redis源码分析(4)-- 基本数据结构字典dict
一、字典结构
Redis中字典采用hash表结构,如下:
typedef struct dictht { dictEntry **table; // hash表数组 unsigned long size; // hash表大小 unsigned long sizemask; // 掩码 unsigned long used; // 已经使用的大小 } dictht;
table是一个数组,每个元素指向一个dictEntry结构。size表示hash表大小,used表示使用的大小。一个size=4的空hash表如下:

dictEntry是一个key-value pair, 定义为:
1 typedef struct dictEntry { 2 void *key; // key 3 union { 4 void *val; 5 uint64_t u64; 6 int64_t s64; 7 double d; 8 } v; // value 9 struct dictEntry *next; // 指向下一个key-value 10 } dictEntry;
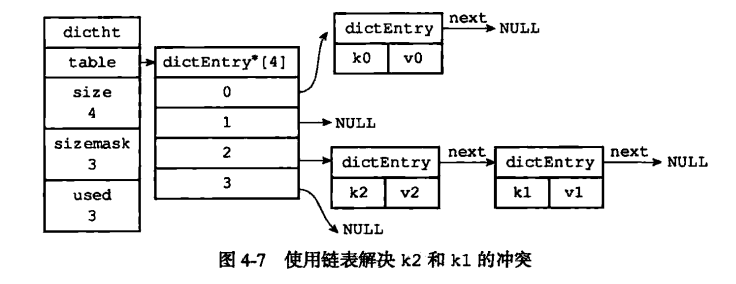
next指针用于解决hash冲突,redis总采用直接链址法解决冲突。举例:

Redis中字典定义:
typedef struct dict { dictType *type; // type和privdata区别操作不同类型key-value void *privdata; dictht ht[2]; long rehashidx; /* rehashing not in progress if rehashidx == -1 */ int iterators; /* number of iterators currently running */ } dict;
ht[2]中一般只有ht[0]使用,ht[1]在rehash时使用,ht[1]和rehashindex使用后续介绍。

二、hash实现
Redis中使用的hash函数为MurmurHash2, 定义为:
1 unsigned int dictGenHashFunction(const void *key, int len)
通过宏定义:
1 #define dictHashKey(d, key) (d)->type->hashFunction(key)
获取hashkey的值,之后使用:
1 idx = hashkey & d->ht[table].sizemask;
得到hash桶的坐标, 如图:
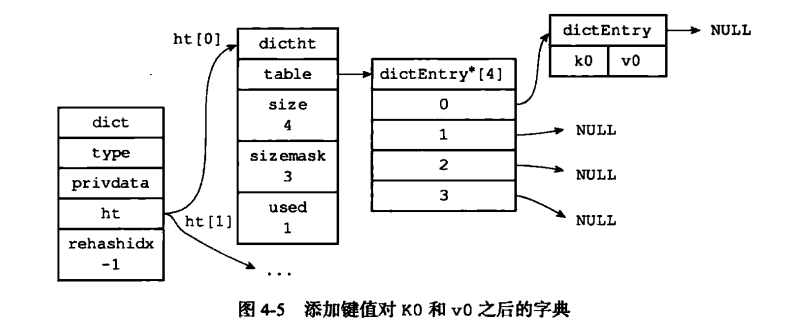
Redis中使用直接链址法解决冲突,如图:
三、Rehash
在函数_dictExpandIfNeeded中会判断是否需要扩展hash表:
static int _dictExpandIfNeeded(dict *d) { /* Incremental rehashing already in progress. Return. */ if (dictIsRehashing(d)) return DICT_OK; /* If the hash table is empty expand it to the initial size. */ if (d->ht[0].size == 0) return dictExpand(d, DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE); /* If we reached the 1:1 ratio, and we are allowed to resize the hash * table (global setting) or we should avoid it but the ratio between * elements/buckets is over the "safe" threshold, we resize doubling * the number of buckets. */ if (d->ht[0].used >= d->ht[0].size && (dict_can_resize || d->ht[0].used/d->ht[0].size > dict_force_resize_ratio)) { return dictExpand(d, d->ht[0].used*2); } return DICT_OK; }
可以看出,当利用率used/size到某个比例时,开始执行hash表扩展,进行rehash。流程为:
1 int dictRehash(dict *d, int n) { 2 int empty_visits = n*10; /* Max number of empty buckets to visit. */ 3 if (!dictIsRehashing(d)) return 0; 4 5 while(n-- && d->ht[0].used != 0) { 6 dictEntry *de, *nextde; 7 8 /* Note that rehashidx can't overflow as we are sure there are more 9 * elements because ht[0].used != 0 */ 10 assert(d->ht[0].size > (unsigned long)d->rehashidx); 11 while(d->ht[0].table[d->rehashidx] == NULL) { 12 d->rehashidx++; 13 if (--empty_visits == 0) return 1; 14 } 15 de = d->ht[0].table[d->rehashidx]; 16 /* Move all the keys in this bucket from the old to the new hash HT */ 17 while(de) { 18 unsigned int h; 19 20 nextde = de->next; 21 /* Get the index in the new hash table */ 22 h = dictHashKey(d, de->key) & d->ht[1].sizemask; 23 de->next = d->ht[1].table[h]; 24 d->ht[1].table[h] = de; 25 d->ht[0].used--; 26 d->ht[1].used++; 27 de = nextde; 28 } 29 d->ht[0].table[d->rehashidx] = NULL; 30 d->rehashidx++; 31 } 32 33 /* Check if we already rehashed the whole table... */ 34 if (d->ht[0].used == 0) {// 迁移完毕,更新ht[0] 35 zfree(d->ht[0].table); 36 d->ht[0] = d->ht[1]; 37 _dictReset(&d->ht[1]); 38 d->rehashidx = -1; 39 return 0; 40 } 41 42 /* More to rehash... */ 43 return 1; 44 }
把ht[0]上的数据逐步迁移到ht[1].
四、字典主要API


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号