python笔记-13 mysql与sqlalchemy
一、RDBMS relational database management system 关系型数据库引入
1、数据库的意义
更有效和合理的存储读取数据的一种方式
关系模型基础上的数据库 ->使用集合代数等数学方法来处理数据库中的数据
2、一些常见的数据库
2.1 非关系型数据库 如redis 表之间没有相应的联系
2.2 关系型数据库
oracle、mysql、(mysql也oracle现在是同一家公司的,oracle收费,mysql开源免费)
sql server microsoft
psql
sqllite
access
3、关系型数据库几个基本概念
表: 表是 数据的矩阵,数据以表格形式展现。
行:一条记录,(一组相关的数据)或各种记录的名称(表头)
列:数据元素,各种记录名称所对应的数据域(实际数据)
表单:许多行和列组成表单
数据库:若干相关联的表单的集合组合成数据库
主键:数据库主键primarykey,唯一标识,不重复,指的是一个列或多列的组合,其值能唯一地标识表中的每一行,通过它可强制表的实体完整性。(可以有多列)
主键只有一个,但是可以设置为多个字段为主键,也即复合主键。
外键:用于关联两个表的key,关系表中的关系主键往往同时也是参考关联表的外键。(要分清随时谁的外键)
冗余:对于一些内容,我们经常使用,但是此内容需要关联多张表才能得到。为了加快效率,我们在几张表中都把此字段保存在表中,这样达到了只要查一张表的情况下,就能完成查询。
冗余具有两面性:他提高了数据查询的速度,但是他占用了更多的存储空间。
索引:使用索引能快速的访问数据表中的某些特定的资源,索引是对数据表中的一列或多列数据进行排序的一种方式(使用hash二分法、二叉树等快速找到资源),类似于数据目录
复合键:有复合主键和复合索引,将多个列作出复合primary key或index
关联:外联的相关联的数据之间必须同时修改或删除,以此来保证数据的完整性
参照完整性:参照的完整性要求关系中不允许引用不存在的实体。
参照完整性和实体完整性是关系模型必须满足的完整性条件,目的是保证数据的一致性。
二、mysql的基本操作
1、登录mysql 并查看已有的数据库 mysql -u root 与 show databases
mysql -u root 指定使用root用户登录mysql
show databases 查看本地mysql中有哪些databases
[root@cenos7_a ~]# mysql -u root Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or \g. Your MariaDB connection id is 50 Server version: 5.5.56-MariaDB MariaDB Server Copyright (c) 2000, 2017, Oracle, MariaDB Corporation Ab and others. Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement. MariaDB [(none)]> show databases; +--------------------+ | Database | +--------------------+ | information_schema | | jumpserver | | mysql | | performance_schema | | schooldb | | student_system | | test | +--------------------+ 7 rows in set (0.00 sec)
2、指定数据库名称进行操作 use databases
在查看了databases后,我们需要使用use 指定数据库名,告知mysql我要使用哪个数据库。
3、查看某数据库中已有的数据表show tables
在指定了数据库后,我们可以使用show tables 来查看该数据库中有哪些表
MariaDB [test]> use schooldb; Reading table information for completion of table and column names You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -A Database changed MariaDB [schooldb]> show tables; +--------------------+ | Tables_in_schooldb | +--------------------+ | address | | school_info | | student_info | | t_student | | t_study_record | | test_user | | user_name | +--------------------+ 7 rows in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [schooldb]>
4、创建数据库,并查看数据库支持的charset create databases charset utf8 、show create databases ;
latin1为拉丁字符 只支持英文字母
MariaDB [(none)]> show create database test; +----------+-----------------------------------------------------------------+ | Database | Create Database | +----------+-----------------------------------------------------------------+ | test | CREATE DATABASE `test` /*!40100 DEFAULT CHARACTER SET latin1 */ | +----------+-----------------------------------------------------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [(none)]> show create database schooldb; +----------+-------------------------------------------------------------------+ | Database | Create Database | +----------+-------------------------------------------------------------------+ | schooldb | CREATE DATABASE `schooldb` /*!40100 DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8 */ | +----------+-------------------------------------------------------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [(none)]> create database blogtest; Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) MariaDB [(none)]> show create database blogtest; +----------+---------------------------------------------------------------------+ | Database | Create Database | +----------+---------------------------------------------------------------------+ | blogtest | CREATE DATABASE `blogtest` /*!40100 DEFAULT CHARACTER SET latin1 */ | +----------+---------------------------------------------------------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [(none)]> create database utf8test charset utf8; Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) MariaDB [(none)]> show create database utf8test; +----------+-------------------------------------------------------------------+ | Database | Create Database | +----------+-------------------------------------------------------------------+ | utf8test | CREATE DATABASE `utf8test` /*!40100 DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8 */ | +----------+-------------------------------------------------------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [(none)]>
5、查看数据表属性 desc tables 、select column from tables
MariaDB [schooldb]> SHOW COLUMNS FROM school_info; +-------------+----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +-------------+----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ | id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment | | school_name | char(32) | NO | | NULL | | | address | char(32) | NO | | NULL | | | tel | char(20) | NO | | NULL | | +-------------+----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [schooldb]> desc school_info; +-------------+----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +-------------+----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ | id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment | | school_name | char(32) | NO | | NULL | | | address | char(32) | NO | | NULL | | | tel | char(20) | NO | | NULL | | +-------------+----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [schooldb]>
6、查看数据表的内容 select * from tables 、select* from tables \G;
MariaDB [schooldb]> select * from school_info; +----+-----------------+-----------+-------------+ | id | school_name | address | tel | +----+-----------------+-----------+-------------+ | 4 | 北京校区 | 朝阳区 | 18511112222 | | 5 | 陕西校区 | 雁塔区 | 18533332222 | | 6 | 北京二校区 | 海淀区 | 18033332222 | | 9 | 上海校区 | 普陀区 | 19966229988 | +----+-----------------+-----------+-------------+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [schooldb]> select * from school_info \G; *************************** 1. row *************************** id: 4 school_name: 北京校区 address: 朝阳区 tel: 18511112222 *************************** 2. row *************************** id: 5 school_name: 陕西校区 address: 雁塔区 tel: 18533332222 *************************** 3. row *************************** id: 6 school_name: 北京二校区 address: 海淀区 tel: 18033332222 *************************** 4. row *************************** id: 9 school_name: 上海校区 address: 普陀区 tel: 19966229988 4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
7、删除数据库 drop databases(谨慎使用)
MariaDB [schooldb]> show databases; +--------------------+ | Database | +--------------------+ | information_schema | | blogtest | | jumpserver | | mysql | | performance_schema | | schooldb | | student_system | | test | | utf8test | +--------------------+ 9 rows in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [schooldb]> MariaDB [schooldb]> drop database utf8test; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) MariaDB [schooldb]> show databases -> ; +--------------------+ | Database | +--------------------+ | information_schema | | blogtest | | jumpserver | | mysql | | performance_schema | | schooldb | | student_system | | test | +--------------------+ 8 rows in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [schooldb]> drop database blogtest; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) MariaDB [schooldb]> show databases; +--------------------+ | Database | +--------------------+ | information_schema | | jumpserver | | mysql | | performance_schema | | schooldb | | student_system | | test | +--------------------+ 7 rows in set (0.01 sec) MariaDB [schooldb]>
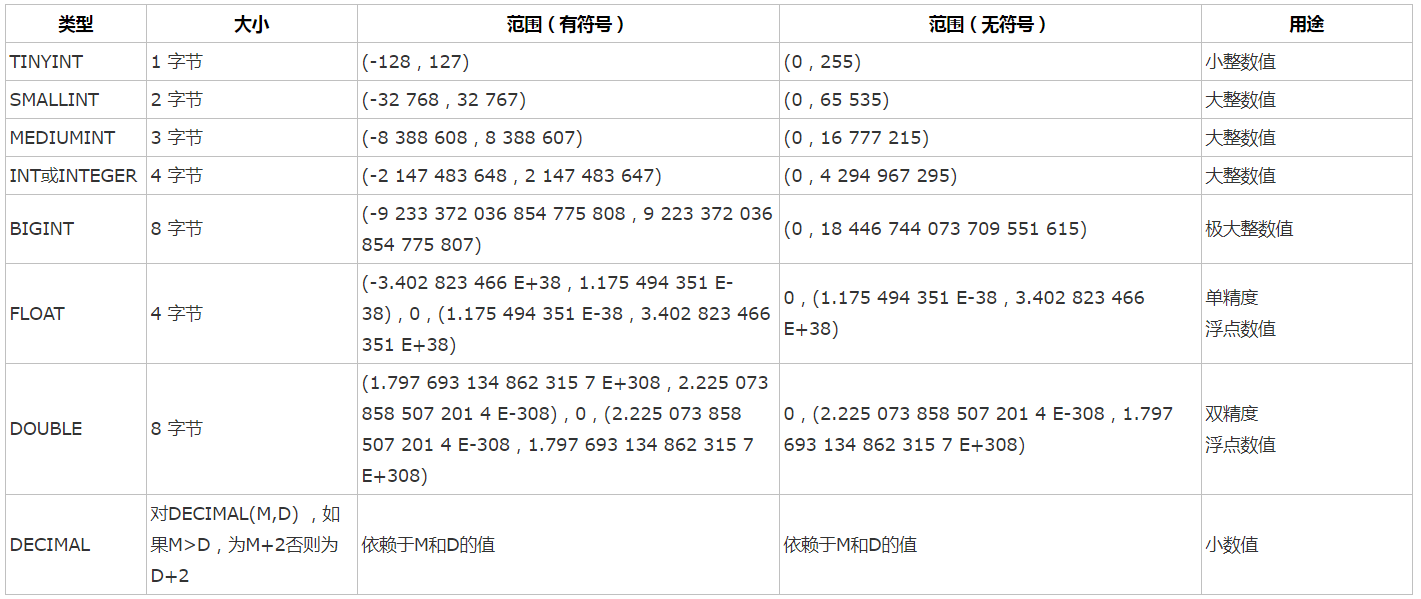
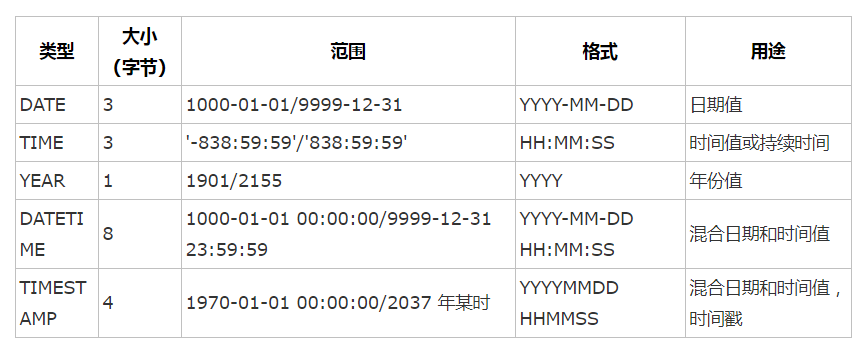
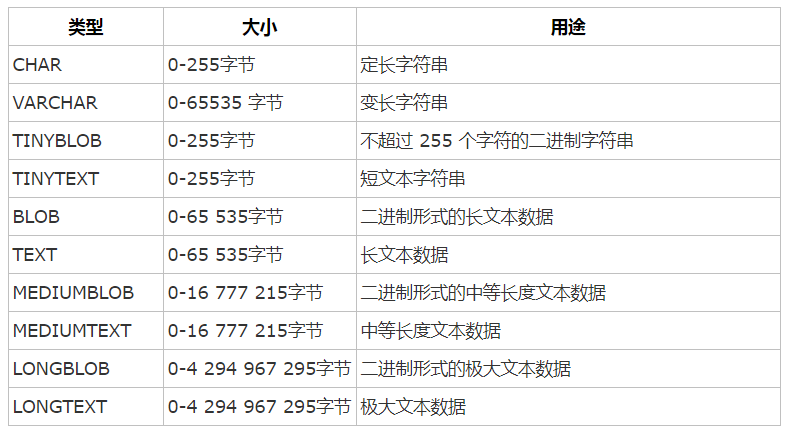
8、3种常见的数据类型
数值类型,字符串类型,日期时间类型
其中初学者常见的数值类型int(4字节)、float(4字节)、char(0-255字节,在设定时要指定长度)、date(3字节,年月日没有具体时间)、time(3字节,时分秒)、datetime(8字节,年月日时分秒组合)
数值类型
日期时间类型
字符串类型
三、基本的sql操作
1、创建表
语法类型
create table 表名(
属性名1 属性类型(INT/CHAR/DATE) 是否为空(NOT NULL) 是否自增(AUTO_INCREMENT),
属性名2 属性类型 是否为空 是否自增,
PRIMARY KEY(属性名)
);
注意char形要指定长度
mysql> create table student( -> sid INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, -> name CHAR(32) NOT NULL, -> age INT NOT NULL, -> birth DATE NULL, -> PRIMARY KEY(sid) -> ); Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.08 sec)
-----------------------------
MariaDB [test]> create table student( sid INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, name CHAR(32) NOT NULL, birth DATE ,PRIMARY KEY(sid));
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
MariaDB [test]> desc student;
+-------+----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+-------+----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| sid | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment |
| name | char(32) | NO | | NULL | |
| birth | date | YES | | NULL | |
+-------+----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
2、表格内容的增删改查
2.1 insert 增加
insert 表名(属性1,属性2) values (属性对应的值1,属性对应的值2)
MariaDB [test]> insert into student (name,birth) values('tom','1990-01-01'); Query OK, 1 row affected (0.21 sec) MariaDB [test]> insert into student (name,birth) values('jack','1980-01-01'); Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) MariaDB [test]> insert into student (name,birth) values('lucy','1993-02-02'); Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) MariaDB [test]> select * from student; +-----+------+------------+ | sid | name | birth | +-----+------+------------+ | 1 | tom | 1990-01-01 | | 2 | jack | 1980-01-01 | | 3 | lucy | 1993-02-02 | +-----+------+------------+ 3 rows in set (0.01 sec) MariaDB [test]>
2.2 删除 delete from tablename where 过滤条件;
mysql> select * from student; +-----+------+-----+------------+ | sid | name | age | birth | +-----+------+-----+------------+ | 1 | tom | 15 | 1990-01-01 | | 2 | jack | 25 | 2000-05-01 | | 3 | 小明 | 25 | 2000-05-01 | | 4 | alex | 10 | 2010-05-03 | | 5 | 东东 | 29 | 2009-05-07 | | 6 | 小楠 | 32 | 1981-12-30 | +-----+------+-----+------------+ 6 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> delete from student where sid =5; Query OK, 1 row affected (0.03 sec) mysql> select * from student; +-----+------+-----+------------+ | sid | name | age | birth | +-----+------+-----+------------+ | 1 | tom | 15 | 1990-01-01 | | 2 | jack | 25 | 2000-05-01 | | 3 | 小明 | 25 | 2000-05-01 | | 4 | alex | 10 | 2010-05-03 | | 6 | 小楠 | 32 | 1981-12-30 | +-----+------+-----+------------+ 5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
2.3 修改 update
update from tablename set key=value,key2=v2 where 过滤条件;
mysql> update student set age=29,birth='2009-05-07' where sid =5 ;#同时改两个 Query OK, 1 row affected (0.10 sec) Rows matched: 1 Changed: 1 Warnings: 0
2.4 查询select 及where过滤条件的说明(以select为例)
2.4.1 select
select */属性1,属性2。。 from tablename where 过滤条件;
MariaDB [test]> select * from student; +-----+------+------------+ | sid | name | birth | +-----+------+------------+ | 1 | tom | 1990-01-01 | | 2 | jack | 1980-01-01 | | 3 | lucy | 1993-02-02 | +-----+------+------------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [test]> select name from student; +------+ | name | +------+ | tom | | jack | | lucy | +------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [test]> select sid,name from student; +-----+------+ | sid | name | +-----+------+ | 1 | tom | | 2 | jack | | 3 | lucy | +-----+------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
2.4.2 where 过滤,以select 为例子
limit 限制输出的数量 offset(只能和limit结合使用),用来对limit 输出结果的偏移
MariaDB [test]> select sid,name from student; +-----+------+ | sid | name | +-----+------+ | 1 | tom | | 2 | jack | | 3 | lucy | +-----+------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [test]> select sid,name from student limit 1; +-----+------+ | sid | name | +-----+------+ | 1 | tom | +-----+------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [test]> select sid,name from student limit 1 offset 1; +-----+------+ | sid | name | +-----+------+ | 2 | jack | +-----+------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [test]> select sid,name from student limit 1 offset 2; +-----+------+ | sid | name | +-----+------+ | 3 | lucy | +-----+------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [test]> select sid,name from student limit 1 offset 3; Empty set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [test]>
2.4.3 逻辑关系 and or 比较关系 > < != 的使用
MariaDB [test]> select * from student where sid != 3; +-----+------+------------+ | sid | name | birth | +-----+------+------------+ | 1 | tom | 1990-01-01 | | 2 | jack | 1980-01-01 | +-----+------+------------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [test]> select * from student where sid =1 or sid =3; +-----+------+------------+ | sid | name | birth | +-----+------+------------+ | 1 | tom | 1990-01-01 | | 3 | lucy | 1993-02-02 | +-----+------+------------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [test]> select * from student where sid < 3; +-----+------+------------+ | sid | name | birth | +-----+------+------------+ | 1 | tom | 1990-01-01 | | 2 | jack | 1980-01-01 | +-----+------+------------+ 2 rows in set (0.01 sec) MariaDB [test]> select * from student where sid < 3 and name ='tom'; +-----+------+------------+ | sid | name | birth | +-----+------+------------+ | 1 | tom | 1990-01-01 | +-----+------+------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [test]>
2.4.4 时间的比较
MariaDB [test]> select * from student where birth > '1990-01-01'; +-----+------+------------+ | sid | name | birth | +-----+------+------------+ | 3 | lucy | 1993-02-02 | +-----+------+------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
2.4.5 模糊匹配 like %
MariaDB [test]> select * from student where birth like '%199%'; +-----+------+------------+ | sid | name | birth | +-----+------+------------+ | 1 | tom | 1990-01-01 | | 3 | lucy | 1993-02-02 | +-----+------+------------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [test]> select * from student where name like '%uc%'; +-----+------+------------+ | sid | name | birth | +-----+------+------------+ | 3 | lucy | 1993-02-02 | +-----+------+------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [test]>
2.5 排序
order by 属性名 以表的某个属性为顺序进行排序
排序的方式有两种
asc 1->2->3 正序
desc 3->2->1 倒序
MariaDB [test]> select * from student order by birth; +-----+------+------------+ | sid | name | birth | +-----+------+------------+ | 2 | jack | 1980-01-01 | | 1 | tom | 1990-01-01 | | 3 | lucy | 1993-02-02 | +-----+------+------------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [test]> select * from student order by birth desc; +-----+------+------------+ | sid | name | birth | +-----+------+------------+ | 3 | lucy | 1993-02-02 | | 1 | tom | 1990-01-01 | | 2 | jack | 1980-01-01 | +-----+------+------------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
2.6 group 排序(对数据进行分类汇总)
group by 对表中某个字段出现的频率count 或总和sum进行分类统计
coumt的使用:
MariaDB [student_system]> select * from study_log; +----+------------+----------+-----------+------------+------------+---------------+-------+ | id | study_date | class_id | lesson_id | student_id | study_stat | homework_stat | score | +----+------------+----------+-----------+------------+------------+---------------+-------+ | 1 | 2018-06-08 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 出勤 | yes | 90 | | 2 | 2018-06-08 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 出勤 | empty | 0 | | 3 | 2018-06-08 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 出勤 | empty | 0 | | 4 | 2018-06-08 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 出勤 | empty | 0 | | 5 | 2018-06-08 | 2 | 11 | 4 | 旷课 | empty | 0 | +----+------------+----------+-----------+------------+------------+---------------+-------+ 5 rows in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [student_system]> select student_id as 学号 ,count(*) as 上课记录 from study_log group by student_id; +--------+--------------+ | 学号 | 上课记录 | +--------+--------------+ | 1 | 1 | | 2 | 1 | | 3 | 1 | | 4 | 2 | +--------+--------------+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [student_system]>
sum的使用:
MariaDB [student_system]> select * from study_log; +----+------------+----------+-----------+------------+------------+---------------+-------+ | id | study_date | class_id | lesson_id | student_id | study_stat | homework_stat | score | +----+------------+----------+-----------+------------+------------+---------------+-------+ | 1 | 2018-06-08 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 出勤 | yes | 90 | | 2 | 2018-06-08 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 出勤 | empty | 0 | | 3 | 2018-06-08 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 出勤 | empty | 0 | | 4 | 2018-06-08 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 出勤 | empty | 0 | | 5 | 2018-06-08 | 2 | 11 | 4 | 旷课 | empty | 0 | +----+------------+----------+-----------+------------+------------+---------------+-------+ 5 rows in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [student_system]> select student_id as 学号 ,sum(score) as 课程总分 from study_log group by student_id;+--------+--------------+ | 学号 | 课程总分 | +--------+--------------+ | 1 | 90 | | 2 | 0 | | 3 | 0 | | 4 | 0 | +--------+--------------+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [student_system]>
rollup 计算全体
MariaDB [student_system]> select student_id as 学号 ,count(*) as `上课记录(次)` from study_log group by student_id with rollup; +--------+-------------------+ | 学号 | 上课记录(次) | +--------+-------------------+ | 1 | 1 | | 2 | 1 | | 3 | 1 | | 4 | 2 | | NULL | 5 | +--------+-------------------+ 5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
coalesce 与rollup结合
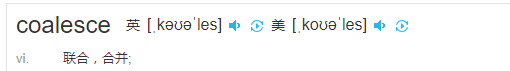
MariaDB [student_system]> select coalesce(student_id,'课程记录总数') as 学号 ,count(*) as `上课记录(次)` from study_log group by student_id with rollup; +--------------------+-------------------+ | 学号 | 上课记录(次) | +--------------------+-------------------+ | 1 | 1 | | 2 | 1 | | 3 | 1 | | 4 | 2 | | 课程记录总数 | 5 | +--------------------+-------------------+ 5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
3、对表属性的增删改查
3.1 添加属性 alter table tables add 属性名 类型 约束;
MariaDB [test]> desc student -> ; +-------+----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +-------+----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ | sid | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment | | name | char(32) | NO | | NULL | | | birth | date | YES | | NULL | | +-------+----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [test]> alter table student add sex char(3) not null; Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.04 sec) Records: 3 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0 MariaDB [test]> desc student; +-------+----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +-------+----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ | sid | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment | | name | char(32) | NO | | NULL | | | birth | date | YES | | NULL | | | sex | char(3) | NO | | NULL | | +-------+----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [test]>
3.2 删除属性 alter table tablename drop 属性名;
MariaDB [test]> desc student; +-------+----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +-------+----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ | sid | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment | | name | char(32) | NO | | NULL | | | birth | date | YES | | NULL | | | sex | char(3) | NO | | NULL | | +-------+----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [test]> alter table student drop sex; Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.03 sec) Records: 3 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0 MariaDB [test]> desc student; +-------+----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +-------+----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ | sid | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment | | name | char(32) | NO | | NULL | | | birth | date | YES | | NULL | | +-------+----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [test]>
3.3 修改属性
修改属性 modify 新写的属性会覆盖旧的属性
alter table tablename modify 属性名 类型 限制;
MariaDB [test]> desc student; +-------+----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +-------+----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ | sid | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment | | name | char(32) | NO | | NULL | | | birth | date | YES | | NULL | | | sex | char(3) | NO | | NULL | | +-------+----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [test]> alter table student modify sex char(4) ; Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.03 sec) Records: 3 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0 MariaDB [test]> desc student; +-------+----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +-------+----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ | sid | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment | | name | char(32) | NO | | NULL | | | birth | date | YES | | NULL | | | sex | char(4) | YES | | NULL | | +-------+----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [test]>
3.4 修改列名称 change
MariaDB [test]> desc student; +-------+----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +-------+----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ | sid | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment | | name | char(32) | NO | | NULL | | | birth | date | YES | | NULL | | | sex | char(4) | YES | | NULL | | +-------+----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [test]> alter table student change sex sexxxx char(4) ; Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.07 sec) Records: 3 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0 MariaDB [test]> desc student; +--------+----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +--------+----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ | sid | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment | | name | char(32) | NO | | NULL | | | birth | date | YES | | NULL | | | sexxxx | char(4) | YES | | NULL | | +--------+----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
3.5 修改表名称 rename
MariaDB [test]> alter table student rename studentnew; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) MariaDB [test]> show tables; +----------------+ | Tables_in_test | +----------------+ | studentnew | +----------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
3.6 查询属性 desc tablename ;不做过多描述
四、外键与外键约束
1、建立外键
两步
一步声明key(可以省略,mysql会自己建立一个,标准的索引此索引有啥用,此处不做深究)
一步建立关联
key shuibianxie(sid), <-key为一个索引index,名称可以随便写
constraint `shuibianxie` foreign key (sid) References student(sid)
注意点
1、建立表时必须要声明谁是primary key 2、涉及表相关变量的内容用撇号`变量`(数字1左边符号圈出),如constraint `index_fk_xxx`,如果涉及为字符内容的用单引号表示'yes'(如default 'yes')
MariaDB [test]> create table study_record( id int not null auto_increment primary key, status char(10) not null default 'yes', sid int not null, KEY index_fk_xxx(sid), constraint `index_fk_xxx` foreign key (sid) references student(sid)); Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec) MariaDB [test]> desc study_record; +--------+----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +--------+----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ | id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment | | status | char(10) | NO | | yes | | | sid | int(11) | NO | MUL | NULL | | +--------+----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [test]>
2、外键约束
MariaDB [test]> desc study_record; +------------+----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +------------+----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ | id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment | | status | char(10) | NO | | yes | | | sid | int(11) | NO | MUL | NULL | | | study_date | date | NO | | NULL | | +------------+----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [test]> select * from student; +-----+------+------------+--------+ | sid | name | birth | sexxxx | +-----+------+------------+--------+ | 1 | tom | 1990-01-01 | | | 2 | jack | 1980-01-01 | | | 3 | lucy | 1993-02-02 | | +-----+------+------------+--------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [test]> insert into study_record (sid,study_date) values (1,'2018-01-01'); Query OK, 1 row affected (0.05 sec) MariaDB [test]> insert into study_record (sid,study_date) values (4,'2018-01-01'); ERROR 1452 (23000): Cannot add or update a child row: a foreign key constraint fails (`test`.`study_record`, CONSTRAINT `index_fk_xxx` FOREIGN KEY (`sid`) REFERENCES `student` (`sid`)) MariaDB [test]> MariaDB [test]> delete from student where sid = 1; ERROR 1451 (23000): Cannot delete or update a parent row: a foreign key constraint fails (`test`.`study_record`, CONSTRAINT `index_fk_xxx` FOREIGN KEY (`sid`) REFERENCES `student` (`sid`)) MariaDB [test]> select * from study_record; +----+--------+-----+------------+ | id | status | sid | study_date | +----+--------+-----+------------+ | 1 | yes | 1 | 2018-01-01 | +----+--------+-----+------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [test]> delete from study_record where id =1; Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
不能插入外链中不存在的值,当关联存在时,数据无法被删除,保证数据完整性。(参照完整性)
3、 连接查询
left join、right join、inner join、full join
最常见的是内连接 inner join
select * from a inner join b on a.a=b.b
select * from a,b where a.a=b.b
实际是a.a和b.b之间求交集(当数据在b中无重复的情况下)
如果有重复,或出现a.a 对应多个b.b 的情况 此处先不考虑
MariaDB [student_system]> select * from school_class inner join school_course on school_class.class_course=school_course.course_id; +----------+------------+--------------+-----------+-------------+ | class_id | class_name | class_course | course_id | course_name | +----------+------------+--------------+-----------+-------------+ | 1 | python001 | 1 | 1 | python | | 2 | linux001 | 3 | 3 | linux | +----------+------------+--------------+-----------+-------------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [student_system]> MariaDB [student_system]> select * from school_class ,school_course where school_class.class_course=school_course.course_id; +----------+------------+--------------+-----------+-------------+ | class_id | class_name | class_course | course_id | course_name | +----------+------------+--------------+-----------+-------------+ | 1 | python001 | 1 | 1 | python | | 2 | linux001 | 3 | 3 | linux | +----------+------------+--------------+-----------+-------------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [student_system]>
left join 与right join 此处都不考虑用来关联的key有重复的情况
MariaDB [test]> select * from a; +---+ | a | +---+ | 1 | | 2 | | 3 | | 4 | +---+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [test]> select * from b; +---+ | b | +---+ | 3 | | 4 | | 5 | | 6 | +---+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [test]> select * from a left join b on a.a=b.b; +---+------+ | a | b | +---+------+ | 1 | NULL | | 2 | NULL | | 3 | 3 | | 4 | 4 | +---+------+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [test]> select * from a right join b on a.a=b.b; +------+---+ | a | b | +------+---+ | 3 | 3 | | 4 | 4 | | NULL | 5 | | NULL | 6 | +------+---+ 4 rows in set (0.01 sec) MariaDB [test]> select * from b left join a on a.a=b.b; +---+------+ | b | a | +---+------+ | 3 | 3 | | 4 | 4 | | 5 | NULL | | 6 | NULL | +---+------+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [test]> select * from b right join a on a.a=b.b; +------+---+ | b | a | +------+---+ | NULL | 1 | | NULL | 2 | | 3 | 3 | | 4 | 4 | +------+---+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
full join
mysql 并不直接支持full join,需要用union组合使用
MariaDB [test]> select * from a left join b on a.a = b.b UNION select * from a right join b on a.a=b.b; +------+------+ | a | b | +------+------+ | 1 | NULL | | 2 | NULL | | 3 | 3 | | 4 | 4 | | NULL | 5 | | NULL | 6 | +------+------+ 6 rows in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [test]>
4、索引
将一列或多列值通过hash等方式生成一个顺序,并存在索引表中,在数据量非常大时,使用索引能有效的提高数据的查询时间
在创建索引时,我们要确保索引时使用在sql语句的过滤条件。
实际上索引也是一张表,保存着主键和索引字段,并指向实体表的记录
索引的优点:加快了查询速度
索引的缺点:占用空间,增加了插入数据,修改数据的时间(因为要刷新索引)
4.1 查询索引
show index
MariaDB [test]> show index from student; +---------+------------+----------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+ | Table | Non_unique | Key_name | Seq_in_index | Column_name | Collation | Cardinality | Sub_part | Packed | Null | Index_type | Comment | Index_comment | +---------+------------+----------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+ | student | 0 | PRIMARY | 1 | sid | A | 3 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | | +---------+------------+----------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [test]> show index from study_record; +--------------+------------+--------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+ | Table | Non_unique | Key_name | Seq_in_index | Column_name | Collation | Cardinality | Sub_part | Packed | Null | Index_type | Comment | Index_comment | +--------------+------------+--------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+ | study_record | 0 | PRIMARY | 1 | id | A | 0 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | | | study_record | 1 | index_fk_xxx | 1 | sid | A | 0 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | | +--------------+------------+--------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
4.2 创建索引
方法一 通过create
MariaDB [test]> create index index_data on study_record(study_date); Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.08 sec) Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0 MariaDB [test]> show index from study_record; +--------------+------------+--------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+ | Table | Non_unique | Key_name | Seq_in_index | Column_name | Collation | Cardinality | Sub_part | Packed | Null | Index_type | Comment | Index_comment | +--------------+------------+--------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+ | study_record | 0 | PRIMARY | 1 | id | A | 0 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | | | study_record | 1 | index_fk_xxx | 1 | sid | A | 0 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | | | study_record | 1 | index_data | 1 | study_date | A | 0 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | | +--------------+------------+--------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [test]>
方法二 在创建表的时候,就添加索引
index index_name (name(32))
MariaDB [test]> create table c ( -> id int not null primary key, -> name char(32) not null, -> index index_name (name(32)) -> ); Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.03 sec) MariaDB [test]> show index from c; +-------+------------+------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+ | Table | Non_unique | Key_name | Seq_in_index | Column_name | Collation | Cardinality | Sub_part | Packed | Null | Index_type | Comment | Index_comment | +-------+------------+------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+ | c | 0 | PRIMARY | 1 | id | A | 0 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | | | c | 1 | index_name | 1 | name | A | 0 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | | +-------+------------+------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
4.3 删除索引
drop index indexname on tablename;
MariaDB [test]> show index from study_record; +--------------+------------+--------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+ | Table | Non_unique | Key_name | Seq_in_index | Column_name | Collation | Cardinality | Sub_part | Packed | Null | Index_type | Comment | Index_comment | +--------------+------------+--------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+ | study_record | 0 | PRIMARY | 1 | id | A | 0 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | | | study_record | 1 | index_fk_xxx | 1 | sid | A | 0 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | | | study_record | 1 | index_data | 1 | study_date | A | 0 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | | +--------------+------------+--------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [test]> drop index index_data on study_record; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.03 sec) Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0 MariaDB [test]> show index from study_record; +--------------+------------+--------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+ | Table | Non_unique | Key_name | Seq_in_index | Column_name | Collation | Cardinality | Sub_part | Packed | Null | Index_type | Comment | Index_comment | +--------------+------------+--------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+ | study_record | 0 | PRIMARY | 1 | id | A | 0 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | | | study_record | 1 | index_fk_xxx | 1 | sid | A | 0 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | | +--------------+------------+--------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [test]>
5 、事务
对于数据库的操作中,为了避免操作过程中出现误操作,设备宕机等意外情况对数据的损坏,出现了事务的概念,即操作完成后,确认成功,再进行保存,如果操作失败,则进行回滚
5.1 了解基本概念
一般来说,事务是必须满足4个条件(ACID): Atomicity(原子性)、Consistency(稳定性)、Isolation(隔离性)、Durability(可靠性)
-
- 1、事务的原子性:一组事务,要么成功;要么撤回。
- 2、稳定性 : 有非法数据(外键约束之类),事务撤回。
- 3、隔离性:事务独立运行。一个事务处理后的结果,影响了其他事务,那么其他事务会撤回。事务的100%隔离,需要牺牲速度。
- 4、可靠性:软、硬件崩溃后,InnoDB数据表驱动会利用日志文件重构修改。可靠性和高速度不可兼得, innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit选项 决定什么时候吧事务保存到日志里
5.2 3个基本操作
begin、commit、rollback
操作流程
begin; 开始一个事务
执行指令
commit;提交
rollback;回滚
五、python与mysql交互
pymysql模块
直接执行原始sql语句
操作思路 1、建立链接 2、建立操作对象 3、excute 或excutemany
查询结果 fetchone 逐个查询、fetchall全部查看 、fetchmany(n)查询指定数量,直接打印返回值,输出查询结果的条数
import pymysql #建立连接 conn=pymysql.connect(host='192.168.99.106',port=3306,user='root',db='test',passwd='123456',charset='utf8') #建立操作对象 cmd_obj=conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) tmp_result=cmd_obj.execute('select * from student') #fetch的三种使用 fetchall fetchone fetchmany print(tmp_result,cmd_obj.fetchall())#直接打印结果tmp_result,为查询到的数量 fetchall()返回一个列表,每个列表元素为一个字典。 #print(cmd_obj.fetchone()) #print(cmd_obj.fetchmany(3)) #操作数据 #x="insert into school_info (school_name,address,tel) values ('上海校区','普陀区',19966229988)" #cmd_obj.execute(x) #tmp_result=cmd_obj.execute('select * from school_info where id >5') #print(tmp_result,cmd_obj.fetchall()) #conn.commit() #cmd_obj.close() #conn.close() student_list=[ ('stu_001','小东','13700010001'), ('stu_002','小明','13700010002'), ('stu_003','jack','13700010004')] #cmd_obj.executemany("insert into student_info (sid,name,tel) values (%s,%s,%s)",student_list) ----------------------------------- 3 [{'sid': 1, 'name': 'tom', 'birth': datetime.date(1990, 1, 1), 'sexxxx': ''}, {'sid': 2, 'name': 'jack', 'birth': datetime.date(1980, 1, 1), 'sexxxx': ''}, {'sid': 3, 'name': 'lucy', 'birth': datetime.date(1993, 2, 2), 'sexxxx': ''}]
六、sqlalchemy orm操作
1、orm的介绍
orm--object relation mapping
orm 编程语言和数据库实现映射关系
使用对象来映射关系
orm的优点::隐藏数据访问细节 交互变得简单
orm的缺点:效率比原生sql低
2、sqlalchemy的介绍
orm为一个框架,不是真实的软件,在Python中,最有名的ORM框架是SQLAlchemy。用户包括openstack\Dropbox等知名公司或应用。
3、sqlalchemy实现数据库的增删改查
3.1 创建table
思路,建立conn、建立Base、class 继承base定义表结构、Base进行create_all
import sqlalchemy from sqlalchemy import Column,String,Integer,DATE,ForeignKey from sqlalchemy.ext.declarative import declarative_base from sqlalchemy import create_engine,Table,UniqueConstraint from sqlalchemy.orm import sessionmaker,relationship #step 1 建立连接 engine=create_engine('mysql+pymysql://root:123456@192.168.99.106/test?charset=utf8') #step2 建立Base Base=declarative_base() #step3 通过base定义表 class tstudent(Base): __tablename__='tstudent' student_id=Column(Integer,primary_key=True,nullable=True) student_name=Column(String(64),nullable=True,unique=True) student_QQ=Column(Integer,unique=True,nullable=True) passwd=Column(String(64)) #repr为打印数据对象时输出的类型。下文会说明 def __repr__(self): return self.username #step4 通过base进行create_all Base.metadata.create_all(engine)
-----------------------------
engine=create_engine('mysql+pymysql://root:123456@192.168.99.106/test?charset=utf8')
echo=True时能看到sqlalchemy生成的sql语句:
CREATE TABLE tstudent (
student_id INTEGER AUTO_INCREMENT,
student_name VARCHAR(64),
`student_QQ` INTEGER,
passwd VARCHAR(64),
PRIMARY KEY (student_id),
UNIQUE (student_name),
UNIQUE (`student_QQ`)
)
进数据库中验证
MariaDB [test]> desc tstudent; +--------------+-------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +--------------+-------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ | student_id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment | | student_name | varchar(64) | YES | UNI | NULL | | | student_QQ | int(11) | YES | UNI | NULL | | | passwd | varchar(64) | YES | | NULL | | +--------------+-------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [test]> show create table tstudent; +----------+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | Table | Create Table | +----------+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | tstudent | CREATE TABLE `tstudent` ( `student_id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `student_name` varchar(64) DEFAULT NULL, `student_QQ` int(11) DEFAULT NULL, `passwd` varchar(64) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`student_id`), UNIQUE KEY `student_name` (`student_name`), UNIQUE KEY `student_QQ` (`student_QQ`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1 | +----------+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [test]>
3.2 数据表中插入数据
思路 先建立连接->建立base->定义表class->建立session_obj->建立session->使用class表生成具体的数据->session.add()->session.commit() / session.rollback()
import sqlalchemy from sqlalchemy import Column,String,Integer,DATE,ForeignKey from sqlalchemy.ext.declarative import declarative_base from sqlalchemy import create_engine,Table,UniqueConstraint from sqlalchemy.orm import sessionmaker,relationship #step 1 建立连接 engine=create_engine('mysql+pymysql://root:123456@192.168.99.106/test?charset=utf8',echo=True) #step2 建立Base Base=declarative_base() #step3 通过base定义表 class tstudent(Base): __tablename__='tstudent' student_id=Column(Integer,primary_key=True,nullable=True) student_name=Column(String(64),nullable=True,unique=True) student_QQ=Column(Integer,unique=True,nullable=True) passwd=Column(String(64)) #repr为打印数据对象时输出的类型。下文会说明 def __repr__(self): return self.username def insert_data(): #step 4 建立session_obj session_obj=sessionmaker(bind=engine) #step5 建立session session = session_obj() #step6 生成具体数据 tmp_data=tstudent(student_name='stu001',student_QQ=11111,passwd='123456') session.add session.add(tmp_data) session.commit() S1 = tstudent(student_name='Student001', passwd='123456', student_QQ='10001') S2 = tstudent(student_name='Student002', passwd='123456', student_QQ='10002') S3 = tstudent(student_name='Student003', passwd='123456', student_QQ='10003') S4 = tstudent(student_name='Student004', passwd='123456', student_QQ='10004') S5 = tstudent(student_name='Student005', passwd='123456', student_QQ='10005') data_list=[S1,S2,S3,S4,S5] session.add_all(data_list) session.commit() insert_data()
需要注意add()和add_all()
echo=True生成的部分log
2018-06-18 12:11:14,757 INFO sqlalchemy.engine.base.Engine INSERT INTO tstudent (student_name, `student_QQ`, passwd) VALUES (%(student_name)s, %(student_QQ)s, %(passwd)s) 2018-06-18 12:11:14,757 INFO sqlalchemy.engine.base.Engine {'student_name': 'Student001', 'student_QQ': '10001', 'passwd': '123456'} 2018-06-18 12:11:14,757 INFO sqlalchemy.engine.base.Engine INSERT INTO tstudent (student_name, `student_QQ`, passwd) VALUES (%(student_name)s, %(student_QQ)s, %(passwd)s) 2018-06-18 12:11:14,757 INFO sqlalchemy.engine.base.Engine {'student_name': 'Student002', 'student_QQ': '10002', 'passwd': '123456'} 2018-06-18 12:11:14,758 INFO sqlalchemy.engine.base.Engine INSERT INTO tstudent (student_name, `student_QQ`, passwd) VALUES (%(student_name)s, %(student_QQ)s, %(passwd)s) 2018-06-18 12:11:14,758 INFO sqlalchemy.engine.base.Engine {'student_name': 'Student003', 'student_QQ': '10003', 'passwd': '123456'} 2018-06-18 12:11:14,758 INFO sqlalchemy.engine.base.Engine INSERT INTO tstudent (student_name, `student_QQ`, passwd) VALUES (%(student_name)s, %(student_QQ)s, %(passwd)s) 2018-06-18 12:11:14,758 INFO sqlalchemy.engine.base.Engine {'student_name': 'Student004', 'student_QQ': '10004', 'passwd': '123456'} 2018-06-18 12:11:14,759 INFO sqlalchemy.engine.base.Engine INSERT INTO tstudent (student_name, `student_QQ`, passwd) VALUES (%(student_name)s, %(student_QQ)s, %(passwd)s) 2018-06-18 12:11:14,759 INFO sqlalchemy.engine.base.Engine {'student_name': 'Student005', 'student_QQ': '10005', 'passwd': '123456'}
进入mysql验证数据
MariaDB [test]> select * from tstudent; +------------+--------------+------------+--------+ | student_id | student_name | student_QQ | passwd | +------------+--------------+------------+--------+ | 1 | stu001 | 11111 | 123456 | | 2 | Student001 | 10001 | 123456 | | 3 | Student002 | 10002 | 123456 | | 4 | Student003 | 10003 | 123456 | | 5 | Student004 | 10004 | 123456 | | 6 | Student005 | 10005 | 123456 | +------------+--------------+------------+--------+ 6 rows in set (0.00 sec)
3.3 数据表中删除数据
要删除数据 首先要把要操作的数据查出来 之后session.delete() 只能一条记录一条记录删 不能全部.all()删除
import sqlalchemy from sqlalchemy import Column,String,Integer,DATE,ForeignKey from sqlalchemy.ext.declarative import declarative_base from sqlalchemy import create_engine,Table,UniqueConstraint from sqlalchemy.orm import sessionmaker,relationship from sqlalchemy import or_ #step 1 建立连接 engine=create_engine('mysql+pymysql://root:123456@192.168.99.106/test?charset=utf8') #step2 建立Base Base=declarative_base() #step3 通过base定义表 class tstudent(Base): __tablename__='tstudent' student_id=Column(Integer,primary_key=True,nullable=True) student_name=Column(String(64),nullable=True,unique=True) student_QQ=Column(Integer,unique=True,nullable=True) passwd=Column(String(64)) #repr为打印数据对象时输出的类型。下文会说明 def __repr__(self): return self.student_name def delete_data(): #step 4 建立session_obj session_obj=sessionmaker(bind=engine) #step5 建立session session = session_obj() #step6 session.query tmp_result=session.query(tstudent).first() print(tmp_result) #step7 session.delete session.delete(tmp_result) session.commit() delete_data() ---------------------------- MariaDB [test]> select * from tstudent; +------------+--------------+------------+--------+ | student_id | student_name | student_QQ | passwd | +------------+--------------+------------+--------+ | 1 | stu001 | 11111 | 123456 | | 2 | Student001 | 10001 | 123456 | | 3 | Student002 | 10002 | 123456 | | 4 | Student003 | 10003 | 123456 | | 5 | Student004 | 10004 | 123456 | | 6 | Student005 | 10005 | 123456 | +------------+--------------+------------+--------+ 6 rows in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [test]> select * from tstudent; +------------+--------------+------------+--------+ | student_id | student_name | student_QQ | passwd | +------------+--------------+------------+--------+ | 2 | Student001 | 10001 | 123456 | | 3 | Student002 | 10002 | 123456 | | 4 | Student003 | 10003 | 123456 | | 5 | Student004 | 10004 | 123456 | | 6 | Student005 | 10005 | 123456 | +------------+--------------+------------+--------+ 5 rows in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [test]>
3.4 数据表中修改数据
要修改数据 首先要把要操作的数据查出来
MariaDB [test]> select * from tstudent; +------------+--------------+------------+--------+ | student_id | student_name | student_QQ | passwd | +------------+--------------+------------+--------+ | 2 | Student001 | 10001 | 123456 | | 3 | Student002 | 10002 | 123456 | | 4 | Student003 | 10003 | 123456 | | 5 | Student004 | 10004 | 123456 | | 6 | Student005 | 10005 | 123456 | +------------+--------------+------------+--------+ 5 rows in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [test]> select * from tstudent; +------------+--------------+------------+--------+ | student_id | student_name | student_QQ | passwd | +------------+--------------+------------+--------+ | 1 | Student001 | 10001 | 123456 | | 3 | Student002 | 10002 | 123456 | | 4 | Student003 | 10003 | 123456 | | 5 | Student004 | 10004 | 123456 | | 6 | Student005 | 10005 | 123456 | +------------+--------------+------------+--------+ 5 rows in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [test]>
3.5 数据表中查询数据
3.5.1 普通查询 无过滤条件
all与first的区别
import sqlalchemy from sqlalchemy import Column,String,Integer,DATE,ForeignKey from sqlalchemy.ext.declarative import declarative_base from sqlalchemy import create_engine,Table,UniqueConstraint from sqlalchemy.orm import sessionmaker,relationship #step 1 建立连接 engine=create_engine('mysql+pymysql://root:123456@192.168.99.106/test?charset=utf8') #step2 建立Base Base=declarative_base() #step3 通过base定义表 class tstudent(Base): __tablename__='tstudent' student_id=Column(Integer,primary_key=True,nullable=True) student_name=Column(String(64),nullable=True,unique=True) student_QQ=Column(Integer,unique=True,nullable=True) passwd=Column(String(64)) #repr为打印数据对象时输出的类型。下文会说明 def __repr__(self): return self.student_name ---------------------------------------- [stu001, Student001, Student002, Student003, Student004, Student005] 学生: Student001 qq号: 10001 stu001
3.5.2 过滤条件
limit session.query().limit()
tmp_result = session.query(tstudent).limit(3).all() print(tmp_result)
filter 与filter_by
一般用filter多一些
tmp_result = session.query(tstudent).filter(tstudent.student_id==1).all() print(tmp_result) tmp_result = session.query(tstudent).filter_by(student_id = 1).all() print(tmp_result)
3.5.3 逻辑关系与数字关系 and or > < !=
#or 关系 from sqlalchemy import or_ tmp_or = session.query(tstudent).filter(or_(tstudent.student_id==1,tstudent.student_id>4)).all() print(tmp_or) #and 关系 tmp_and = session.query(tstudent).filter(tstudent.student_id==1,tstudent.student_QQ=='11111').all() print(tmp_and) #> != 对比 tmp_compare = session.query(tstudent).filter(tstudent.student_id>1,tstudent.student_id != 3).all() print(tmp_result) ----------------------------------- [stu001, Student004, Student005] [stu001] [stu001, Student001, Student002, Student003, Student004, Student005]
3.5.4 多表组合查询与order排序
多表查询,最后结果为列表,每个列表中又嵌套列表,对于query里面的每张表。用下标取具体的表来取相应的属性
排序 用session.query().order_by(key.desc()).all()
study_data = session.query(study_log, School_class, Lesson_info, Student).filter( study_log.class_id == School_class.class_id, study_log.lesson_id == Lesson_info.lesson_id, study_log.student_id == Student.student_id, study_log.student_id == student_data.student_id, study_log.homework_stat == 'yes' ).all() print('目前已经交了%s份作业' % len(study_data)) for i in study_data: print('*******************************************************') print('班级名:[%s],课程名:[%s],学生姓名:[%s],作业分数:[%s]' % ( i[1].class_name, i[2].lesson_name, i[3].student_name, i[0].score)) print('*******************************************************') print('该作业班级排名:') class_rank_data = session.query(study_log, School_class, Lesson_info, Student).filter( study_log.class_id == School_class.class_id, study_log.lesson_id == Lesson_info.lesson_id, study_log.student_id == Student.student_id, study_log.study_date==i[0].study_date, study_log.class_id == i[1].class_id, study_log.lesson_id==i[2].lesson_id ).order_by(study_log.score.desc()).all() for j in class_rank_data: print('班级名:[%s],课程名:[%s],学生姓名:[%s],作业分数:[%s]' % ( j[1].class_name, j[2].lesson_name, j[3].student_name, j[0].score))
3.5.5 模糊匹配like
session.query.filter(xx,like(%%)).all()
data=session.query(Lesson_info).filter(Lesson_info.lesson_desc.like('%rhc%')).all()
3.5.6 统计与分组count() group_by()
auto_increment 设置为0
alter table tbname auto_increment = x ;重置increment
4、外键关联 foreignkey与relationship的使用
4.1 建立外链
ForeignKey('tstudent.student_id')
4.2 组合唯一
from sqlalchemy import create_engine,Table,UniqueConstraint
__table_args__ = (UniqueConstraint('key1', 'key2'),)
class tstudent(Base): __tablename__='tstudent' student_id=Column(Integer,primary_key=True,nullable=True) student_name=Column(String(64),nullable=True,unique=True) student_QQ=Column(Integer,unique=True,nullable=True) passwd=Column(String(64)) def __repr__(self): return self.student_name class tstudy_record(Base): __tablename__ = 'tstudy_record' id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True, nullable=True) sid = Column(Integer,ForeignKey('tstudent.student_id'),nullable=False) study_date = Column(DATE,nullable=False) __table_args__ = (UniqueConstraint('sid', 'study_date'),)#from sqlalchemy import create_engine,Table,UniqueConstraint
在mysql中查看
MariaDB [test]> desc tstudy_record; +------------+---------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +------------+---------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ | id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment | | sid | int(11) | NO | MUL | NULL | | | study_date | date | NO | | NULL | | +------------+---------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ 3 rows in set (0.01 sec)
数据插入
d1 = tstudy_record(sid=1, study_date='2018-01-01') d2 = tstudy_record(sid=1, study_date='2018-01-02') d3 = tstudy_record(sid=1, study_date='2018-01-03') d4 = tstudy_record(sid=1, study_date='2018-01-04') d5 = tstudy_record(sid=4, study_date='2018-01-04') d6 = tstudy_record(sid=3, study_date='2018-01-04') d_list=[d1,d5,d6,d2,d3,d4] session.add_all(d_list) session.commit()
mysql验证
MariaDB [test]> select * from tstudy_record; +----+-----+------------+ | id | sid | study_date | +----+-----+------------+ | 1 | 1 | 2018-01-01 | | 4 | 1 | 2018-01-02 | | 5 | 1 | 2018-01-03 | | 6 | 1 | 2018-01-04 | | 3 | 3 | 2018-01-04 | | 2 | 4 | 2018-01-04 | +----+-----+------------+ 6 rows in set (0.00 sec)
组合查询
MariaDB [test]> select tstudent.student_name as 学号,study_date 上课记录 from tstudent,tstudy_record where tstudy_record.sid = tstudent.student_id; +------------+--------------+ | 学号 | 上课记录 | +------------+--------------+ | Student001 | 2018-01-01 | | Student001 | 2018-01-02 | | Student001 | 2018-01-03 | | Student001 | 2018-01-04 | | Student002 | 2018-01-04 | | Student003 | 2018-01-04 | +------------+--------------+ 6 rows in set (0.00 sec)
重复数据报错
(1062, "Duplicate entry '1-2018-01-01' for key 'sid'") [SQL: 'INSERT INTO tstudy_record (sid, study_date) VALUES (%(sid)s, %(study_date)s)'] [parameters: {'sid': 1, 'study_date': '2018-01-01'}] (Background on this error at: http://sqlalche.me/e/gkpj)
4.3 relation的使用
建立表格之间的联系,方便查询出来的数据查询其他表中的相关数据
此方法需要有外链相对应的情况下使用
两个关键 relationship 、backref
from sqlalchemy.orm import relationship
record_to_student=relationship(tstudent,backref='student_to_record')
class tstudent(Base): __tablename__='tstudent' student_id=Column(Integer,primary_key=True,nullable=True) student_name=Column(String(64),nullable=True,unique=True) student_QQ=Column(Integer,unique=True,nullable=True) passwd=Column(String(64)) #repr为打印数据对象时输出的类型。下文会说明 def __repr__(self): return self.student_name class tstudy_record(Base): __tablename__ = 'tstudy_record' id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True, nullable=True) sid = Column(Integer,ForeignKey('tstudent.student_id'),nullable=False) study_date = Column(DATE,nullable=False) record_to_student=relationship(tstudent,backref='student_to_record') __table_args__ = (UniqueConstraint('sid', 'study_date'),) def relationship_test(): # step 4 建立session_obj session_obj = sessionmaker(bind=engine) # step5 建立session session = session_obj() # step6 session.query tmp_result = session.query(tstudent).first() print(tmp_result) # step7 通过查询出的student列出对应的上课记录 tmp_record = tmp_result.student_to_record for i in tmp_record: print(tmp_result.student_name,i.study_date) create_tables() relationship_test() --------------------------------------------------- Student001 Student001 2018-01-01 Student001 2018-01-02 Student001 2018-01-03 Student001 2018-01-04
与mysql的对比
MariaDB [test]> select tstudent.student_name as 学号,study_date 上课记录 from tstudent,tstudy_record where tstudent.student_id=1 and tstudy_record.sid = tstudent.student_id; +------------+--------------+ | 学号 | 上课记录 | +------------+--------------+ | Student001 | 2018-01-01 | | Student001 | 2018-01-02 | | Student001 | 2018-01-03 | | Student001 | 2018-01-04 | +------------+--------------+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
4.4 一张表多外键关联同一张表的情况
此情况使用relationship时需要标注出foreign_keys,让程序合理区分通过哪个关系去查表
import sqlalchemy from sqlalchemy.ext.declarative import declarative_base from sqlalchemy import String,Column,Integer,DATE from sqlalchemy.orm import sessionmaker,relationship from sqlalchemy import create_engine from sqlalchemy import ForeignKey engine=create_engine('mysql+pymysql://root:123456@192.168.99.106/schooldb') Base=declarative_base() class address(Base): __tablename__='address' id=Column(Integer,nullable=False,primary_key=True) L1=Column(String(32),nullable=False) class user_name(Base): __tablename__='user_name' id=Column(Integer,nullable=False,primary_key=True) name=Column(String(32),nullable=False) home_address=Column(Integer,ForeignKey(address.id)) study_address=Column(Integer,ForeignKey(address.id)) home_to_addr=relationship('address',foreign_keys=[home_address]) study_to_addr=relationship('address',foreign_keys=[study_address]) ''' MariaDB [schooldb]> desc user_name; +---------------+-------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +---------------+-------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ | id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment | | name | varchar(32) | NO | | NULL | | | home_address | int(11) | YES | MUL | NULL | | | study_address | int(11) | YES | MUL | NULL | | +---------------+-------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [schooldb]> desc address; +-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ | id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment | | L1 | varchar(32) | NO | | NULL | | +-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [schooldb]> ''' #Base.metadata.create_all(engine) session_obj=sessionmaker(bind=engine) session=session_obj() #A1=address(L1='BJ') #A2=address(L1='SH') #A3=address(L1='GZ') #A4=address(L1='SZ') P1=user_name(name='a1',home_address=1,study_address=4) P2=user_name(name='a2',home_address=1,study_address=3) P3=user_name(name='a3',home_address=3,study_address=2) P4=user_name(name='a4',home_address=3,study_address=4) P5=user_name(name='a5',home_address=2,study_address=2) P6=user_name(name='alex',home_address=1,study_address=1) #session.add_all([P1,P2,P3,P4,P5,P6]) #session.commit() ''' MariaDB [schooldb]> select * from address; +----+----+ | id | L1 | +----+----+ | 1 | BJ | | 2 | SH | | 3 | GZ | | 4 | SZ | +----+----+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [schooldb]> select * from user_name; +----+------+--------------+---------------+ | id | name | home_address | study_address | +----+------+--------------+---------------+ | 3 | a1 | 1 | 4 | | 4 | a2 | 1 | 3 | | 5 | a3 | 3 | 2 | | 6 | a4 | 3 | 4 | | 7 | a5 | 2 | 2 | | 8 | alex | 1 | 1 | +----+------+--------------+---------------+ 6 rows in set (0.00 sec) ''' data=session.query(user_name).filter_by().all() for i in data: print('姓名:',i.name,'家乡:',i.home_to_addr.L1,'毕业学校:',i.study_to_addr.L1) ''' 姓名: a1 家乡: BJ 毕业学校: SZ 姓名: a2 家乡: BJ 毕业学校: GZ 姓名: a3 家乡: GZ 毕业学校: SH 姓名: a4 家乡: GZ 毕业学校: SZ 姓名: a5 家乡: SH 毕业学校: SH 姓名: alex 家乡: BJ 毕业学校: BJ
没有多个外键的情况下,同样也可以补充这个说明,并不矛盾
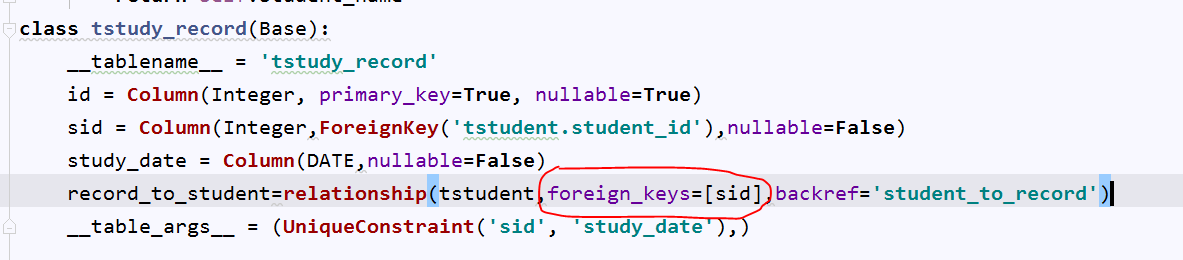
5、 多对多的关系处理
几个作者
几本书
一本书有几个作者
一个作者有几本书
书和作者直接存在着多对多的关系
为了表示这种关系,我们引入第三张表来表示这种关系
book author book_to_author
关键点1 关系表需要用table来建立,不能用class
关键点2 relationship的secondary
关键点3 关系的删除
关键点4 重复插入不会重复
import sqlalchemy from sqlalchemy.ext.declarative import declarative_base from sqlalchemy.orm import sessionmaker,relationship from sqlalchemy import DATE,String,Integer,Column,ForeignKey,Table,create_engine engine=create_engine('mysql+pymysql://root:123456@192.168.99.106/test') Base=declarative_base() book_to_author=Table('book_to_author',Base.metadata, Column('id',Integer,primary_key=Table,nullable=ForeignKey), Column( 'book_id',Integer,ForeignKey('book.id') ), Column('author_id',Integer,ForeignKey('author.id')), ) class book(Base): __tablename__='book' id=Column(Integer,primary_key=True,nullable=False) name=Column(String(32),nullable=False) myauthor=relationship('author',secondary='book_to_author',backref='mybooks') def __repr__(self): return self.name class author(Base): __tablename__='author' id=Column(Integer,primary_key=True,nullable=False) name=Column(String(32),nullable=False) def __repr__(self): return self.name Base.metadata.create_all(engine) session_obj=sessionmaker(engine) session=session_obj() b1=book(name='book1') b2=book(name='book2') b3=book(name='book3') a1=author(name='author1') a2=author(name='author2') a3=author(name='author3') b1.myauthor=[a1,a2,a3] b2.myauthor=[a1,a3] b3.myauthor=[a1,a2] #session.add_all([b1,b2,b3,a1,a2,a3]) #session.commit() data=session.query(book).all() print(data) for i in data: print(i.name,i.myauthor) for j in i.myauthor: print(j.name,j.mybooks) print('-----------------------------------') tmp_author=session.query(author).first() print(tmp_author,tmp_author.mybooks) tmp_book=session.query(book).first() print(tmp_book,tmp_book.myauthor) #tmp_book.myauthor.remove(tmp_author) #从书中删除作者,关系里面作者也删除了书 print(tmp_author,tmp_author.mybooks) print(tmp_book,tmp_book.myauthor) session.commit() print('**********************') data=session.query(author).filter_by(name='author2').first() print(data,data.mybooks) session.delete(data) data=session.query(book).all() for i in data: print(i.name,i.myauthor) for i in range(10): b1=session.query(book).filter(book.id==2).first() a1=session.query(author).filter(author.id==2).first() #print(b1.id,a1.id) a1.mybooks.append(b1) session.commit() #a1.mybooks.append() #循环执行 不会重复 ''' MariaDB [test]> select * from book_to_author; +----+---------+-----------+ | id | book_id | author_id | +----+---------+-----------+ | 1 | 1 | 2 | | 2 | 3 | 2 | | 3 | 1 | 1 | | 4 | 2 | 1 | | 5 | 3 | 1 | | 6 | 1 | 3 | | 7 | 2 | 3 | +----+---------+-----------+ 7 rows in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [test]> select * from book_to_author; +----+---------+-----------+ | id | book_id | author_id | +----+---------+-----------+ | 1 | 1 | 2 | | 2 | 3 | 2 | | 3 | 1 | 1 | | 4 | 2 | 1 | | 5 | 3 | 1 | | 6 | 1 | 3 | | 7 | 2 | 3 | | 8 | 2 | 2 | +----+---------+-----------+ 8 rows in set (0.00 sec) '''
mysql中显示
MariaDB [test]> select * from book_to_author; +----+---------+-----------+ | id | book_id | author_id | +----+---------+-----------+ | 1 | 1 | 2 | | 2 | 3 | 2 | | 3 | 1 | 1 | | 4 | 2 | 1 | | 5 | 3 | 1 | | 6 | 1 | 3 | | 7 | 2 | 3 | | 8 | 2 | 2 | +----+---------+-----------+ 8 rows in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [test]> select * from book; +----+-------+ | id | name | +----+-------+ | 1 | book1 | | 2 | book2 | | 3 | book3 | +----+-------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [test]> select * from author; +----+---------+ | id | name | +----+---------+ | 1 | author1 | | 2 | author2 | | 3 | author3 | +----+---------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [test]>
一点补充:
统计 count
Session.query(User).filter(User.name.like("Ra%")).count()
group_by 分类汇总
from sqlalchemy import func
print(Session.query(func.count(User.name),User.name).group_by(User.name).all() )



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号