单例集合List和Set
首先了解集合框架构成:
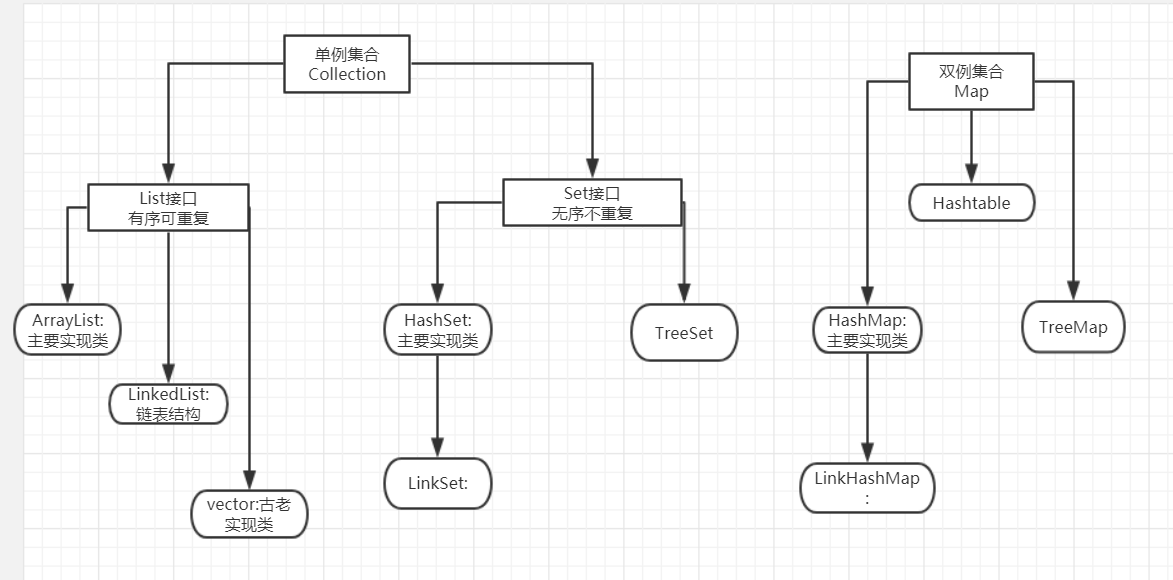
首先了解到List与Set是单例集合Collection接口的两个重要子接口
1.LIst:有序,可重复的接口
---->ArrayList:主要实现类,底层使用Object[] 存储,效率高,但线程不安全
Collections工具类中提供了将ArrayList转换为线程安全的方法
---->LinkedList: 频繁的插入和删除操作,使用该类,因为效率高,底层使用双向链表实现
---->Vector ;底层使用Object[] 存储,效率低,但线程安全
面试题:你如何区分List接口下的三个实现类
ArrayList源码分析:jdk7:
1.1ArrayList:主要实现类,底层使用Objec[ ]存储,效率高,但线程不安全
package list; /* * 增:add() * 删:remove() * 改:set(int index ,Object ele) * 查:get(int index) * 插:add(int index ,Object ele) * 遍历:iterator/增强for循环 */ import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.List; import org.junit.Test; public class ListTest { @Test public void test1() { List list =new ArrayList<>(); list.add(123456); list.add(1, 66); System.out.println(list); //list.remove(1); System.out.println(list); System.out.println(list.size()); list.set(1, new String[]{"123","11"}); /*for (Object obj : list) { System.out.println(obj); }*/ Iterator it =list.iterator(); while (it.hasNext()) { System.out.println(it.next()); } } }
2. Set:不可重复,无序性的接口
|--->HashSet:主要实现类,底层使用的数据结构,主要是hashMap()实现
--->LinkedHashSet:HashSet的子类:底层使用数据结构+链表;可以按照添加元素的顺序实现遍历
|--->TreeSet:底层使用红黑树实现;按照添加元素的指定属性大小实现遍历
set在继承Collection基础上没有定义额外的方法
无序性:指的是添加数据是,不是依次紧密排列
不可重复性:添加到Set中的元素是不可重复的----->重写hashcode方法获取hash值,确保不重复
set在开发中用来去重,确保重写的hashcode方法和equals方法一致
package list; import java.util.HashSet; import java.util.Set; import org.junit.Test; /* * Set接口:存储是无序的,不可重复的 * |--->HashSet:主要实现类,底层使用的数据结构 * --->LinkedHashSet:HashSet的子类:底层使用数据结构+链表;可以按照添加元素的顺序实现遍历 * |--->TreeSet:底层使用红黑树实现;按照添加元素的指定属性大小实现遍历 * * set在继承Collection基础上没有定义额外的方法 * 无序性:指的是添加数据是,不是依次紧密排列 * 不可重复性:添加到Set中的元素是不可重复的----->重写hashcode方法获取hash值,确保不重复 * set在开发中用来去重,确保重写的hash方法和equals方法一致 */ public class SetTest { @Test public void test1(){ Set set=new HashSet<>(); set.add("aa"); set.add("ss"); set.add("dd"); set.add("dds"); set.add("dxs"); set.add(new Person("tom", 13)); set.add(new Person("tom", 13)); for (Object object : set) { System.out.println(object); } } }
TreeSet:向TreeSet中添加数据,必须是同一个类创建的对象 ,必须指定排序方式
例如:定义一个person类,使用TreeSet集合装person类对象的数据,必须先重写该person类的hashCode方法和equals方法
在使用TreeSet()时,确定他的排序方式,是自然排序还是自定义排序
TreeSet指定自然排序,添加的数据必须是同一个类创建的对象,必须重写Equals()方法和hashCode()方法
package list; import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.instanceOf; public class Person implements Comparable { private String name; private int age; public Person() { super(); // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } public Person(String name, int age) { super(); this.name = name; this.age = age; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } @Override public String toString() { return "Person [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]"; } //重写hashcode方法和equals方法 @Override public int hashCode() { final int prime = 31; int result = 1; result = prime * result + age; result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode()); return result; } @Override public boolean equals(Object obj) { if (this == obj) return true; if (obj == null) return false; if (getClass() != obj.getClass()) return false; Person other = (Person) obj; if (age != other.age) return false; if (name == null) { if (other.name != null) return false; } else if (!name.equals(other.name)) return false; return true; } //定义自然排序 @Override public int compareTo(Object o) { if (this ==o) { return 0; } if (o instanceof Person) { Person p1=(Person) o; if( this.age-p1.age==0) { return this.name.compareTo(p1.name); } } throw new RuntimeException(); } }
TreeSet指定定制排序,添加的数据必须是同一个类创建的对象,必须重写Equals()方法和hashCode()方法
/* * 要求:向TreeSet中添加的数据,必须是同一个类创建的对象 * 向TreeSet中添加数据,必须指定排序方式 */ public class TreeSetTest { public void test() { Set s=new TreeSet(); s.add(new Person("jacklbo", 15)); s.add(new Person("jaclbo", 15)); s.add(new Person("lbo", 15)); s.add(new Person("onglbo", 15)); s.add(new Person("tonglbo", 15)); for (Object object : s) { System.out.println(object); } } @Test public void test1() { Set s=new TreeSet(); s.add(new Person("jacklbo", 15)); s.add(new Person("jaclbo", 15)); s.add(new Person("lbo", 15)); s.add(new Person("onglbo", 15)); s.add(new Person("tonglbo", 15));
Comparator com=new Comparator() { //实现compartor,定制排序 @Override public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) { if (o1 instanceof Person && o2 instanceof Person) { Person p1=(Person) o1; Person p2=(Person) o2; return p1.getName().compareTo(p2.getName()); } return 0; } }; for (Object object : s) { System.out.println(object); } } }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号