LeeCode 二叉树问题(一)
二叉树的遍历
二叉树节点定义
public class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode() {}
TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
LeeCode 144: 二叉树的前序遍历
题目描述
给你一棵二叉树的根节点
root,返回其节点值的前序遍历。
Java代码实现
递归实现
public List<Integer> preorderRecursive(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
preorderRecursiveImpl(root, res);
return res;
}
public void preorderRecursiveImpl(TreeNode root, List<Integer> res) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
res.add(root.val);
preorderRecursiveImpl(root.left, res);
preorderRecursiveImpl(root.right, res);
return;
}
迭代实现
递归实现本质上是维护了一个隐藏的栈结构,而在迭代时需要手动维护。
public List<Integer> preorderIterative(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) {
return res;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
/**
* 添加顺序: 根 -> 左 -> 右
*/
while (root != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while (root != null) {
res.add(root.val);
stack.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
root = stack.pop();
root = root.right;
}
return res;
}
Morris 实现
public List<Integer> preorderMorris(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
TreeNode cur = root;
TreeNode prev = null;
while (cur != null) {
// 当前节点没有左子节点,则直接访问当前节点,并将指针指向右子节点
if (cur.left == null) {
res.add(cur.val);
cur = cur.right; // 通过 cur.right 返回父节点
continue;
}
prev = cur.left;
// 寻找当前节点左子节点的最右子结点
while (prev.right != null && prev.right != cur) {
prev = prev.right;
}
if (prev.right == null) {
prev.right = cur;
res.add(cur.val); // 前序访问根节点
cur = cur.left;
}
else {
prev.right = null;
cur = cur.right;
}
}
return res;
}
LeeCode 94: 二叉树的中序遍历
题目描述
给你一棵二叉树的根节点
root,返回其节点值的中序遍历。
Java代码实现
递归实现
public List<Integer> inorderRecursive(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
inorderRecursiveImpl(root, res);
return res;
}
public void inorderRecursiveImpl(TreeNode root, List<Integer> res) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
inorderRecursiveImpl(root.left, res);
res.add(root.val);
inorderRecursiveImpl(root.right, res);
return;
}
迭代实现
public List<Integer> inorderIterative(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) {
return res;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
/**
* 添加顺序: 左 -> 根 -> 右
*/
while (root != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while (root != null) {
stack.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
root = stack.pop();
res.add(root.val);
root = root.right;
}
return res;
}
Morris 实现
Morris实现的核心想法是找到当前节点的左子节点的最右子结点,即当前节点中序遍历的前一个节点。
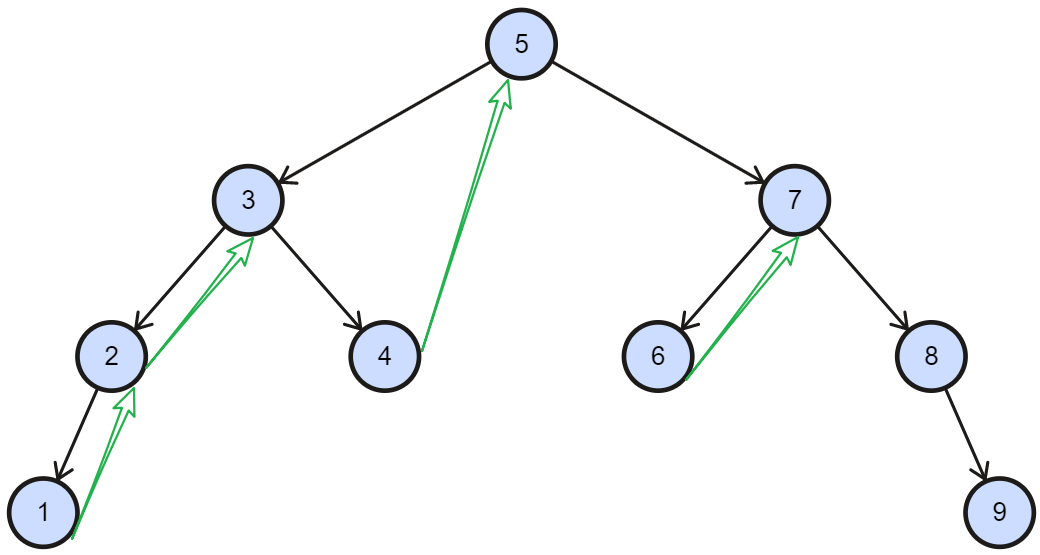
public List<Integer> inorderMorris(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
TreeNode cur = root;
TreeNode prev = null;
while (cur != null) {
// 当前节点没有左子节点,则直接访问该节点,然后将指针指向右子结点
if (cur.left == null) {
res.add(cur.val);
cur = cur.right; // 通过 cur.right 返回父节点
continue;
}
prev = cur.left;
// 寻找当前节点左子节点的最右子结点,即中序遍历中当前节点的前一个节点
while (prev.right != null && prev.right != cur) {
prev = prev.right;
}
if (prev.right == null) {
prev.right = cur;
cur = cur.left;
}
else {
prev.right = null;
res.add(cur.val); // 中序访问根节点
cur = cur.right;
}
}
return res;
}
LeeCode 145: 二叉树的后序遍历
题目描述
给你一棵二叉树的根节点
root,返回其节点值的后序遍历。
Java代码实现
递归实现
public List<Integer> postorderRecursive(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
postorderRecursiveImpl(root, res);
return res;
}
public void postorderRecursiveImpl(TreeNode root, List<Integer> res) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
postorderRecursiveImpl(root.left, res);
postorderRecursiveImpl(root.right, res);
res.add(root.val);
return;
}
迭代实现
public List<Integer> postorderIterative(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) {
return res;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode previous = null;
/**
* 添加顺序: 左 -> 右 -> 根
*/
while (root != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while (root != null) {
stack.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
root = stack.pop();
// 若右子树为空 或 右子树已经访问过,则添加根节点值
if (root.right == null || root.right == previous) {
res.add(root.val);
previous = root;
root = null;
}
else {
stack.push(root);
root = root.right;
}
}
return res;
}
LeeCode 102: 二叉树的层序遍历
题目描述
给你一棵二叉树的根节点
root,返回其节点值的层序遍历。(即逐层地从左到右访问所有节点)。
建立模型
- 这是一个广度优先搜索的问题,先遍历顶层所有节点,再往下遍历
- 使用一个队列来维护遍历的节点
- 使用变量
size记录当前层节点个数
代码实现
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) {
return res;
}
// 使用基于双向链表实现的队列维护
Deque<TreeNode> deque = new LinkedList<>();
deque.offer(root); // 添加到队尾
while (!deque.isEmpty()) {
int size = deque.size();
List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode node = deque.poll(); // 从队首取出
temp.add(node.val);
if (node.left != null) {
deque.offer(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
deque.offer(node.right);
}
}
res.add(new ArrayList<>(temp));
}
return res;
}

