openssl命令学习笔记--第一周
开始学习openssl命令,目前处于啥也不懂的状态。因为不是所有命令都能找到详尽的使用方法(部分可能因为版本问题,甚至找不到对应功能)。仅为我那可怜兮兮的7条命令做个学习记录。
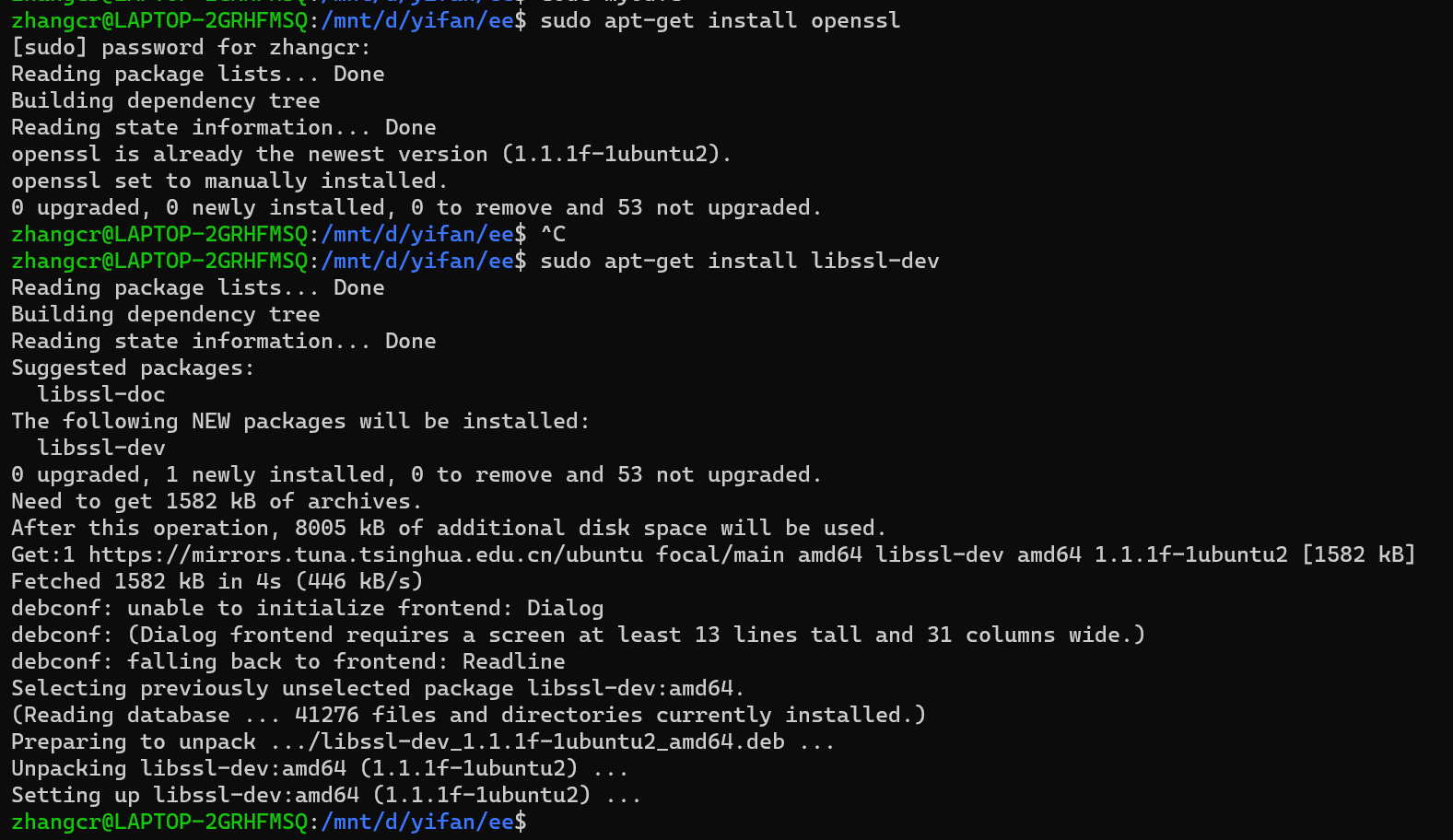
一、在linux环境下下载openssl(用的wsl)
使用命令:
sudo apt-get install openssl sudo apt-get install libssl-dev
二、命令集合
1、prime
1.用途
生成素数/判断输入值是否为素数(当前的众多加密技术高度依赖素数的产生和判断)
2.支持功能
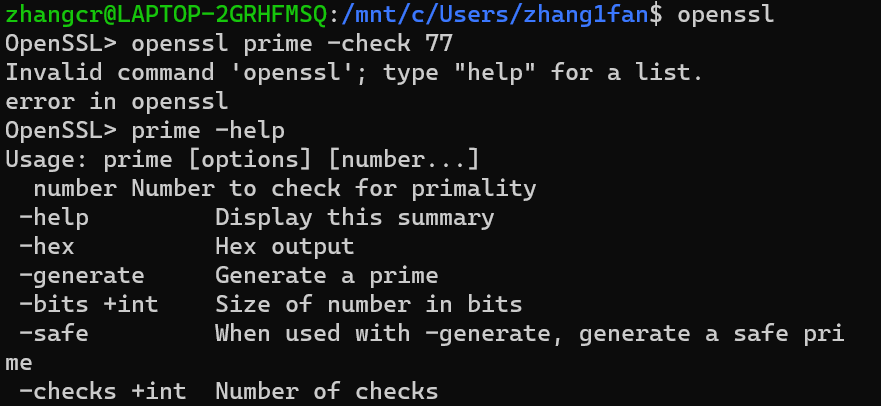
-generate 生成一个素数(无法单独使用。需要设定输出的位数)
![]()
-bits +int 设定生成数的位数( -hex 返回值为16进制)
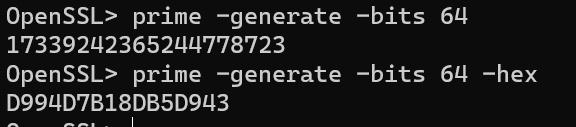
-safe 和-generate搭配使用,生成安全素数
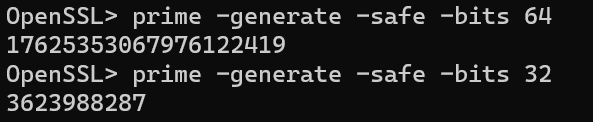
-checks +int 需要检查的数
![]()
直接使用prime 判断输入值是否为素数
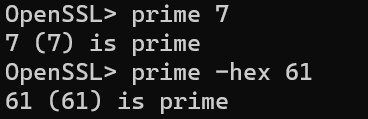
2、rand命令
1.用途
用来产生伪随机字节
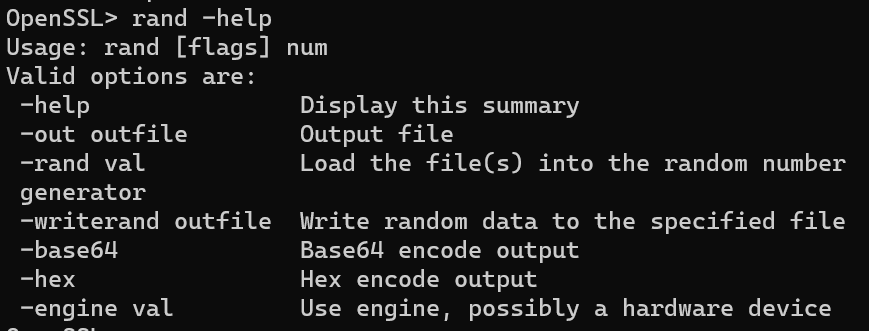
语法:
openssl rand [-out file] [-rand file(s)] [-base64] [-hex] num
2.支持功能
3.具体应用举例
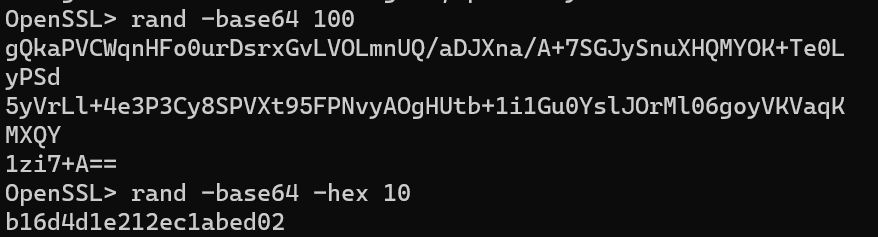
-base64:输出结果为BASE64编码数据。
-hex:输出结果为16进制数据。
-out file:结果输出到file中。
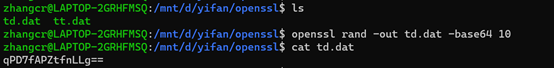
num:随机数长度。
三、req
1.用途
生成证书请求、验证证书请求文件和创建根CA
openssl req [-inform PEM|DER] [-outform PEM|DER] [-in filename] [-passin arg] [-out filename] [-passout arg] [-text] [-pubkey] [-noout] [-verify] [-modulus] [-new] [-rand file(s)] [-newkey rsa:bits][-newkey alg:file] [-nodes] [-key filename] [-keyform PEM|DER] [-keyout filename] [-keygen_engine id] [-[digest]] [-config filename] [-subj arg] [-multivalue-rdn] [-x509] [-days n] [-set_serial n][-asn1-kludge] [-no-asn1-kludge] [-newhdr] [-extensions section] [-reqexts section] [-utf8] [-nameopt] [-reqopt] [-subject] [-subj arg] [-batch] [-verbose] [-engine id]
2.实现功能
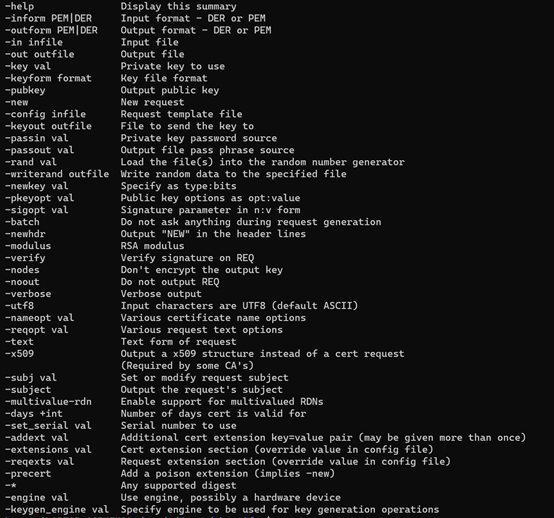
-new:说明生成证书请求文件 -x509:说明生成自签名证书 -key:指定已有的秘钥文件生成秘钥请求,只与生成证书请求选项-new配合。 -newkey :-newkey是与-key互斥的,-newkey是指在生成证书请求或者自签名证书的时候自动生成密钥,然后生成的密钥名称由-keyout参数指定。当指定newkey选项时,后面指定rsa:bits说明产生rsa密钥,位数由bits指定。 如果没有指定选项-key和-newkey,默认自动生成秘钥。 -out :-out 指定生成的证书请求或者自签名证书名称 -config:默认参数在ubuntu上为 /etc/ssl/openssl.cnf, 可以使用-config指定特殊路径的配置文件 -nodes :如果指定-newkey自动生成秘钥,那么-nodes选项说明生成的秘钥不需要加密,即不需要输入passphase. -batch :指定非交互模式,直接读取config文件配置参数,或者使用默认参数值
3.具体应用举例
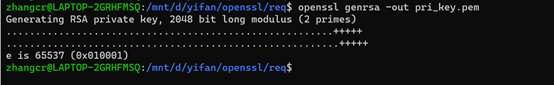
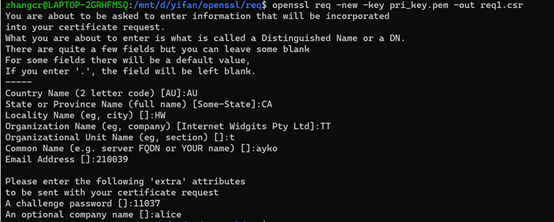
1、根据私钥pri_key.pem生成一个新的证书请求文件。其中"-new"表示新生成一个新的证书请求文件,"-key"指定私钥文件,"-out"指定输出文件,此处输出文件即为证书请求文件
openssl genrsa -out pri_key.pem openssl req -new -key pri_key.pem -out req1.csr
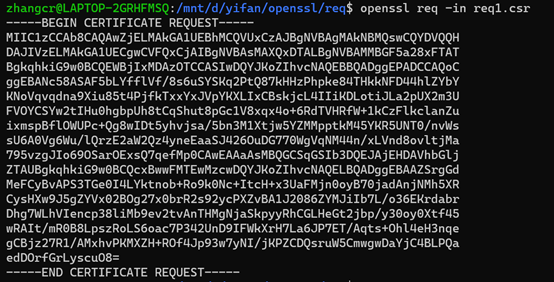
2、查看证书请求文件内容
openssl req -in req1.csr或cat req1.csr或openssl req -in req1.csr -text
3、指定证书请求文件中的签名算法
openssl req -new -key pri_key.pem -out req2.csr -md5
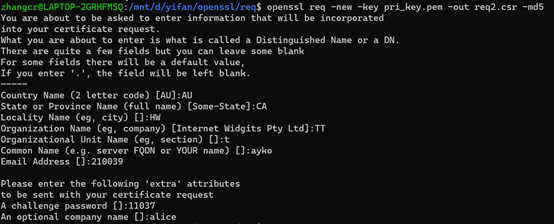
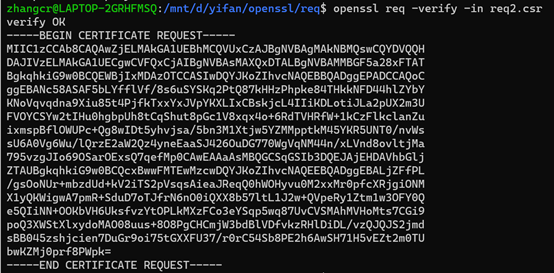
4、验证请求文件的数字签名,这样可以验证出证书请求文件是否被篡改过
openssl req -verify -in req2.csr
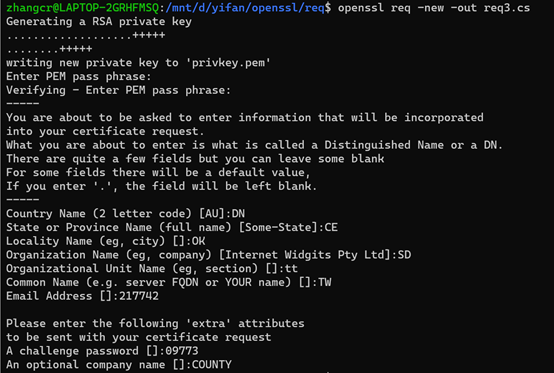
5、自签署证书,可用于自建根CA时
openssl req -new -out req3.csr openssl req -new -out req3.csr -nodes -keyout myprivkey.pem
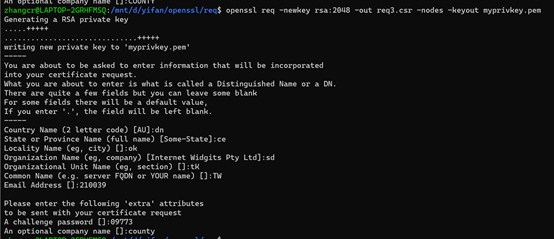
6、使用"-newkey"选项
openssl req -newkey rsa:2048 -out req3.csr -nodes -keyout myprivkey.pem
7、生成自签名证书,证书名client.crt,采用自动生成秘钥的方式,指定生成秘钥长度为1024,加密,秘钥文件client.key.
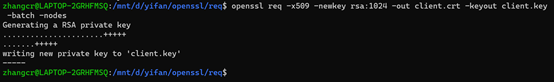
四、rsa
1.用途
用于处理RSA密钥、格式转换和打印信息
语法:openssl rsa [-inform PEM|NET|DER] [-outform PEM|NET|DER] [-in filename] [-passin arg] [-out filename] [-passout arg] [-sgckey] [-text] [-noout] [-modulus] [-check] [-pubin] [-pubout] [-engine id] [-des] [-des3] [-idea]
2.实现功能
3.具体应用举例
1、 生成从私钥导出公钥(生成pub_key.pem)
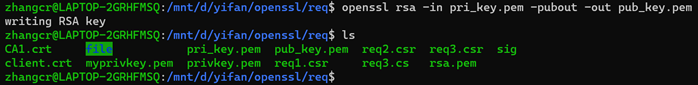
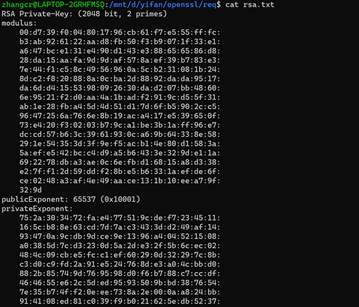
2、 将PEM格式的私钥导出到文本格式:

//查看rsa.txt
3、rsa添加和去除密钥的保护口令
//生成不加密的RSA密钥
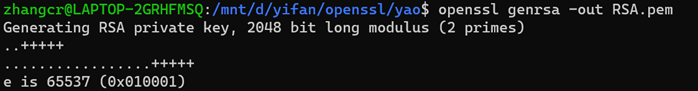
//为RSA密钥增加口令保护*//*为RSA密钥去除口令保护

4、修改密钥的保护口令和算法
//生成RSA密钥
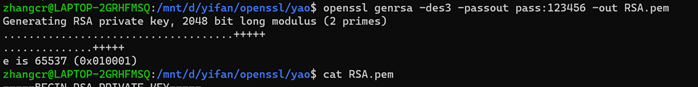
//修改加密算法为aes128,口令是123456

5、查看密钥对中的各个参数
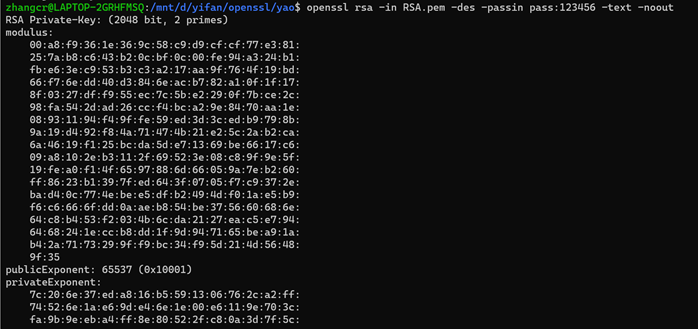
6、提取密钥中的公钥并打印模数值
//提取公钥,用pubout参数指定输出为公钥

//打印公钥中模数值
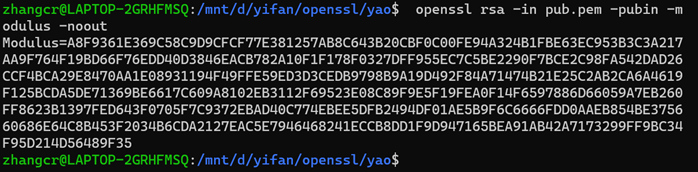
7、转换密钥的格式
//把pem格式转化成der格式,使用outform指定der格式

//把der格式转化成pem格式,使用inform指定der格式

五、rsautl
1.用途
能够使用RSA算法签名,验证身份,加密/解密数据
语法:openssl rsautl [-in file] [-out file] [-inkey file] [-passin arg] [-keyform PEM|DER|NET] [-pubin] [-certin][-asn1parse] [-hexdump] [-raw] [-oaep] [-ssl] [-pkcs] [-x931] [-sign] [-verify][-encrypt] [-decrypt] [-rev] [-engine e]
2.可实现功能
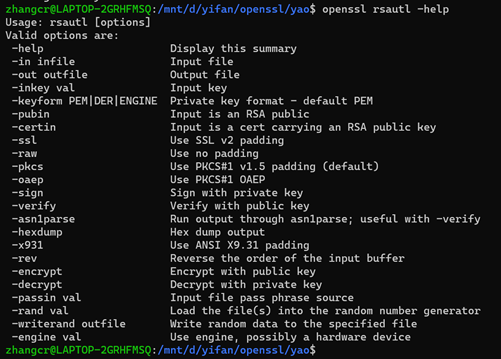
3.具体应用举例
1、使用rsautl进行加密和解密操作
//先生成一个plain.txt内容为“sunnyday”,之后我们将对其进行加密解密操作

//生成RSA密钥

//提取公钥,查看目录,生成了pub.pem

//使用RSA作为密钥进行加密,实际上使用其中的公钥进行加密,此时查看enc.txt,输出结果为加密后结果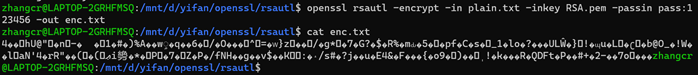
//使用RSA作为密钥进行解密,实际上使用其中的私钥进行解密,这时查看replain.txt,输出结果为“sunnyday”
//比较原始文件和解密后文件,无差别,无输出

在进行相同步骤操作时,可能得出加密结果与上文显示不同,这是因为rsa公钥加密的时候根据填充模式填充随机数,导致每次加密结果不同。
2、使用rsautl进行签名和验证操作
//先生成一个plain.txt内容为“sunnyday”,之后我们将对其进行加密解密操作

//提取PCKS8格式的私钥

//使用RSA密钥进行签名,实际上使用私钥进行加密

//使用RSA密钥进行验证,实际上使用公钥进行解密

//对比原始文件和签名解密后的文件

要注意这里的签名和验证过程其本质上是加解密操作,不是标准意义上的签名和验证。标准意义上签名和验证是需要增加摘要操作的。
六、c_slient
1.用途
一个SSL/TLS客户端程序,与s_server对应,它不仅能与s_server进行通信,也能与任何使用ssl协议的其他服务程序进行通信
openssl s_client [-host host] [-port port] [-connect host:port] [-verify depth] [-cert filename] [-certform DER|PEM] [-key filename] [-keyform DER|PEM] [-pass arg] [-CApath directory] [-CAfile filename] [-reconnect][-pause] [-showcerts] [-debug] [-msg] [-state] [-nbio_test] [-nbio][-crlf] [-ign_eof] [-no_ign_eof] [-quiet] [-ssl2] [-ssl3] [-tls1_1] [-tls1_2] [-tls1] [-dtls1] [-no_ssl2][-no_ssl3] [-no_tls1] [-no_tls1_1] [-no_tls1_2] [-bugs] [-cipher cipherlist] [-starttls protocol] [-engine id] [-tlsextdebug] [-no_ticket] [-sess_out filename] [-sess_in filename] [-rand file(s)]
2.支持功能:
zhangcr@LAPTOP-2GRHFMSQ:/mnt/d/yifan/openssl/yao$ openssl s_client -help Usage: s_client [options] Valid options are: -help Display this summary -host val Use -connect instead -port +int Use -connect instead -connect val TCP/IP where to connect (default is :4433) -bind val bind local address for connection -proxy val Connect to via specified proxy to the real server -unix val Connect over the specified Unix-domain socket -4 Use IPv4 onl y -6 Use IPv6 only -verify +int Turn on peer certificate verification -cert infile Certificate file to use, PEM format assumed -certform PEM|DER Certificate format (PEM or DER) PEM default -nameopt val Various certificate name options -key val Private key file to use, if not in -cert file -keyform PEM|DER|ENGINE Key format (PEM, DER or engine) PEM default -pass val Private key file pass phrase source -CApath dir PEM format directory of CA's -CAfile infile PEM format file of CA's -no-CAfile Do not load the default certificates file -no-CApath Do not load certificates from the default certificates directory -requestCAfile infile PEM format file of CA names to send to the server -dane_tlsa_domain val DANE TLSA base domain -dane_tlsa_rrdata val DANE TLSA rrdata presentation form -dane_ee_no_namechecks Disable name checks when matching DANE-EE(3) TLSA records -reconnect Drop and re-make the connection with the same Session-ID -showcerts Show all certificates sent by the server -debug Extra output -msg Show protocol messages -msgfile outfile File to send output of -msg or -trace, instead of stdout -nbio_test More ssl protocol testing -state Print the ssl states -crlf Convert LF from terminal into CRLF -quiet No s_client output -ign_eof Ignore input eof (default when -quiet) -no_ign_eof Don't ignore input eof -starttls val Use the appropriate STARTTLS command before starting TLS -xmpphost val Alias of -name option for "-starttls xmpp[-server]" -rand val Load the file(s) into the random number generator -writerand outfile Write random data to the specified file -sess_out outfile File to write SSL session to -sess_in infile File to read SSL session from -use_srtp val Offer SRTP key management with a colon-separated profile list -keymatexport val Export keying material using label -keymatexportlen +int Export len bytes of keying material (default 20) -maxfraglen +int Enable Maximum Fragment Length Negotiation (len values: 512, 1024, 2048 and 4096) -fallback_scsv Send the fallback SCSV -name val Hostname to use for "-starttls lmtp", "-starttls smtp" or "-starttls xmpp[-server]" -CRL infile CRL file to use -crl_download Download CRL from distribution points -CRLform PEM|DER CRL format (PEM or DER) PEM is default -verify_return_error Close connection on verification error -verify_quiet Restrict verify output to errors -brief Restrict output to brief summary of connection parameters -prexit Print session information when the program exits -security_debug Enable security debug messages -security_debug_verbose Output more security debug output -cert_chain infile Certificate chain file (in PEM format) -chainCApath dir Use dir as certificate store path to build CA certificate chain -verifyCApath dir Use dir as certificate store path to verify CA certificate -build_chain Build certificate chain -chainCAfile infile CA file for certificate chain (PEM format) -verifyCAfile infile CA file for certificate verification (PEM format) -nocommands Do not use interactive command letters -servername val Set TLS extension servername (SNI) in ClientHello (default) -noservername Do not send the server name (SNI) extension in the ClientHello -tlsextdebug Hex dump of all TLS extensions received -status Request certificate status from server -serverinfo val types Send empty ClientHello extensions (comma-separated numbers) -alpn val Enable ALPN extension, considering named protocols supported (comma-separated list) -async Support asynchronous operation -ssl_config val Use specified configuration file -max_send_frag +int Maximum Size of send frames -split_send_frag +int Size used to split data for encrypt pipelines -max_pipelines +int Maximum number of encrypt/decrypt pipelines to be used -read_buf +int Default read buffer size to be used for connections -no_ssl3 Just disable SSLv3 -no_tls1 Just disable TLSv1 -no_tls1_1 Just disable TLSv1.1 -no_tls1_2 Just disable TLSv1.2 -no_tls1_3 Just disable TLSv1.3 -bugs Turn on SSL bug compatibility -no_comp Disable SSL/TLS compression (default) -comp Use SSL/TLS-level compression -no_ticket Disable use of TLS session tickets -serverpref Use server's cipher preferences -legacy_renegotiation Enable use of legacy renegotiation (dangerous) -no_renegotiation Disable all renegotiation. -legacy_server_connect Allow initial connection to servers that don't support RI -no_resumption_on_reneg Disallow session resumption on renegotiation -no_legacy_server_connect Disallow initial connection to servers that don't support RI -allow_no_dhe_kex In TLSv1.3 allow non-(ec)dhe based key exchange on resumption -prioritize_chacha Prioritize ChaCha ciphers when preferred by clients -strict Enforce strict certificate checks as per TLS standard -sigalgs val Signature algorithms to support (colon-separated list) -client_sigalgs val Signature algorithms to support for client certificate authentication (colon-separated list) -groups val Groups to advertise (colon-separated list) -curves val Groups to advertise (colon-separated list) -named_curve val Elliptic curve used for ECDHE (server-side only) -cipher val Specify TLSv1.2 and below cipher list to be used -ciphersuites val Specify TLSv1.3 ciphersuites to be used -min_protocol val Specify the minimum protocol version to be used -max_protocol val Specify the maximum protocol version to be used -record_padding val Block size to pad TLS 1.3 records to. -debug_broken_protocol Perform all sorts of protocol violations for testing purposes -no_middlebox Disable TLSv1.3 middlebox compat mode -policy val adds policy to the acceptable policy set -purpose val certificate chain purpose -verify_name val verification policy name -verify_depth int chain depth limit -auth_level int chain authentication security level -attime intmax verification epoch time -verify_hostname val expected peer hostname -verify_email val expected peer email -verify_ip val expected peer IP address -ignore_critical permit unhandled critical extensions -issuer_checks (deprecated) -crl_check check leaf certificate revocation -crl_check_all check full chain revocation -policy_check perform rfc5280 policy checks -explicit_policy set policy variable require-explicit-policy -inhibit_any set policy variable inhibit-any-policy -inhibit_map set policy variable inhibit-policy-mapping -x509_strict disable certificate compatibility work-arounds -extended_crl enable extended CRL features -use_deltas use delta CRLs -policy_print print policy processing diagnostics -check_ss_sig check root CA self-signatures -trusted_first search trust store first (default) -suiteB_128_only Suite B 128-bit-only mode -suiteB_128 Suite B 128-bit mode allowing 192-bit algorithms -suiteB_192 Suite B 192-bit-only mode -partial_chain accept chains anchored by intermediate trust-store CAs -no_alt_chains (deprecated) -no_check_time ignore certificate validity time -allow_proxy_certs allow the use of proxy certificates -xkey infile key for Extended certificates -xcert infile cert for Extended certificates -xchain infile chain for Extended certificates -xchain_build build certificate chain for the extended certificates -xcertform PEM|DER format of Extended certificate (PEM or DER) PEM default -xkeyform PEM|DER format of Extended certificate's key (PEM or DER) PEM default -tls1 Just use TLSv1 -tls1_1 Just use TLSv1.1 -tls1_2 Just use TLSv1.2 -tls1_3 Just use TLSv1.3 -dtls Use any version of DTLS -timeout Enable send/receive timeout on DTLS connections -mtu +int Set the link layer MTU -dtls1 Just use DTLSv1 -dtls1_2 Just use DTLSv1.2 -nbio Use non-blocking IO -psk_identity val PSK identity -psk val PSK in hex (without 0x) -psk_session infile File to read PSK SSL session from -srpuser val SRP authentication for 'user' -srppass val Password for 'user' -srp_lateuser SRP username into second ClientHello message -srp_moregroups Tolerate other than the known g N values. -srp_strength +int Minimal length in bits for N -nextprotoneg val Enable NPN extension, considering named protocols supported (comma-separated list) -engine val Use engine, possibly a hardware device -ssl_client_engine val Specify engine to be used for client certificate operations -ct Request and parse SCTs (also enables OCSP stapling) -noct Do not request or parse SCTs (default) -ctlogfile infile CT log list CONF file -keylogfile outfile Write TLS secrets to file -early_data infile File to send as early data -enable_pha Enable post-handshake-authentication
-host host:设置服务地址。 -port port:设置服务端口,默认为4433。 -connect host:port:设置服务器地址和端口号。如果没有设置,则默认为本地主机以及端口号4433。 -verify depth:设置证书的验证深度。记得CA也是分层次的吧?如果对方的证书的签名CA不是Root CA,那么你可以再去验证给该CA的证书签名的CA,一直到Root CA. 目前的验证操作即使这条CA链上的某一个证书验证有问题也不会影响对更深层的CA的身份的验证。所以整个CA链上的问题都可以检查出来。当然CA的验证出问题并不会直接造成连接马上断开,好的应用程序可以让你根据验证结果决定下一步怎么走。 -cert filename:使用的证书文件。如果server不要求要证书,这个可以省略。 -certform DER|PEM:证书的格式,一般为DER和PEM。默认为PEM格式。 -key filename:使用的证书私钥文件。 -keyform DER|PEM:证书私钥文件的格式,一般为DER和PEM。默认为PEM格式。 -pass arg:私钥保护口令来源,比如:-pass file:pwd.txt,将私钥保护口令存放在一个文件中,通过此选项来指定,不需要用户来输入口令。 -CApath directory:设置信任CA文件所在路径,此路径中的ca文件名采用特殊的形式:xxx.0,其中xxx为CA证书持有者的哈希值,它通过x509 -hash命令获得。 -CAfile filename:某文件,里面是所有你信任的CA的证书的内容。当你要建立client的证书链的时候也需要用到这个文件。 -reconnect:使用同样的session-id连接同一个server五次,用来测试server的session缓冲功能是否有问题。 -pause:每当读写数据时,sleep 1秒。 -showcerts:显示整条server的证书的CA的证书链。否则只显示server的证书。 -debug:打印所有的调试信息。 -msg:用16进制显示所有的协议数据。 -state:打印SSL session的状态, ssl也是一个协议,当然有状态。 -nbio_test:检查非阻塞socket的I/O运行情况。 -nbio:使用非阻塞socket。 -crlf:把在终端输入的换行回车转化成/r/n送出去。 -ign_eof:当输入文件到达文件尾的时候并不断开连接。 -no_ign_eof:当输入文件到达文件尾的时候断开连接。 -quiet:不打印出session和证书的信息。同时会打开-ign_eof这个选项。 -ssl2、-ssl3、-tls1_1、-tls1_2、-tls1、-dtls1、-no_ssl2、-no_ssl3、-no_tls1、-no_tls1_1、-no_tls1_2:使用的协议状态值。 -bugs:兼容老版本服务端的中的bug。 -cipher cipherlist:由我们自己来决定选用什么加密算法,尽管是由server来决定使用什么算法列表,但它一般都会采用我们送过去的cipher列表里的第一个cipher。 -starttls protocol:protocol可以为smtp或pop3,用于邮件安全传输。 -engine id:硬件引擎。 -tlsextdebug:打印TLS协议中服务器端接收到的额外信息值。 -no_ticket:不支持RFC4507bis会话类型。 -sess_out filename:输出SSL会话信息值到filename中。 -sess_in filename:从filename中获取SSL Session值。 -rand file(s):指定随机数种子文件,多个文件间用分隔符分开,windows用“;”,OpenVMS用“,“,其他系统用“:”。
3.具体应用举例
1.。连接某个网站
语法:-connect host:port
以下达成的是连接百度网址,显示连接成功(显示了证书信息,连接状态,会话状态等):
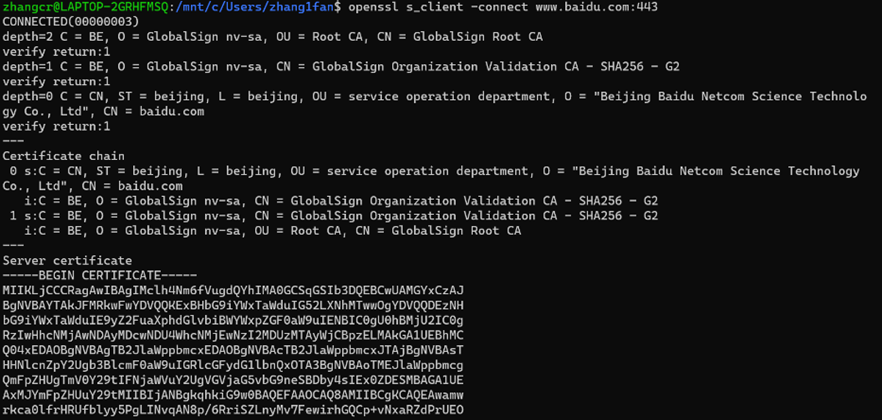
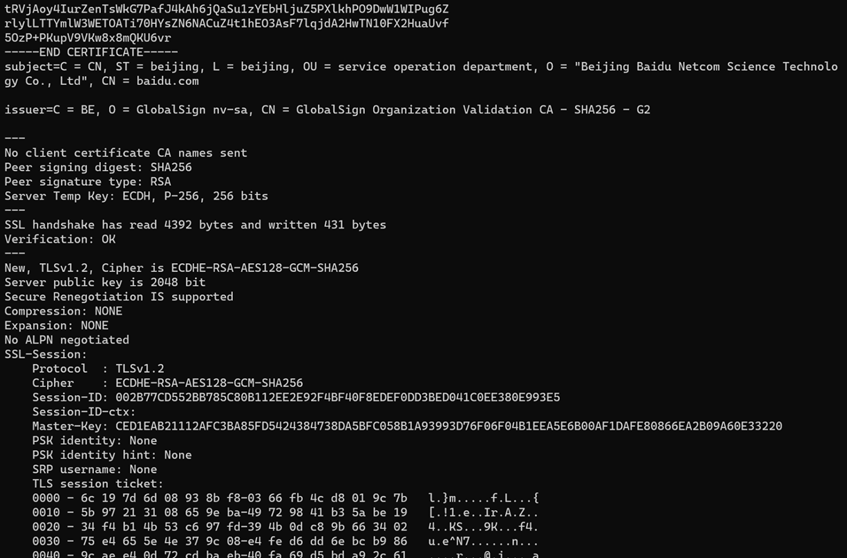
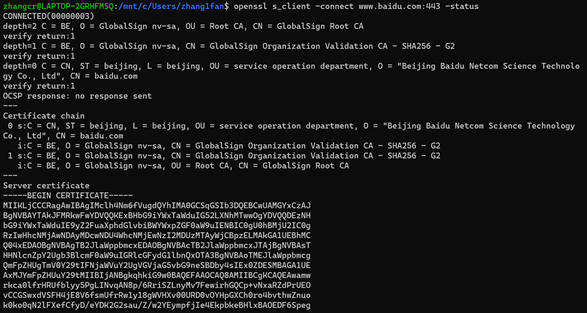
2.。使用自定CA列表进行验证
语法:-status
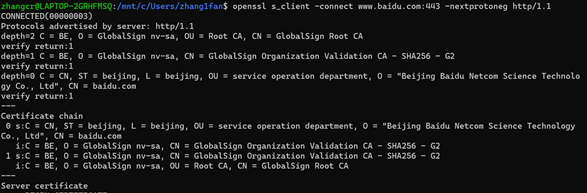
3.。使用指定协议
语法:-snextprotoneg protocols
七、pkeyutl
1.用途
pkeyutl命令能够测试所支持的密钥算法的性能
2.实现功能
3.具体应用举例
//首先我们有已产生的私钥,以及包含数据“1234567”的.txt文件
1、用私钥对数据进行签名:(产生了sig)

2、恢复签名数据(用RSA密钥):

3、用DSA算法来验证签名://RSA大整数的因式分解被认为是‘难以破解’(困难的),而DSA安全性基于离散对数问题。

参考网址:https://www.cnblogs.com/aixiaoxiaoyu/articles/8872382.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/274914765qq/p/4675649.html
https://blog.csdn.net/funtasty/article/details/41822095
https://www.dazhuanlan.com/2019/12/07/5deb102344333/?__cf_chl_jschl_tk__=95fcf51902cf6d8955f44dc6664f2f84d841657d-1603025632-0-AQTNJQ_An0XNxay_ve7Rw5UfDqvthL0aSHRWsgoSiKHzdOkJ-VrlldiUlxICgsZEkoTSr4q2mM1O2kNqQaFX9huMJVylNN1RQl-K9W_IGb5Ls0o514l04xaOschMHuCHcN7uh-ToLGdCV7NKxzzshPOCuU_We4bFRTg4cLQDMQ3KFODTtJqB39mD42k1-91beOIcQXzZiPfBnSGZNIOxWL9GhVsfLLoMUyGhGXftmTNy48FCI8X9NZ6VVkpsdz2f3Q1sLy93qDlybZuy4r6W7vJKJnAB6e9EPs0Ci9sXI2Ttj_OTIyZSZUq8W-0L99W8JA
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/news/254061



