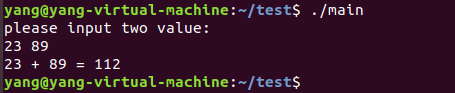
写一个简单的Makefile
yang@yang-virtual-machine:~/test$ gcc --help
Usage: gcc [options] file...
Options:
-pass-exit-codes Exit with highest error code from a phase.
--help Display this information.
--target-help Display target specific command line options.
--help={common|optimizers|params|target|warnings|[^]{joined|separate|undocumented}}[,...].
Display specific types of command line options.
(Use '-v --help' to display command line options of sub-processes).
--version Display compiler version information.
-dumpspecs Display all of the built in spec strings.
-dumpversion Display the version of the compiler.
-dumpmachine Display the compiler's target processor.
-print-search-dirs Display the directories in the compiler's search path.
-print-libgcc-file-name Display the name of the compiler's companion library.
-print-file-name=<lib> Display the full path to library <lib>.
-print-prog-name=<prog> Display the full path to compiler component <prog>.
-print-multiarch Display the target's normalized GNU triplet, used as
a component in the library path.
-print-multi-directory Display the root directory for versions of libgcc.
-print-multi-lib Display the mapping between command line options and
multiple library search directories.
-print-multi-os-directory Display the relative path to OS libraries.
-print-sysroot Display the target libraries directory.
-print-sysroot-headers-suffix Display the sysroot suffix used to find headers.
-Wa,<options> Pass comma-separated <options> on to the assembler.
-Wp,<options> Pass comma-separated <options> on to the preprocessor.
-Wl,<options> Pass comma-separated <options> on to the linker.
-Xassembler <arg> Pass <arg> on to the assembler.
-Xpreprocessor <arg> Pass <arg> on to the preprocessor.
-Xlinker <arg> Pass <arg> on to the linker.
-save-temps Do not delete intermediate files.
-save-temps=<arg> Do not delete intermediate files.
-no-canonical-prefixes Do not canonicalize paths when building relative
prefixes to other gcc components.
-pipe Use pipes rather than intermediate files.
-time Time the execution of each subprocess.
-specs=<file> Override built-in specs with the contents of <file>.
-std=<standard> Assume that the input sources are for <standard>.
--sysroot=<directory> Use <directory> as the root directory for headers
and libraries.
-B <directory> Add <directory> to the compiler's search paths.
-v Display the programs invoked by the compiler.
-### Like -v but options quoted and commands not executed.
-E Preprocess only; do not compile, assemble or link.
-S Compile only; do not assemble or link.
-c Compile and assemble, but do not link.
-o <file> Place the output into <file>.
-pie Create a position independent executable.
-shared Create a shared library.
-x <language> Specify the language of the following input files.
Permissible languages include: c c++ assembler none
'none' means revert to the default behavior of
guessing the language based on the file's extension.
Options starting with -g, -f, -m, -O, -W, or --param are automatically
passed on to the various sub-processes invoked by gcc. In order to pass
other options on to these processes the -W<letter> options must be used.
For bug reporting instructions, please see:
<file:///usr/share/doc/gcc-7/README.Bugs>.
如果只有数量很少的几个.c文件需要编译,使用gcc 可以很快完成,但是如果文件很多,使用gcc命令一个个进行编译就会变得很繁琐,所以需要用到Makefile。
1、首先需要编写几个.c文件和.h文件
①main.c
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include "input.h" 3 #include "calculate.h" 4 5 int main(int argc,char * argv[]) 6 { 7 int a,b,sum; 8 printf("please input two value:\r\n"); 9 get_input_values(&a,&b); 10 sum = calculate(a,b); 11 printf("%d + %d = %d\r\n",a,b,sum); 12 return 0; 13 }
②input.c
1 #include "input.h" 2 #include <stdio.h> 3 4 void get_input_values(int * a,int * b) 5 { 6 scanf("%d %d",a,b); 7 }
③calculate.c
1 #include "calculate.h" 2 3 int calculate(int a,int b) 4 { 5 return a+b; 6 }
④input.h
1 #ifndef _INPUT_H_ 2 #define _INPUT_H_ 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 void get_input_values(int * a,int * b); 11 12 13 #endif
⑤calculate.h
1 #ifndef _CALCULATE_H_ 2 #define _CALCULATE_H_ 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 int calculate(int a,int b); 10 11 12 #endif
2、编写Makefile
1 main: main.o input.o calculate.o 2 gcc -o main main.o input.o calculate.o 3 main.o: main.c 4 gcc -c main.c 5 input.o: input.c 6 gcc -c input.c 7 calculate.o: calculate.c 8 gcc -c calculate.c 9 10 clean: 11 rm *.o 12 rm main
3、make

4、运行程序