Spring Security 官网文档学习
文章目录
通过maven向普通的WEB项目中引入spring security
<!-- spring核心包 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-core</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-web</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-oxm</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-tx</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aop</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context-support</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 解决spring security传递依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-framework-bom</artifactId>
<version>5.1.4.RELEASE</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
<!--
项目配置,使用spring security 依赖的相关jar包
1、按照文档,将可能需要的包都全部添加进来,即使目前有的包,我们暂且没用到(remoting 远程访问的除外)
2、包含 core、web、config、LDAP、OAuth、ACL、CAS、OpenID、test
-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-core</artifactId>
<version>${spring.security.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-web</artifactId>
<version>${spring.security.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-config</artifactId>
<version>${spring.security.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-ldap</artifactId>
<version>${spring.security.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-oauth2-core</artifactId>
<version>5.1.0.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-oauth2-client</artifactId>
<version>5.1.0.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-oauth2-jose</artifactId>
<version>5.1.0.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-jwt</artifactId>
<version>1.0.9.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-acl</artifactId>
<version>${spring.security.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-cas</artifactId>
<version>${spring.security.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-openid</artifactId>
<version>${spring.security.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-test</artifactId>
<version>${spring.security.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!--
否则会提示
Error:(9, 8) java: 无法访问javax.servlet.ServletException
找不到javax.servlet.ServletException的类文件
-->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax</groupId>
<artifactId>javaee-api</artifactId>
<version>7.0</version>
</dependency>
配置 spring security
示例代码:
package hello;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService;
import org.springframework.security.provisioning.InMemoryUserDetailsManager;
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/", "/home").permitAll()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin()
.loginPage("/login")
.permitAll()
.and()
.logout()
.permitAll();
}
@Bean
@Override
public UserDetailsService userDetailsService() {
UserDetails user =
User.withDefaultPasswordEncoder()
.username("user")
.password("password")
.roles("USER")
.build();
return new InMemoryUserDetailsManager(user);
}
}
我们在WebSecurityConfig 类使用了 @EnableWebSecurity 注解 ,该注解提供 spring security的支持以及springMvc的集成支持,配合 @Configuration 注解,即可构成一个 spring security 的配置;
其中我们自己写的WebSecurityConfig 类必须是扩展了 WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter 抽象类的类;我们就是通过它,告诉 spring security ,哪些用户需要经过身份验证,通过何种方式验证;
其中我们选择覆写一些方法,来做一些安全的细节设置,达到上面的目的,比如,配置 :拦截什么URL、设置什么权限,检验表单数据 等 ;
userDetailsService() 方法,在内存中添加了一个用户,并设置了其角色、用户名、密码,不多讲;
configure(HttpSecurity) 方法
其中 configure(HttpSecurity) 方法里面定义了哪些路径需要被保护,那些路径不需要被保护。简单而言,只有 / 、/home 不需要保护,可以被任何权限、角色查看,其他的路径都需要进行验证;
代码中配置:
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.authorizeRequests()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin()
.and()
.httpBasic();
}
其实上面的配置,就是一个 xml 配置:
<http>
<intercept-url pattern="/**" access="authenticated"/>
<form-login />
<http-basic />
</http>
每个方法或多或少都对应着一个标签,想象成这样以后,就便于我们看懂代码的配置;
配置规则都是使用方法,诸多方法的具体含义如下(图内容来自 spring4All 社区 ):
其中有一个特殊的方法 and() ,类比于 xml 的标签结束符;
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| openidLogin() | 用于基于 OpenId 的验证 |
| headers() | 将安全标头添加到响应 |
| cors() | 配置跨域资源共享( CORS ) |
| sessionManagement() | 允许配置会话管理 |
| portMapper() | 允许配置一个PortMapper(HttpSecurity#(getSharedObject(class))),其他提供 SecurityConfigurer的对象使用 PortMapper 从 HTTP 重定向到 HTTPS 或者从 HTTPS 重定向到 HTTP。 默认情况下,Spring Security使用一个PortMapperImpl映射 HTTP 端口8080到 HTTPS 端口8443,HTTP 端口80到 HTTPS 端口443 |
| jee() | 配置基于容器的预认证。 在这种情况下,认证由Servlet容器管理 |
| x509() | 配置基于x509的认证 |
| rememberMe | 允许配置“记住我”的验证 |
| authorizeRequests() | 允许基于使用HttpServletRequest限制访问 |
| requestCache() | 允许配置请求缓存 |
| exceptionHandling() | 允许配置错误处理 |
| securityContext() | 在HttpServletRequests之间的SecurityContextHolder上设置SecurityContext的管理。 当使用WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter时,这将自动应用 |
| servletApi() | 将HttpServletRequest方法与在其上找到的值集成到SecurityContext中。 当使用 WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter时,这将自动应用 |
| csrf() | 添加 CSRF 支持,使用WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter时,默认启用 |
| logout() | 添加退出登录支持。当使用WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter时,这将自动应用。 默认情况是,访问"URL/logout”,使HTTP Session无效来清除用户,清除已配置的任何#rememberMe()身份验证,清除SecurityContextHolder,然后重定向到”/login?success” |
| anonymous() | 允许配置匿名用户的表示方法。 当与WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter结合使用时,这将自动应用。 默认情况下,匿名用户将使用org.springframework.security.authentication.AnonymousAuthenticationToken表示,并包含角色 “ROLE_ANONYMOUS” |
| formLogin() | 指定支持基于表单的身份验证。如果未指定 FormLoginConfigurer#loginPage(String),则将生成默认登录页面 |
| oauth2Login() | 根据外部OAuth 2.0或OpenID Connect 1.0提供程序配置身份验证 |
| requiresChannel() | 配置通道安全。为了使该配置有用,必须提供至少一个到所需信道的映射 |
| httpBasic() | 配置 Http Basic 验证 |
| addFilterAt() | 在指定的Filter类的位置添加过滤器 |
自定义URL身份验证
-
缺省登陆路径
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { http // 表示允许使用HttpServletRequest限制访问 .authorizeRequests() // 对任何请求都进行身份验证 .anyRequest().authenticated() .and() // 启动基于表单验证 .formLogin() // 该路径允许所有人访问到 .permitAll(); }上面的
.formLogin()没有配置登陆页面,spring security会默认的生成一个页面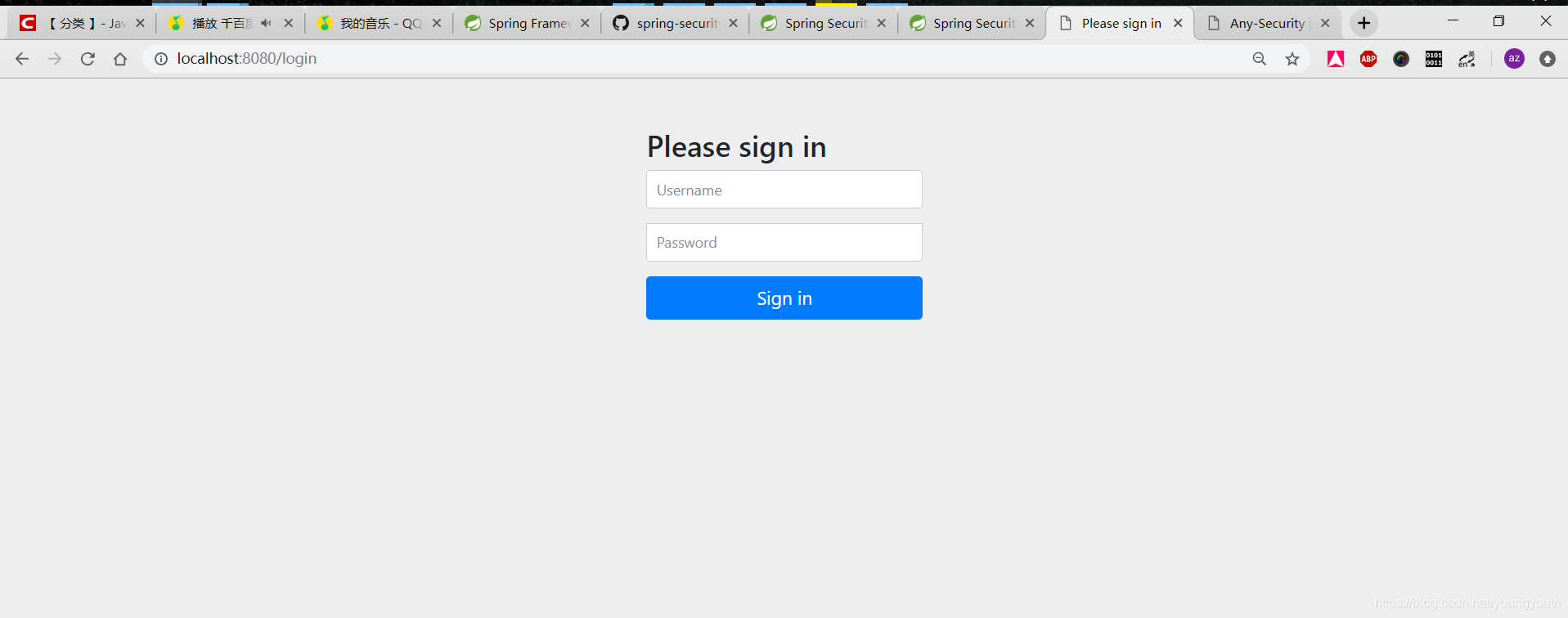
配置自己的登陆页面,使用
.loginPage("路径"):.formLogin() .loginPage("/login") .permitAll();自定义的页面表单中,需要包含下面的代码:
<input type="hidden" name="${_csrf.parameterName}" value="${_csrf.token}"/>防止
CSRF攻击; -
授权请求
上面配置的只是,一刀切,对除了登陆路径的其他任何路径都进行身份验证,实际开发中,我们应该有细粒度的配置,比如权限控制;
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { http .authorizeRequests() // 如果URL以 "/resources/**", "/signup", "/about" 开头,则任何用户都可以访问 .antMatchers("/resources/**", "/signup", "/about").permitAll() // 如果访问 "/admin/**" ,则必须具有 ”ADMIN" 角色才可以访问 ; // 其中,因为调用的就是 hasRole 方法,所以 前缀 ROLE_ 可以省略不写; .antMatchers("/admin/**").hasRole("ADMIN") // 如果访问 /db/** 开头的 URL ,则必须同时拥有 "ADMIN" "DBA" 两个角色; // 对于这样多角色判断的,使用 access 连接 .antMatchers("/db/**").access("hasRole('ADMIN') and hasRole('DBA')") // 任何URL ,经过上面几道工序,如果还没有得到匹配的,则只要求进行身份的验证; // 这里说明下,匹配 URL 的规则是从上到下,按照顺序匹配的,如果前面的已经匹配了,则后面的不再进行匹配; .anyRequest().authenticated() .and() // ... .formLogin(); } -
注销操作
因为我们使用的是
WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter,logout功能默认就有,不需要我们自己编码,只需要访问/logout即可,然后spring security会自动的帮我们完成注销操作;并且
spring security会完成以下几件事:1、销毁对应的会话
session;
2、清楚任何已经配置的记住我身份验证;
3、清除SecurityContextHolder;
4、重定向到/login?logout;上面都是
spring security默认的行为(前提是使用WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter),我们还可以自己定制更细节的行为 :protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { http // 提供注销支持,如果使用 `WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter` 则默认提供支持,不需要显式配置了 .logout() // 触发注销行为的 URL ,默认是 /logout ,如果启用了 CSRF ,则该请求必须是 post ;但是默认就是启用 CSRF ,so 默认就必须使用 post 访问 ; .logoutUrl("/my/logout") // 触发注销操作以后,重定到具体的页面,默认是 /login?logout .logoutSuccessUrl("/my/index") // 我们指定一个自定义的LogoutSuccessHandler。如果指定了此参数,则忽略logoutSuccessUrl 的配置 .logoutSuccessHandler(logoutSuccessHandler) // 指定在注销时是否使HttpSession无效。默认情况下为 真 .invalidateHttpSession(true) // 添加LogoutHandler。默认情况下,SecurityContextLogoutHandler被添加为最后一个LogoutHandler。 .addLogoutHandler(logoutHandler) // 指定注销成功以后,要删除的cookie的名字 // 同时这里也是显式添加 CookieClearingLogoutHandler 处理器的快捷方式 .deleteCookies(cookieNamesToClear) .and() ... }
身份验证 and 授权
应用程序的安全问题,或许可以简单的归结为两类:身份验证 and 授权,Spring Security 致力于将二者分开,为两者提供各自的问题解决方法;
Authentication
AuthenticationManager 是用于身份认证的主要策略接口,它仅有一个方法;
public interface AuthenticationManager {
Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication)
throws AuthenticationException;
}
该接口的方法,可以返回下面的三种数据的任何一个:
-
authenticated=true如果认为输入的主体(可以理解为用户),是有效的,即账号密码角色都对,则验证通过,返回
authenticated=true; -
AuthenticationException如果验证没有通过没,则抛出一个
AuthenticationException异常,这个异常是一个运行时异常,官网文档里面建议,不需要我们代码中捕捉然后处理,我们应该做一个统一处理,让其跳到特定页面(网站全局异常页面) -
null如果无法决定是否验证成功,则返回
null,为什么会出现无法决定呢,因为一个AuthenticationManager实例,可能只管理一部分身份的验证,另外一些身份验证有其他AuthenticationManager实例验证,因此这时候,就会返回一个null;
AuthenticationProvider
AuthenticationManager最常用的实现是ProviderManager,它委托一系列AuthenticationProvider实例。AuthenticationProvider有点像AuthenticationManager,但它有一个额外的方法允许调用者查询它是否支持给定的身份验证类型:
public interface AuthenticationProvider {
Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication)
throws AuthenticationException;
boolean supports(Class<?> authentication);
}
一个 ProviderManager 支持多种不同验证机制,通过委托多个小弟 AuthenticationProvider 来完成,小弟的方法 supports(Class<?> authentication) ,用于校验传给它的验证身份类型是否支持,如果不支持,则返回 false, 然后 ProviderManager就会跳过该小弟,询问下一位小弟;(有待考证)
ProviderManager 有一个可选的父级,如果所有小弟都返回 null,它可以参考。如果父级不可用,则null验证会导致AuthenticationException。
有时候,web应用有多个受保护的逻辑组,比如:/db/**、/login/** 等等,每个受保护的逻辑组可能有他们自己的专用的 AuthenticationManager,通常情况下这些 AuthenticationManager ,都是 ProviderManager,他们共享一个父级——这个父级是一个全局资源,充当所有的 ProviderManager 的后备资源,也是一个 ProviderManager,走投无路的时候,就去找老爹;
自定义身份验证器
spring security 提供了配置帮助程序,用于快速获取程序中设置的身份管理;其中,最常用的是 AuthenticationManagerBuilder ,它很适用于 内存、JDBC、LDAP ,或者增加一个 UserDetailsService;
配置全局的 AuthenticationManager:
@Configuration
public class ApplicationSecurity extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
... // web stuff here
@Autowired
public initialize(AuthenticationManagerBuilder builder, DataSource dataSource) {
builder.jdbcAuthentication().dataSource(dataSource).withUser("dave")
.password("secret").roles("USER");
}
}
上面的配置中,关于 AuthenticationManagerBuilder 的用法是一种广泛的使用方式;它被使用 @Autowired 注入到方法中,这将导致它可以构建全局的 AuthenticationManager ;
当然也有另外一种写法:
@Configuration
public class ApplicationSecurity extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
DataSource dataSource;
... // web stuff here
@Override
public configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder builder) {
builder.jdbcAuthentication().dataSource(dataSource).withUser("dave")
.password("secret").roles("USER");
}
}
这里是覆盖父类方法,这样的 AuthenticationManagerBuilder 只能被用来构建局部的 AuthenticationManager ,构建出的 AuthenticationManager 将是全局 AuthenticationManager 的小弟;
在 springBoot 中可以使用 @Autowired 将一个全局的 bean 直接注入到另外一个 bean 里面 ,但是不能对局部的 bean 使用这种操作;
springBoot 中,如果自己没有全局的自定义身份验证,它默认提供一个全局的 AuthenticationManager,默认的 AuthenticationManager的安全性不需要我们去担心;我们可以在局部的 AuthenticationManager 里面做配置,从而不去影响到全局的 AuthenticationManager ;
授权
身份认证成功以后,就需要我们进行授权了;
在 spring Security 中的对应的核心类是 AccessDecisionManager ,框架本身有三个默认实现,并且这三个实现都委托给 AccessDecisionVoter 管理,跟身份验证的 AuthenticationProvider 委托给 ProviderManager;
AccessDecisionVoter 如下:
public interface AccessDecisionVoter<S> {
int ACCESS_GRANTED = 1;
int ACCESS_ABSTAIN = 0;
int ACCESS_DENIED = -1;
boolean supports(ConfigAttribute attribute);
boolean supports(Class<?> clazz);
int vote(Authentication authentication, S object,
Collection<ConfigAttribute> attributes);
}
其中 S object 的Object 对象,在 AccessDecisionManager 、AccessDecisionVoter 中是通用的,代表用户想访问的东西,大部分时候都代表一个 web 资源,或者一个 java 类的方法 ;
ConfigAttribute 接口也是通用的,是安全对象的封装,里面封装一些元数据,用于确定访问 Object 所需要的权限 ;它只有一个方法,返回 String ,代表开发者制定的规则,谁可以访问 Object ;其中返回的字符串格式,一般都是以 ROLE_ 为前缀的角色名称,比如 ROLE_ADMIN 、ROLE_AUDIT 等;
使用 SPEL 表达式 的 ConfigAttribute 是很常见的,比如 isFullyAuthenticated()&& hasRole('FOO') ,这些表达式被 AccessDecisionVoter 所支持,它可以处理这些表达式,并且创建对应的上下文;
如果你想扩展 SPEL 的表达式范围,需要自定义实现 SecurityExpressionRoot,有时还需要SecurityExpressionHandler。
大部分人都使用默认的 AccessDecisionManager — AffirmativeBased,它的内部是只要有一个投票通过,即可进行授权访问,要想进行细致的投票定制,可以自定义实现 AccessDecisionManager ;
Spring Security 的过滤器
Spring Security 是基于 Filter 进行实现的;
当客户端向应用程序发送请求,Spring Security 根据请求URI的路径决定哪些过滤器和哪个servlet处理它 ;一个 servlet 处理一个请求,所有的 Filter 构建成一个 拦截链 ,它们是有序的,其中的任何一个都可以中断请求,或者修改掉 request 、response;
Spring Security 本身是在 Spring 容器中是作为作为一个 Filter 的,其类型是 FilterChainProxy,但是其本身之中,又包含多个 Filter ;
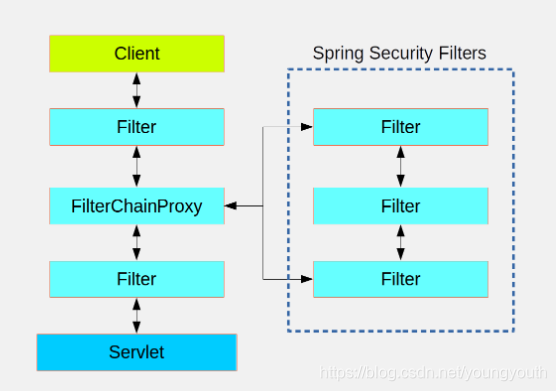
Spring Security 在 Spring容器中仅仅是一个物理的过滤器,也就是它本身其实不进行任何拦截,都是交给它背后的过滤器;
实际上在 Spring Security 的内部还有一个间接层,它通常作为 DelegatingFilterProxy安装在 Spring Security 容器中,它不需要在 Spring 中进行注册,这个间接层最后委托 FilterChainProxy 在 spring 容器中进行注册,并且名字必须是 springSecurityFilterChain; 。
DelegatingFilterProxy 背后的那一堆 Filter 都实现了相同接口,只是具体逻辑不同,并且都可以决定后续的 Filter 是否进行拦截 ;
Spring Security 背后可以管理多个过滤器,但是这些过滤器对 Spring 都是不可见的,并且这些过滤器可以进行分组,然后 Spring Security 将 request 进行派发给第一个匹配的分组;
如图所示:
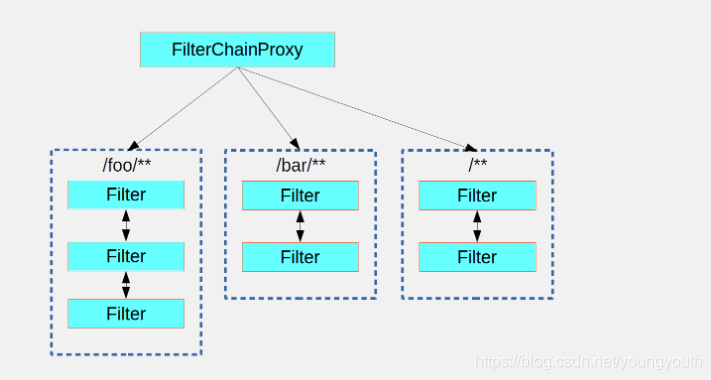
这只是 Spring Security 分配请求的一种方法,用此种方法分配时,只有一组拦截链可以处理请求 ;
创建和自定义 拦截链
在 SpringBoot 中有一个默认的最低级别的拦截器 ,它拦截 /** 请求,预定义的顺序为 SecurityProperties.BASIC_AUTH_ORDER,如果不想使用它的话,设置 SecurityProperties.BASIC_AUTH_ORDER = false 即可 ;
但是一般都将其作为一个基准,便于我们自己创建拦截器的时候,定义顺序 ;
比如新建一个拦截器,只需要继承 WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter 或 WebSecurityConfigurer 即可,然后定义一个顺序,这时候就可以使用 SecurityProperties.BASIC_AUTH_ORDER 作为基准;
使用 @Order(SecurityProperties.BASIC_AUTH_ORDER - 10) 定义顺序,数值越少,级别越高 ;
@Configuration
@Order(SecurityProperties.BASIC_AUTH_ORDER - 10)
public class ApplicationConfigurerAdapter extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.antMatcher("/foo/**")
...;
}
}
其中对于同一组资源可能有多个拦截器设置匹配规则,此时匹配规则重叠,则哪一个拦截器的优先级高,就使用谁 ;
请求匹配调度和授权
一个 WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter 就是一组拦截链,使用 http.antMatcher("/foo/**") 决定匹配什么请求;
然后再使用antMatchers("/foo/bar").hasRole("BAR") ,设置访问该组拦截链拦截的URL的角色 ;
@Configuration
@Order(SecurityProperties.BASIC_AUTH_ORDER - 10)
public class ApplicationConfigurerAdapter extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.antMatcher("/foo/**")
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/foo/bar").hasRole("BAR")
.antMatchers("/foo/spam").hasRole("SPAM")
.anyRequest().isAuthenticated();
}
}
方法安全
前面讲的都是基于 url 级别的授权,下面说的授权,粒度更细,是基于方法的 ;
对于 Spring Security 来说,方法也是一种受保护的资源类型 ;
在应用程序的顶级配置中,启动方法安全性 @EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(securedEnabled = true) ;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(securedEnabled = true)
public class SampleSecureApplication {
}
然后在需要保护的方法上配置:
@Service
public class MyService {
@Secured("ROLE_USER")
public String secure() {
return "Hello Security";
}
}
这样配置以后,如果Spring创建了这种类型的 Bean 对象,那么它将被代理,并且调用者必须在实际执行该方法之前通过安全拦截器。如果访问被拒绝,则调用者将获得AccessDeniedException而不是实际的方法结果 ;
还有其他注释可用于强制执行安全约束的方法,特别是@PreAuthorize和@PostAuthorize,它们允许您编写包含对方法参数和返回值的引用的表达式。
spring Security 线程问题
-
SecurityContextSpring Security是线程绑定的,最基本的组件是SecurityContext里面包含Authentication,可以通过下面的方式,获取和修改SecurityContext;SecurityContext context = SecurityContextHolder.getContext(); Authentication authentication = context.getAuthentication(); assert(authentication.isAuthenticated); -
@AuthenticationPrincipal注解@RequestMapping("/foo") public String foo(@AuthenticationPrincipal User user) { ... // do stuff with user }此注解可以将当前的
Authentication从SecurityContext中抽取出来,然后调用getPrincipal()填充方法参数;至于调用getPrincipal()获取的Principal类型,取决于AuthenticationManager使用什么类型来进行验证Authentication;如果使用
Spring Security的HttpServletRequest中的Principal,那么Principal将是Authentication类型,我们可以向下面这样操作,获取User:@RequestMapping("/foo") public String foo(Principal principal) { Authentication authentication = (Authentication) principal; User = (User) authentication.getPrincipal(); ... // do stuff with user } -
异步处理安全方法由于
SecurityContext是线程绑定的,因此如果要进行任何调用安全方法的后台处理,例如使用@Async(Runnable, Callable等等异步执行方法),需要确保传播上下文。要将
SecurityContext传播到@Async方法,需要提供AsyncConfigurer并确保Executor的类型正确:@Configuration public class ApplicationConfiguration extends AsyncConfigurerSupport { @Override public Executor getAsyncExecutor() { return new DelegatingSecurityContextExecutorService(Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5)); } }


【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】凌霞软件回馈社区,博客园 & 1Panel & Halo 联合会员上线
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】博客园社区专享云产品让利特惠,阿里云新客6.5折上折
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步