ReentrantLock原理及源码阅读
ReentrantLock原理及源码阅读
1、ReentrantLock介绍
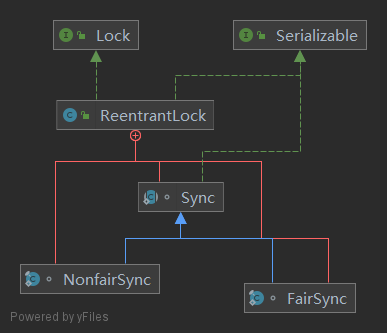
ReentrantLock是可重入的独占锁,同时只能有一个线程可以获取到该锁,其他线程获取该锁的线程将会被阻塞而被放入该锁的AQS阻塞队列里面。
ReentrantLock最终还是使用AQS来实现的,并且根据参数来决定其内部是一个公平还是非公平锁。
其中Sync类直接继承自AQS,它的子类NonfairSync和FairSync分别实现了获取锁的公平和非公平策略
2、获取锁的方法
void lock()方法
当一个线程调用该方法时,说明该线程希望获取该锁,如果锁当前没有被其他线程占用,并且当前线程之前没有获取过该锁,则当前线程会获取到该锁,然后设置当前锁的拥有者为当前线程,并设置AQS的状态值为1,然后直接返回。如果当前线程之前已经获取过该锁,则这次只是简单的把AQS的状态值加1后返回。如果该锁寂静被其他线程持有,则调用该方法的线程会被放入AQS队列后阻塞挂起。
ReentranLock的lock委托给了sync类,根据创建ReentranLock的构造函数选择sync的实现是非公平还是公平,这个锁是一个非公平锁或公平锁。以下是sync的子类NonfairSync的情况,也就是非公平锁。
上述代码中,默认AQS状态值state为0,所以此一个调用lock的线程会通过CAS设置状态值为1,CAS成功则代表当前线程获取到了锁,然后通过setExclusiveOwnerThread设置该锁的持有者为当前线程。
如果有其他线程调用lock方法获取该锁,CAS会失败,然后调用AQS的acquire方法,传递的参数为1.
AQS并没有实现tryAcquire方法,tryAcquire方法需要子类自己定制化,所以上面的tryAcquire实际上会调用ReentrantLock重写的tryAcquire方法。
非公平锁的体现:假设线程1调用lock方法时发现state状态值不为0,且当前线程不是锁的持有者则返回false,然后当前线程被放入AQS阻塞队列。这时线程2也调用了lock方法,发现当前状态值为0了(假设占有该锁的其他线程释放了该锁),所以通过CAS设置获取到了该锁。明明是线程1先请求获取的该锁,然而线程2获取到了锁,这就是非公平的体现。这里线程2获取锁前并没有查看当前AQS队列里面是否有比自己更早请求该锁的线程,而是使用了抢夺策略。
上述代码为公平锁的方法,公平锁的话只需要看FairSync重写的tryAcquire方法。
上面代码中,是实现公平性的核心代码,如果当前AQS队列为空或者当前线程是AQS的第一个节点则返回false。其中如果ht则说明当前队列为空,直接返回false。如果h!=t且snull则说明有一个元素将要作为AQS的第一个节点入队列,那么返回true,如果h!=t并且s!=null和s.thread !=Thread.currentThread则说明队列里面的第一个元素不是当前线程,那么返回true。
3、释放锁的方法
void unlock()方法
尝试释放锁,如果当前线程持有该锁,则调用该方法会让该线程对该线程持有的AQS状态值减1,如果减去1后当前状态值为0,则当前线程会释放锁,否则仅仅只是减1而已。如果当前线程没有持有该锁而调用了该方法则会抛出异常。
__EOF__

本文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/youngerwb/p/16326577.html
关于博主:评论和私信会在第一时间回复。或者直接私信我。
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
声援博主:如果您觉得文章对您有帮助,可以点击文章右下角【推荐】一下。您的鼓励是博主的最大动力!



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· Docker 太简单,K8s 太复杂?w7panel 让容器管理更轻松!