C++类型转换
类型转换
隐式类型转换
显式类型转换
【1】隐式类型转换
有些类型转换是自动进行的,不需要人为的介入,比如算术运算时发生的类型转换(int i = 1.0 + 2,double->int),我们称之为隐式的。
其中场景大概会分为 左值到右值 整型提升 表达式提升 数组到指针 右值到左值 指针与指针 派生类基类 等。
最详细的资料可参考cppreffrence:https://zh.cppreference.com/w/cpp/language/implicit_conversion
具体使用场景(来自C++ primer)
1. 表达式中,比int类型小的整型值先转换成较大的整数类型(如:short)即:整型提升
2. 条件中,非布尔值转换为布尔值(如: if(1) ->if(true))
3. 初始化时,初始值转换为变量的类型
4. 赋值语句中,右侧运算对象转换成左侧运算对象 (如:int m = 2.0 编译器可能会提示精度损失)
5. 如果算术运算或者关系运算对象有多种类型,需要先转换成一种类型(并且是最大/宽的那个类型)。(如:int sum = 1.234 + 2)
6. 数组当作函数传入参数会转换为指针(但是sizeof不会)
7. 派生类对象可以隐式的转化为基类对象
8. 指针的转换(0/unllptr 可转为任意指针类型;指向非const的指针可转为 void*;任意对象指针可转为 const void*)
1 //赋值和算术运算 2 char c = 'a'; 3 char ch = 20; 4 int m = 3.0 + c; 5 bool flag = 100; 6 long l = 1.0L; 7 unsigned short us = 2.0 + 3;
//用typeid().name来输出当前变量类型 8 cout << typeid(c).name() << endl;//char 9 cout << typeid(ch).name() << endl;//char 10 cout << typeid(us).name() << endl;//usigned short 11 cout << typeid(m).name() << endl;//int 12 cout << typeid(3.0 + 'a').name() << endl;//double 13 cout << typeid(flag).name() << endl;//bool 14 cout << typeid(3 + 'a'*5.0).name() << endl;//int 15 cout << typeid(3 + 'a'*5.0 == l).name() << endl;//bool 16 17 if (m)//转换为bool true 18 cout << "m 转换为 bool型" << endl; 19 20 //指针转换 21 int* p = 0; 22 double* d = nullptr; 23 const void* cvp = nullptr; 24 cvp = d; 25 const int* cip = nullptr; 26 void* vp = 0; 27 vp = p;//这里赋值是无意义的,可以输出一下vp试试,会报错 28 cout << typeid(vp).name() << endl; 29 //vp = cip; 错,不可将const类型指针赋给void* 30 cvp = cip; 31 cout << typeid(cvp).name() << endl;//
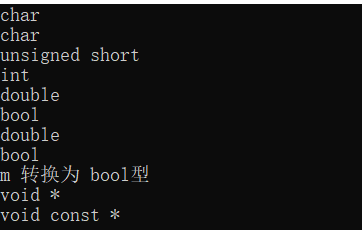
说明:类型转换可能会因为编译器的不同而不同。
【2】显式转换(强制类型转换)
老一套的强制类型转换已经过时了,如果你还在用形如 double val =(double)(express...) / x 的话,你过时了。
格式:cast-name<type>(express)
有时候我们需要将对象强制转换为另一种类型(虽然有时候不得不这样做,但本质上很危险)
static_cast:只要不包含底层const就可以用(VS中例外)
1 int i = 10; 2 double div = static_cast<double>(i) / 3; 3 cout << div << endl; 4 5 const int t = 10; 6 double div2 = static_cast<double>(t) / 3; 7 cout << div2 << endl;
const_cast:只用于“去const性质”(顶层/底层const都可以消除)
1 //2. const_cast<typename>(...)专为const设计,用于消除const属性 2 const int* cx = &i; 3 int* dc = const_cast<int*>(cx);//dc - int * 类型
dynamic_cast:支持运行时类型识别(多态的时候)
沿着继承层级向上、向下、侧向(同级别类),安全的转换到其他类的指针或引用。
只有三种使用方式
dynamic_cast<type *>(...) 用于指针转换
dynamic_cast<type &>(...) 用于引用转换
dynamic_cast<type &&>(...) 用于右值引用的转换
其中...即表达式的类型必须为type/type的派生类/type公有基类
即:利用该转换可以进行派生类对象到基类对象、基类对象到派生类对象、不同/相同派生类对象之间的转换
一些转换规则

1 #include <iostream> 2 3 struct V { 4 virtual void f() {}; // 必须为多态以使用运行时检查的 dynamic_cast 5 }; 6 struct A : virtual V {}; 7 struct B : virtual V { 8 B(V* v, A* a) { 9 // 构造中转型(见后述 D 的构造函数中的调用) 10 dynamic_cast<B*>(v); // 良好定义:v 有类型 V*,B 的 V 基类,产生 B* 11 dynamic_cast<B*>(a); // 未定义行为:a 有类型 A*,A 非 B 的基类 12 } 13 void foo() 14 { std::cout << "This is inside of B " << std::endl; } 15 }; 16 struct D : A, B { 17 D() : B((A*)this, this) { } 18 void foo() 19 { std::cout << "This is inside of D " << std::endl; } 20 }; 21 22 struct Base { 23 virtual ~Base() {} 24 void foo() 25 { std::cout << "This is inside of Base " << std::endl; } 26 }; 27 28 struct Derived: Base { 29 virtual void name() {} 30 void foo() 31 { std::cout << "This is inside of Derived " << std::endl; } 32 }; 33 34 int main() 35 { 36 D d; // 最终派生对象 37 A& a = d; // 向上转型,可以用 dynamic_cast,但不必须 38 D& new_d = dynamic_cast<D&>(a); // 向下转型 39 new_d.foo(); 40 41 B& new_b = dynamic_cast<B&>(a); // 侧向转型 42 new_b.foo(); 43 44 std::cout << "\nthe base odject init derived object" << std::endl; 45 Base* b1 = new Base; 46 b1->foo(); 47 if(Derived* d = dynamic_cast<Derived*>(b1))//转换失败,到目前为止我还没有搞懂,为什么该种类型的基类指针为什么不能转换为派生类指针。 48 { 49 std::cout << "downcast from b1 to d successful\n"; 50 d->name(); // 可以安全调用 51 d->foo(); 52 } 53 else 54 std::cout << "cast fail" << std::endl;// cast fail 55 56 std::cout << "\nthe derived odject init base object" << std::endl; 57 Base* b2 = new Derived; 58 b2->foo(); 59 if(Derived* d = dynamic_cast<Derived*>(b2)) 60 { 61 std::cout << "downcast from b2 to d successful\n"; 62 d->name(); // 可以安全调用 63 d->foo(); 64 } 65 else 66 std::cout << "cast fail" << std::endl; 67 68 delete b1; 69 delete b2; 70 }

//结果 This is inside of D This is inside of B the base odject init derived object This is inside of Base cast fail the derived odject init base object This is inside of Base downcast from b2 to d successful This is inside of Derived



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号