SpringBoot环境下静态资源配置原理
环境:SpringBoot 2.4.2
静态资源的访问规则
首先,在SpringBoot启动时,会默认加载自动配置类(XXXAutoConfiguration类)。其中,SpringMVC功能的自动配置类WebMvcAutoConfiguration会生效
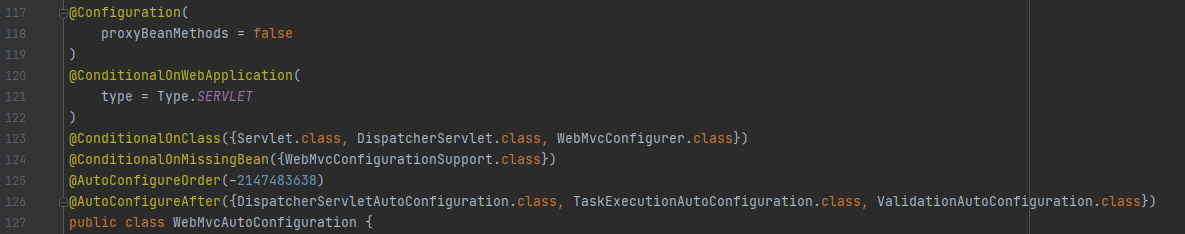
在这个自动配置类中,给IOC容器中放入了一个组件
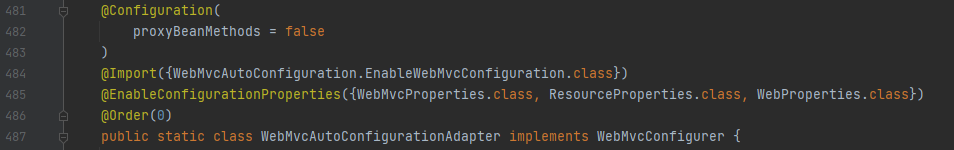
可以看到,这是一个配置类,且开启了WebMvcProperties,ResourceProperties,WebProperties类的属性绑定,这三个类分别和配置文件中前缀名为spring.mvc,spring.resources,spring.web的属性进行了绑定
另外,这个配置类还将WebMvcAutoConfiguration.EnableWebMvcConfiguration.class这个静态内部类放入容器中,可以看到这个类的代码
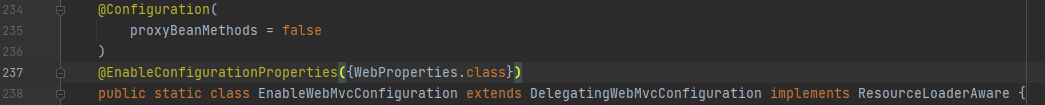
这个类开启了WebProperties.class类的属性绑定,绑定了配置文件中spring.web前缀的属性
这个配置类中只有一个有参构造器,而当配置类中只有一个有参构造器的时候,有参构造器的所有参数都从容器中获取确定
public EnableWebMvcConfiguration(ResourceProperties resourceProperties, // 从容其中找到ResourceProperties组件(和spring.resource绑定的所有的值的对象)
WebMvcProperties mvcProperties, // 找到WebMvcProperties组件(和spring.mvc绑定的所有的值的对象)
WebProperties webProperties, // 找到WebProperties组件(和spring.web绑定的所有的值的对象)
ObjectProvider<WebMvcRegistrations> mvcRegistrationsProvider,
// 找到资源处理器的自定义器 ResourceHandlerRegistrationCustomizer
ObjectProvider<WebMvcAutoConfiguration.ResourceHandlerRegistrationCustomizer> resourceHandlerRegistrationCustomizerProvider,
// 找到spring的beanFactory
ListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
this.resourceProperties = (Resources)(resourceProperties.hasBeenCustomized() ? resourceProperties : webProperties.getResources());
this.mvcProperties = mvcProperties;
this.webProperties = webProperties;
this.mvcRegistrations = (WebMvcRegistrations)mvcRegistrationsProvider.getIfUnique();
this.resourceHandlerRegistrationCustomizer =
(WebMvcAutoConfiguration.ResourceHandlerRegistrationCustomizer)resourceHandlerRegistrationCustomizerProvider.getIfAvailable();
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
webjars的规则
在这个配置类中和静态资源相关的方法为addResourceHandlers(),我们在此加上一个断点,开启debug
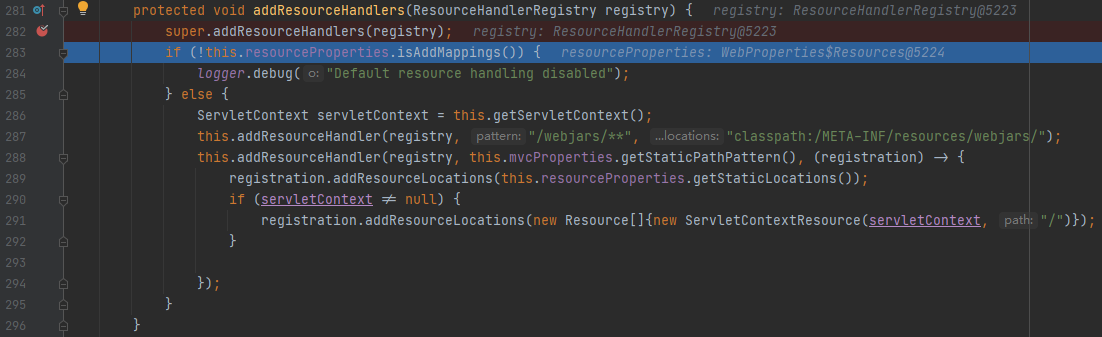
if语句判断的是静态资源是否被禁用,我们可以在配置文件中spring.web.resources.add-mappings=false来禁用静态资源,这样就无法访问静态资源,这一项默认为true
这个方法内的核心就是调用了两个addResourceHandler()方法,第一个addResourceHandler方法是注册了/webjars/**的访问规则,也就是访问/webjars/**时,系统会去找classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/路径下的内容
静态资源的规则
第二个addResourceHandler方法的第二个参数是this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern(),意思是获取到staticPathPattern,这和配置文件中的spring.mvc.static-path-pattern绑定,代表静态资源的访问路径,这个值默认为/**。我们可以查看WebMvcProperties.class的源代码

而在lambda表达式中,注册器注册了资源路径this.resourceProperties.getStaticLocations(),意思是获取到staticLocations,这个配置文件中的spring.web.resource.static-locations绑定,代表静态资源实际放置路径,这个路径默认为classpath:/META-INF/resources/, classpath:/resources/, classpath:/static/, classpath:/public/。我们可以查看WebProperties.class的源代码,其中有个静态内部类Resource
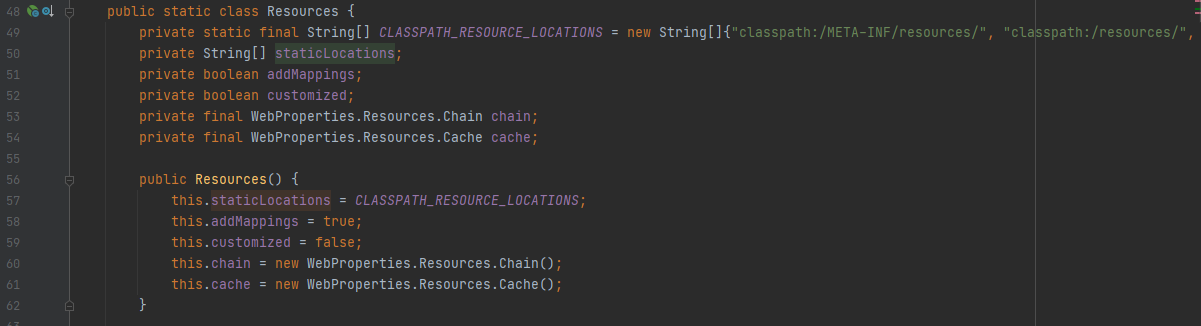
总之,第二个addResourceHandler方法就是注册了静态资源访问路径的访问规则,默认是/**的访问路径,映射到classpath:/META-INF/resources/, classpath:/resources/, classpath:/static/, classpath:/public/这四个地址上。当然,从代码中看到,这其中还包括了缓存的设置
欢迎页的处理规则
另外,在这个EnableWebMvcConfiguration类中,还可以看到这样一段代码
@Bean
public WelcomePageHandlerMapping welcomePageHandlerMapping(ApplicationContext applicationContext,
FormattingConversionService mvcConversionService,
ResourceUrlProvider mvcResourceUrlProvider) {
WelcomePageHandlerMapping welcomePageHandlerMapping =
new WelcomePageHandlerMapping(new TemplateAvailabilityProviders(applicationContext),
applicationContext,
this.getWelcomePage(),
this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern());
welcomePageHandlerMapping.setInterceptors(this.getInterceptors(mvcConversionService, mvcResourceUrlProvider));
welcomePageHandlerMapping.setCorsConfigurations(this.getCorsConfigurations());
return welcomePageHandlerMapping;
}
这段代码将WelcomePageHandlerMapping放入容器中,这是欢迎页面的处理器映射,我们查看WelcomePageHandlerMapping的构造函数
WelcomePageHandlerMapping(TemplateAvailabilityProviders templateAvailabilityProviders,
ApplicationContext applicationContext,
Resource welcomePage,
String staticPathPattern) {
if (welcomePage != null && "/**".equals(staticPathPattern)) { // 当欢迎页存在且静态资源的访问路径为/**时,转发到index.html欢迎页
logger.info("Adding welcome page: " + welcomePage);
this.setRootViewName("forward:index.html");
} else if (this.welcomeTemplateExists(templateAvailabilityProviders, applicationContext)) { // 调用Controller处理/index请求
logger.info("Adding welcome page template: index");
this.setRootViewName("index");
}
}
总结
SpringBoot中静态资源的访问规则大体上分为两种
一种是webjars,也就是以jar包的方式引入静态资源,当我们以/webjars/**方式访问静态资源时,系统会找classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/这个路径下的资源
另外一种是将静态资源存放在staticLocations下,默认是classpath:/META-INF/resources/, classpath:/resources/, classpath:/static/, classpath:/public/这四个路径,而访问路径为staticPathPattern,默认为/**。也就是说,当我们以/**方式访问静态资源时,系统会去上面四个路径下寻找资源


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号