【认证与授权】Spring Security系列之认证流程解析
上面我们一起开始了Spring Security的初体验,并通过简单的配置甚至零配置就可以完成一个简单的认证流程。可能我们都有很大的疑惑,这中间到底发生了什么,为什么简单的配置就可以完成一个认证流程啊,可我啥都没看见,没有写页面,没有写接口。这一篇我们将深入到源码层面一起来了解一下spring security到底是怎么工作的。
1|0准备工作
在开始源码理解前,我们先来做一项基本的准备工作,从日志中去发现线索,因为我们发现什么都没有配置的情况下,他也可以正常的工作,并给我们预置了一个临时的用户user。那么他肯定是在工程启动的时候做了什么事情,上一篇我们也提到了是如果生成user用户和密码的。这篇我们将仔细的去了解一下。
1、首先我们配置在applicaiton.yml中调整一下日志级别
我们将security相关的日志打印出来,一起来启动或者运行的时候到底发生了什么。
2、启动spring-security-basic 工程
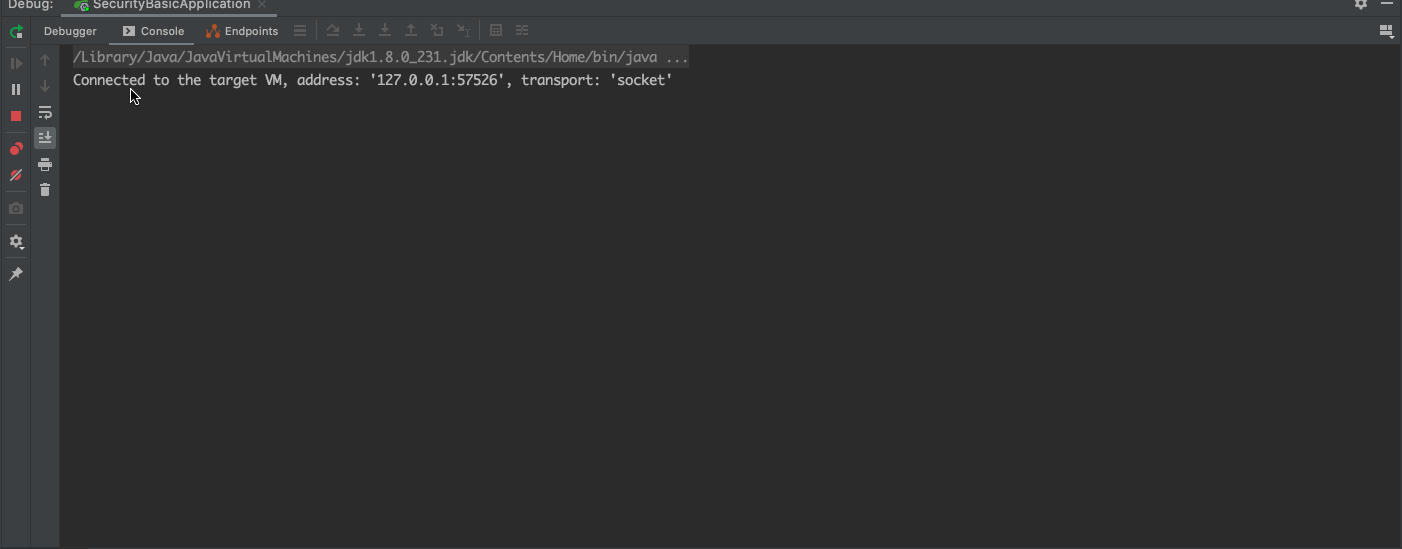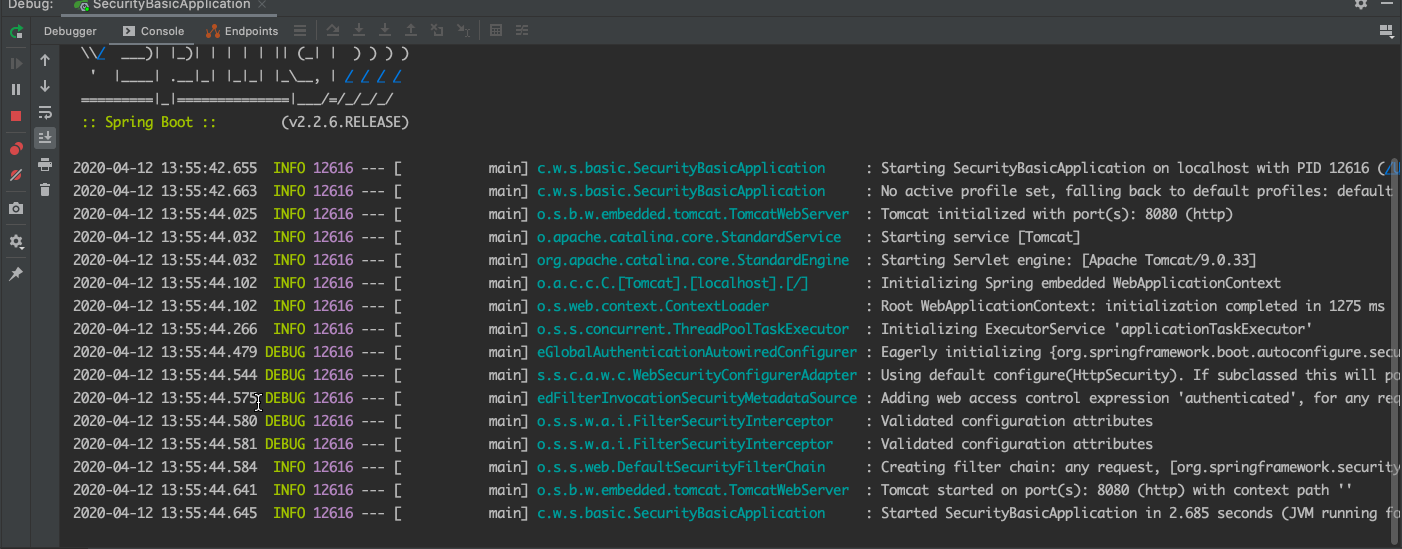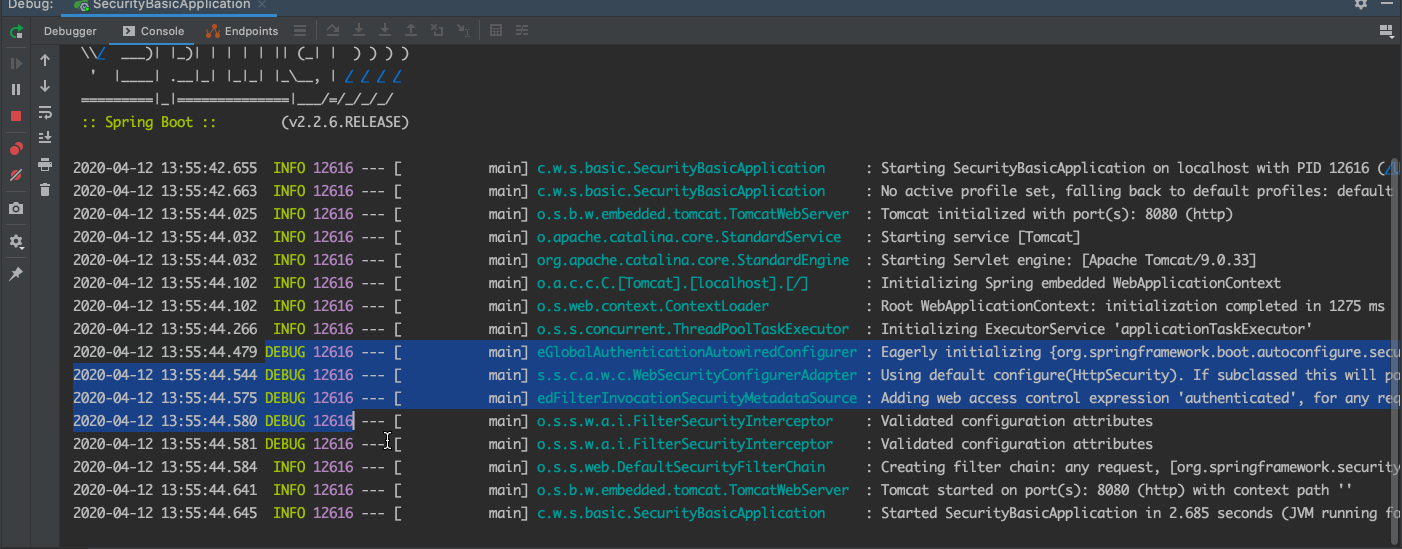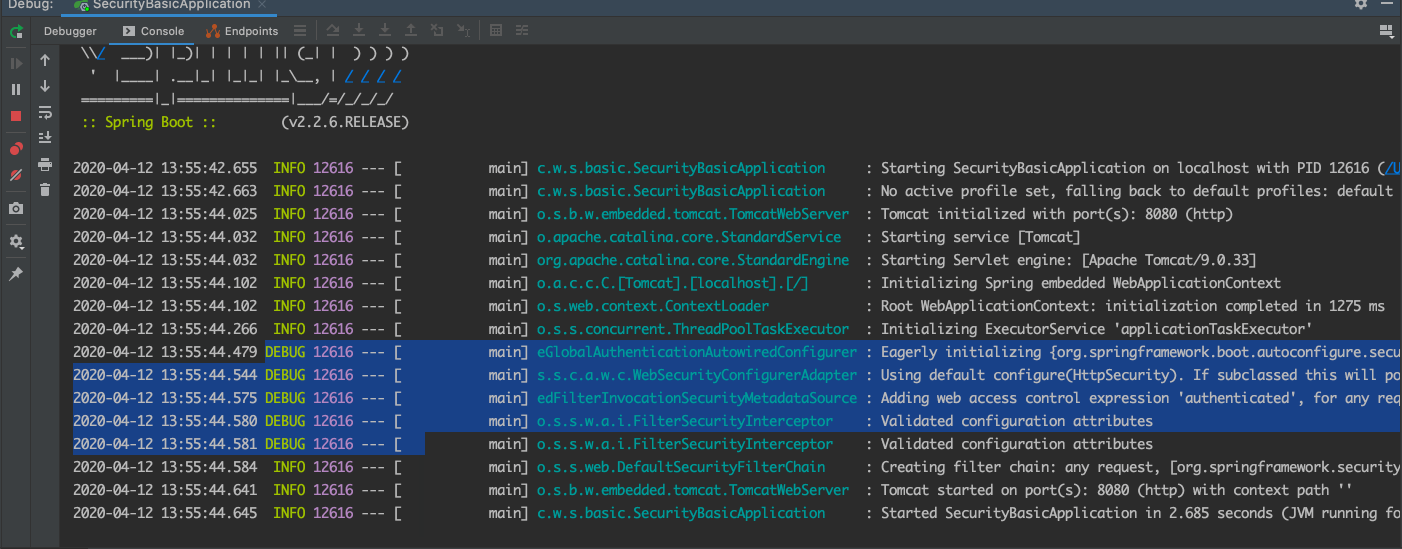
!!!找到了
2|0日志过滤
3|0逐个解析
3|11、WebSecurityEnablerConfiguration
告诉我们它初始化了一个配置类WebSecurityEnablerConfiguration 不管!找到源码再说
???怎么只有这么一点东西,这个类为什么会在初始化的时候启动?这里简单的指出来
首先找到spring-boot-autoconfigure-版本.jar下的META-INF/spring.factorites文件,其中有这样一段
我们可以暂时不去深究这是什么意思,总之,在springboot启动的时候,会将这里配置走一遍(后期可能也会写一点关于springboot启动原理的文章...)我们一个一个来看一下
1.1 SecurityAutoConfiguration
在这个类中我们重点关注
首先是SecurityProperties
篇幅问题这里我删除了很多代码。直接看里面的注释就好了,这也就是为什么我们不配置任何信息,也有一个默认的用户,以及我们用配置信息覆盖了默认用户的关键信息所在。
其次是@Import注解,这个其实就是xml配置方式中的标签 引入另外的配置,这里引入了SpringBootWebSecurityConfiguration WebSecurityEnablerConfiguration SecurityDataConfiguration
他们指向了一个关键的配置@ConditionalOnBean({WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter.class}) 需要WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter才会进行加载,那这个关键的类是什么时候加载的呢?这就回到了我们在日志中发现的第一个加载的类信息WebSecurityEnablerConfiguration 上面有个一非常关键的注解@EnableWebSecurity
瞧瞧干了啥
1.2 WebSecurityConfiguration
原来,首先他是个配置注解,也import了WebSecurityConfiguration
上面我们已经看到了步骤7,通常情况下都会去build
不知不觉我们已经找到了spring中的关键方法init了,很多时候我们在定义接口是都会有一个init方法来定义注入时调用
前面我们知道 SpringBootWebSecurityConfiguration初始化了一个对象,同时也通过AutowiredWebSecurityConfigurersIgnoreParents拿到了WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter的子类 DefaultConfigurerAdapter,现在开始init(),其实就是开始WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter的init()方法。说了这里可能有的同学就会比较熟悉了,这就是关键配置的适配器类。
代码稍后贴出来,暂时先不看,到这里为止,我们才梳理了springboot自动配置中的SecurityAutoConfiguration
下面我们才开始第二个类
3|22、 UserDetailsServiceAutoConfiguration
这里也出现了一个info日志,当我们使用默认user用户时,密码会从这里打印在控制台
这个配置类的关键就是生成一个默认的InMemoryUserDetailsManager对象。
3|34、SecurityFilterAutoConfiguration
这个类就不详细介绍了,就是注册一些过滤器。
回到WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter 这个适配器类,我们关注基本的init()方法,其他的都是一些默认的配置
这里有一个关键的方法getHttp()
我们简单列举几个重要的方法
上面我们都是通过启动日志的信息来理解应用在启动时到底做了什么,加载了什么关键信息,接下来我们将通过运行时的日志看来看一下我们在认证过程中是如何进行用户名密码的校验的。
4|0登录流程
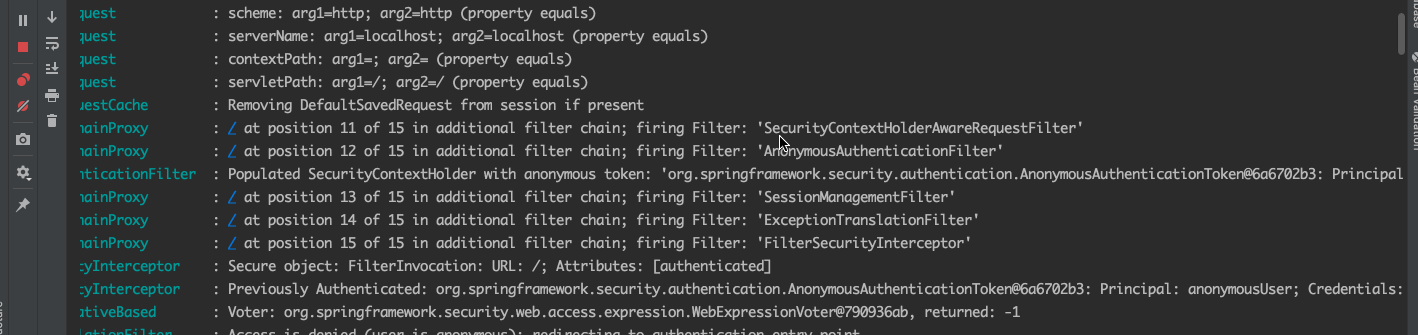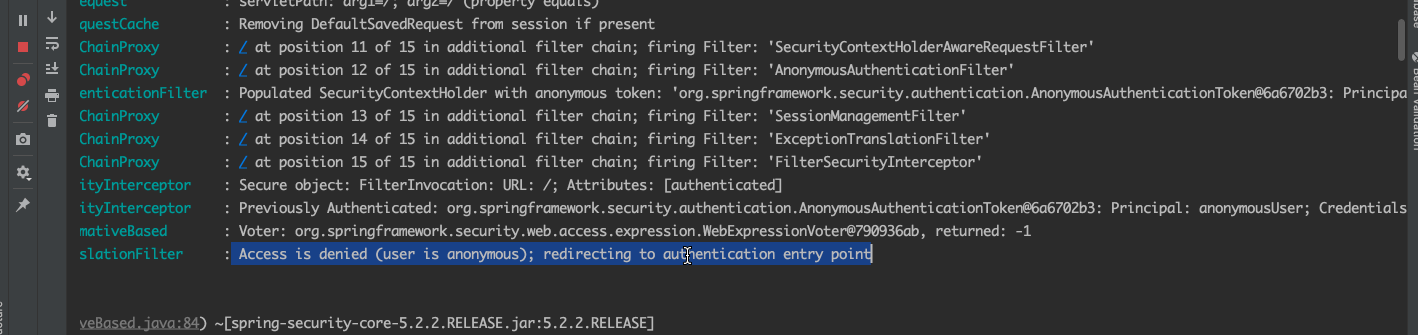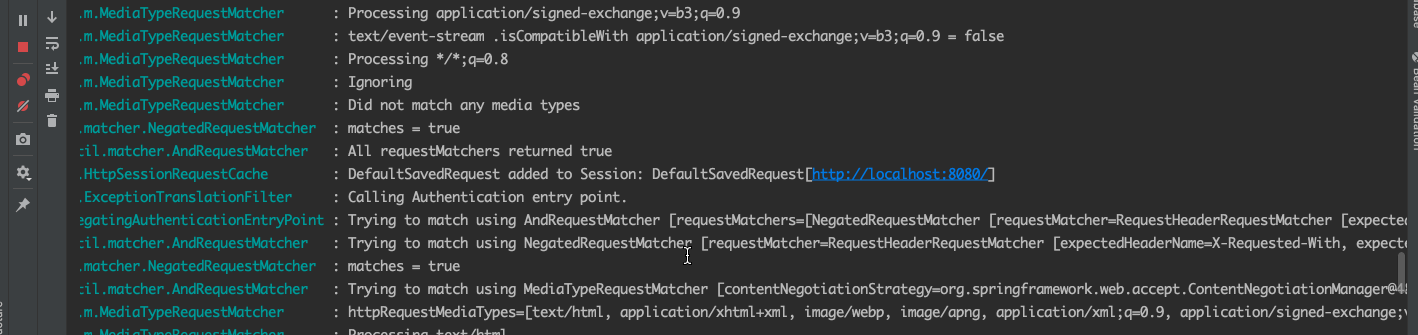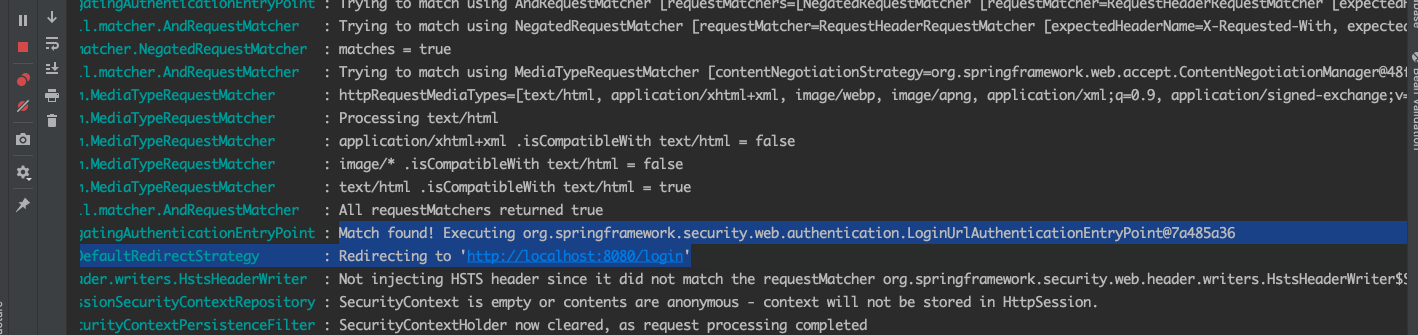
我们打开浏览器输入localhost:8080 由于我们没有进行登录,所以会被redirecting到登录页面。我们一起过滤一下控制台信息,抓取到关键的信息。
我们看到,这里加载了各种过滤器,当访问/时没发现并没有登录,则重定向到默认的/login页面,这也是spirng security的核心。今天重点讨论登录流程,我们先清空控制台,用正确的用户名和密码登录进去。
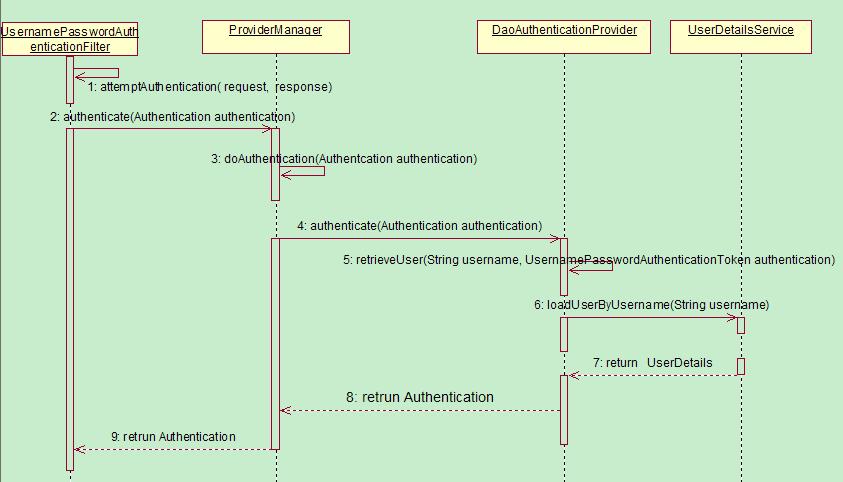
从控制台我们可以看到很多的过滤器,我们至关注认证流程的一部分,已上图为准。
4|11、UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter
这理解这个过滤器前,我们先从他的父类AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter 入手,既然是过滤器,我们既要入doFilter入手, 这里是关键的流程,子类只是做具体的实现,我们稍后再看
上面的关键方法attemptAuthentication(request, response);在UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter中
在UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 的关键流程中,我们将请求的参数进行符合入参的封装,
4|22、AuthenticationManager
AuthenticationManager本身不包含认证逻辑,其核心是用来管理所有的 AuthenticationProvider,通过交由合适的 AuthenticationProvider 来实现认证。
4|33、AuthenticationProvider
Spring Security 支持多种认证逻辑,每一种认证逻辑的认证方式其实就是一种 AuthenticationProvider。通过 getProviders()方法就能获取所有的AuthenticationProvider,通过provider.supports()来判断 provider 是否支持当前的认证逻辑。
当选择好一个合适的AuthenticationProvider 后,通过 provider.authenticate(authentication) 来让 AuthenticationProvider进行认证。
4|44、AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider
表单登录的 AuthenticationProvider主要是由 AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider 来进行处理的,我们来看下它的 authenticate()方法。
那么关键的retrieveUser里面是什么样呢?
由于我们的用户信息是在UserDetailsServiceAutoConfiguration 的配置类中生成了 InMemoryUserDetailsManager,所以这里的loadUserByUsername的代码则是这样
在内存中维护的用户中去获取,那么如果是其他的用户存储则需要对应的获取方式,如果是保存在数据库那么就需要通过sql语句去获取了,感兴趣的可以直接点击JdbcUserDetailsManager查看相关代码。
其实真个认证的流程到这里也就结束了,至于成功或失败后的逻辑最后还是回到了UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter中的结果,如果是成功this.successfulAuthentication(request, response, chain, authResult);
5|0总结
以上便是spring security的认证流程,没想到篇幅会这么长,断点追踪的方式很痛苦,大致方向应该是对的,基本的认证流程也应该浮出水面了。本篇主要是从自动配置的方式出发,后续将展示其他的配置方式甚至自定义认证流程,加油!!!


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号