Flutter JSON 和序列化数据
使用代码生成库序列化 JSON 数据
尽管有其它库可以使用,本指南使用了 json_serializable package,一个自动化源代码生成器来为你生成 JSON 序列化数据模板。
由于序列化数据代码不再需要手动编写或者维护,你可以将序列化 JSON 数据在运行时的异常风险降到最低。
在项目中设置 json_serializable
要在你的项目中包含 json_serializable,你需要一个常规依赖,以及两个 dev 依赖。简单来说,dev 依赖 是不包括在我们的 App 源代码中的依赖 - 它们只会被用在开发环境中。
在序列化 JSON 数据的例子中,这些必须的依赖的最新版本可以在下面 pubspec 文件 中查看。
pubspec.yaml
dependencies:
# Your other regular dependencies here
json_annotation: ^3.0.0
dev_dependencies:
# Your other dev_dependencies here
build_runner: ^1.0.0
json_serializable: ^3.2.0
在你的项目根文件夹下运行 flutter pub get (或者在你的编辑器中点击 Packages Get)以确保在你的项目中可以使用这些新的依赖。
以 json_serializable 的方式创建模型类
下面显示了怎样将 User 类转换为 json_serializable 后的类。简单起见,该代码使用了前面的例子中的简化的 JSON 模型。
user.dart
import 'package:json_annotation/json_annotation.dart';
/// This allows the `User` class to access private members in
/// the generated file. The value for this is *.g.dart, where
/// the star denotes the source file name.
part 'user.g.dart';
/// An annotation for the code generator to know that this class needs the
/// JSON serialization logic to be generated.
@JsonSerializable()
class User {
User(this.name, this.email);
String name;
String email;
/// A necessary factory constructor for creating a new User instance
/// from a map. Pass the map to the generated `_$UserFromJson()` constructor.
/// The constructor is named after the source class, in this case, User.
factory User.fromJson(Map<String, dynamic> json) => _$UserFromJson(json);
/// `toJson` is the convention for a class to declare support for serialization
/// to JSON. The implementation simply calls the private, generated
/// helper method `_$UserToJson`.
Map<String, dynamic> toJson() => _$UserToJson(this);
}
通过这个设置,源代码生成器将生成用于 JSON 编码及解码 name 以及 email 字段的代码。
如果需要,你可以很容易自定义命名策略。例如,如果 API 返回带有蛇形命名方式的对象,并且你想要在你的模型里使用 小驼峰的命名方式,你可以使用带有一个 name 参数的 @JsonKey 注解。
/// Tell json_serializable that "registration_date_millis" should be
/// mapped to this property.
@JsonKey(name: 'registration_date_millis')
final int registrationDateMillis;
运行代码生成工具
当你首次创建 json_serializable 类时,你会得到类似下图的错误。
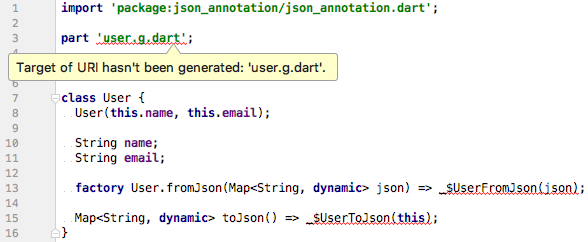
这些错误完全正常,很简单,因为这些模型类的生成代码并不存在。要解决这个问题,运行代码生成器来生成序列化数据模板。
有两种方式运行代码生成器。
一次性代码生成
通过在项目根目录运行 flutter pub run build_runner build,你可以在任何需要的时候为你的模型生成 JSON 序列化数据代码。这会触发一次构建,遍历源文件,选择相关的文件,然后为它们生成必须的序列化数据代码。
By running flutter pub run build_runner build in the project root, you generate JSON serialization code for your models whenever they are needed. This triggers a one-time build that goes through the source files, picks the relevant ones, and generates the necessary serialization code for them.
虽然这样很方便,但是如果你不需要在每次修改了你的模型类后都要手动构建那将会很棒。
持续生成代码
监听器 让我们的源代码生成过程更加方便。它监听我们项目中的文件变化并且会在需要的时候自动构建必要的文件。通过在项目根目录运行 flutter pub run build_runner watch 启动监听。
一旦启动监听并让它留在后台运行是安全的。
使用 json_serializable 模型
为了以 json_serializable 的方式解码 JSON 字符串,事实上你不必对以前的代码做任何的改动。
Map userMap = jsonDecode(jsonString);
var user = User.fromJson(userMap);
编码也是如此。调用 API 和以前一样。
String json = jsonEncode(user);
使用 json_serializable,在 User 类中你可以忘记手动序列化任意的 JSON 数据。源代码生成器会创建一个名为 user.g.dart的文件,它包含了所有必须的序列化数据逻辑。你不必再编写自动化测试来确保序列化数据奏效。现在由 库来负责 确保序列化数据能正确地奏效。
为嵌套类 (Nested Classes) 生成代码
你可能类在代码中用了嵌套类,在你把类作为参数传递给一些服务(比如 Firebase)的时候,你可能会遇到Invalid argument错误。
比如下面的这个 Address 类:
import 'package:json_annotation/json_annotation.dart';
part 'address.g.dart';
@JsonSerializable()
class Address {
String street;
String city;
Address(this.street, this.city);
factory Address.fromJson(Map<String, dynamic> json) => _$AddressFromJson(json);
Map<String, dynamic> toJson() => _$AddressToJson(this);
}
一个 Address 类被嵌套在 User 类中使用:
import 'address.dart';
import 'package:json_annotation/json_annotation.dart';
part 'user.g.dart';
@JsonSerializable()
class User {
String firstName;
Address address;
User(this.firstName, this.address);
factory User.fromJson(Map<String, dynamic> json) => _$UserFromJson(json);
Map<String, dynamic> toJson() => _$UserToJson(this);
}
在终端中运行 flutter pub run build_runner build 创建 * .g.dart文件,但私有函数如 _ $ UserToJson() 会看起来像下面这样:
(
Map<String, dynamic> _$UserToJson(User instance) => <String, dynamic>{
'firstName': instance.firstName,
'address': instance.address,
};
看起来没有什么问题,如果 print 用户对象时:
Address address = Address("My st.", "New York");
User user = User("John", address);
print(user.toJson());
结果会是:
{name: John, address: Instance of 'address'}但实际上你希望的输出结果是这样的:
{name: John, address: {street: My st., city: New York}}为了得到正常的输出,你需要在类声明之前为 @JsonSerializable 方法加入 explicitToJson: true 参数, User类现在看起来是这样的:
import 'address.dart';
import 'package:json_annotation/json_annotation.dart';
part 'user.g.dart';
@JsonSerializable(explicitToJson: true)
class User {
String firstName;
Address address;
User(this.firstName, this.address);
factory User.fromJson(Map<String, dynamic> json) => _$UserFromJson(json);
Map<String, dynamic> toJson() => _$UserToJson(this);
}
了解更多信息,请查阅 json_annotation 这个 package 里的 JsonSerializable 类的 explicitToJson 参数等相关文档。

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号