、当Glue插入在两组件之间,会将两组件挤到最左与最右(或最上与最下),透明的Glue会占满整个中间空间。
Strut、设置两个组件间间隔差距多少像素
Rigid、设置两个组件二维间隔差距多少像素限制
Filler、跟Rigid相同,但是可以指定最大、最小、较佳的长宽大小。

5.Box提供的方法




