【Java】 大话数据结构(5) 线性表之双向链表
本文根据《大话数据结构》一书,实现了Java版的双向链表。
在每个数据结点中都有两个指针,分别指向直接后继和直接前驱,这样的链表称为双向链表。
双向链表的结构如图所示:
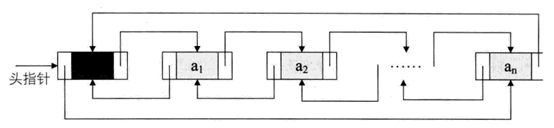
- 查找元素可以根据元素的位置,分别沿正向和反向查找。
双向链表实现程序:
package DuLinkList;
public class DuLinkList<E> {
private Node<E> head;
private int count;
/**
* 结点
*/
class Node<E> {
E data;
Node<E> prior;
Node<E> next;
public Node(E data, Node<E> prior, Node<E> next) {
this.data = data;
this.prior = prior;
this.next = next;
}
}
/**
* 线性表的初始化
*/
public DuLinkList() {
head = new Node<E>(null, null, null);
head.prior = head.next = head;
count = 0;
}
/**
* 获取第i个元素
*/
public Node<E> getElement(int i) {
if (count == 0)
throw new RuntimeException("空表,无法查找!");
if (i < 1 || i > count)
throw new RuntimeException("查找位置错误!");
Node<E> node = head.next;
for (int j = 1; j < i; j++) {
node = node.next;
}
return node;
}
/**
* 在第i个位置插入元素
*/
public void listInsert(int i, E data) {
if (i < 1 || i > count + 1)
throw new RuntimeException("插入位置错误!");
Node<E> node = new Node<E>(data, null, null);
if (i == 1) {
node.next = head.next;
node.prior = head;
head.next.prior = node;
head.next = node;
} else {
Node<E> pNode = getElement(i - 1);
node.next = pNode.next;
node.prior = pNode;
pNode.next.prior = node;
pNode.next = node;
}
count++;
}
/**
* 删除第i个元素
*/
public E listDelete(int i) {
if (i < 1 || i > count)
throw new RuntimeException("删除位置错误!");
Node<E> node = getElement(i);
E e = node.data;
if (i == 1) {
head.next = node.next;
node.next.prior = node.prior;
node = null;
} else {
node.next.prior = node.prior;
node.prior.next = node.next;
node = null;
}
count--;
return e;
}
public int listLength() {
return count;
}
}
测试程序:
package DuLinkList;
public class DuLinkListTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DuLinkList<Student> students = new DuLinkList<Student>();
System.out.println("——————————插入1到5,并读取内容——————————");
Student[] stus = { new Student("小A", 11), new Student("小B", 12), new Student("小C", 13), new Student("小D", 14),
new Student("小E", 151) };
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++)
students.listInsert(i, stus[i - 1]);
System.out.println("表长:" + students.listLength());
Student stu;
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
stu = students.getElement(i).data;
System.out.println("第" + i + "个位置为:" + stu.name);
}
System.out.println("——————————删除小A、小E——————————");
stu = students.listDelete(1);
System.out.println("已删除:" + stu.name);
stu = students.listDelete(4);
System.out.println("已删除:" + stu.name);
System.out.println("当前表长:" + students.listLength());
for (int i = 1; i <= students.listLength(); i++) {
stu = students.getElement(i).data;
System.out.println("第" + i + "个位置为:" + stu.name);
}
}
}
class Student {
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
String name;
int age;
}

——————————插入1到5,并读取内容—————————— 表长:5 第1个位置为:小A 第2个位置为:小B 第3个位置为:小C 第4个位置为:小D 第5个位置为:小E ——————————删除小A、小E—————————— 已删除:小A 已删除:小E 当前表长:3 第1个位置为:小B 第2个位置为:小C 第3个位置为:小D
——————————————————————————
在阅读过他人的博客后,发现自己的查找方法没有利用好双链表的特性,重写查找方法如下:
/**
* 获取第i个元素
*/
public Node<E> getElement(int i) {
if (count == 0)
throw new RuntimeException("空表,无法查找!");
if (i < 1 || i > count)
throw new RuntimeException("查找位置错误!");
if (i <= count / 2) { // 正向查找
Node<E> node = head.next;
for (int j = 1; j < i; j++) {
node = node.next;
}
return node;
} else { // 反向查找
Node<E> node = head.prior;
int k = count - i;
for (int j = 0; j < k; j++) {
node = node.prior;
}
return node;
}
}
本文中只编写了查找和删除部分的程序,完整的双向链表程序可参阅这篇博客:数组、单链表和双链表介绍 以及 双向链表的C/C++/Java实现




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号