异常类型变量的生命周期
传统的错误处理机制:
#include<iostream> using namespace std; //传统的处理机制 int my_strcopy(char* from, char* to) { if (from == NULL) return 1; if (to == NULL) return 2; //拷贝场景检查 if (*from == 'a') return 3; while (*from != '\0') { *to = *from; to ++; from ++; } *to = '\0'; return 0; } int main() { int ret = 0; char buf1[] = "abcdefg"; char buf2[1024] = { 0 }; ret = my_strcopy(buf1, buf2); if (ret != 0) { switch (ret) { case 1: cout << "源buf出错!" << endl; break; case 2: cout << "目的buf出错!" << endl; case 3: cout << "拷贝过程出错!" << endl; default: cout << "未知错误" << endl; break; } } cout << "buf2 = " << buf2 << endl; system("pause"); return 0; }
用异常解决:
#include<iostream> using namespace std; //传统的处理机制 //throw int 类型异常 void my_strcopy2(char* from, char* to) { if (from == NULL) throw 1; if (to == NULL) throw 2; //拷贝场景检查 if (*from == 'a') throw 3; while (*from != '\0') { *to = *from; to ++; from ++; } *to = '\0'; } //throw char 类型异常 void my_strcopy1(char* from, char* to) { if (from == NULL) throw "源buf出错"; if (to == NULL) throw "目的buf出错"; //拷贝场景检查 if (*from == 'a') throw "copy时出错"; while (*from != '\0') { *to = *from; to++; from++; } *to = '\0'; } class BadSrcType{}; class BadDestType{}; class BadProcessType{}; //throw 类对象类型异常 void my_strcopy3(char* from, char* to) { if (from == NULL) throw BadSrcType(); //会不会产生匿名对象 if (to == NULL) throw BadDestType(); //拷贝场景检查 if (*from == 'a') throw BadProcessType(); while (*from != '\0') { *to = *from; to++; from++; } *to = '\0'; } int main() { int ret = 0; char buf1[] = "abcdefg"; char buf2[1024] = { 0 }; try { my_strcopy3(buf1, buf2); } catch (int e )//变量名可以写可以不写 { cout << "int类型异常" << endl; } catch (char *e) { cout << e << "char*类型异常" << endl; } //--- catch (BadSrcType e)//是把匿名对象拷贝给e,还是e直接就是匿名对象 { cout << "BadSrcType类型异常" << endl; } catch (BadDestType e) { cout << "BadDestType类型异常" << endl; } catch (BadProcessType e) { cout << "BadProcessType类型异常" << endl; } //-- catch (...) { cout << "未知异常 " << endl; } system("pause"); return 0; }
接下来解决代码中提出的问题:
catch (BadSrcType e)//是把匿名对象拷贝给e,还是e直接就是匿名对象
先添加完类的定义:
class BadProcessType { public: BadProcessType() { cout << "BadProcessType构造函数do \n"; } BadProcessType(const BadProcessType& obj) { cout << "BadProcessType拷贝构造函数do \n"; } ~BadProcessType() { cout << "BadProcessType析构函数do \n"; } };
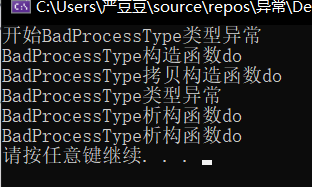
结论1:如果 接受异常的时候,使用一个异常变量,则拷贝构造异常变量
接下来测试引用:
catch (BadProcessType &e) { cout << "BadProcessType类型异常" << endl; }
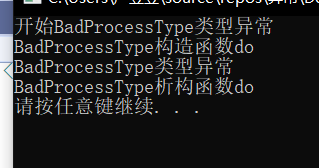 没有拷贝新的变量
没有拷贝新的变量
结论2:如果使用引用,会使用throw的那个对象
下面测试指针:
catch (BadProcessType &e) { cout << "BadProcessType类型异常" << endl; } catch (BadProcessType* e) { cout << "BadProcessType类型异常" << endl; }
结论3:指针可以和引用和元素写在一块,但是元素和引用不能写在一块
此时抛出异常时应该抛出地址:
if (*from == 'b') throw& (BadProcessType());
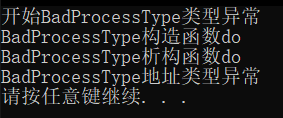
此时因为析构函数已经完成,指针变成了野指针。
所以指针应当这样抛出:
if (*from == 'c') throw new BadProcessType;
catch (BadProcessType* e) { cout << "BadProcessType地址类型异常" << endl; delete e; }
略烦,所以最好选择引用来抓取异常。所有操作都自动处理。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号