MyBatis实战之解析与运行
本次所谈的原理仅仅只涉及基本的框架和核心代码,并不会全部都说到,比如关于MyBatis是如何解析XML文件和其他配置文件从而的到内容,还有就是JDBC如何使用,关于JDBC如何使用,可以参考我的这篇博客:单例模式和JDBC
还有就是关于Java基础方面的内容,个人建议大家抽空看看《Java编程思想》这本书,这本书可以作为一本参考书来看,不要从头开始看,有选择的阅读是最好的,从头开始看,别说看懂问题,估计你看的都想睡觉了。另外最好的话还是可以通过知识付费看看人家是怎么讲Java的,通过知识付费获取的Java相关知识,应该是不错的,比如在极客时间这个APP中看到的杨晓峰《Java核心技术36讲》,口碑目前还不错,不过建议朋友们最好还是自己时不时根据一些参考书或者官网再加上自己工作用到时刻复习一下,总结一下。这样还是有很大好处的。
MyBatis的运行分为两大部分,第一部分是读取配置文件缓存到Configuration对象,用以创建SqlSessionFactory,第二部分是SqlSession的执行过程。相对而言,SqlSessionFactory的创建比较容易理解,而SqlSession的执行过程远远不是那么简单了,它将包括许多复杂的技术,我们需要讨论反射技术和动态代理技术,这是揭示MyBatis底层架构的基础。
当我们掌握了MyBatis的运行原理,我们就可以知道MyBatis是怎么运行的,同时当我们在深入理解MyBatis相关的源码和涉及到的设计模式后,我们也许就能像MyBatis-Plus的开发者那样,开发出一个比MyBatis或者MyBatis-Plus还要好的持久层框架。
一、涉及的技术难点简介
Mapper仅仅只是一个接口,而不是一个包含逻辑的实现类。我们知道一个接口是没有办法去执行的,那么它是怎么运行的呢?这不是违反教科书上说的接口不能运行的道理吗?相信不少初学者会对此有疑惑。
答案就是动态代理。
首先,什么是代理模式?所谓的代理模式就是在原有的服务商多加以占位,通过这个占位去控制服务的访问。这句话不太容易理解,举例而言,假设你是一个公司的工程师,能提供一些技术服务,公司的客服就一个美女,她不懂技术。而我是一个客户需要你们公司提供技术服务。显然,我只会找到你们的客服,和客服沟通,而不是找你沟通。客服会根据公司的规章制度和业务规则来决定找不找你服务。那么这个时候客服就等同于你的一个代理,她通过和我的交流来控制对你的访问,当然她也可以提供一些你们公司对外的服务。而我只能通过她的代理访问你。对我而言,根本不需要认识你,只需要认识客服就可以了。事实上,站在我的角度,我会认为客服就代表你们公司,而不管真正为我服务的你是怎么样的。
其次,为什么要使用代理模式?通过代理,一方面可以控制如何访问真正的服务对象,提供额外服务。另外一方面有机会通过重写一些类来满足特定的需要,正如客服也可以根据公司的业务规则,提供一些服务,这个时候就不需要劳你大驾。
动态代理示意图:
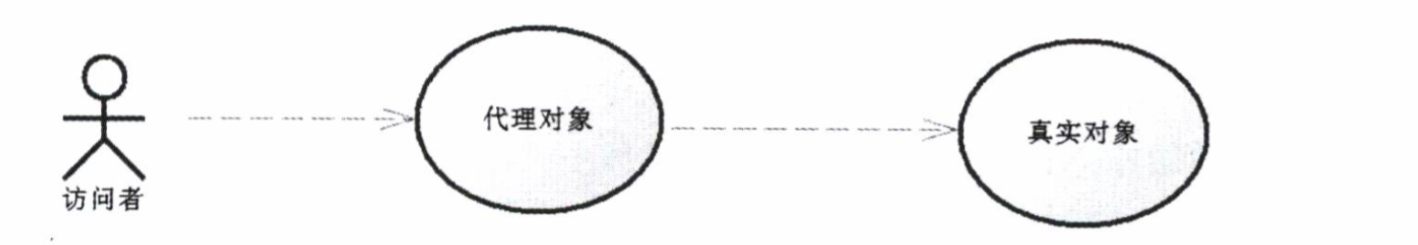
一般而言,动态代理分为两种,一种是JDK反射机制提供的代理,另一种是CGLIB代理。在JDK提供的代理,我们必须要提供接口,而CGLIB则不需要提供接口,在MyBatis里面两种动态代理技术都已经使用了。但是在此之前我们需要学习的技术就是反射。
1.反射技术
关于反射技术详细可以参考我的这篇博客:MyBatis之反射技术+JDK动态代理+cglib代理
不过在此基础上,我还是要说说什么是反射?

注意,这张图并没有将所有的方法和属性都列举出来,只列举了主要的属性和方法。
MappedStatement对象涉及的东西较多,我们一般都不去修改它,因为容易产生不必要的错误。SqlSource是一个接口,它的主要作用是根据参数和其他的规则组装SQL。这些都是很复杂的东西,好在MyBatis本身已经实现了它,一般也不需要去修改它。对于参数和SQL而言,主要的规则都反映在BoundSql类对象上,在插件中往往需要拿到它进而可以拿到当前运行的SQL的参数以及参数规则,做出适当的修改,来满足我们特殊的需求。
BoundSql会提供3个主要的属性:parameterMappings、paramterObject和sql。
(1)其中parameterObject为参数本身,前面我们说到过,参数可以是简单对象,Pojo、Map或者@Param注解的参数,由于它在插件中相当常用,后面我们有必要讨论一下它的规则;
(2)传递简对象(包括int、String、float、double等),比如当我们传递int类型时,MyBatis会把参数变为Integer对象传递,类似的long、String、float、double也是如此;
(3)如果我们传递的是Pojo或者Map,那么这个parameterObject就是你传入的Pojo或者Map不变;
(4)当然我们也可以传递多个参数,如果没有@Param注解,那么MyBatis就会把parameterObject变为一个Map<String,Object>对象,其键值的关系是按顺序来规划的;
(5)如果我们使用@Param注解,那么MyBatis就会把parameterObject变为一个Map<String,Object>对象,类似于没有@Param注解,只是把其数字的键值对应置换为@Param注解的键值;
(6)parameterMappings,它是一个List,每个元素都是ParameterMapping的对象。这个对象会描述我们的参数。参数包括属性、名称、表达式、javaType、jdbcType、typeHandler等重要信息,我们一般不需要去改变它。通过它可以实现参数和SQL的结合,以便PreparedStatement能够通过它找到parameterObject对象的属性并设置参数,使得程序准确运行;
(7)sql属性就是我们书写在映射器里面的一条SQL,在大多数时候无需修改它,只有在插件的情况下,我们可以根据需要进行改写。改写SQL将是一件危险的事情,请务必慎重行事;
3.构建SqlSessionFactory
有了Configuration对象构建SqlSessionFactory就很简单了,我们只要写很简短的代码便可以了。
例如:
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource));
MyBatis会根据Configuration的配置读取所配置的信息,构建SqlSessionFactory对象。
三、SqlSession运行过程
SqlSession的运行过程是整个MyBatis最难以理解的部分。SqlSession是一个接口,使用它并不复杂。我们构建SqlSessionFactory就可以轻易地拿到SqlSession了。SqlSession给出了查询、插入、更新、删除的方法,在旧版本的MyBatis或iBatis中常常使用这些接口方法,而在新版的MyBatis中我们建议使用Mapper,所以它就是MyBatis最为常用和重要的接口之一。
SqlSession内部并没有那么容易,因为它的内部实现相当复杂。
1.映射器的动态代理
Mapper映射是通过动态代理来实现的,我们来看看代码清单:
MapperProxyFactory源码如下:
/** * Copyright 2009-2015 the original author or authors. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package org.apache.ibatis.binding; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.lang.reflect.Proxy; import java.util.Map; import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession; /** * @author Lasse Voss */ public class MapperProxyFactory<T> { private final Class<T> mapperInterface; private final Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<Method, MapperMethod>(); public MapperProxyFactory(Class<T> mapperInterface) { this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface; } public Class<T> getMapperInterface() { return mapperInterface; } public Map<Method, MapperMethod> getMethodCache() { return methodCache; } @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) { return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy); } public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) { final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<T>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache); return newInstance(mapperProxy); } }
这里我们可以看到动态代理对接口的绑定,它的作用就是生成动态代理对象(占位)。
而代理的方法则被放到MapperProxy类中。
MapperProxy源码如下:
/** * Copyright 2009-2017 the original author or authors. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package org.apache.ibatis.binding; import java.io.Serializable; import java.lang.invoke.MethodHandles; import java.lang.reflect.Constructor; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.lang.reflect.Modifier; import java.util.Map; import org.apache.ibatis.lang.UsesJava7; import org.apache.ibatis.reflection.ExceptionUtil; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession; /** * @author Clinton Begin * @author Eduardo Macarron */ public class MapperProxy<T> implements InvocationHandler, Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = -6424540398559729838L; private final SqlSession sqlSession; private final Class<T> mapperInterface; private final Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache; public MapperProxy(SqlSession sqlSession, Class<T> mapperInterface, Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache) { this.sqlSession = sqlSession; this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface; this.methodCache = methodCache; } @Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { try { if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) { return method.invoke(this, args); } else if (isDefaultMethod(method)) { return invokeDefaultMethod(proxy, method, args); } } catch (Throwable t) { throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t); } final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method); return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args); } private MapperMethod cachedMapperMethod(Method method) { MapperMethod mapperMethod = methodCache.get(method); if (mapperMethod == null) { mapperMethod = new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration()); methodCache.put(method, mapperMethod); } return mapperMethod; } @UsesJava7 private Object invokeDefaultMethod(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { final Constructor<MethodHandles.Lookup> constructor = MethodHandles.Lookup.class .getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, int.class); if (!constructor.isAccessible()) { constructor.setAccessible(true); } final Class<?> declaringClass = method.getDeclaringClass(); return constructor .newInstance(declaringClass, MethodHandles.Lookup.PRIVATE | MethodHandles.Lookup.PROTECTED | MethodHandles.Lookup.PACKAGE | MethodHandles.Lookup.PUBLIC) .unreflectSpecial(method, declaringClass).bindTo(proxy).invokeWithArguments(args); } /** * Backport of java.lang.reflect.Method#isDefault() */ private boolean isDefaultMethod(Method method) { return (method.getModifiers() & (Modifier.ABSTRACT | Modifier.PUBLIC | Modifier.STATIC)) == Modifier.PUBLIC && method.getDeclaringClass().isInterface(); } }
上面运用了invoke方法。一旦mapper是一个代理对象,那么它就会运行到invoke方法里面,invoke首先判断它是否是一个类,显然这里Mapper是一个接口而不是类,所以判定失败。那么就会生成MapperMethod对象,它是通过cachedMapperMethod方法对其初始化的,然后执行execute方法,把sqlSession和当前运行的参数传递进去。
这个exexute方法的源码如下:
/** * Copyright 2009-2017 the original author or authors. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package org.apache.ibatis.binding; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Flush; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.MapKey; import org.apache.ibatis.cursor.Cursor; import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.MappedStatement; import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.SqlCommandType; import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.StatementType; import org.apache.ibatis.reflection.MetaObject; import org.apache.ibatis.reflection.ParamNameResolver; import org.apache.ibatis.reflection.TypeParameterResolver; import org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration; import org.apache.ibatis.session.ResultHandler; import org.apache.ibatis.session.RowBounds; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession; import java.lang.reflect.Array; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.lang.reflect.ParameterizedType; import java.lang.reflect.Type; import java.util.*; /** * @author Clinton Begin * @author Eduardo Macarron * @author Lasse Voss */ public class MapperMethod { private final SqlCommand command; private final MethodSignature method; public MapperMethod(Class<?> mapperInterface, Method method, Configuration config) { this.command = new SqlCommand(config, mapperInterface, method); this.method = new MethodSignature(config, mapperInterface, method); } public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) { Object result; switch (command.getType()) { case INSERT: { Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args); result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param)); break; } case UPDATE: { Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args); result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param)); break; } case DELETE: { Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args); result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param)); break; } case SELECT: if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) { executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args); result = null; } else if (method.returnsMany()) { result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args); } else if (method.returnsMap()) { result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args); } else if (method.returnsCursor()) { result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args); } else { Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args); result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param); } break; case FLUSH: result = sqlSession.flushStatements(); break; default: throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName()); } if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) { throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName() + " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ")."); } return result; } private Object rowCountResult(int rowCount) { final Object result; if (method.returnsVoid()) { result = null; } else if (Integer.class.equals(method.getReturnType()) || Integer.TYPE.equals(method.getReturnType())) { result = rowCount; } else if (Long.class.equals(method.getReturnType()) || Long.TYPE.equals(method.getReturnType())) { result = (long)rowCount; } else if (Boolean.class.equals(method.getReturnType()) || Boolean.TYPE.equals(method.getReturnType())) { result = rowCount > 0; } else { throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName() + "' has an unsupported return type: " + method.getReturnType()); } return result; } private void executeWithResultHandler(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) { MappedStatement ms = sqlSession.getConfiguration().getMappedStatement(command.getName()); if (!StatementType.CALLABLE.equals(ms.getStatementType()) && void.class.equals(ms.getResultMaps().get(0).getType())) { throw new BindingException("method " + command.getName() + " needs either a @ResultMap annotation, a @ResultType annotation," + " or a resultType attribute in XML so a ResultHandler can be used as a parameter."); } Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args); if (method.hasRowBounds()) { RowBounds rowBounds = method.extractRowBounds(args); sqlSession.select(command.getName(), param, rowBounds, method.extractResultHandler(args)); } else { sqlSession.select(command.getName(), param, method.extractResultHandler(args)); } } private <E> Object executeForMany(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) { List<E> result; Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args); if (method.hasRowBounds()) { RowBounds rowBounds = method.extractRowBounds(args); result = sqlSession.<E>selectList(command.getName(), param, rowBounds); } else { result = sqlSession.<E>selectList(command.getName(), param); } // issue #510 Collections & arrays support if (!method.getReturnType().isAssignableFrom(result.getClass())) { if (method.getReturnType().isArray()) { return convertToArray(result); } else { return convertToDeclaredCollection(sqlSession.getConfiguration(), result); } } return result; } private <T> Cursor<T> executeForCursor(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) { Cursor<T> result; Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args); if (method.hasRowBounds()) { RowBounds rowBounds = method.extractRowBounds(args); result = sqlSession.<T>selectCursor(command.getName(), param, rowBounds); } else { result = sqlSession.<T>selectCursor(command.getName(), param); } return result; } private <E> Object convertToDeclaredCollection(Configuration config, List<E> list) { Object collection = config.getObjectFactory().create(method.getReturnType()); MetaObject metaObject = config.newMetaObject(collection); metaObject.addAll(list); return collection; } @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") private <E> Object convertToArray(List<E> list) { Class<?> arrayComponentType = method.getReturnType().getComponentType(); Object array = Array.newInstance(arrayComponentType, list.size()); if (arrayComponentType.isPrimitive()) { for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) { Array.set(array, i, list.get(i)); } return array; } else { return list.toArray((E[])array); } } private <K, V> Map<K, V> executeForMap(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) { Map<K, V> result; Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args); if (method.hasRowBounds()) { RowBounds rowBounds = method.extractRowBounds(args); result = sqlSession.<K, V>selectMap(command.getName(), param, method.getMapKey(), rowBounds); } else { result = sqlSession.<K, V>selectMap(command.getName(), param, method.getMapKey()); } return result; } public static class ParamMap<V> extends HashMap<String, V> { private static final long serialVersionUID = -2212268410512043556L; @Override public V get(Object key) { if (!super.containsKey(key)) { throw new BindingException("Parameter '" + key + "' not found. Available parameters are " + keySet()); } return super.get(key); } } public static class SqlCommand { private final String name; private final SqlCommandType type; public SqlCommand(Configuration configuration, Class<?> mapperInterface, Method method) { final String methodName = method.getName(); final Class<?> declaringClass = method.getDeclaringClass(); MappedStatement ms = resolveMappedStatement(mapperInterface, methodName, declaringClass, configuration); if (ms == null) { if (method.getAnnotation(Flush.class) != null) { name = null; type = SqlCommandType.FLUSH; } else { throw new BindingException("Invalid bound statement (not found): " + mapperInterface.getName() + "." + methodName); } } else { name = ms.getId(); type = ms.getSqlCommandType(); if (type == SqlCommandType.UNKNOWN) { throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + name); } } } public String getName() { return name; } public SqlCommandType getType() { return type; } private MappedStatement resolveMappedStatement(Class<?> mapperInterface, String methodName, Class<?> declaringClass, Configuration configuration) { String statementId = mapperInterface.getName() + "." + methodName; if (configuration.hasStatement(statementId)) { return configuration.getMappedStatement(statementId); } else if (mapperInterface.equals(declaringClass)) { return null; } for (Class<?> superInterface : mapperInterface.getInterfaces()) { if (declaringClass.isAssignableFrom(superInterface)) { MappedStatement ms = resolveMappedStatement(superInterface, methodName, declaringClass, configuration); if (ms != null) { return ms; } } } return null; } } public static class MethodSignature { private final boolean returnsMany; private final boolean returnsMap; private final boolean returnsVoid; private final boolean returnsCursor; private final Class<?> returnType; private final String mapKey; private final Integer resultHandlerIndex; private final Integer rowBoundsIndex; private final ParamNameResolver paramNameResolver; public MethodSignature(Configuration configuration, Class<?> mapperInterface, Method method) { Type resolvedReturnType = TypeParameterResolver.resolveReturnType(method, mapperInterface); if (resolvedReturnType instanceof Class<?>) { this.returnType = (Class<?>) resolvedReturnType; } else if (resolvedReturnType instanceof ParameterizedType) { this.returnType = (Class<?>) ((ParameterizedType) resolvedReturnType).getRawType(); } else { this.returnType = method.getReturnType(); } this.returnsVoid = void.class.equals(this.returnType); this.returnsMany = configuration.getObjectFactory().isCollection(this.returnType) || this.returnType.isArray(); this.returnsCursor = Cursor.class.equals(this.returnType); this.mapKey = getMapKey(method); this.returnsMap = this.mapKey != null; this.rowBoundsIndex = getUniqueParamIndex(method, RowBounds.class); this.resultHandlerIndex = getUniqueParamIndex(method, ResultHandler.class); this.paramNameResolver = new ParamNameResolver(configuration, method); } public Object convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(Object[] args) { return paramNameResolver.getNamedParams(args); } public boolean hasRowBounds() { return rowBoundsIndex != null; } public RowBounds extractRowBounds(Object[] args) { return hasRowBounds() ? (RowBounds) args[rowBoundsIndex] : null; } public boolean hasResultHandler() { return resultHandlerIndex != null; } public ResultHandler extractResultHandler(Object[] args) { return hasResultHandler() ? (ResultHandler) args[resultHandlerIndex] : null; } public String getMapKey() { return mapKey; } public Class<?> getReturnType() { return returnType; } public boolean returnsMany() { return returnsMany; } public boolean returnsMap() { return returnsMap; } public boolean returnsVoid() { return returnsVoid; } public boolean returnsCursor() { return returnsCursor; } private Integer getUniqueParamIndex(Method method, Class<?> paramType) { Integer index = null; final Class<?>[] argTypes = method.getParameterTypes(); for (int i = 0; i < argTypes.length; i++) { if (paramType.isAssignableFrom(argTypes[i])) { if (index == null) { index = i; } else { throw new BindingException(method.getName() + " cannot have multiple " + paramType.getSimpleName() + " parameters"); } } } return index; } private String getMapKey(Method method) { String mapKey = null; if (Map.class.isAssignableFrom(method.getReturnType())) { final MapKey mapKeyAnnotation = method.getAnnotation(MapKey.class); if (mapKeyAnnotation != null) { mapKey = mapKeyAnnotation.value(); } } return mapKey; } } }
MapperMethod采用命令模式运行,根据上下文跳转,它可能跳转到许多方法中,我们不需要全部明白。我们可以看到里面的exexuteForMany方法,再看看它的实现,实际上它最后就是通过sqlSession对象去运行对象的SQL。
3.SqlSession运行总结
SqlSession的运行原理十分重要,它是插件的基础,这里我们对一次查询胡总更新进行总结以加深对MyBatis内部运行的掌握。SqlSession内部运行图,如图所示:

SqlSession是通过Executor构建StatementHandler来运行的,而StatementHandler要经过下面三步。
(1)prepared预编译SQL;
(2)parameterize设置参数;
(3)query/update执行SQL;
其中parameterize是调用parameterHandler的方法去设置的,而参数是根据类型处理器typeHandler去处理的。query/update方法是通过resultHandler进行处理结果的封装,如果是update的语句,它就返回整数,否则它就通过typeHandler处理结果类型,然后用ObjectFactory提供的规则组装对象,返回给调用者。这便是SqlSession执行的过程,我们清楚四大对象是如何运作的,同时也更好地理解了typeHandler和ObjectFactory在MyBatis中的应用。





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 周边上新:园子的第一款马克杯温暖上架
· Open-Sora 2.0 重磅开源!
· 分享 3 个 .NET 开源的文件压缩处理库,助力快速实现文件压缩解压功能!
· Ollama——大语言模型本地部署的极速利器
· [AI/GPT/综述] AI Agent的设计模式综述
2017-12-15 Redis的安装和客户端使用注意事项