Linux下各种压缩与解压笔记
1、gzip
yang@yang-virtual-machine:~$ gzip --help Usage: gzip [OPTION]... [FILE]... Compress or uncompress FILEs (by default, compress FILES in-place). Mandatory arguments to long options are mandatory for short options too. -c, --stdout write on standard output, keep original files unchanged -d, --decompress decompress -f, --force force overwrite of output file and compress links -h, --help give this help -k, --keep keep (don't delete) input files -l, --list list compressed file contents -L, --license display software license -n, --no-name do not save or restore the original name and time stamp -N, --name save or restore the original name and time stamp -q, --quiet suppress all warnings -r, --recursive operate recursively on directories -S, --suffix=SUF use suffix SUF on compressed files -t, --test test compressed file integrity -v, --verbose verbose mode -V, --version display version number -1, --fast compress faster -9, --best compress better --rsyncable Make rsync-friendly archive With no FILE, or when FILE is -, read standard input. Report bugs to <bug-gzip@gnu.org>.
其中几个比较常用的参数是:
①-d :解压;②-r:递归;③-v:输出详细的信息,可以看到压缩或解压的过程;
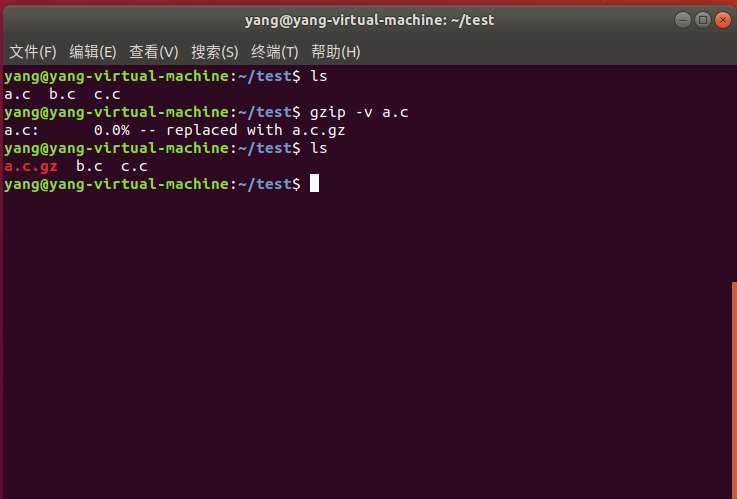
压缩一个文件:
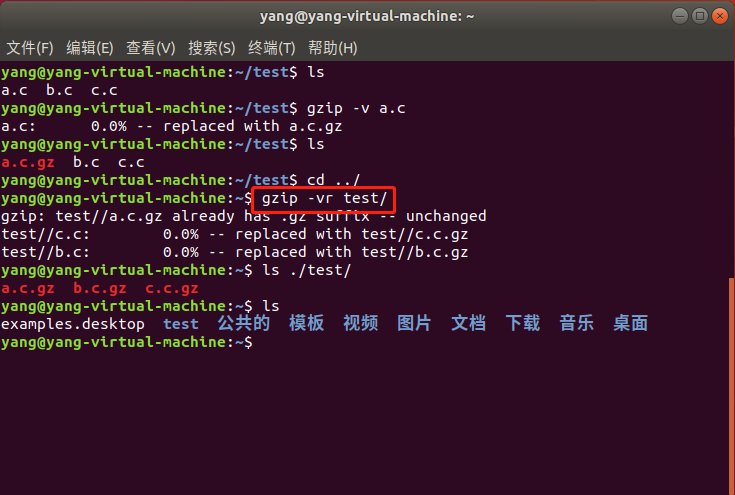
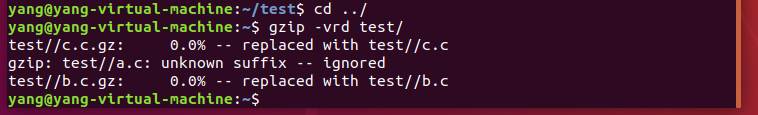
对一个文件夹进行压缩,用到r参数,注意只是对其中的文件进行压缩,但是文件夹并不能压缩:
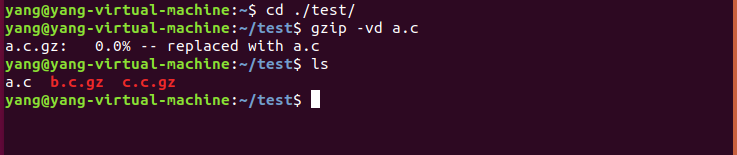
对一个文件进行解压:
对一个文件夹中的文件进行解压:
2、bzip2
yang@yang-virtual-machine:~$ bzip2 --help
bzip2, a block-sorting file compressor. Version 1.0.6, 6-Sept-2010.
usage: bzip2 [flags and input files in any order]
-h --help print this message
-d --decompress force decompression
-z --compress force compression
-k --keep keep (don't delete) input files
-f --force overwrite existing output files
-t --test test compressed file integrity
-c --stdout output to standard out
-q --quiet suppress noncritical error messages
-v --verbose be verbose (a 2nd -v gives more)
-L --license display software version & license
-V --version display software version & license
-s --small use less memory (at most 2500k)
-1 .. -9 set block size to 100k .. 900k
--fast alias for -1
--best alias for -9
If invoked as `bzip2', default action is to compress.
as `bunzip2', default action is to decompress.
as `bzcat', default action is to decompress to stdout.
If no file names are given, bzip2 compresses or decompresses
from standard input to standard output. You can combine
short flags, so `-v -4' means the same as -v4 or -4v, &c.
常用的几个参数:① d:解压;②z:压缩;③v:输出详细的信息,可以看到解压或压缩的过程;
对一个文件进行压缩:
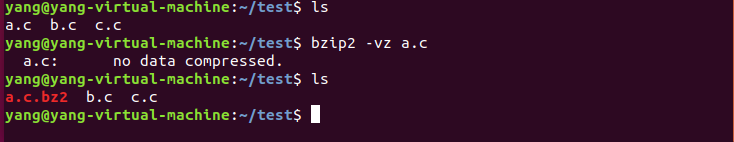
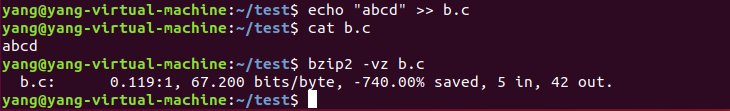
这里之所以会有一个"no data compressed"的提示,只是因为这个a.c里面并没有任何内容,现在我对同样是一个没有任何内容的b.c文件输入一串字符后再进行压缩,就不会出现这个提示:
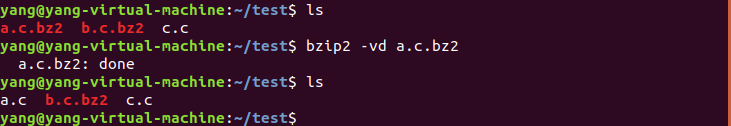
对一个文件进行解压:
3、tar
yang@yang-virtual-machine:~$ tar --help
用法: tar [选项...] [FILE]...
GNU ‘tar’
将许多文件一起保存至一个单独的磁带或磁盘归档,并能从归档中单独还原所需文件。
示例
tar -cf archive.tar foo bar # 从文件 foo 和 bar 创建归档文件
archive.tar。
tar -tvf archive.tar # 详细列举归档文件 archive.tar
中的所有文件。
tar -xf archive.tar # 解开归档文件 archive.tar
中的所有文件。
本地文件名选择:
--add-file=FILE 添加指定的 FILE 至归档(如果名字以 -
开始会很有用的)
-C, --directory=DIR 改变至目录 DIR
--exclude=PATTERN 排除以 PATTERN 指定的文件
--exclude-backups 排除备份和锁文件
--exclude-caches 除标识文件本身外,排除包含
CACHEDIR.TAG 的目录中的内容
--exclude-caches-all 排除包含 CACHEDIR.TAG 的目录
--exclude-caches-under 排除包含 CACHEDIR.TAG
的目录中所有内容
--exclude-ignore=FILE 若存在FILE,
则从其中读取每个目录的例外匹配项
--exclude-ignore-recursive=FILE
若存在FILE,
则从其中为每个目录及其子目录读取需要排除的例外匹配项
--exclude-tag=FILE 除 FILE 自身外,排除包含 FILE
的目录中的内容
--exclude-tag-all=FILE 排除包含 FILE 的目录
--exclude-tag-under=FILE 排除包含 FILE 的目录中的所有内容
--exclude-vcs 排除版本控制系统目录
--exclude-vcs-ignores 从VCS 忽略文件中读取排除匹配项
--no-null 禁用上一次的效果 --null 选项
--no-recursion 避免目录中的自动降级
--no-unquote 不要unquote 输入文件或成员名称
--no-verbatim-files-from -T
把以‘-’开始的文件作为选项(默认)
--null -T 读取以空终止的名字; 隐含
--verbatim-files-from
--recursion 目录递归(默认)
-T, --files-from=FILE 从 FILE
中获取文件名来解压或创建文件
--unquote unquote 输入文件或成员名称(默认)
--verbatim-files-from -T 逐字读取文件名(不处理选项)
-X, --exclude-from=FILE 排除 FILE 中列出的模式串
文件名匹配选项(同时影响排除和包括模式串):
--anchored 模式串匹配文件名头部
--ignore-case 忽略大小写
--no-anchored 模式串匹配任意‘/’后字符(默认对
exclusion 有效)
--no-ignore-case 匹配大小写(默认)
--no-wildcards 逐字匹配字符串
--no-wildcards-match-slash 通配符不匹配‘/’
--wildcards 使用通配符(默认对 exclusion )
--wildcards-match-slash 通配符匹配‘/’(默认对exclusion
有效)
主操作模式:
-A, --catenate, --concatenate 追加 tar 文件至归档
-c, --create 创建一个新归档
-d, --diff, --compare 找出归档和文件系统的差异
--delete 从归档(非磁带!)中删除
-r, --append 追加文件至归档结尾
-t, --list 列出归档内容
--test-label 测试归档卷标并退出
-u, --update 仅追加比归档中副本更新的文件
-x, --extract, --get 从归档中解出文件
操作修饰符:
--check-device 当创建增量归档时检查设备号(默认)
-g, --listed-incremental=FILE 处理新式的 GNU 格式的增量备份
-G, --incremental 处理老式的 GNU 格式的增量备份
--hole-detection=TYPE 用于探测holes 的技术
--ignore-failed-read
当遇上不可读文件时不要以非零值退出
--level=NUMBER 所创建的增量列表归档的输出级别
-n, --seek 归档可检索
--no-check-device 当创建增量归档时不要检查设备号
--no-seek 归档不可检索
--occurrence[=NUMBER] 仅处理归档中每个文件的第 NUMBER
个事件;仅当与以下子命令 --delete,
--diff, --extract 或是 --list
中的一个联合使用时,此选项才有效。而且不管文件列表是以命令行形式给出或是通过
-T 选项指定的;NUMBER 值默认为 1
--sparse-version=MAJOR[.MINOR]
设置所用的离散格式版本(隐含
--sparse)
-S, --sparse 高效处理离散文件
重写控制:
-k, --keep-old-files 解压时不替换存在的文件,
而将其认为是错误
--keep-directory-symlink 解压时保留已存在的目录符号链接
--keep-newer-files
不要替换比归档中副本更新的已存在的文件
--no-overwrite-dir 保留已存在目录的元数据
--one-top-level[=DIR] 创建子目录以避免解压松散文件
--overwrite 解压时重写存在的文件
--overwrite-dir
解压时重写已存在目录的元数据(默认)
--recursive-unlink 解压目录之前先清除目录层次
--remove-files 在添加文件至归档后删除它们
--skip-old-files
解压时不替换存在的文件,而是自动忽略
-U, --unlink-first 在解压要重写的文件之前先删除它们
-W, --verify 在写入以后尝试校验归档
选择输出流:
--ignore-command-error 忽略子进程的退出代码
--no-ignore-command-error
将子进程的非零退出代码认为发生错误
-O, --to-stdout 解压文件至标准输出
--to-command=COMMAND
将解压的文件通过管道传送至另一个程序
操作文件属性:
--atime-preserve[=METHOD]
在输出的文件上保留访问时间,要么通过在读取(默认
METHOD=‘replace’)后还原时间,要不就不要在第一次(METHOD=‘system’)设置时间
--clamp-mtime 当文件比 --mtime
指定的文件更新时仅更新时间
--delay-directory-restore
直到解压结束才设置修改时间和所解目录的权限
--group=名称 强制将 NAME
作为所添加的文件的组所有者
--group-map=FILE 用FILE 映射文件所有者GIDs 和名字
--mode=CHANGES 强制将所添加的文件(符号)更改为权限
CHANGES
--mtime=DATE-OR-FILE 从 DATE-OR-FILE 中为添加的文件设置 mtime
-m, --touch 不要解压文件的修改时间
--no-delay-directory-restore
取消 --delay-directory-restore 选项的效果
--no-same-owner
将文件解压为您所有(普通用户默认此项)
--no-same-permissions
从归档中解压权限时使用用户的掩码位(默认为普通用户服务)
--numeric-owner 总是以数字代表用户/组的名称
--owner=名称 强制将 NAME
作为所添加的文件的所有者
--owner-map=FILE 用FILE 映射文件所有者UIDs 和名字
-p, --preserve-permissions, --same-permissions
解压文件权限信息(默认只为超级用户服务)
--same-owner
尝试解压时保持所有者关系一致(超级用户默认此项)
-s, --preserve-order, --same-order
成员参数按归档中的文件顺序列出
--sort=ORDER 目录排序顺序: none(默认), name 或inode
操作extended 文件属性:
--acls 开启POSIX ACLs 支持
--no-acls 关闭POSIX ACLs 支持
--no-selinux 关闭SELinux 上下文支持
--no-xattrs 关闭extended 属性支持
--selinux 开启SELinux 上下文支持
--xattrs 开启extended 属性支持
--xattrs-exclude=MASK 为xattr 关键字指定排除匹配项
--xattrs-include=MASK 为xattr 关键字指定包含匹配项
设备选择和切换:
-f, --file=ARCHIVE 使用归档文件或 ARCHIVE 设备
--force-local
即使归档文件存在副本还是把它认为是本地归档
-F, --info-script=名称, --new-volume-script=名称
在每卷磁带最后运行脚本(隐含 -M)
-L, --tape-length=NUMBER 写入 NUMBER × 1024 字节后更换磁带
-M, --multi-volume 创建/列出/解压多卷归档文件
--rmt-command=COMMAND 使用指定的 rmt COMMAND 代替 rmt
--rsh-command=COMMAND 使用远程 COMMAND 代替 rsh
--volno-file=FILE 使用/更新 FILE 中的卷数
设备分块:
-b, --blocking-factor=BLOCKS 每个记录 BLOCKS x 512 字节
-B, --read-full-records 读取时重新分块(只对 4.2BSD 管道有效)
-i, --ignore-zeros 忽略归档中的零字节块(即文件结尾)
--record-size=NUMBER 每个记录的字节数 NUMBER,乘以 512
选择归档格式:
-H, --format=FORMAT 创建指定格式的归档
FORMAT 是以下格式中的一种:
gnu GNU tar 1.13.x 格式
oldgnu GNU 格式 as per tar <= 1.12
pax POSIX 1003.1-2001 (pax) 格式
posix 等同于 pax
ustar POSIX 1003.1-1988 (ustar) 格式
v7 old V7 tar 格式
--old-archive, --portability
等同于 --format=v7
--pax-option=关键字[[:]=值][,关键字[[:]=值]]...
控制 pax 关键字
--posix 等同于 --format=posix
-V, --label=TEXT 创建带有卷名 TEXT
的归档;在列出/解压时,使用 TEXT
作为卷名的模式串
压缩选项:
-a, --auto-compress 使用归档后缀名来决定压缩程序
-I, --use-compress-program=PROG
通过 PROG 过滤(必须是能接受 -d
选项的程序)
-j, --bzip2 通过 bzip2 过滤归档
-J, --xz 通过 xz 过滤归档
--lzip 通过 lzip 过滤归档
--lzma 通过 xz 过滤归档
--lzop 通过 xz 过滤归档
--no-auto-compress 不使用归档后缀名来决定压缩程序
-z, --gzip, --gunzip, --ungzip 通过 gzip 过滤归档
-Z, --compress, --uncompress 通过 compress 过滤归档
本地文件选择:
--backup[=CONTROL] 在删除前备份,选择 CONTROL 版本
-h, --dereference
跟踪符号链接;将它们所指向的文件归档并输出
--hard-dereference
跟踪硬链接;将它们所指向的文件归档并输出
-K, --starting-file=MEMBER-NAME
从归档中的 MEMBER-NAME
成员处开始读取归档
--newer-mtime=DATE 当只有数据改变时比较数据和时间
-N, --newer=DATE-OR-FILE, --after-date=DATE-OR-FILE
只保存比 DATE-OR-FILE 更新的文件
--one-file-system 创建归档时保存在本地文件系统中
-P, --absolute-names 不要从文件名中清除引导符‘/’
--suffix=STRING 在删除前备份,除非被环境变量
SIMPLE_BACKUP_SUFFIX
覆盖,否则覆盖常用后缀(‘’)
文件名变换:
--strip-components=NUMBER 解压时从文件名中清除 NUMBER
个引导部分
--transform=EXPRESSION, --xform=EXPRESSION
使用 sed 代替 EXPRESSION
来进行文件名变换
提示性输出:
--checkpoint[=NUMBER] 每隔 NUMBER
个记录显示进度信息(默认为 10 个)
--checkpoint-action=ACTION 在每个检查点上执行 ACTION
--full-time 按文件原本时间格式打印
--index-file=FILE 将详细输出发送至 FILE
-l, --check-links
只要不是所有链接都被输出就打印信息
--no-quote-chars=STRING 禁用来自 STRING 的字符引用
--quote-chars=STRING 来自 STRING 的额外的引用字符
--quoting-style=STYLE 设置名称引用风格;有效的 STYLE
值请参阅以下说明
-R, --block-number 每个信息都显示归档内的块数
--show-defaults 显示 tar 默认选项
--show-omitted-dirs
列表或解压时,列出每个不匹配查找标准的目录
--show-snapshot-field-ranges
显示快照文件区的有效范围
--show-transformed-names, --show-stored-names
显示变换后的文件名或归档名
--totals[=SIGNAL] 处理归档后打印出总字节数;当此
SIGNAL 被触发时带参数 -
打印总字节数;允许的信号为:
SIGHUP,SIGQUIT,SIGINT,SIGUSR1 和
SIGUSR2;同时也接受不带 SIG
前缀的信号名称
--utc 以 UTC 格式打印文件修改时间
-v, --verbose 详细地列出处理的文件
--warning=KEYWORD 警告控制:
-w, --interactive, --confirmation
每次操作都要求确认
兼容性选项:
-o 创建归档时,相当于
--old-archive;展开归档时,相当于
--no-same-owner
其它选项:
-?, --help 显示此帮助列表
--restrict 禁用某些潜在的有危险的选项
--usage 显示简短的用法说明
--version 打印程序版本
长选项和相应短选项具有相同的强制参数或可选参数。
除非以 --suffix 或 SIMPLE_BACKUP_SUFFIX
设置备份后缀,否则备份后缀就是“~”。
可以用 --backup 或 VERSION_CONTROL 设置版本控制,可能的值为:
none, off 从不做备份
t, numbered 进行编号备份
nil, existing
如果编号备份存在则进行编号备份,否则进行简单备份
never, simple 总是使用简单备份
--quoting-style 选项的有效参数为:
literal
shell
shell-always
c
c-maybe
escape
locale
clocale
此 tar 默认为:
--format=gnu -f- -b20 --quoting-style=escape --rmt-command=/usr/lib/tar/rmt
--rsh-command=/usr/bin/rsh
比较常用的参数有:①c:创建一个新归档;②x: 从归档中解出文件;③f:使用归档文件或 ARCHIVE 设备;④j:bzip2格式;⑤z:gzip格式;⑥v: 详细地列出处理的文件
打包文件:
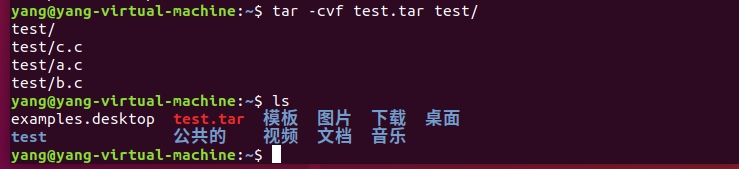
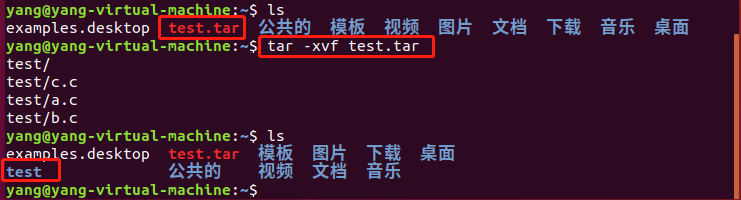
解包:
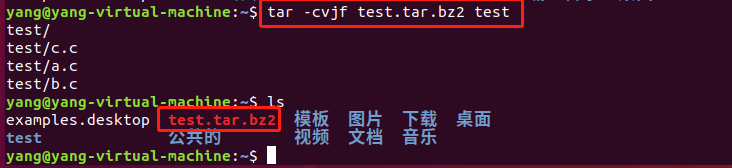
以bzip2的格式压缩:
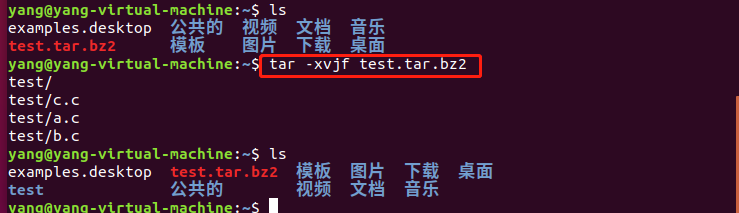
解压
以gzip格式压缩:

解压:
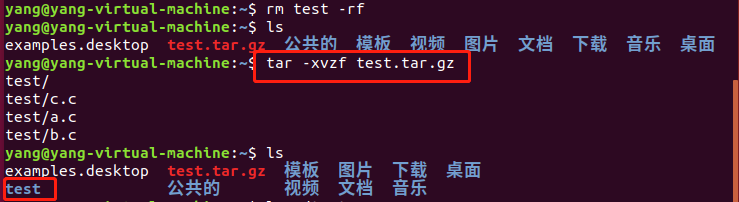
以tgz格式压缩:
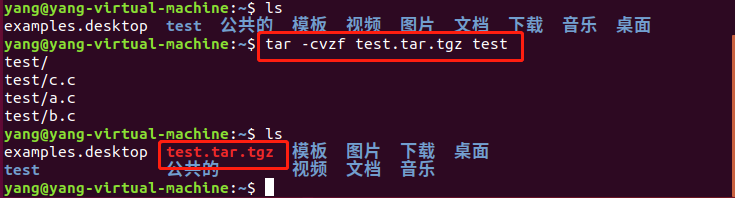
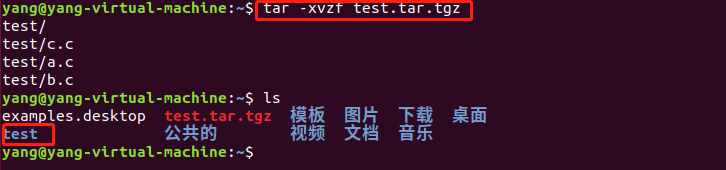
解压:
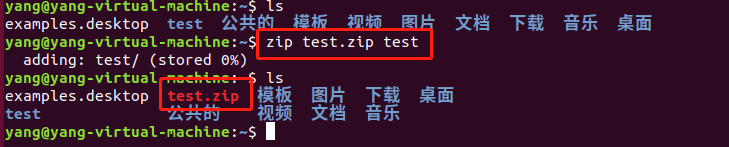
4.zip
压缩:
解压:
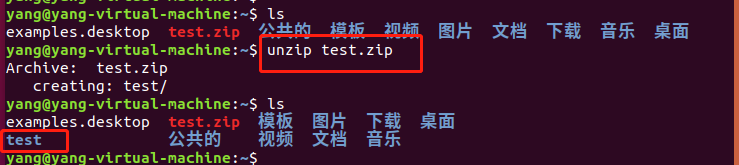
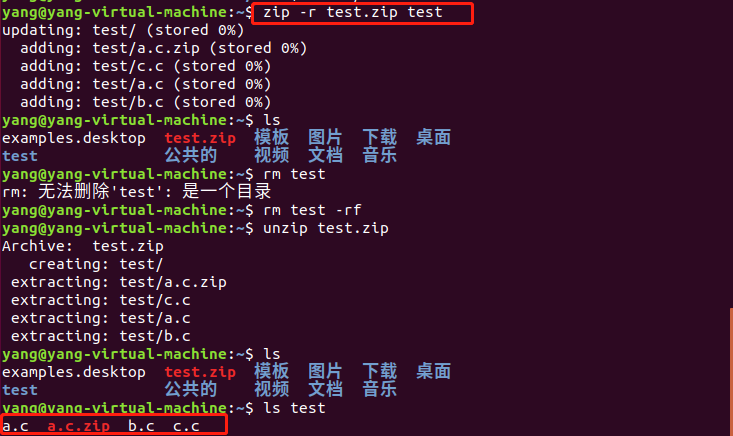
PS:这里的test是一个目录,使用zip test.zip test 压缩后,再用unzip命令解压出来的test目录会丢失原来的文件,经过验证,如果是对一个目录中的子文件进行递归压缩,应该使用-r参数,这样才不会损坏源文件:
5.rar
Ubuntu系统没有自带rar,需要自己下载,下载完成后,查看rar命令的使用方法只需要输入rar即可:
yang@yang-virtual-machine:~$ rar
RAR 5.50 Copyright (c) 1993-2017 Alexander Roshal 11 Aug 2017
Trial version Type 'rar -?' for help
Usage: rar <command> -<switch 1> -<switch N> <archive> <files...>
<@listfiles...> <path_to_extract\>
<Commands>
a Add files to archive
c Add archive comment
ch Change archive parameters
cw Write archive comment to file
d Delete files from archive
e Extract files without archived paths
f Freshen files in archive
i[par]=<str> Find string in archives
k Lock archive
l[t[a],b] List archive contents [technical[all], bare]
m[f] Move to archive [files only]
p Print file to stdout
r Repair archive
rc Reconstruct missing volumes
rn Rename archived files
rr[N] Add data recovery record
rv[N] Create recovery volumes
s[name|-] Convert archive to or from SFX
t Test archive files
u Update files in archive
v[t[a],b] Verbosely list archive contents [technical[all],bare]
x Extract files with full path
<Switches>
- Stop switches scanning
@[+] Disable [enable] file lists
ad Append archive name to destination path
ag[format] Generate archive name using the current date
ai Ignore file attributes
ap<path> Set path inside archive
as Synchronize archive contents
c- Disable comments show
cfg- Disable read configuration
cl Convert names to lower case
cu Convert names to upper case
df Delete files after archiving
dh Open shared files
ds Disable name sort for solid archive
dw Wipe files after archiving
e[+]<attr> Set file exclude and include attributes
ed Do not add empty directories
en Do not put 'end of archive' block
ep Exclude paths from names
ep1 Exclude base directory from names
ep3 Expand paths to full including the drive letter
f Freshen files
hp[password] Encrypt both file data and headers
ht[b|c] Select hash type [BLAKE2,CRC32] for file checksum
id[c,d,p,q] Disable messages
ierr Send all messages to stderr
ilog[name] Log errors to file (registered versions only)
inul Disable all messages
isnd Enable sound
iver Display the version number
k Lock archive
kb Keep broken extracted files
log[f][=name] Write names to log file
m<0..5> Set compression level (0-store...3-default...5-maximal)
ma[4|5] Specify a version of archiving format
mc<par> Set advanced compression parameters
md<n>[k,m,g] Dictionary size in KB, MB or GB
ms[ext;ext] Specify file types to store
mt<threads> Set the number of threads
n<file> Additionally filter included files
n@ Read additional filter masks from stdin
n@<list> Read additional filter masks from list file
o[+|-] Set the overwrite mode
oh Save hard links as the link instead of the file
oi[0-4][:min] Save identical files as references
ol[a] Process symbolic links as the link [absolute paths]
or Rename files automatically
ow Save or restore file owner and group
p[password] Set password
p- Do not query password
qo[-|+] Add quick open information [none|force]
r Recurse subdirectories
r- Disable recursion
r0 Recurse subdirectories for wildcard names only
rr[N] Add data recovery record
rv[N] Create recovery volumes
s[<N>,v[-],e] Create solid archive
s- Disable solid archiving
sc<chr>[obj] Specify the character set
sfx[name] Create SFX archive
si[name] Read data from standard input (stdin)
sl<size> Process files with size less than specified
sm<size> Process files with size more than specified
t Test files after archiving
ta<date> Process files modified after <date> in YYYYMMDDHHMMSS format
tb<date> Process files modified before <date> in YYYYMMDDHHMMSS format
tk Keep original archive time
tl Set archive time to latest file
tn<time> Process files newer than <time>
to<time> Process files older than <time>
ts[m|c|a] Save or restore file time (modification, creation, access)
u Update files
v<size>[k,b] Create volumes with size=<size>*1000 [*1024, *1]
ver[n] File version control
vn Use the old style volume naming scheme
vp Pause before each volume
w<path> Assign work directory
x<file> Exclude specified file
x@ Read file names to exclude from stdin
x@<list> Exclude files listed in specified list file
y Assume Yes on all queries
z[file] Read archive comment from file
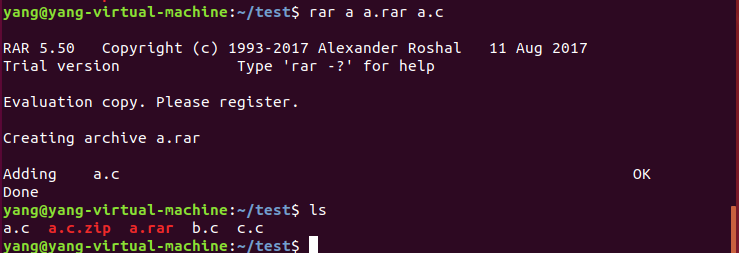
对一个文件进行压缩:
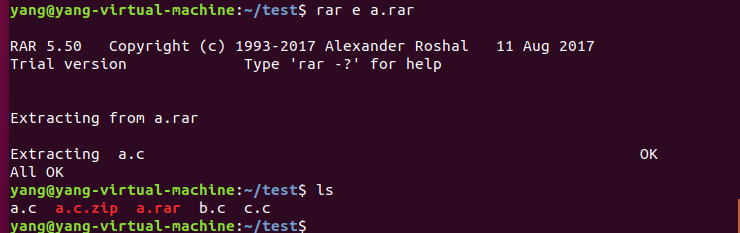
解压:
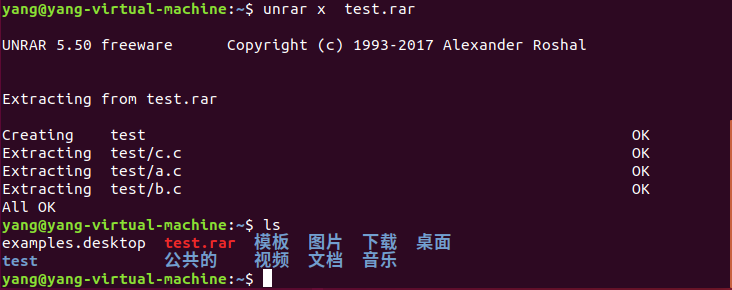
对一个目录中的子文件进行递归压缩:
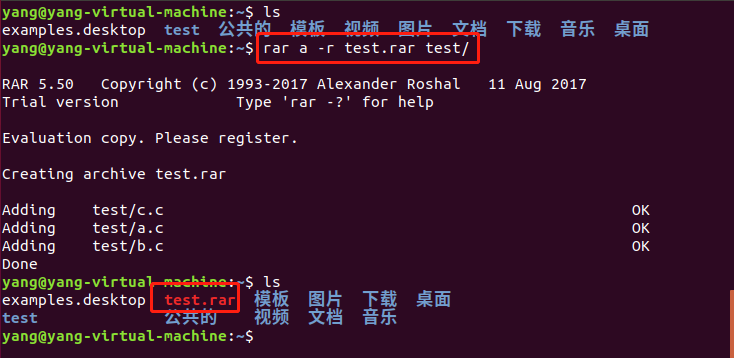
解压的时候可以用:rar e test.rar,但是解压出来的是子文件,不包含test目录。也可以用另外一个命令:unrar来解压rar格式的压缩档,这个也需要自行安装。