next_permutation(a,a+n)
早就听说了了next_permutation 产生全排列的强大,一直到昨晚遇到一个对字符串产生全排列的问题才知道这个函数的强大,我们队是按照dfs去搞全排列,然后在进行字符串的匹配,结果写的很长,过程中还各种debug。。。于是决定今天学一下…
next_permutation函数
组合数学中经常用到排列,这里介绍一个计算序列全排列的函数:next_permutation(start,end),和prev_permutation(start,end)。这两个函数作用是一样的,区别就在于前者求的是当前排列的下一个排列,后一个求的是当前排列的上一个排列。至于这里的“前一个”和“后一个”,我们可以把它理解为序列的字典序的前后,严格来讲,就是对于当前序列pn,他的下一个序列pn+1满足:不存在另外的序列pm,使pn<pm<pn+1.
对于next_permutation函数,其函数原型为:
#include <algorithm>
bool next_permutation(iterator start,iterator end)
当当前序列不存在下一个排列时,函数返回false,否则返回true
我们来看下面这个例子:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int num[3]={1,2,3};
do
{
cout<<num[0]<<" "<<num[1]<<" "<<num[2]<<endl;
}while(next_permutation(num,num+3));
return 0;
}
输出结果为:
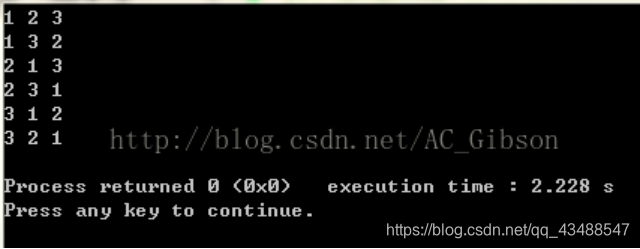
当我们把while(next_permutation(num,num+3))中的3改为2时,输出就变为了:
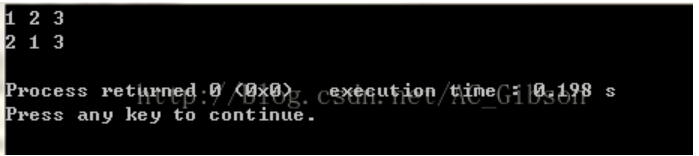
由此可以看出,next_permutation(num,num+n)函数是对数组num中的前n个元素进行全排列,同时并改变num数组的值。
另外,需要强调的是,next_permutation()在使用前需要对欲排列数组按升序排序,否则只能找出该序列之后的全排列数。比如,如果数组num初始化为2,3,1,那么输出就变为了:
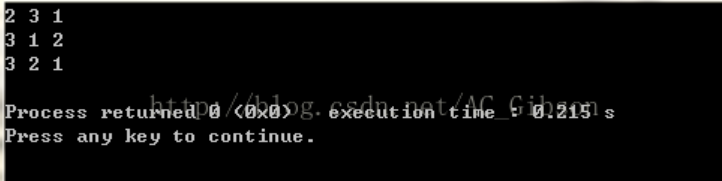
此外,next_permutation(node,node+n,cmp)可以对结构体num按照自定义的排序方式cmp进行排序。
也可以对字符…
next_permutation 自定义比较函数 POJ 1256
题目中要求的字典序是
//'A'<'a'<'B'<'b'<...<'Z'<'z'.
#include<iostream> //poj 1256 Anagram
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int cmp(char a,char b)
{
if(tolower(a)!=tolower(b))//tolower 是将大写字母转化为小写字母.
return tolower(a)<tolower(b);
else
return a<b;
}
int main()
{
char ch[20];
int n;
cin>>n;
while(n--)
{
scanf("%s",ch);
sort(ch,ch+strlen(ch),cmp);
do
{
printf("%s\n",ch);
}while(next_permutation(ch,ch+strlen(ch),cmp));
}
return 0;
}
char 类型的next_permutation
int main()
{
char ch[205];
cin >> ch;
sort(ch, ch + strlen(ch) );
//该语句对输入的数组进行字典升序排序。如输入9874563102 cout<<ch; 将输出0123456789,这样就能输出全排列了
char *first = ch;
char *last = ch + strlen(ch);
do {
cout<< ch << endl;
}while(next_permutation(first, last));
return 0;
}
//这样就不必事先知道ch的大小了,是把整个ch字符串全都进行排序
//若采用 while(next_permutation(ch,ch+5)); 如果只输入1562,就会产生错误,因为ch中第五个元素指向未知
//若要整个字符串进行排序,参数5指的是数组的长度,不含结束符
string 类型的next_permutation
int main()
{
string line;
while(cin>>line&&line!="#")
{
if(next_permutation(line.begin(),line.end())) //从当前输入位置开始
cout<<line<<endl;
else cout<<"Nosuccesor\n";
}
}
int main()
{
string line;
while(cin>>line&&line!="#")
{
sort(line.begin(),line.end());//全排列
cout<<line<<endl;
while(next_permutation(line.begin(),line.end()))
cout<<line<<endl;
}
}






