SpringBoot实战(五)之Thymeleaf
Thymeleaf同jsp、volocity、freemarker等共同的职能是MVC模式中的视图展示层,即View。
当然了,SpringBoot中也可以用jsp,不过不推荐这种用法,比较推崇的就是使用Thymeleaf。
关于Thymeleaf学习,建议参考官方文档:https://www.thymeleaf.org/documentation.html
官方文档例子,应有尽有。
之前接触过Thymeleaf是因为公司项目初建期间用过它搭建过测试环境,后来根据领导的指示,需要快速开发,而且当时对于Thymeleaf不是十分了解,当时对于它的了解认识只是展示前端数据的,同jsp职能一样,当然这也是它们的共性。比较详细的深入了解和使用,是帮助一位学妹解决毕业论文的项目问题。那时帮助她写了好十几个类代码和对应的十几个html代码。当时感触比较深的是,Thymeleaf是如此的好用,比jsp还好用,jsp要遍历之类,要么加<%%>,或者引用jstl标签库进行数据遍历等。而Thymeleat就不需要。简洁直观,我比较推崇Thymeleaf,特别是在前后端分离的项目,有的时候不用jsp,光纯html+js的确有点吃力,即便使用了vue.js或者angular.js、react.js等虽然增加了便利性,但是了,如果一个项目前端语言不是十分统一的话,对于将来维护成本方面会大大提高,不易维护。
Thymeleaf对于前后端分离,我认为还是不错的。
下面进入demo例子讲解:
一、导入maven依赖
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>gs-uploading-files</artifactId>
<version>0.1.0</version>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>1.5.8.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
二、编写实体
package hello; public class User { private Integer id; private String name; public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } }
三、编写Controller
package hello; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.ui.Model; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; @Controller public class TestController { @GetMapping(value="/test") public String test(Model model) { List<User> userList = new ArrayList<User>(); for (int i = 0; i <10; i++) { User user =new User(); user.setId(1); user.setName("张三"); userList.add(user); } model.addAttribute("users", userList); return "test"; } }
四、编写配置文件,将其放置在/src/main/resources下
application.properties
server.port=8080
spring.thymeleaf.cache=false
spring.thymeleaf.prefix=classpath:/templates/
spring.thymeleaf.check-template-location=true
spring.thymeleaf.suffix=.html
spring.thymeleaf.encoding=UTF-8
spring.thymeleaf.content-type=text/html
spring.thymeleaf.mode=HTML5
五、在src/main/resources目录下新建templates目录并新建html文件
test.htm
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <body> <h2>用户列表</h2> <div> <ul> <li th:each="user:${users}"> <span th:text="${user.id}"></span>- <span th:text="${user.name}"></span>- </li> </ul> </div> </body> </html>
六、编写启动类
package hello; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; @SpringBootApplication public class Application { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args); } }
最后结果如下图所示:
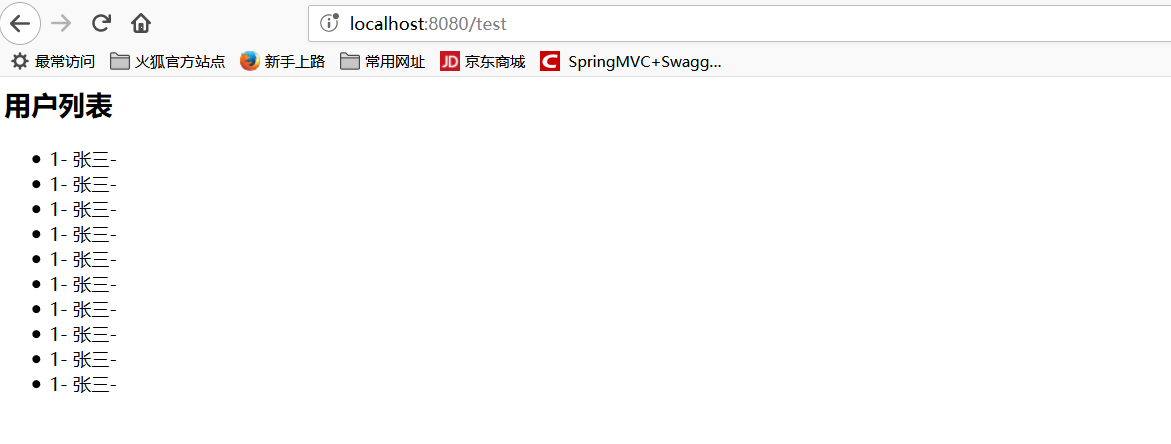
这里没有加入mysql或者其他数据相关的,如果要引用数据库,引用对应数据库的依赖和配置对应的数据库连接池即可。
这里可以参考我的关于Springboot+MyBatis+Thymeleaf
示例地址为:https://github.com/youcong1996/springboot-mybatis-demo



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号