【LeetCode】142. Linked List Cycle II
Difficulty:medium
More:【目录】LeetCode Java实现
Description
Given a linked list, return the node where the cycle begins. If there is no cycle, return null.
Note: Do not modify the linked list.
Follow up:
Can you solve it without using extra space?
Intuition
1) find out whether there is a cycle, refer to141. Linked List Cycle
2) if there is a cycle, we can get the meetingNode, meanwhile we use a pointer named entry to point to the head Node.
3) let the meetingNode and entry move one step at a time, where they meet is where the cycle begins.
why will they meet at the beginning of the cycle? here is the proof:
1. define L1 as the distance between the head node and entry node;
2.defined L2 as the distance between the entry node and meeting node;
3.defined C as the length of the cycle
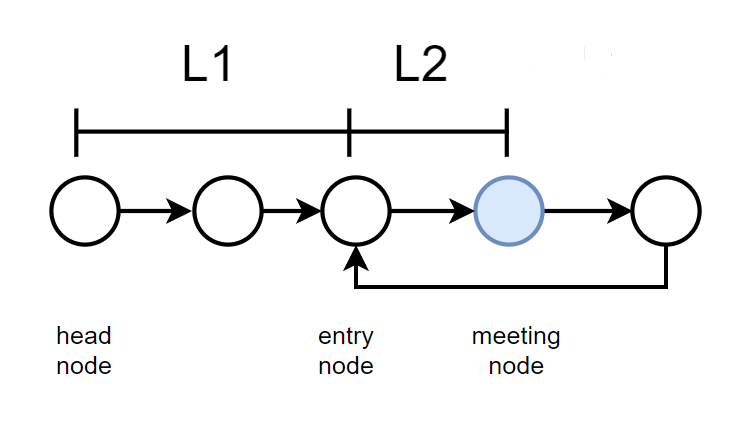
We can know that:
the distance of slow node=L1+L2; while the distance of fast node=L1+L2+n*C
because of the speed, we have :
2*(L1+L2)=L1+L2+n*C => L1=n*C-L2 => L1=(n-1)C+(C-L2)
it means that: the distance between the head node and entry node equals the distance between the meeting node and entry node;
Solution
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
if(head==null)
return null;
ListNode fast=head;
ListNode slow=head;
ListNode entry=head;
while(fast.next!=null && fast.next.next!=null){
fast=fast.next.next;
slow=slow.next;
if(fast==slow){
while(entry!=slow){
entry=entry.next;
slow=slow.next;
}
return entry;
}
}
return null;
}
Complexity
Time complexity : O(n)
Space complexity : O(1)
What I've learned
1. How to prove the distance relation.
More:【目录】LeetCode Java实现



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号