ASP.NET Web API(三):安全验证之使用摘要认证(digest authentication)
在前一篇文章中,主要讨论了使用HTTP基本认证的方法,因为HTTP基本认证的方式决定了它在安全性方面存在很大的问题,所以接下来看看另一种验证的方式:digest authentication,即摘要认证。
摘要认证原理
在基本认证的方式中,主要的安全问题来自于用户信息的明文传输,而在摘要认证中,主要通过一些手段避免了此问题,大大增加了安全性。
下图为摘要验证的验证原理流程图。

下面大致看一下这部分的验证流程:
- 客户端请求 /api/employees;
- 服务端返回401未验证的状态,并且在返回的信息中包含了验证方式Digest,realm的值,QOP(quality of protection)只设置成auth,nonce为一串随机值,在下面的请求中会一直使用到,当过了存活期后服务端将刷新生成一个新的nonce值;
- 客户端接受到请求返回后,将username:realm:password进行HASH运算,假设运算后的值为HA1。又将请求的路径/api/employees进行HASH运算,假设运算后的值为HA2。再将HA1:nonce:nc:cnonce:qop:HA2进行HASH运算,得到的值放在response中。这里的cnonce为客户端生成的nonce值,而nc用于统计,假设开始时为00000001,下次请求后就变成了00000002,不一定每次都加1,但是后面请求中的nc值肯定大于前一次请求中的nc值。
- 服务端收到请求后将验证nonce是否过期,如果过期,那么直接返回401,即第二步的状态。如果没有过期,那么比较nc值,如果比前一次nc值小或者前一次根本没有存储的nc值,那么也将直接返回401状态。如果前面的验证都通过,那么服务端也将按照步骤3中计算最终HASH值的步骤计算出HASH值与客户端的进行比较,然后比较客户端提交过来的HASH值与服务端计算出来的HASH进行比较,不匹配返回401,匹配获取请求的数据并返回状态200。
摘要验证主要就是通过上面的HASH比较的步骤避免掉了基本验证中的安全性问题。
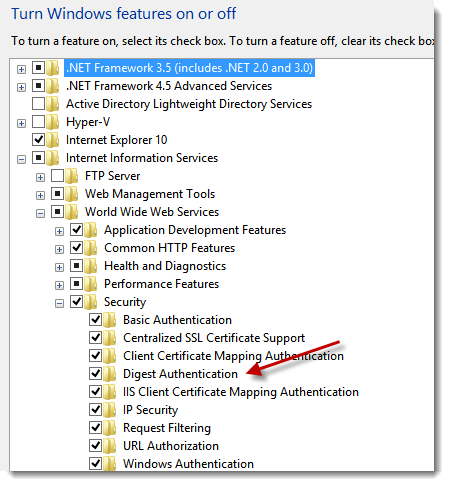
需要注意的是,如果需要IIS支持摘要验证,需要把IIS摘要验证的特性勾上。
摘要验证的实现
在理解了摘要验证的原理之后,只需要用代码实现即可。
判断nonce是否过期的方法。

public static bool IsValid(string nonce, string nonceCount) { Tuple<int, DateTime> cachedNonce = null; nonces.TryGetValue(nonce, out cachedNonce); if (cachedNonce != null) // nonce is found { // nonce count is greater than the one in record if (Int32.Parse(nonceCount) > cachedNonce.Item1) { // nonce has not expired yet if (cachedNonce.Item2 > DateTime.Now) { // update the dictionary to reflect the nonce count just received in this request nonces[nonce] = new Tuple<int, DateTime>(Int32.Parse(nonceCount), cachedNonce.Item2); // Every thing looks ok - server nonce is fresh and nonce count seems to be // incremented. Does not look like replay. return true; } } } return false; } 判断nonce是否过期的代码
下面为摘要验证实现的核心方法

namespace DigestAuthentication { public class AuthenticationHandler : DelegatingHandler { protected async override Task<HttpResponseMessage> SendAsync(HttpRequestMessage request, CancellationToken cancellationToken) { try { var headers = request.Headers; if (headers.Authorization != null) { Header header = new Header(request.Headers.Authorization.Parameter, request.Method.Method); if (Nonce.IsValid(header.Nonce, header.NounceCounter)) { // Just assuming password is same as username for the purpose of illustration string password = header.UserName; string ha1 = String.Format("{0}:{1}:{2}", header.UserName, header.Realm, password).ToMD5Hash(); string ha2 = String.Format("{0}:{1}", header.Method, header.Uri).ToMD5Hash(); string computedResponse = String .Format("{0}:{1}:{2}:{3}:{4}:{5}", ha1, header.Nonce, header.NounceCounter, header.Cnonce, "auth", ha2).ToMD5Hash(); if (String.CompareOrdinal(header.Response, computedResponse) == 0) { // digest computed matches the value sent by client in the response field. // Looks like an authentic client! Create a principal. var claims = new List<Claim> { new Claim(ClaimTypes.Name, header.UserName), new Claim(ClaimTypes.AuthenticationMethod, AuthenticationMethods.Password) }; var principal = new ClaimsPrincipal(new[] { new ClaimsIdentity(claims, "Digest") }); Thread.CurrentPrincipal = principal; if (HttpContext.Current != null) HttpContext.Current.User = principal; } } } var response = await base.SendAsync(request, cancellationToken); if (response.StatusCode == HttpStatusCode.Unauthorized) { response.Headers.WwwAuthenticate.Add(new AuthenticationHeaderValue("Digest", Header.UnauthorizedResponseHeader.ToString())); } return response; } catch (Exception) { var response = request.CreateResponse(HttpStatusCode.Unauthorized); response.Headers.WwwAuthenticate.Add(new AuthenticationHeaderValue("Digest", Header.UnauthorizedResponseHeader.ToString())); return response; } } } } 摘要验证实现的核心方法
实现完成后,使用摘要验证只需要在对应的方法加上[Authorize]属性标签即可。

摘要验证的优缺点
摘要验证很好地解决了使用基本验证所担心的安全性问题。
但是永远没有绝对的安全,当用户使用字典进行穷举破解时,还是会存在一些被破解的隐患。





