uboot顶层Makefile
1. 工作目录

如上图代码,编译之后将解压包放到windows解压观看。
目录如下:
文件夹:
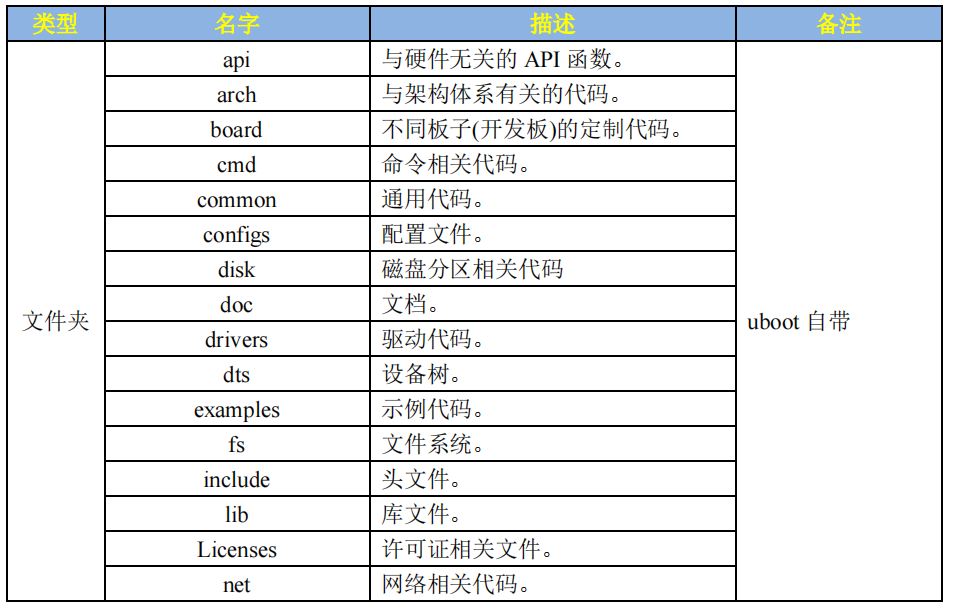

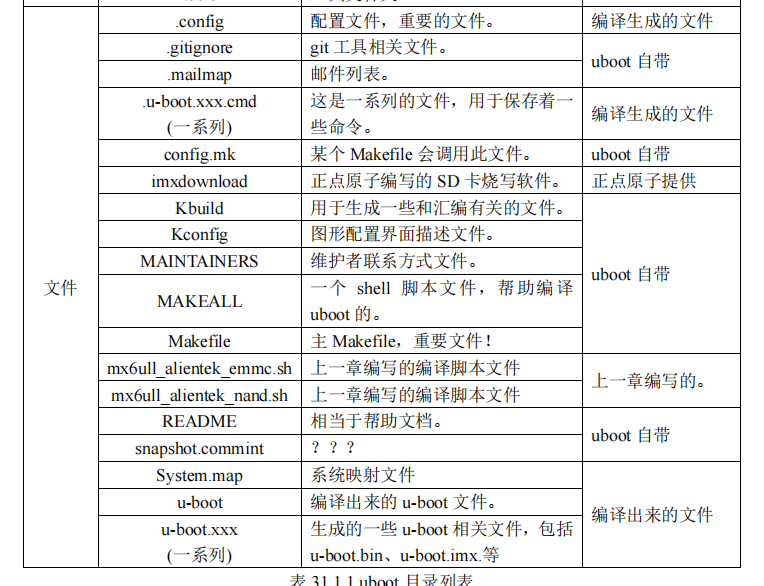
文件:
1.1 arch
这里面存放着和架构有关的文件
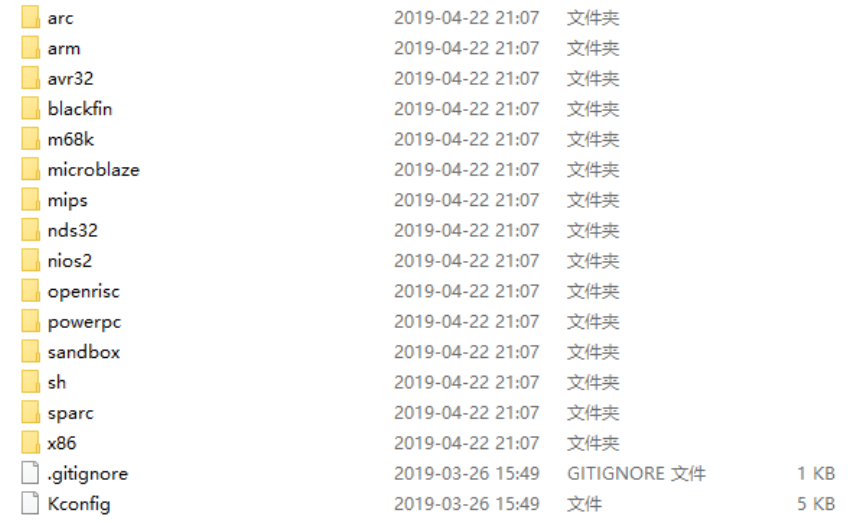
我们用的是arm架构的文件,打开arm文件夹:
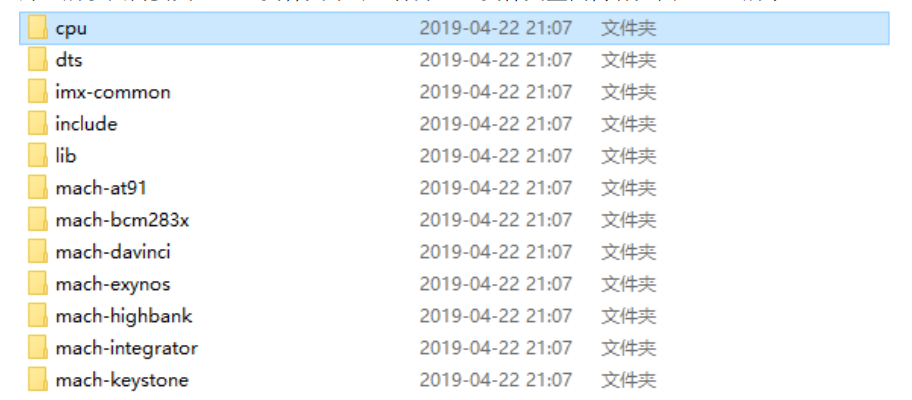
其中mach开头的是和设备有关的文件,比如exynos是和三星有关的,我们使用的是imx-common,所以要使用这个文件夹,cpu也是和CPU有关的文件,打开之后:
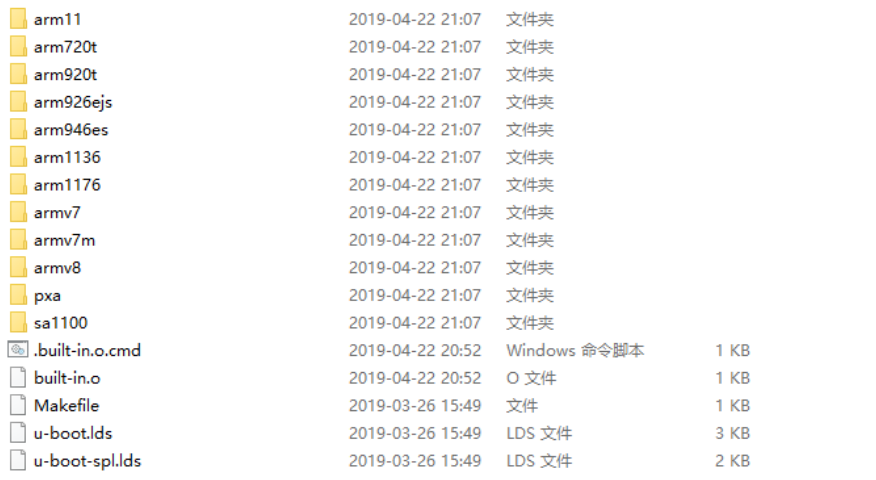
我们使用的开发板是armv7的,u-boot.lds就是链接文件。
1.2 board
board文件夹里面的文件是和板子有关的,我们打开里面的飞思卡尔的文件夹
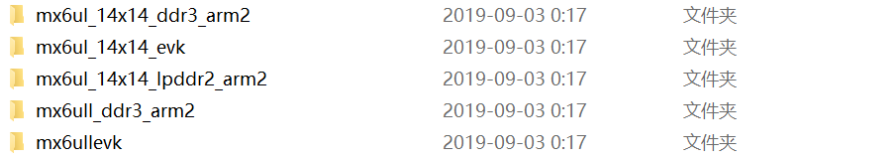
evk后缀是正点原子在这个基础上开发的,移植uboot的时候要参考这个文件夹
1.3 config
此文件夹为 uboot 配置文件,uboot 是可配置的,但是你要是自己从头开始一个一个项目的配置,那就太麻烦了,因此一般半导体或者开发板厂商都会制作好一个配置文件。我们可以在这个做好的配置文件基础上来添加自己想要的功能,这些半导体厂商或者开发板厂商制作好的配置文件统一命名为“xxx_defconfig”,xxx 表示开发板名字,这些 defconfig 文件都存放在configs文件夹,因此,NXP 官方开发板和正点原子的开发板配置文件肯定也在这个文件夹中,
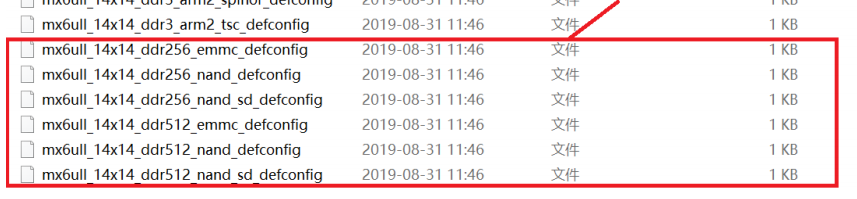
我们使用的mx6ull_14x14_ddr512_emmc_deconfig
在编译uboot之前一定要用这个配置文件

1.4 u_boot.xxx.cmd文件
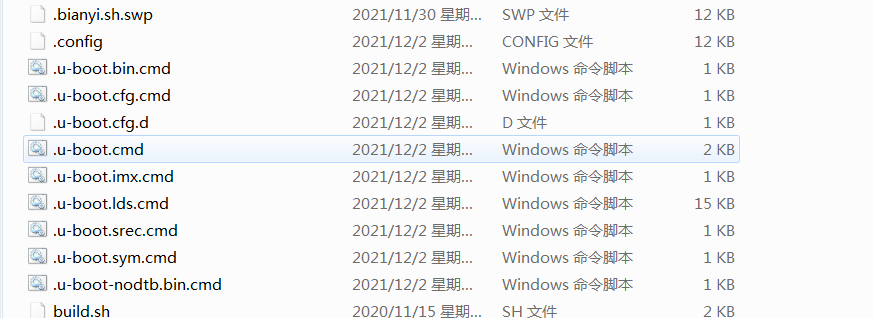
这些文件都是编译生成的,是一些命令文件
.u-boot.bin.cmd
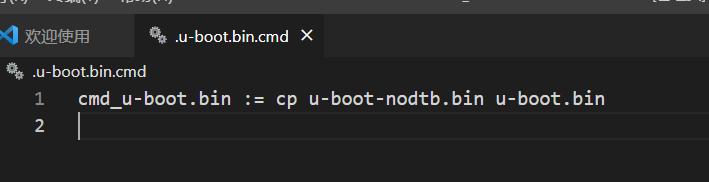
里面定义了一个变量叫cmd_u-boot.bin 拷贝了u-boot-nodtb.bin一份改成u-boot.bin
那我们就看u-boot-nodtb.bin
u-boot-nodtb.bin.cmd
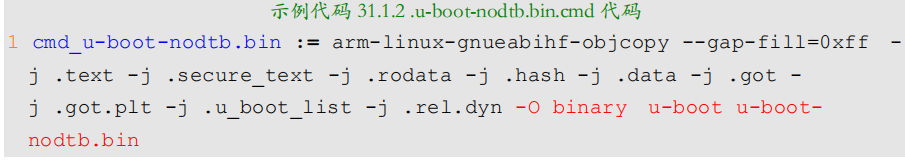
使用arm-linux-gnueabihf-objcopy将elf文件转化为bin文件
那就是u-boot.elf 变成u-boot-nodtb.bin
u-boot.cmd
注意和上面的bin.cmd分开,这个是生成elf的,所以猜测是链接文件

输出是u-boot, 后面也可以不用加elf,和最开始交叉编译的联系起来
还有一个是用来烧写用的,把bin变成imx文件,就是.u-boot.imx.cmd

1.5 u-boot.xxx

1.6 .config文件
配置文件,在上面有一个make mx6ull_14x14_ddr512_emmc_deconfig就会生成
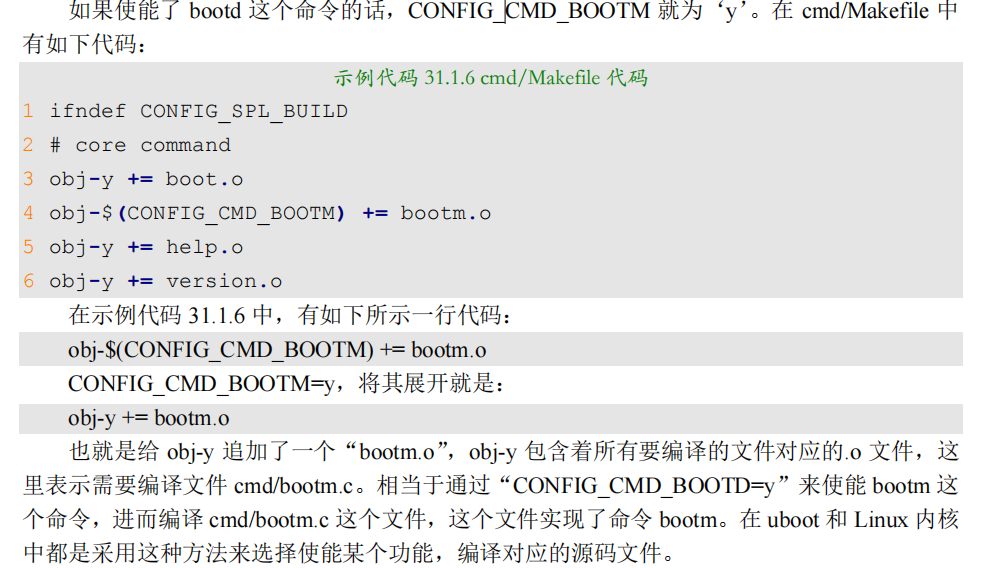
可以看出.config 文件中都是以“CONFIG_”开始的配置项,这些配置项就是 Makefile 中的变量,因此后面都跟有相应的值,uboot 的顶层 Makefile 或子 Makefile 会调用这些变量值。在.config 中会有大量的变量值为‘y’,这些为‘y’的变量一般用于控制某项功能是否使能,为'y’的话就表示功能使能,比如:
2.屏蔽我们不要的文件
在vscode中新建一个.vscode文件夹
在里面建立一个setting.json排除不需要的文件
{
"search.exclude":
{
"**/*.o":true,
"**/*.su":true,
"**/*.cmd":true,
"arch/arc":true,
"arch/avr32":true,
"arch/blackfin":true,
"arch/m68k":true,
"arch/microblaze":true,
"arch/mips":true,
"arch/nds32":true,
"arch/nios2":true,
"arch/openrisc":true,
"arch/powerpc":true,
"arch/sandbox":true,
"arch/sh":true,
"arch/sparc":true,
"arch/x86":true,
"arch/arm/mach*":true,
"arch/arm/cpu/arm11*":true,
"arch/arm/cpu/arm720t":true,
"arch/arm/cpu/arm9*":true,
"arch/arm/cpu/armv7m":true,
"arch/arm/cpu/armv8":true,
"arch/arm/cpu/pxa":true,
"arch/arm/cpu/sa1100":true,
"board/[a-e]*":true,
"board/[g-z]*":true,
"board/[0-9]*":true,
"board/[A-Z]*":true,
"board/fir*":true,
"board/freescale/b*":true,
"board/freescale/l*":true,
"board/freescale/m5*":true,
"board/freescale/mp*":true,
"board/freescale/c29*":true,
"board/freescale/cor*":true,
"board/freescale/mx7*":true,
"board/freescale/mx2*":true,
"board/freescale/mx3*":true,
"board/freescale/mx5*":true,
"board/freescale/p*":true,
"board/freescale/q*":true,
"board/freescale/t*":true,
"board/freescale/v*":true,
"configs/[a-l]*":true,
"configs/[n-z]*":true,
"configs/[A-Z]*":true,
"configs/M[a-z]*":true,
"configs/M[A-Z]*":true,
"configs/M[0-9]*":true,
"configs/m[a-w]*":true,
"configs/m[0-9]*":true,
"configs/[0-9]*":true,
"include/configs/[a-l]*":true,
"include/configs/[n-z]*":true,
"include/configs/[A-Z]*":true,
"include/configs/m[a-w]*":true,
},
"files.exclude":
{
"**/*.o":true,
"**/*.su":true,
"**/*.cmd":true,
"arch/arc":true,
"arch/avr32":true,
"arch/blackfin":true,
"arch/m68k":true,
"arch/microblaze":true,
"arch/mips":true,
"arch/nds32":true,
"arch/nios2":true,
"arch/openrisc":true,
"arch/powerpc":true,
"arch/sandbox":true,
"arch/sh":true,
"arch/sparc":true,
"arch/x86":true,
"arch/arm/mach*":true,
"arch/arm/cpu/arm11*":true,
"arch/arm/cpu/arm720t":true,
"arch/arm/cpu/arm9*":true,
"arch/arm/cpu/armv7m":true,
"arch/arm/cpu/armv8":true,
"arch/arm/cpu/pxa":true,
"arch/arm/cpu/sa1100":true,
"board/[a-e]*":true,
"board/[g-z]*":true,
"board/[0-9]*":true,
"board/[A-Z]*":true,
"board/fir*":true,
"board/freescale/b*":true,
"board/freescale/l*":true,
"board/freescale/m5*":true,
"board/freescale/mp*":true,
"board/freescale/c29*":true,
"board/freescale/cor*":true,
"board/freescale/mx7*":true,
"board/freescale/mx2*":true,
"board/freescale/mx3*":true,
"board/freescale/mx5*":true,
"board/freescale/p*":true,
"board/freescale/q*":true,
"board/freescale/t*":true,
"board/freescale/v*":true,
"configs/[a-l]*":true,
"configs/[n-z]*":true,
"configs/[A-Z]*":true,
"configs/M[a-z]*":true,
"configs/M[A-Z]*":true,
"configs/M[0-9]*":true,
"configs/m[a-w]*":true,
"configs/m[0-9]*":true,
"configs/[0-9]*":true,
"include/configs/[a-l]*":true,
"include/configs/[n-z]*":true,
"include/configs/[A-Z]*":true,
"include/configs/m[a-w]*":true,
}
}
其中"search.exclude"里面是需要在搜索结果中排除的文件或者文件夹,"files.exclude"是左侧工程目录中需要排除的文件或者文件夹。我们需要将 arch/avr32 文件夹下的所有文件从搜索结果和左侧的工程目录中都排除掉,因此在"search.exclude"和"files.exclude"中输入
3.Makefile分析(我真的看的爆炸)
3.1 版本号
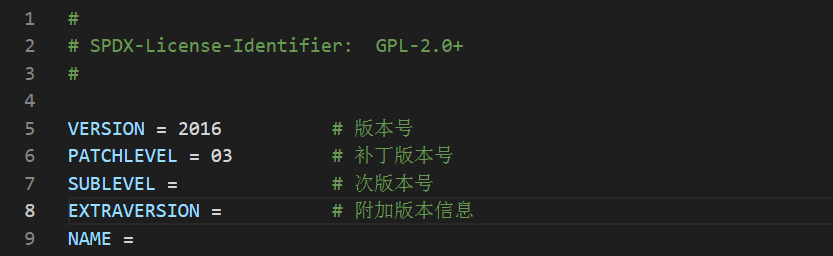
3.2 MakeFlags变量
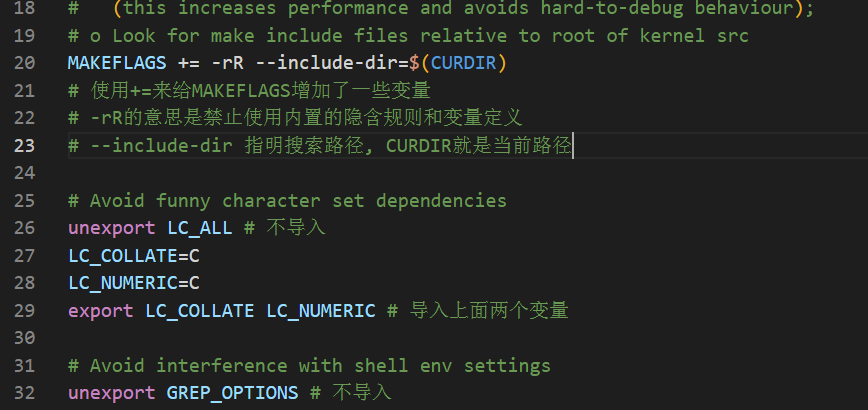
make 是支持递归调用的,也就是在 Makefile 中使用“make”命令来执行其他的 Makefile文件,一般都是子目录中的 Makefile 文件。假如在当前目录下存在一个“subdir”子目录,这个子目录中又有其对应的 Makefile 文件,那么这个工程在编译的时候其主目录中的 Makefile 就可以调用子目录中的 Makefile,以此来完成所有子目录的编译。主目录的 Makefile 可以使用如下代码来编译这个子目录:
$(MAKE) -C subdir
subdir就是子目录,有时候需要将变量导入子目录,export就是导入,unxeport就是不导入,需要注意的是,“SHELL”和“MAKEFLAGS”,这两个变量除非使用“unexport”声明,否则的话在整个make的执行过程中,它们的值始终自动的传递给子make
3.3 命令输出
uboot 默认编译是不会在终端中显示完整的命令,都是短命令
在终端中输出短命令虽然看起来很清爽,但是不利于分析 uboot 的编译过程。可以通过设置变量“V=1“来实现完整的命令输出
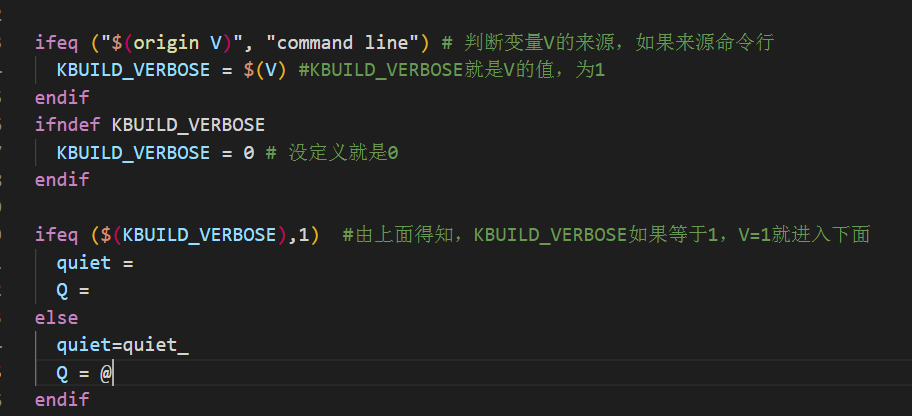
在Makefile文件中有许多下面的
$(Q)$(MAKE) $(build)=tool
如果V = 0, Q=@,就不会在中断输出命令了;否则就会输出命令
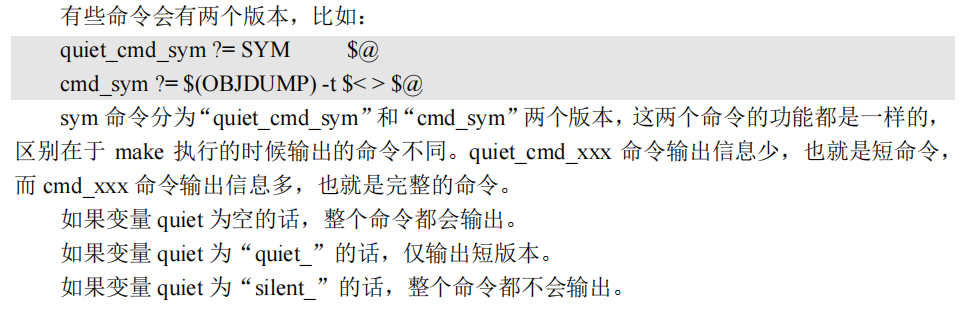
3.4 静默输出
由上一节可知,如果V=1就输出很多命令,如果V不等于0就会短命令输出,有时候不需要输出命令,这时候就是静默输出。make -s也可以实现。
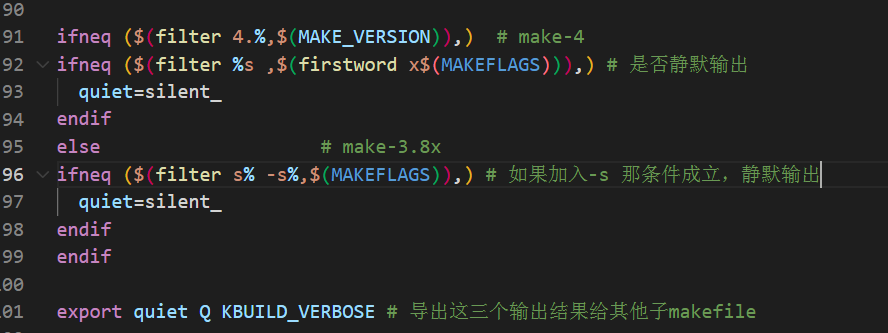
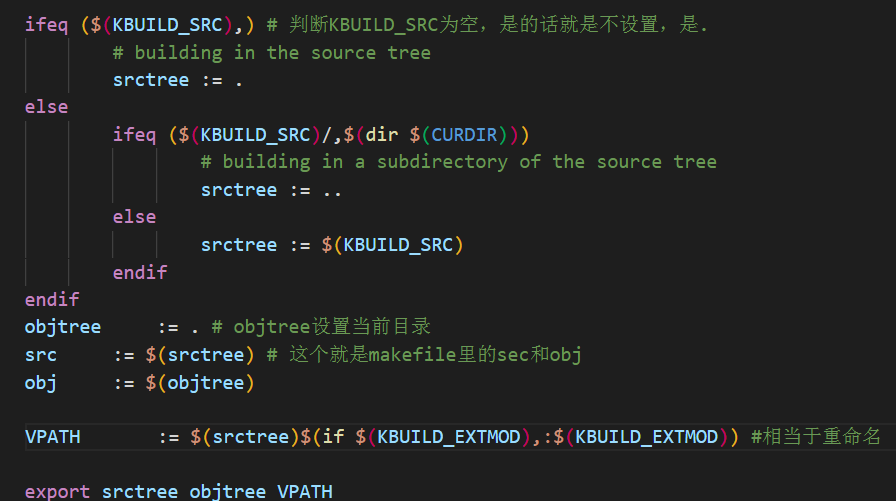
3.5 设置编译结果输出目录
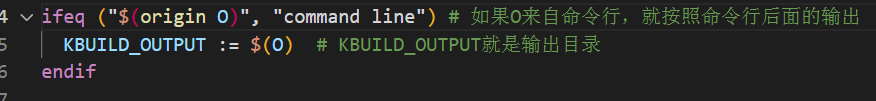
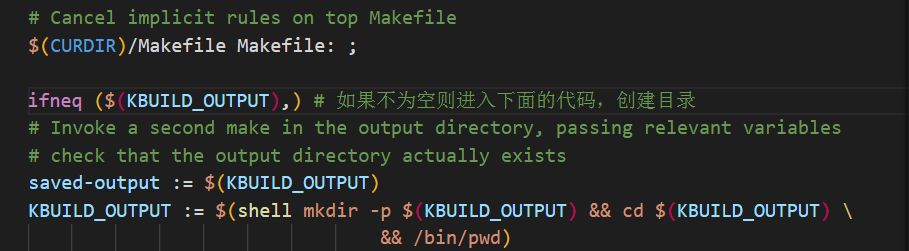
3.6 代码检查
make C=1使能代码检查,C=2是全部文件检查
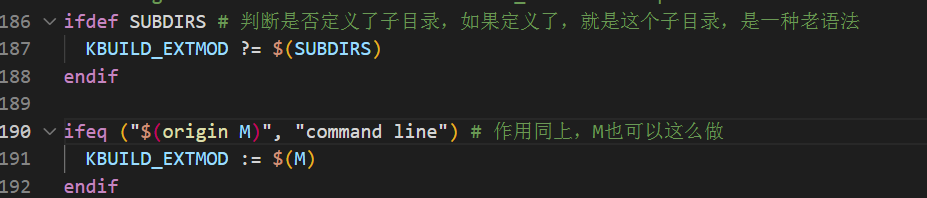
3.7 模块编译
在 uboot 中允许单独编译某个模块,使用命令“make M=dir”即可,旧语法“make SUBDIRS=dir”也是支持的。顶层 Makefile 中的代码如下:
3.8 获取主机架构和系统
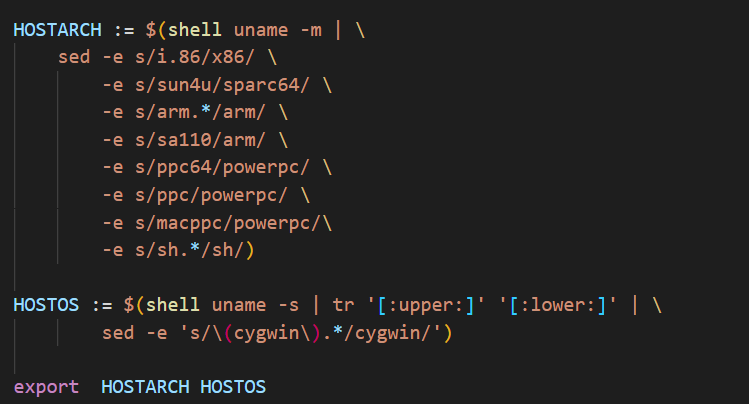
从图 31.3.8.1 可以看出当前电脑主机架构为“x86_64”,shell 中的“|”表示管道,意思是将左边的输出作为右边的输入,sed -e 是替换命令,“sed -e s/i.86/x86/”表示将管道输入的字符串中的“i.86”替换为“x86”,其他的“sed -s”命令同理。对于我的电脑而言,HOSTARCH=x86_64。
可以看出此时的主机 OS 为“Linux”,使用管道将“Linux”作为后面“tr '[:upper:]'
'[:lower:]'”的输入,“tr '[:upper:]' '[:lower:]'”表示将所有的大写字母替换为小写字母,因此得到“linux”。最后同样使用管道,将“linux”作为“sed -e's/(cygwin)./cygwin/'”的输入,用于将cygwin.替换为 cygwin。因此,HOSTOS=linux。
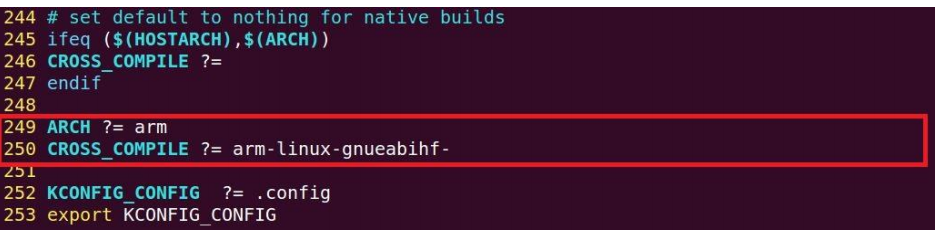
3.9 设置目标架构、交叉编译器和配置文件


3.10 调用Script/Kbuild
主 Makefile 会调用文件 scripts/Kbuild.include 这个文件
3.11 交叉编译工具变脸设置
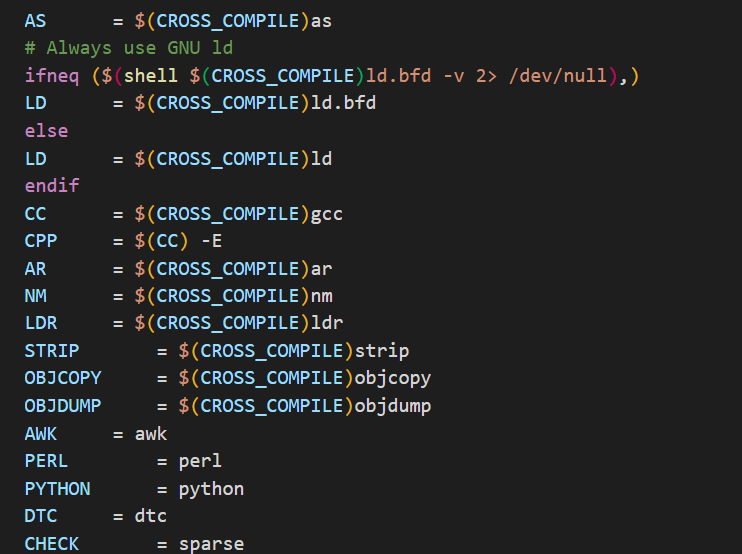
3.12 导出其他变量
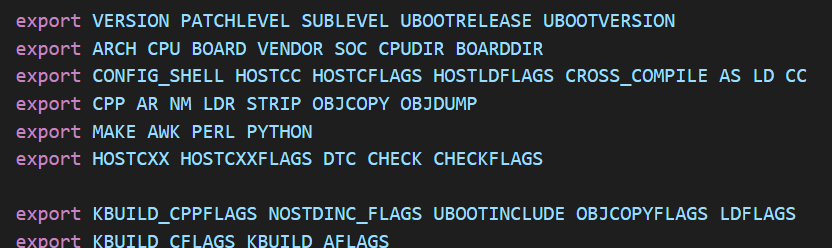
ARCH CPU BOARD VENDOR SOC CPUDIR BOARDDIR
这 7 个变量在顶层 Makefile 是找不到的,说明这 7 个变量是在其他文件里面定义的,先来
看一下这 7 个变量都是什么内容

在 uboot 根目录下有个文件叫做 config.mk,这 7 个变量就是在 config.mk 里面定义的
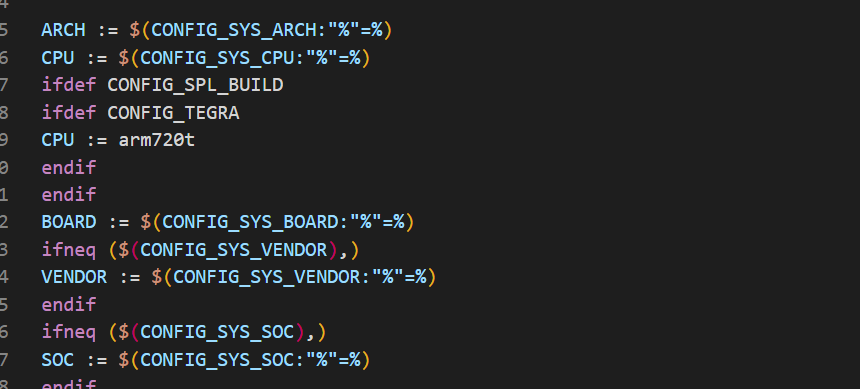
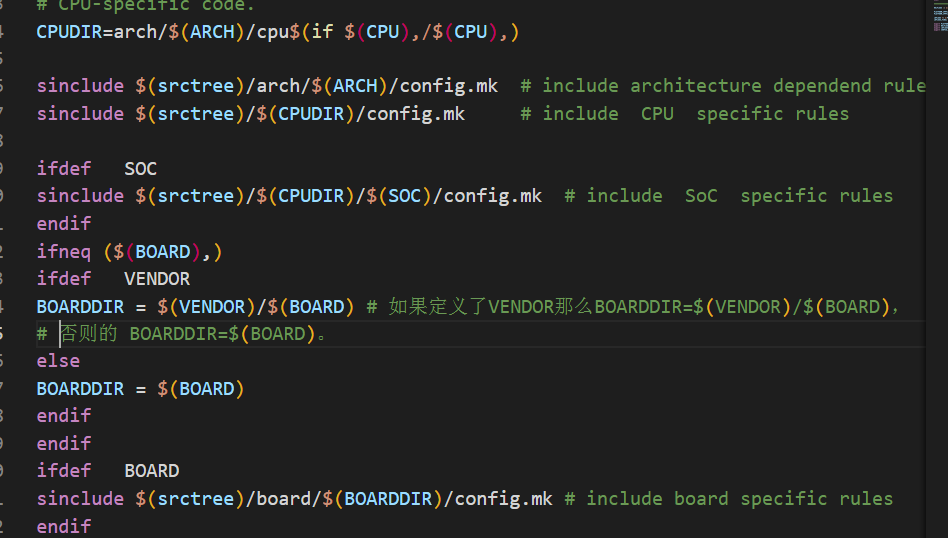
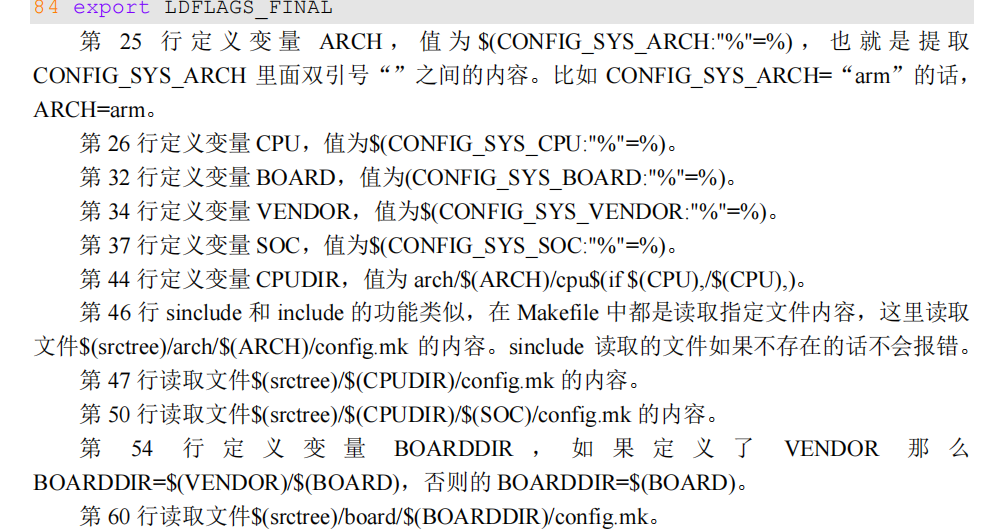
接下来需要找到 CONFIG_SYS_ARCH、CONFIG_SYS_CPU、CONFIG_SYS_BOARD、CONFIG_SYS_VENDOR 和 CONFIG_SYS_SOC 这 5 个变量的值。这 5 个变量在 uboot 根目录下的.config 文件中有定义,定义如下:
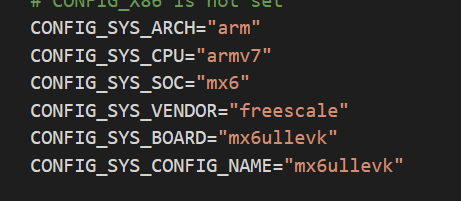
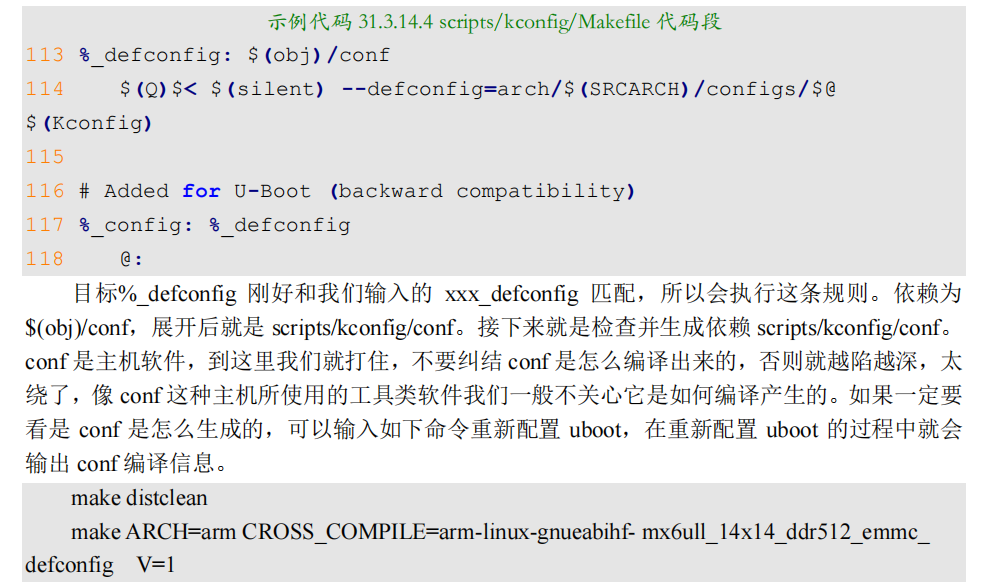
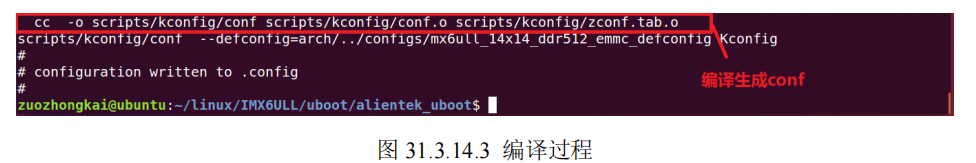
3.13 make xxx_deconfig过程
在编译 uboot 之前要使用“make xxx_defconfig”命令来配置 uboot
version_h := include/generated/version_autogenerated.h
timestamp_h := include/generated/timestamp_autogenerated.h
no-dot-config-targets := clean clobber mrproper distclean \
help %docs check% coccicheck \
ubootversion backup
config-targets := 0
mixed-targets := 0
dot-config := 1
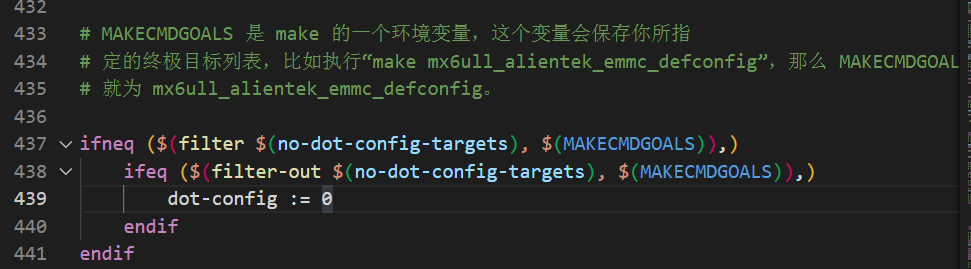
ifneq ($(filter $(no-dot-config-targets), $(MAKECMDGOALS)),)
ifeq ($(filter-out $(no-dot-config-targets), $(MAKECMDGOALS)),)
dot-config := 0
endif
endif
ifeq ($(KBUILD_EXTMOD),)
ifneq ($(filter config %config,$(MAKECMDGOALS)),)
config-targets := 1
ifneq ($(words $(MAKECMDGOALS)),1)
mixed-targets := 1
endif
endif
endif
ifeq ($(mixed-targets),1)
# ===========================================================================
# We're called with mixed targets (*config and build targets).
# Handle them one by one.
PHONY += $(MAKECMDGOALS) __build_one_by_one
$(filter-out __build_one_by_one, $(MAKECMDGOALS)): __build_one_by_one
@:
__build_one_by_one:
$(Q)set -e; \
for i in $(MAKECMDGOALS); do \
$(MAKE) -f $(srctree)/Makefile $$i; \
done
else
ifeq ($(config-targets),1)
# ===========================================================================
# *config targets only - make sure prerequisites are updated, and descend
# in scripts/kconfig to make the *config target
KBUILD_DEFCONFIG := sandbox_defconfig
export KBUILD_DEFCONFIG KBUILD_KCONFIG
config: scripts_basic outputmakefile FORCE
$(Q)$(MAKE) $(build)=scripts/kconfig $@
%config: scripts_basic outputmakefile FORCE
$(Q)$(MAKE) $(build)=scripts/kconfig $@
else
# ===========================================================================
# Build targets only - this includes vmlinux, arch specific targets, clean
# targets and others. In general all targets except *config targets.
ifeq ($(dot-config),1)
# Read in config
-include include/config/auto.conf
定义了变量 no-dot-config-targets。
定义了变量 config-targets,初始值为 0。
定义了变量 mixed-targets,初始值为 0。


# ===========================================================================
# Rules shared between *config targets and build targets
# Basic helpers built in scripts/
PHONY += scripts_basic
scripts_basic:
$(Q)$(MAKE) $(build)=scripts/basic
$(Q)rm -f .tmp_quiet_recordmcount
# To avoid any implicit rule to kick in, define an empty command.
scripts/basic/%: scripts_basic ;
PHONY += outputmakefile
# outputmakefile generates a Makefile in the output directory, if using a
# separate output directory. This allows convenient use of make in the
# output directory.
outputmakefile:
ifneq ($(KBUILD_SRC),) #经过刚才的判断,KBUILD_SRC为空,所以不会执行下面的语句
$(Q)ln -fsn $(srctree) source
$(Q)$(CONFIG_SHELL) $(srctree)/scripts/mkmakefile \
$(srctree) $(objtree) $(VERSION) $(PATCHLEVEL)
endif


3.14 makefile.build脚本分析
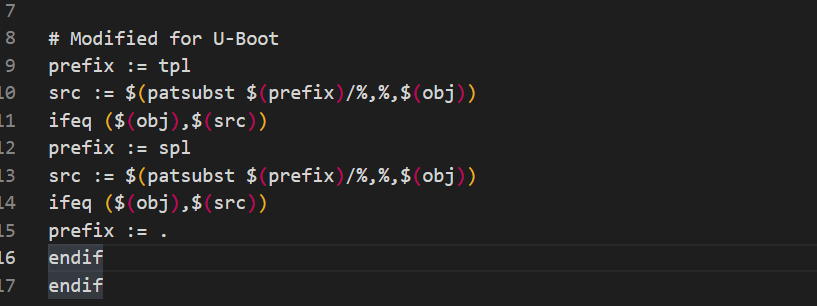
是在“scripts/basic”中查找符合“tpl/%”的部分,然后将“tpl/”取消掉,但是“scripts/basic”没有“tpl/”,所以 src= scripts/basic。
第 12 行和第 9 行一样,只是这里处理的是“spl”,“scripts/basic”里面也没有“spl/”,所以src 继续为 scripts/basic。 第 15 行因为变量 obj 和 src 相等,所以 prefix=.。
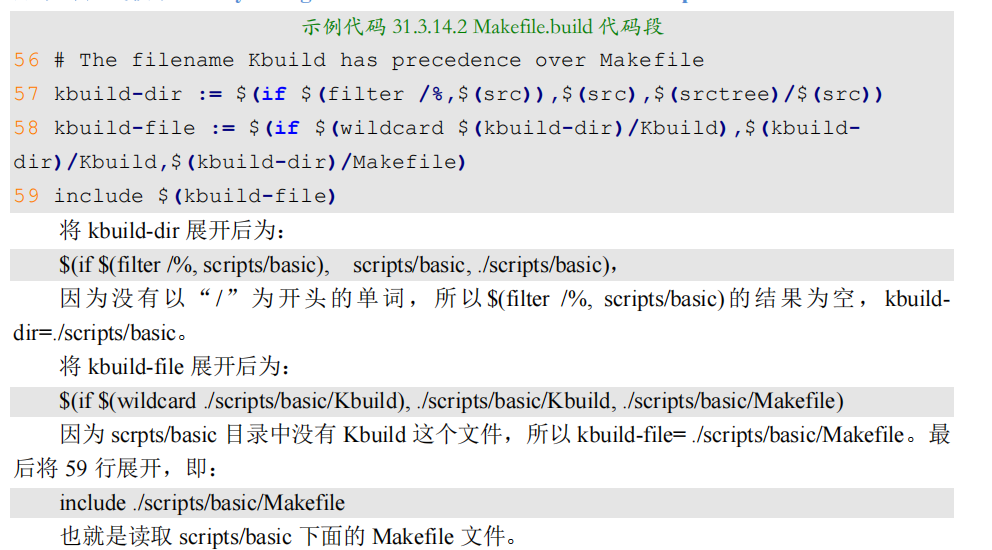

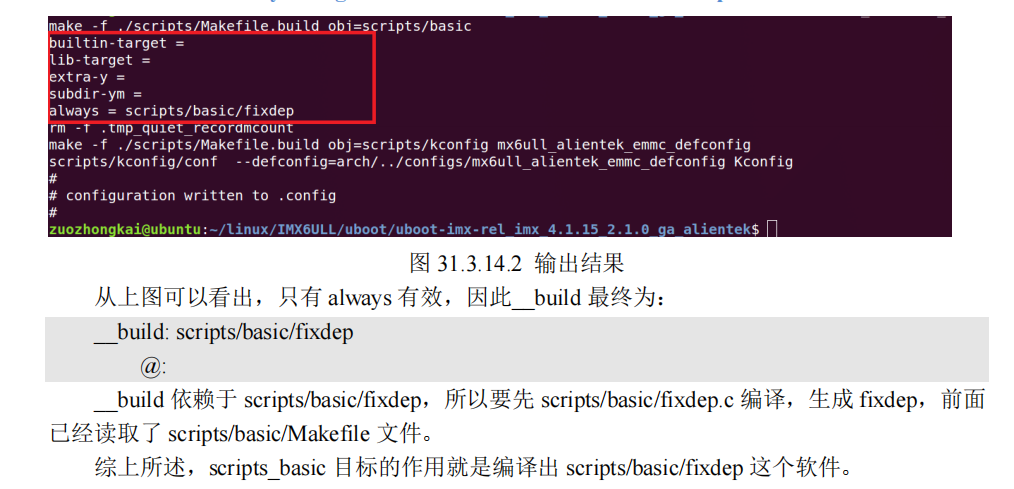


3.15 make过程


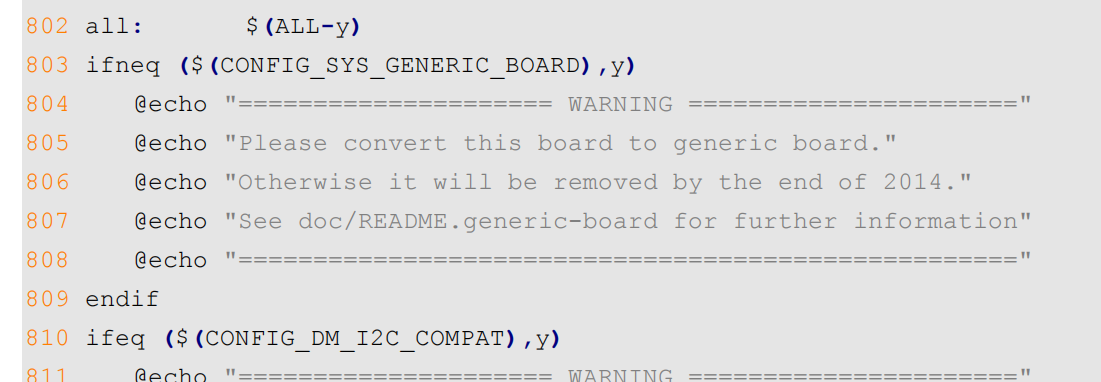
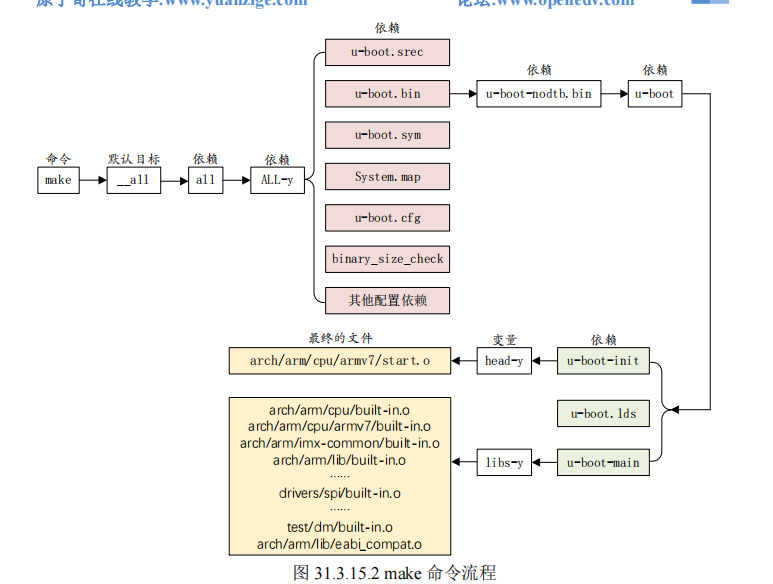
从 802 行可以看出,all 目标依赖$(ALL-y),而在顶层 Makefile 中,ALL-y 如下:



ifeq ($(CONFIG_OF_SEPARATE),y)
u-boot-dtb.bin: u-boot-nodtb.bin dts/dt.dtb FORCE
$(call if_changed,cat)
u-boot.bin: u-boot-dtb.bin FORCE
$(call if_changed,copy)
else
u-boot.bin: u-boot-nodtb.bin FORCE
$(call if_changed,copy)
endif
第 825 行判断 CONFIG_OF_SEPARATE 是否等于 y,如果相等,那条件就成立,在.config中搜索“CONFIG_OF_SEPARAT”,没有找到,说明条件不成立。第 832 行就是目标 u-boot.bin 的规则,目标 u-boot.bin 依赖于 u-boot-nodtb.bin,命令为$(call if_changed,copy), 这里调用了if_changed,if_changed是一个函数,这个函数在scripts/Kbuild.include 中有定义,而顶层 Makefile 中会包含scripts/Kbuild.include 文件,这个前面已经说过了。
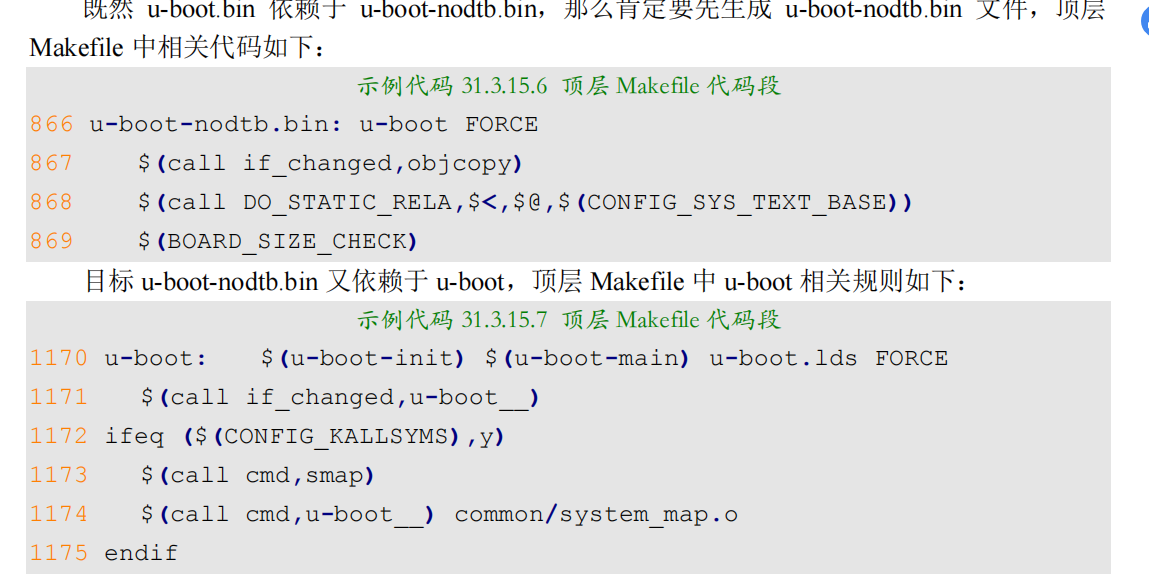









【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律