[数据结构] 2.7 Heap 堆
* 注: 本文/本系列谢绝转载,如有转载,本人有权利追究相应责任。
1.堆是什么?
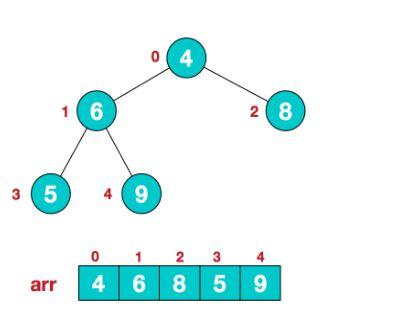
(如图所示是一个小堆)
1)堆是一颗完全二叉树,它的最后一层不是满的,其他每一层都是满的,最后一层从左到右也没有空隙。
简单的说? 完全二叉树也就是没有缝隙的二叉树。
2)堆常常通过数组实现,因为 父子节点直接的关系直接可以通过数组的索引换算
parent(i) = i/2
left child(i) = 2*i + 1
right child(i) = 2*i + 2
3)对于最大堆来说,每个节点的值都不大于其父节点的值,也就是根节点是最大的。
对于最小堆来说,每个节点的值都不小于其父节点的值,也就是根节点是最小的
4)堆进行插入和删除的时间复杂度均为 O(LogN)
2.堆的应用
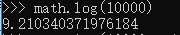
堆可以解决的首先就是topK问题,假设要从N大小的实数数组中找到topK,那么需要K*logN的时间。
当N=10000时
当N=10000*10000时
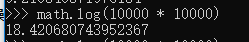
也就是说N可以放的足够大,K可以适当大一些,经过本机实验,堆在单机单线程下只需要14s就可以处理一亿数据的Top1W操作。
3.堆的实现
堆的操作主要是两个 add、remove,有些地方也会存在buildHeap的操作,我们分别捋一下它们的思路。
一下基于一个最大堆。
1) add操作,添加元素
思路:
将添加的元素放在数组尾部,进行“上浮”操作。也就是比较父元素,如果大于父元素则上浮。
实际长度 ++
/** * 插入过程需要上浮比较 * @param node */ public void insert(Node node){ if(actualSize == MAX_N){ System.out.println("当前堆已满!"); return; } // 插入 // 插入节点 nodes[actualSize] = node; // 上浮过程 // 调整堆,从这个节点开始与其夫节点进行比较,如果大于父节点则交换上浮 for(int i = actualSize; i > 0 ;i = getParentIndex(i)){ Node current = nodes[i]; Node parent = nodes[getParentIndex(i)]; if(parent.data < current.data){ nodes[i] = parent; nodes[getParentIndex(i)] = current; } } actualSize ++; }
2) remove操作,删除元素
思路:
获得堆顶的值,然后用堆底节点替换堆顶节点。并针对此节点进行"下沉"操作,所谓下沉,就是如果比较当前元素与左右子节点的值,如果比它们小,则与最大者交换。
实际长度 --
/** * 删除过程需要下沉比较 * @param node */ public void remove(Node node){ if(actualSize == 0){ System.out.println("当前堆已空!"); return; } if(actualSize == 1){ actualSize --; return; } // 删除过程 // 使用最后一个节点替换掉顶点 Node tailNode = nodes[actualSize-1]; nodes[0] = tailNode; actualSize --; // 下沉比较 for(int i = 0; i < actualSize;){ Node current = nodes[i]; Node leftChild = null; if(getLeftChildIndex(i) < actualSize){ leftChild = nodes[getLeftChildIndex(i)]; } Node rightChild = null; if(getRightChildIndex(i) < actualSize){ rightChild = nodes[getRightChildIndex(i)]; } if(leftChild == null && rightChild == null){ return; } if(leftChild != null && leftChild.data > current.data){ if(rightChild != null && rightChild.data > leftChild.data){ // 右枝最大 nodes[i] = rightChild; nodes[getRightChildIndex(i)] = current; // i走右枝 i = getRightChildIndex(i); continue; }else{ // 左枝最大 nodes[i] = leftChild; nodes[getLeftChildIndex(i)] = current; // i走左枝 i = getLeftChildIndex(i); continue; } }else{ if(rightChild != null && rightChild.data > current.data){ // 右枝最大 nodes[i] = rightChild; nodes[getRightChildIndex(i)] = current; // i走右枝 i = getRightChildIndex(i); continue; }else if(rightChild != null && rightChild.data <= current.data){ // 当前点最大 //保持现状,直接结束循环 break; } } } }
3)buildHeap操作,给一个数组,进行建立堆操作
思路:
遍历数组的每一个节点,针对每个节点进行"上浮"操作.
Code:
package ds6.heap; import java.util.Arrays; public class Heap { static class Node{ long data; public Node(long data) { this.data = data; } @Override public String toString() { return "Node{" + "data=" + data + '}'; } } /** * TopN最大值堆 */ static class TopNMaxHeap{ int MAX_N = 10; // Top N ,指定堆的最大大小 Node[] nodes; int actualSize = 0; public TopNMaxHeap(int MAX_N) { this.MAX_N = MAX_N; nodes = new Node[MAX_N]; } public void foreachPrint(){ System.out.println(Arrays.toString(nodes)); } /** * 删除过程需要下沉比较 * @param node */ public void remove(Node node){ if(actualSize == 0){ System.out.println("当前堆已空!"); return; } if(actualSize == 1){ actualSize --; return; } // 删除过程 // 使用最后一个节点替换掉顶点 Node tailNode = nodes[actualSize-1]; nodes[0] = tailNode; actualSize --; // 下沉比较 for(int i = 0; i < actualSize;){ Node current = nodes[i]; Node leftChild = null; if(getLeftChildIndex(i) < actualSize){ leftChild = nodes[getLeftChildIndex(i)]; } Node rightChild = null; if(getRightChildIndex(i) < actualSize){ rightChild = nodes[getRightChildIndex(i)]; } if(leftChild == null && rightChild == null){ return; } if(leftChild != null && leftChild.data > current.data){ if(rightChild != null && rightChild.data > leftChild.data){ // 右枝最大 nodes[i] = rightChild; nodes[getRightChildIndex(i)] = current; // i走右枝 i = getRightChildIndex(i); continue; }else{ // 左枝最大 nodes[i] = leftChild; nodes[getLeftChildIndex(i)] = current; // i走左枝 i = getLeftChildIndex(i); continue; } }else{ if(rightChild != null && rightChild.data > current.data){ // 右枝最大 nodes[i] = rightChild; nodes[getRightChildIndex(i)] = current; // i走右枝 i = getRightChildIndex(i); continue; }else{ // 当前点最大 //保持现状,直接结束循环 break; } } } } /** * 插入过程需要上浮比较 * @param node */ public void insert(Node node){ if(actualSize == MAX_N){ System.out.println("当前堆已满!"); return; } // 插入 // 插入节点 nodes[actualSize] = node; // 上浮过程 // 调整堆,从这个节点开始与其夫节点进行比较,如果大于父节点则交换上浮 for(int i = actualSize; i > 0 ;i = getParentIndex(i)){ Node current = nodes[i]; Node parent = nodes[getParentIndex(i)]; if(parent.data < current.data){ nodes[i] = parent; nodes[getParentIndex(i)] = current; } } actualSize ++; } public int getParentIndex(int x){ return (x-1)/2; } public int getLeftChildIndex(int x){ return 2*x + 1; } public int getRightChildIndex(int x){ return 2*x + 2; } } public static void main(String[] args) { TopNMaxHeap topNMaxHeap = new TopNMaxHeap(10); topNMaxHeap.insert(new Node(27)); topNMaxHeap.insert(new Node(33)); topNMaxHeap.insert(new Node(30)); topNMaxHeap.insert(new Node(31)); Node nodeToRemove = new Node(40); topNMaxHeap.insert(nodeToRemove); topNMaxHeap.insert(new Node(20)); topNMaxHeap.foreachPrint(); topNMaxHeap.remove(nodeToRemove); topNMaxHeap.foreachPrint(); } }
result:
[Node{data=40}, Node{data=33}, Node{data=30}, Node{data=27}, Node{data=31}, Node{data=20}, null, null, null, null]
[Node{data=33}, Node{data=31}, Node{data=30}, Node{data=27}, Node{data=20}, Node{data=20}, null, null, null, null]
4.堆排序
因为堆的这个特性,通过不断poll出堆顶元素就可以对元素列表进行排序。
测试:
public static void test2(){ int[] toSort = new int[]{ 7,10,6,8,9,3,5,4 }; TopNMaxHeap heap = new TopNMaxHeap(toSort.length); for(int i = 0 ; i < toSort.length; i++ ){ heap.insert(new Node(toSort[i])); } int[] result = new int[toSort.length]; for(int i = 0; i < toSort.length; i++ ){ result[i]=(int)heap.nodes[0].data; heap.remove(heap.nodes[0]); } System.out.println(Arrays.toString(result)); }
result:
[10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3]

