【Java】 大话数据结构(16) 排序算法(3) (堆排序)
本文根据《大话数据结构》一书,实现了Java版的堆排序。
更多:数据结构与算法合集
基本概念
堆排序种的堆指的是数据结构中的堆,而不是内存模型中的堆。
堆:可以看成一棵完全二叉树,每个结点的值都大于等于(小于等于)其左右孩子结点的值,称为大顶堆(小顶堆)。
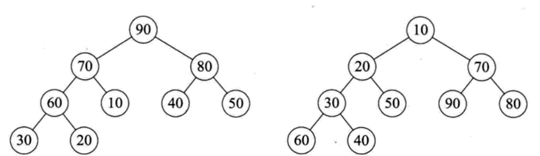
大顶堆(左)与小顶堆(右)
堆排序的基本思想:将带排序的序列构造成大顶堆,最大值为根结点。将根结点与最后一个元素交换,对除最大值外的剩下n-1个元素重新构造成大顶堆,可以获得次大的元素。反复执行,就可以得到一个有序序列了。
构造大顶堆的方法:
1.首先复习完全二叉树的性质,层序遍历,当第一个元素索引从0开始时,索引为i的左孩子的索引是 (2*i+1),右孩子的索引是 (2*i+2)。
2.设计一个函数heapAdjust(),对于一个序列(除了第一个根结点外,其余结点均满足最大堆的定义),通过这个函数可以将序列调整为正确的大顶堆。
3.正式构造:将带排序的序列看成一棵完全二叉树的层序遍历,我们从下往上,从右往左,依次将每个非叶子结点当作根结点,使用heapAdjust()调整成大顶堆。
具体细节的实现参阅代码,比较清楚,不再赘述。
完整Java代码
(含测试代码)
/**
*
* @Description 堆排序
*
* @author yongh
*
*/
public class HeapSort {
public void heapSort(int[] arr) {
if(arr==null || arr.length<=0)
return;
int len=arr.length;
for(int i=len/2-1;i>=0;i--) { //从最后一个父结点开始构建最大堆
heapAdjust(arr,i,len-1);
}
for(int i=len-1;i>=0;i--) {
int temp=arr[0];
arr[0]=arr[i];
arr[i]=temp;
heapAdjust(arr, 0, i-1);
}
}
/*
* 功能:调整堆为最大堆
* [i……j]中,除了i之外,部分子树都满足最大堆定义
*/
private void heapAdjust(int[] arr, int start, int end) {
int temp=arr[start];
int child=2*start+1;
while(child<=end) {
if(child+1<=end && arr[child+1]>arr[child]) //记得child+1<=end的判断
child++; //较大的孩子
if(arr[child]<=temp)
break;
arr[start]=arr[child];
start=child;
child=child*2+1;
}
arr[start]=temp;
}
// =========测试代码=======
public void test1() {
int[] a = null;
heapSort(a);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
public void test2() {
int[] a = {};
heapSort(a);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
public void test3() {
int[] a = { 1 };
heapSort(a);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
public void test4() {
int[] a = { 3, 3, 3, 3, 3 };
heapSort(a);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
public void test5() {
int[] a = { -3, 6, 3, 1, 3, 7, 5, 6, 2 };
heapSort(a);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
HeapSort demo = new HeapSort();
demo.test1();
demo.test2();
demo.test3();
demo.test4();
demo.test5();
}
}

null [] [1] [3, 3, 3, 3, 3] [-3, 1, 2, 3, 3, 5, 6, 6, 7]
复杂度分析
构建堆的时间复杂度为O(n);每次调整堆的时间为O(logn),共要调整n-1次,所以重建堆的时间复杂度为O(nlogn)。
因此总体来说,堆排序的复杂度为O(nlogn)。不过由于记录的比较和交换是跳跃式进行的,因此堆排序是不稳定的排序方法。
更多:数据结构与算法合集




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号