私人订制属于自己的Linux系统
简介
Linux操作系统至1991年10月5日诞生以来,就其开源性和自由性得到了很多技术大牛的青睐,每个Linux爱好者都为其贡献了自己的一份力,不管是在Linux内核还是开源软件等方面,都为我们后来人提供了一个良好的学习和研究环境。
本文主要通过裁剪现有Linux系统,根据自己的需要,打造一个属于自己的Linux小系统,让其能够具备Linux的一些常用小功能。
原理
启动流程介绍
制作Linux小系统之前,我们有必要再了解一下Linux的启动流程
# 1、首先Linux要通过POST自检,检查硬件设备有没有故障
# 2、如果有多块启动盘的话,需要在BIOS中选择启动磁盘
# 3、启动MBR中的bootloader引导程序
# 4、加载内核文件
# 5、执行所有进程的父进程、老祖宗init
# 6、打印欢迎界面
在Linux的启动流程中,加载内核文件时还需要借助别外两个文件
# 1)initrd,是CentOS5上用内存模拟的磁盘设备
# 2)initramfs,是CentOS6上用内存模拟的文件系统
在启程的流程中,init主要是用来做哪些操作的呢?
init通过调用/etc/inittab这个配置文件,然后再去执行/etc/rc.d/rc.sysinit的系统初始化脚本
操作步骤
目标磁盘分区
我们先在一个已有的CentOS6系统上添加一块大小为20G的硬盘.



添加完成后,我们打开宿主机,使用fdisk来给我们新加的硬盘分区
如果添加了硬盘,lsblk,fdisk -l看不到,又不想重启机器可以使用下面命令
echo "- - -" > /sys/class/scsi_host/host0/scan
lsblk
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT
sda 8:0 0 20G 0 disk
├─sda1 8:1 0 1G 0 part /boot
└─sda2 8:2 0 19G 0 part
├─cl-root 253:0 0 17G 0 lvm /
└─cl-swap 253:1 0 2G 0 lvm
sdb 8:16 0 20G 0 disk
sr0 11:0 1 4.1G 0 rom
fdisk /dev/sdb
Welcome to fdisk (util-linux 2.23.2).
Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to write them.
Be careful before using the write command.
Command (m for help): n
Partition type:
p primary (0 primary, 0 extended, 4 free)
e extended
Select (default p): p
Partition number (1-4, default 1):
First sector (2048-41943039, default 2048):
Using default value 2048
Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (2048-41943039, default 41943039): +200M
Partition 1 of type Linux and of size 200 MiB is set
Command (m for help): n
Partition type:
p primary (1 primary, 0 extended, 3 free)
e extended
Select (default p): p
Partition number (2-4, default 2):
First sector (411648-41943039, default 411648):
Using default value 411648
Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (411648-41943039, default 41943039):
Using default value 41943039
Partition 2 of type Linux and of size 19.8 GiB is set
Command (m for help): p
Disk /dev/sdb: 21.5 GB, 21474836480 bytes, 41943040 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk label type: dos
Disk identifier: 0xe97b6d01
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 2048 411647 204800 83 Linux
/dev/sdb2 411648 41943039 20765696 83 Linux
Command (m for help): w
The partition table has been altered!
Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
Syncing disks.
# 对分区进行格式化
mkfs.ext4 /dev/sdb1
mkfs.ext4 /dev/sdb2
# 创建一个文件夹进行挂载,此处名字必须是boot
mkdir /mnt/boot -p
mount /dev/sdb1 /mnt/boot/
安装grub至目标磁盘
我们直接用grub-install --root-directory=/mnt命令来安装。用这个命令会安装grub引导第二阶段的文件。
grub-install --root-directory=/mnt /dev/sdb
Probing devices to guess BIOS drives. This may take a long time.
Installation finished. No error reported.
This is the contents of the device map /mnt/boot/grub/device.map.
Check if this is correct or not. If any of the lines is incorrect,
fix it and re-run the script `grub-install'.
(fd0) /dev/fd0
(hd0) /dev/sda
(hd1) /dev/sdb
# 验证下是否安装成功
hexdump -C -n 512 /dev/sdb
00000000 eb 63 90 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |.c..............|
00000010 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
*
00000050 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 80 01 00 00 00 |................|
00000060 00 00 00 00 ff fa 90 90 f6 c2 80 74 05 f6 c2 70 |...........t...p|
00000070 74 02 b2 80 ea 79 7c 00 00 31 c0 8e d8 8e d0 bc |t....y|..1......|
00000080 00 20 fb a0 64 7c 3c ff 74 02 88 c2 52 be 05 7c |. ..d|<.t...R..||
00000090 b4 41 bb aa 55 cd 13 5a 52 72 3d 81 fb 55 aa 75 |.A..U..ZRr=..U.u|
000000a0 37 83 e1 01 74 32 31 c0 89 44 04 40 88 44 ff 89 |7...t21..D.@.D..|
000000b0 44 02 c7 04 10 00 66 8b 1e 5c 7c 66 89 5c 08 66 |D.....f..\|f.\.f|
000000c0 8b 1e 60 7c 66 89 5c 0c c7 44 06 00 70 b4 42 cd |..`|f.\..D..p.B.|
000000d0 13 72 05 bb 00 70 eb 76 b4 08 cd 13 73 0d 5a 84 |.r...p.v....s.Z.|
000000e0 d2 0f 83 de 00 be 85 7d e9 82 00 66 0f b6 c6 88 |.......}...f....|
000000f0 64 ff 40 66 89 44 04 0f b6 d1 c1 e2 02 88 e8 88 |d.@f.D..........|
00000100 f4 40 89 44 08 0f b6 c2 c0 e8 02 66 89 04 66 a1 |.@.D.......f..f.|
00000110 60 7c 66 09 c0 75 4e 66 a1 5c 7c 66 31 d2 66 f7 |`|f..uNf.\|f1.f.|
00000120 34 88 d1 31 d2 66 f7 74 04 3b 44 08 7d 37 fe c1 |4..1.f.t.;D.}7..|
00000130 88 c5 30 c0 c1 e8 02 08 c1 88 d0 5a 88 c6 bb 00 |..0........Z....|
00000140 70 8e c3 31 db b8 01 02 cd 13 72 1e 8c c3 60 1e |p..1......r...`.|
00000150 b9 00 01 8e db 31 f6 bf 00 80 8e c6 fc f3 a5 1f |.....1..........|
00000160 61 ff 26 5a 7c be 80 7d eb 03 be 8f 7d e8 34 00 |a.&Z|..}....}.4.|
00000170 be 94 7d e8 2e 00 cd 18 eb fe 47 52 55 42 20 00 |..}.......GRUB .|
00000180 47 65 6f 6d 00 48 61 72 64 20 44 69 73 6b 00 52 |Geom.Hard Disk.R|
00000190 65 61 64 00 20 45 72 72 6f 72 0d 0a 00 bb 01 00 |ead. Error......|
000001a0 b4 0e cd 10 ac 3c 00 75 f4 c3 00 00 00 00 00 00 |.....<.u........|
000001b0 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 01 6d 7b e9 00 00 00 20 |.........m{.... |
000001c0 21 00 83 9f 06 19 00 08 00 00 00 40 06 00 00 9f |!..........@....|
000001d0 07 19 83 d4 a2 32 00 48 06 00 00 b8 79 02 00 00 |.....2.H....y...|
000001e0 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
000001f0 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 55 aa |..............U.|
00000200
安装内核文件和initrd文件
将内核文件和initrd文件复制到/dev/sdb下的boot目录中
cp /boot/vmlinuz-2.6.32-573.el6.x86_64 /mnt/boot/
cp /boot/initramfs-2.6.32-573.el6.x86_64.img /mnt/boot/
建立grub.conf文件
上面已经移植了内核和initrd文件,我们可以根据其版本编写grub.conf文件
vim /mnt/boot/grub/grub.conf
default=0
timeout=3
title linux owner
kernel /vmlinuz-2.6.32-573.el6.x86_64 root=UUID=1feac471-08c5-4b5b-aaff-bb6a1da60e26 selinux=0 init=/bin/bash
initrd /initramfs-2.6.32-573.el6.x86_64.img
注意
我们要把selinux给关掉,同时设定一下init,告诉内核不要再去找这个程序了,不然开机的时候会出现错误
创建一级目录并复制文件
创建开机后的一级目录,同时把/dev/sdb2挂载至/mnt/sysroot,使该目录作为根目录:
mkdir /mnt/sysroot
mkdir -pv /mnt/sysroot/{etc,tmp,var,usr,sys,proc,opt,home,root,dev,mnt,media}
复制文件,复制文件我们通过脚本执行,复制我们平时常用的命令即可,小编这里复制了ls,ifconfig,bash,reboot,rm,modprobe,mount,ip,mkdir,touch,cat,vi,less,shutdown,insmod。我们可以用tree查看一下这些命令的复制情况:
#!/bin/bash
# 定义变量
destdir=/mnt/sysroot
SETCOLOR_FAILURE="echo -en \\033[1;35;5m"
SETCOLOR_NORMAL="echo -en \\033[0m"
echo_jiantou() {
echo -en \\033[40G
$SETCOLOR_FAILURE
}
echo_copy() {
echo -en \\033[80G
$SETCOLOR_FAILURE
echo -n $"复制完成!"
$SETCOLOR_NORMAL
}
# 定义函数
# 复制命令
copy_cmd(){
# 定义变量
local cmd_path=`which --skip-alias $cmd`
local cmd_dir=`dirname $cmd_path`
local cmd_destdir=$destdir$cmd_dir
if [ ! -d $cmd_destdir ] ;then
mkdir -pv $cmd_destdir &> /dev/null
fi
cp $cmd_path $cmd_destdir &> /dev/null
echo -e "\t$cmd_path `echo_jiantou` \t $cmd_destdir `echo_copy` "
}
#复制库文件 判断库文件是否存在,若存在,跳过该次循环;如不存在,判断库文件所在目录是否存在,若存在,复制库文件;若不存在,则新建目录并复制库文件
copy_libfile(){
local cmd_path=`which --skip-alias $cmd`
local lib_list=`ldd $cmd_path |egrep -o "/.* " `
for i in $lib_list ;do
local lib_dir=$destdir$i
local lib_destdir=$destdir`dirname $i`
echo -e "\t$i `echo_jiantou` \t $lib_destdir `echo_copy` "
if [ -e $lib_dir ];then
continue
elif [ -d $lib_destdir ];then
cp $i $lib_destdir
else
mkdir -pv $lib_destdir &> /dev/null
cp $i $lib_destdir
fi
done
}
# 若/mnt/sysroot不存在,则创建
if [ ! d $destdir ];then
mkdir $destdir
fi
#死循环,清空屏幕
while true ; do
tput clear
# 正式:
cat <<-EOF
**********************************************************************
*** 命令复制脚本 ***
*** 请输入一个命令 ***
*** 按q或quit退出脚本 ***
**********************************************************************
EOF
read -p "Please input a execute command:" cmd
if [ "$cmd" == 'q' -o "$cmd" == 'quit' ];then
unset cmd destdir
break
fi
# 判断输入的命令是否存在
if [ -n "$cmd" ];then
which --skip-alias "$cmd" &> /dev/null
if [ $? -eq 0 ];then
copy_cmd $cmd
copy_libfile $cmd
else
echo "$cmd is not exist"
fi
else
echo "Please enter at leastone command"
fi
echo -e "Please enter \\033[31;1menter\\033[0m and we continue"
read input
done
# 执行脚本需要在后面加参数
**********************************************************************
*** 命令复制脚本 ***
*** 请输入一个命令 ***
*** 按q或quit退出脚本 ***
**********************************************************************
Please input a execute command:cat
/bin/cat /mnt/sysroot/bin 复制完成!
/lib64/libc.so.6 /mnt/sysroot/lib64 复制完成!
/lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 /mnt/sysroot/lib64 复制完成!
# 下面是我cp的命令
tree /mnt/sysroot/
/mnt/sysroot/
├── bin
│ ├── bash
│ ├── cat
│ ├── ls
│ ├── mkdir
│ ├── mount
│ ├── rm
│ └── touch
├── dev
├── etc
├── home
├── lib64
│ ├── ld-linux-x86-64.so.2
│ ├── libacl.so.1
│ ├── libattr.so.1
│ ├── libaudit.so.1
│ ├── libblkid.so.1
│ ├── libcap.so.2
│ ├── libcrypt.so.1
│ ├── libc.so.6
│ ├── libdbus-1.so.3
│ ├── libdl.so.2
│ ├── libfreebl3.so
│ ├── libgcc_s.so.1
│ ├── libm.so.6
│ ├── libnih-dbus.so.1
│ ├── libnih.so.1
│ ├── libnsl.so.1
│ ├── libpcre.so.0
│ ├── libpthread.so.0
│ ├── libresolv.so.2
│ ├── librt.so.1
│ ├── libselinux.so.1
│ ├── libsepol.so.1
│ ├── libtinfo.so.5
│ ├── libutil.so.1
│ └── libuuid.so.1
├── media
├── mnt
├── opt
├── proc
├── root
├── sbin
│ ├── ip
│ ├── reboot
│ └── shutdown
├── sys
├── tmp
├── usr
│ ├── bin
│ │ ├── less
│ │ └── vim
│ └── lib64
│ ├── libgpm.so.2
│ └── perl5
│ └── CORE
│ └── libperl.so
└── var
19 directories, 39 files
复制网卡驱动
我们基本工作已经完成了,如果想使这个虚拟机带有网卡功能,我们就必须把网卡驱动拷过来,具体操作如下:
# 查询网卡详细信息
modinfo e1000
filename: /lib/modules/2.6.32-573.el6.x86_64/kernel/drivers/net/e1000/e1000.ko
version: 7.3.21-k8-NAPI
license: GPL
description: Intel(R) PRO/1000 Network Driver
author: Intel Corporation, <linux.nics@intel.com>
srcversion: 43DCE0C8FB4DD663A55F0C5
# 将网卡模块路径复制到/mnt/sysroot的库文件下
cp /lib/modules/2.6.32-573.el6.x86_64/kernel/drivers/net/e1000/e1000.ko /mnt/sysroot/lib64/
# 接下来我们可以关机,将/dev/sdb这个硬盘拆下来,放到新虚拟机运行
测试开机

我们创建一个新的虚拟机,启动的时候会带一个硬盘,我们不用它的,删掉再把我们自己定义的硬盘加进去,
注意,将以前磁盘全删掉,然后重新添加,添加时选择使用现有虚拟磁盘
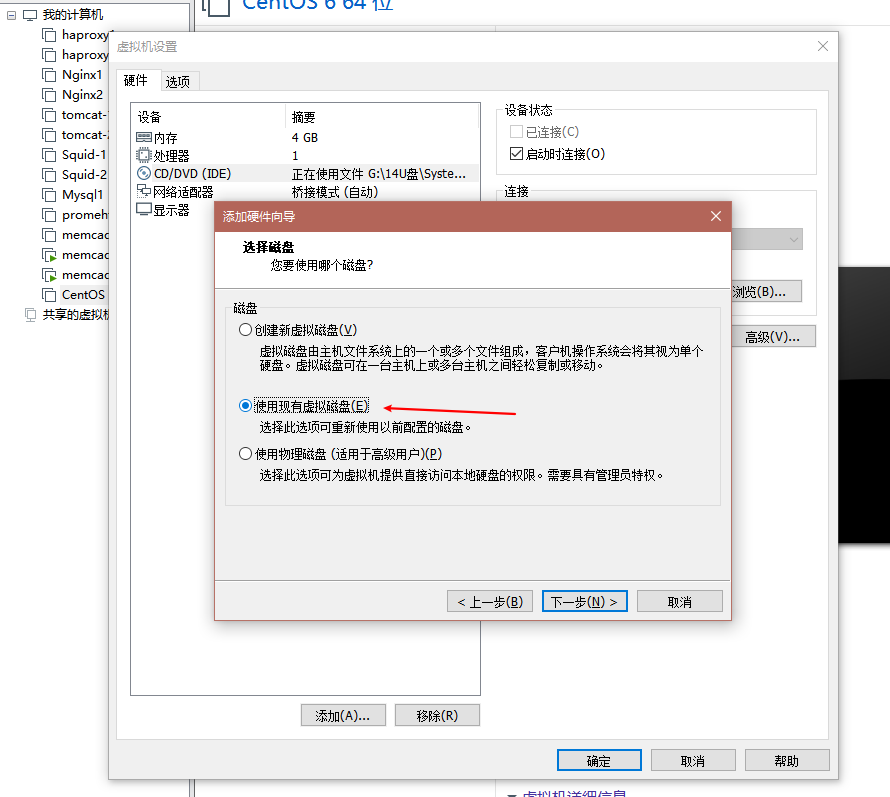

此时,我们做好的硬盘已经加进去了。我们可以试试能不能启动了,如果虚拟机可以正常开启,就说明我们的实验成功
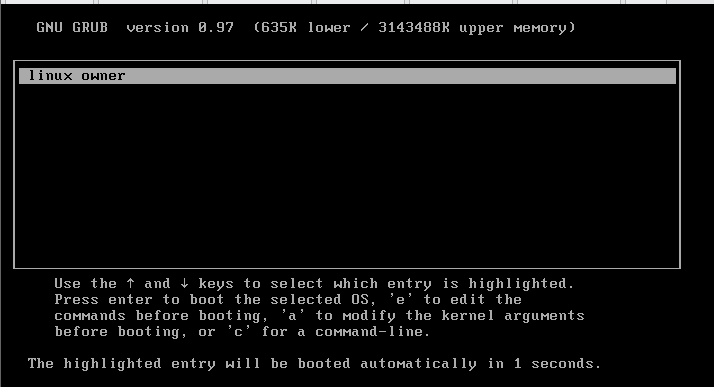
实现网络功能
# 手动添加网卡驱动
insmod /lib64/e1000.ko
# 查看ip
ip a
# 添加IP地址
ifconfig eth0 192.168.252.62/24 up
# 查看ip
ip a
# 可以用其他机器ping一下这台机器,如果能ping通说明联网也没问题,至此就OK了



