Python之路--Python基础11--并发编程之线程
一、threading模块介绍
multiprocess模块的完全模仿了threading模块的接口,二者在使用层面,有很大的相似性,因而不再详细介绍
官网链接:https://docs.python.org/3/library/threading.html?highlight=threading#
二、开启线程的两种方式
#方式一
from threading import Thread
import time
def sayhi(name):
time.sleep(2)
print('%s say hello' %name)
if __name__ == '__main__':
t=Thread(target=sayhi,args=('egon',))
t.start()
print('主线程')
#方式二
from threading import Thread
import time
class Sayhi(Thread):
def __init__(self,name):
super().__init__()
self.name=name
def run(self):
time.sleep(2)
print('%s say hello' % self.name)
if __name__ == '__main__':
t = Sayhi('egon')
t.start()
print('主线程')
三、在一个进程下开启多个线程与在一个进程下开启多个子进程的区别
在同一个进程下面,线程开启的速度比进程开启的速度快。
from threading import Thread
from multiprocessing import Process
import os
def work():
print('hello')
if __name__ == '__main__':
#在主进程下开启线程
t=Thread(target=work)
t.start()
print('主线程/主进程')
'''
打印结果:
hello
主线程/主进程
'''
#在主进程下开启子进程
t=Process(target=work)
t.start()
print('主线程/主进程')
'''
打印结果:
主线程/主进程
hello
'''
线程的pid与主进程的pid相同,每个子进程pid都跟主进程的pid不同
from threading import Thread
from multiprocessing import Process
import os
def work():
print('hello',os.getpid())
if __name__ == '__main__':
#part1:在主进程下开启多个线程,每个线程都跟主进程的pid一样
t1=Thread(target=work)
t2=Thread(target=work)
t1.start()
t2.start()
print('主线程/主进程pid',os.getpid())
#part2:开多个进程,每个进程都有不同的pid
p1=Process(target=work)
p2=Process(target=work)
p1.start()
p2.start()
print('主线程/主进程pid',os.getpid())
# hello 11148
# hello 11148
# 主线程/主进程pid 11148
# 主线程/主进程pid 11148
# hello 11484
# hello 1208
同一进程内的线程共享该进程的数据
from threading import Thread
from multiprocessing import Process
import os
def work():
global n
n=0
if __name__ == '__main__':
# n=100
# p=Process(target=work)
# p.start()
# p.join()
# print('主',n) #毫无疑问子进程p已经将自己的全局的n改成了0,但改的仅仅是它自己的,查看父进程的n仍然为100
n=1
t=Thread(target=work)
t.start()
t.join()
print('主',n) #查看结果为0,因为同一进程内的线程之间共享进程内的数据
四、线程相关方法
Thread实例对象的方法
# isAlive(): 返回线程是否活动的。
# getName(): 返回线程名。
# setName(): 设置线程名。
threading模块提供的一些方法:
# threading.currentThread(): 返回当前的线程变量。
# threading.enumerate(): 返回一个包含正在运行的线程的list。正在运行指线程启动后、结束前,不包括启动前和终止后的线程。
# threading.activeCount(): 返回正在运行的线程数量,与len(threading.enumerate())有相同的结果。
from threading import Thread
import threading
from multiprocessing import Process
import os
def work():
import time
time.sleep(3)
print(threading.current_thread().getName())
if __name__ == '__main__':
#在主进程下开启线程
t=Thread(target=work)
t.start()
print(threading.current_thread().getName())
print(threading.current_thread()) #主线程
print(threading.enumerate()) #连同主线程在内有两个运行的线程
print(threading.active_count())
print('主线程/主进程')
'''
打印结果:
MainThread
<_MainThread(MainThread, started 140735268892672)>
[<_MainThread(MainThread, started 140735268892672)>, <Thread(Thread-1, started 123145307557888)>]
主线程/主进程
Thread-1
'''
主线程等待子线程结束
from threading import Thread
import time
def sayhi(name):
time.sleep(2)
print('%s say hello' %name)
if __name__ == '__main__':
t=Thread(target=sayhi,args=('egon',))
t.start()
t.join()
print('主线程')
print(t.is_alive())
'''
egon say hello
主线程
False
'''
五、守护线程
无论是进程还是线程,都遵循:守护xxx会等待主xxx运行完毕后被销毁
需要强调的是:运行完毕并非终止运行
对主进程来说,运行完毕指的是主进程代码运行完毕
对主线程来说,运行完毕指的是主线程所在的进程内所有非守护线程统统运行完毕,主线程才算运行完毕
主进程在其代码结束后就已经算运行完毕了(守护进程在此时就被回收),然后主进程会一直等非守护的子进程都运行完毕后回收子进程的资源(否则会产生僵尸进程),才会结束,
主线程在其他非守护线程运行完毕后才算运行完毕(守护线程在此时就被回收)。因为主线程的结束意味着进程的结束,进程整体的资源都将被回收,而进程必须保证非守护线程都运行完毕后才能结束。
from threading import Thread
import time
def sayhi(name):
time.sleep(2)
print('%s say hello' %name)
if __name__ == '__main__':
t=Thread(target=sayhi,args=('egon',))
t.setDaemon(True) #必须在t.start()之前设置
t.start()
print('主线程')
print(t.is_alive())
'''
主线程
True
'''
#诱惑人的栗子
from threading import Thread
import time
def foo():
print(123)
time.sleep(1)
print("end123")
def bar():
print(456)
time.sleep(3)
print("end456")
t1=Thread(target=foo)
t2=Thread(target=bar)
t1.daemon=True
t1.start()
t2.start()
print("main-------")
六、Python GIL(Global Interpreter Lock)
GIL本质就是一把互斥锁,既然是互斥锁,所有互斥锁的本质都一样,都是将并发运行变成串行,以此来控制同一时间内共享数据只能被一个任务所修改,进而保证数据安全。
有了GIL的存在,同一时刻同一进程中只有一个线程被执行,看到这里,有的同学立马质问:进程可以利用多核,但是开销大,而python的多线程开销小,但却无法利用多核优势。
要解决这个问题,我们需要在几个点上达成一致:
1. cpu到底是用来做计算的,还是用来做I/O的?
2. 多cpu,意味着可以有多个核并行完成计算,所以多核提升的是计算性能
3. 每个cpu一旦遇到I/O阻塞,仍然需要等待,所以多核对I/O操作没什么用处
一个工人相当于cpu,此时计算相当于工人在干活,I/O阻塞相当于为工人干活提供所需原材料的过程,工人干活的过程中如果没有原材料了,则工人干活的过程需要停止,直到等待原材料的到来。如果你的工厂干的大多数任务都要有准备原材料的过程(I/O密集型),那么你有再多的工人,意义也不大,还不如一个人,在等材料的过程中让工人去干别的活,反过来讲,如果你的工厂原材料都齐全,那当然是工人越多,效率越高
结论:
对计算来说,cpu越多越好,但是对于I/O来说,再多的cpu也没用
当然对运行一个程序来说,随着cpu的增多执行效率肯定会有所提高(不管提高幅度多大,总会有所提高),这是因为一个程序基本上不会是纯计算或者纯I/O,所以我们只能相对的去看一个程序到底是计算密集型还是I/O密集型,从而进一步分析python的多线程到底有无用武之地。
分析:
我们有四个任务需要处理,处理方式肯定是要玩出并发的效果,解决方案可以是:
方案一:开启四个进程
方案二:一个进程下,开启四个线程
单核情况下,分析结果:
如果四个任务是计算密集型,没有多核来并行计算,方案一徒增了创建进程的开销,方案二胜
如果四个任务是I/O密集型,方案一创建进程的开销大,且进程的切换速度远不如线程,方案二胜
多核情况下,分析结果:
如果四个任务是计算密集型,多核意味着并行计算,在python中一个进程中同一时刻只有一个线程执行用不上多核,方案一胜
如果四个任务是I/O密集型,再多的核也解决不了I/O问题,方案二胜
结论:现在的计算机基本上都是多核,python对于计算密集型的任务开多线程的效率并不能带来多大性能上的提升,甚至不如串行(没有大量切换),但是,对于IO密集型的任务效率还是有显著提升的。
多线程性能测试
#计算密集型:多进程效率高
from multiprocessing import Process
from threading import Thread
import os,time
def work():
res=0
for i in range(100000000):
res*=i
if __name__ == '__main__':
l=[]
print(os.cpu_count()) #本机为4核
start=time.time()
for i in range(4):
p=Process(target=work) #耗时5s多
#p=Thread(target=work) #耗时18s多
l.append(p)
p.start()
for p in l:
p.join()
stop=time.time()
print('run time is %s' %(stop-start))
#I/O密集型:多线程效率高
from multiprocessing import Process
from threading import Thread
import threading
import os,time
def work():
time.sleep(2)
print('===>')
if __name__ == '__main__':
l=[]
print(os.cpu_count()) #本机为4核
start=time.time()
for i in range(400):
# p=Process(target=work) #耗时12s多,大部分时间耗费在创建进程上
p=Thread(target=work) #耗时2s多
l.append(p)
p.start()
for p in l:
p.join()
stop=time.time()
print('run time is %s' %(stop-start))
应用:
多线程用于IO密集型,如socket,爬虫,web
多进程用于计算密集型,如金融分析
七、同步锁
三个需要注意的点:
1.线程抢的是GIL锁,GIL锁相当于执行权限,拿到执行权限后才能拿到互斥锁Lock,其他线程也可以抢到GIL,但如果发现Lock仍然没有被释放则阻塞,即便是拿到执行权限GIL也要立刻交出来
2.join是等待所有,即整体串行,而锁只是锁住修改共享数据的部分,即部分串行,要想保证数据安全的根本原理在于让并发变成串行,join与互斥锁都可以实现,毫无疑问,互斥锁的部分串行效率要更高
3. 一定要看本小节最后的GIL与互斥锁的经典分析
GIL VS Lock
机智的同学可能会问到这个问题,就是既然你之前说过了,Python已经有一个GIL来保证同一时间只能有一个线程来执行了,为什么这里还需要lock?
首先我们需要达成共识:锁的目的是为了保护共享的数据,同一时间只能有一个线程来修改共享的数据
然后,我们可以得出结论:保护不同的数据就应该加不同的锁。
最后,问题就很明朗了,GIL 与Lock是两把锁,保护的数据不一样,前者是解释器级别的(当然保护的就是解释器级别的数据,比如垃圾回收的数据),后
者是保护用户自己开发的应用程序的数据,很明显GIL不负责这件事,只能用户自定义加锁处理,即Lock
过程分析:所有线程抢的是GIL锁,或者说所有线程抢的是执行权限
线程1抢到GIL锁,拿到执行权限,开始执行,然后加了一把Lock,还没有执行完毕,即线程1还未释放Lock,有可能线程2抢到GIL锁,开始执行,执行过
程中发现Lock还没有被线程1释放,于是线程2进入阻塞,被夺走执行权限,有可能线程1拿到GIL,然后正常执行到释放Lock。。。这就导致了串行运行的效果
既然是串行,那我们执行
t1.start()
t1.join
t2.start()
t2.join()
这也是串行执行啊,为何还要加Lock呢,需知join是等待t1所有的代码执行完,相当于锁住了t1的所有代码,而Lock只是锁住一部分操作共享数据的代码。
from threading import Thread
import os,time
def work():
global n
temp=n
time.sleep(0.1)
n=temp-1
if __name__ == '__main__':
n=100
l=[]
for i in range(100):
p=Thread(target=work)
l.append(p)
p.start()
for p in l:
p.join()
print(n) #结果可能为99
锁通常被用来实现对共享资源的同步访问。为每一个共享资源创建一个Lock对象,当你需要访问该资源时,调用acquire方法来获取锁对象(如果其它线程已经获得了该锁,则当前线程需等待其被释放),待资源访问完后,再调用release方法释放锁:
#模板
import threading
R=threading.Lock()
R.acquire()
'''
对公共数据的操作
'''
R.release()
栗子:
from threading import Thread,Lock
import os,time
def work():
global n
lock.acquire()
temp=n
time.sleep(0.1)
n=temp-1
lock.release()
if __name__ == '__main__':
lock=Lock()
n=100
l=[]
for i in range(100):
p=Thread(target=work)
l.append(p)
p.start()
for p in l:
p.join()
print(n) #结果肯定为0,由原来的并发执行变成串行,牺牲了执行效率保证了数据安全
分析:
1.100个线程去抢GIL锁,即抢执行权限
2. 肯定有一个线程先抢到GIL(暂且称为线程1),然后开始执行,一旦执行就会拿到lock.acquire()
3. 极有可能线程1还未运行完毕,就有另外一个线程2抢到GIL,然后开始运行,但线程2发现互斥锁lock还未被线程1释放,于是阻塞,被迫交出执行权限,即释放GIL
4.直到线程1重新抢到GIL,开始从上次暂停的位置继续执行,直到正常释放互斥锁lock,然后其他的线程再重复2 3 4的过程
#不加锁:并发执行,速度快,数据不安全
from threading import current_thread,Thread,Lock
import os,time
def task():
global n
print('%s is running' %current_thread().getName())
temp=n
time.sleep(0.5)
n=temp-1
if __name__ == '__main__':
n=100
lock=Lock()
threads=[]
start_time=time.time()
for i in range(100):
t=Thread(target=task)
threads.append(t)
t.start()
for t in threads:
t.join()
stop_time=time.time()
print('主:%s n:%s' %(stop_time-start_time,n))
'''
Thread-1 is running
Thread-2 is running
......
Thread-100 is running
主:0.5216062068939209 n:99
'''
#不加锁:未加锁部分并发执行,加锁部分串行执行,速度慢,数据安全
from threading import current_thread,Thread,Lock
import os,time
def task():
#未加锁的代码并发运行
time.sleep(3)
print('%s start to run' %current_thread().getName())
global n
#加锁的代码串行运行
lock.acquire()
temp=n
time.sleep(0.5)
n=temp-1
lock.release()
if __name__ == '__main__':
n=100
lock=Lock()
threads=[]
start_time=time.time()
for i in range(100):
t=Thread(target=task)
threads.append(t)
t.start()
for t in threads:
t.join()
stop_time=time.time()
print('主:%s n:%s' %(stop_time-start_time,n))
'''
Thread-1 is running
Thread-2 is running
......
Thread-100 is running
主:53.294203758239746 n:0
'''
#有的同学可能有疑问:既然加锁会让运行变成串行,那么我在start之后立即使用join,就不用加锁了啊,也是串行的效果啊
#没错:在start之后立刻使用jion,肯定会将100个任务的执行变成串行,毫无疑问,最终n的结果也肯定是0,是安全的,但问题是
#start后立即join:任务内的所有代码都是串行执行的,而加锁,只是加锁的部分即修改共享数据的部分是串行的
#单从保证数据安全方面,二者都可以实现,但很明显是加锁的效率更高.
from threading import current_thread,Thread,Lock
import os,time
def task():
time.sleep(3)
print('%s start to run' %current_thread().getName())
global n
temp=n
time.sleep(0.5)
n=temp-1
if __name__ == '__main__':
n=100
lock=Lock()
start_time=time.time()
for i in range(100):
t=Thread(target=task)
t.start()
t.join()
stop_time=time.time()
print('主:%s n:%s' %(stop_time-start_time,n))
'''
Thread-1 start to run
Thread-2 start to run
......
Thread-100 start to run
主:350.6937336921692 n:0 #耗时是多么的恐怖
'''
八、死锁现象与递归锁
进程也有死锁与递归锁,在进程那里忘记说了,放到这里一起说。
所谓死锁: 是指两个或两个以上的进程或线程在执行过程中,因争夺资源而造成的一种互相等待的现象,若无外力作用,它们都将无法推进下去。此时称系统处于死锁状态或系统产生了死锁,这些永远在互相等待的进程称为死锁进程,如下就是死锁。
from threading import Thread,Lock
import time
mutexA=Lock()
mutexB=Lock()
class MyThread(Thread):
def run(self):
self.func1()
self.func2()
def func1(self):
mutexA.acquire()
print('\033[41m%s 拿到A锁\033[0m' %self.name)
mutexB.acquire()
print('\033[42m%s 拿到B锁\033[0m' %self.name)
mutexB.release()
mutexA.release()
def func2(self):
mutexB.acquire()
print('\033[43m%s 拿到B锁\033[0m' %self.name)
time.sleep(2)
mutexA.acquire()
print('\033[44m%s 拿到A锁\033[0m' %self.name)
mutexA.release()
mutexB.release()
if __name__ == '__main__':
for i in range(10):
t=MyThread()
t.start()
'''
Thread-1 拿到A锁
Thread-1 拿到B锁
Thread-1 拿到B锁
Thread-2 拿到A锁
然后就卡住,死锁了
'''
解决方法,递归锁,在Python中为了支持在同一线程中多次请求同一资源,python提供了可重入锁RLock。
这个RLock内部维护着一个Lock和一个counter变量,counter记录了acquire的次数,从而使得资源可以被多次require。直到一个线程所有的acquire都被release,其他的线程才能获得资源。上面的例子如果使
用RLock代替Lock,则不会发生死锁:
mutexA=mutexB=threading.RLock()
#一个线程拿到锁,counter加1,该线程内又碰到加锁的情况,则counter继续加1,这期间所有其他线程都只能等待,等待该线程释放所有锁,即counter递减到0为止。
九、信号量Semaphore
同进程的一样Semaphore管理一个内置的计数器,每当调用acquire()时内置计数器-1;调用release() 时内置计数器+1;计数器不能小于0;当计数器为0时,
acquire()将阻塞线程直到其他线程调用release()。
实例:(同时只有5个线程可以获得semaphore,即可以限制最大连接数为5):
from threading import Thread,Semaphore
import threading
import time
# def func():
# if sm.acquire():
# print (threading.currentThread().getName() + ' get semaphore')
# time.sleep(2)
# sm.release()
def func():
sm.acquire()
print('%s get sm' %threading.current_thread().getName())
time.sleep(3)
sm.release()
if __name__ == '__main__':
sm=Semaphore(5)
for i in range(23):
t=Thread(target=func)
t.start()
与进程池是完全不同的概念,进程池Pool(4),最大只能产生4个进程,而且从头到尾都只是这四个进程,不会产生新的,而信号量是产生一堆线程/进程
十、Event
同进程的一样,线程的一个关键特性是每个线程都是独立运行且状态不可预测。如果程序中的其他线程需要通过判断某个线程的状态来确定自己下一步的操
作,这时线程同步问题就会变得非常棘手。为了解决这些问题,我们需要使用threading库中的Event对象。 对象包含一个可由线程设置的信号标志,它允许线程等待
某些事件的发生。在初始情况下,Event对象中的信号标志被设置为假。如果有线程等待一个Event对象, 而这个Event对象的标志为假,那么这个线程将会被一直阻
塞直至该标志为真。一个线程如果将一个Event对象的信号标志设置为真,它将唤醒所有等待这个Event对象的线程。如果一个线程等待一个已经被设置为真的
Event对象,那么它将忽略这个事件, 继续执行。
方法介绍:
event.isSet():返回event的状态值;
event.wait():如果 event.isSet()==False将阻塞线程;
event.set(): 设置event的状态值为True,所有阻塞池的线程激活进入就绪状态, 等待操作系统调度;
event.clear():恢复event的状态值为False。
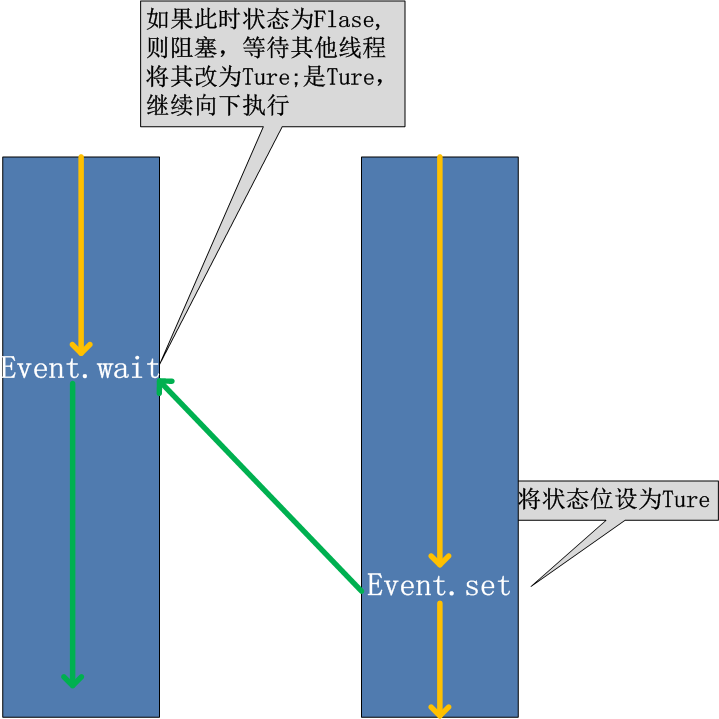
例如,有多个工作线程尝试链接MySQL,我们想要在链接前确保MySQL服务正常才让那些工作线程去连接MySQL服务器,如果连接不成功,都会去尝试重新连接。那么我们就可以采用threading.Event机制来协调各个工作线程的连接操作
from threading import Thread,Event
import threading
import time,random
def conn_mysql():
count=1
while not event.is_set():
if count > 3:
raise TimeoutError('链接超时')
print('<%s>第%s次尝试链接' % (threading.current_thread().getName(), count))
event.wait(0.5)
count+=1
print('<%s>链接成功' %threading.current_thread().getName())
def check_mysql():
print('\033[45m[%s]正在检查mysql\033[0m' % threading.current_thread().getName())
time.sleep(random.randint(2,4))
event.set()
if __name__ == '__main__':
event=Event()
conn1=Thread(target=conn_mysql)
conn2=Thread(target=conn_mysql)
check=Thread(target=check_mysql)
conn1.start()
conn2.start()
check.start()
十一、条件Condition
使得线程等待,只有满足某条件时,才释放n个线程
import threading
def run(n):
con.acquire()
con.wait()
print("run the thread: %s" %n)
con.release()
if __name__ == '__main__':
con = threading.Condition()
for i in range(10):
t = threading.Thread(target=run, args=(i,))
t.start()
while True:
inp = input('>>>')
if inp == 'q':
break
con.acquire()
con.notify(int(inp))
con.release()
import threading
def condition_func():
ret = False
inp = input('>>>')
if inp == '1':
ret = True
return ret
def run(n):
con.acquire()
con.wait_for(condition_func)
print("run the thread: %s" %n)
con.release()
if __name__ == '__main__':
con = threading.Condition()
for i in range(10):
t = threading.Thread(target=run, args=(i,))
t.start()
十二、定时器
定时器,指定n秒后执行某操作
from threading import Timer
def hello():
print("hello, world")
t = Timer(1, hello)
t.start() # after 1 seconds, "hello, world" will be printed
#验证码定时器
from threading import Timer
import random,time
class Code:
def __init__(self):
self.make_cache()
def make_cache(self,interval=5):
self.cache=self.make_code()
print(self.cache)
self.t=Timer(interval,self.make_cache)
self.t.start()
def make_code(self,n=4):
res=''
for i in range(n):
s1=str(random.randint(0,9))
s2=chr(random.randint(65,90))
res+=random.choice([s1,s2])
return res
def check(self):
while True:
inp=input('>>: ').strip()
if inp.upper() == self.cache:
print('验证成功',end='\n')
self.t.cancel()
break
if __name__ == '__main__':
obj=Code()
obj.check()
十三、线程queue
queue队列 :使用import queue,用法与进程Queue一样。
queue is especially useful in threaded programming when information must be exchanged safely between multiple threads.
import queue
q=queue.Queue()
q.put('first')
q.put('second')
q.put('third')
print(q.get())
print(q.get())
print(q.get())
'''
结果(先进先出):
first
second
third
'''
import queue
q=queue.LifoQueue()
q.put('first')
q.put('second')
q.put('third')
print(q.get())
print(q.get())
print(q.get())
'''
结果(后进先出):
third
second
first
'''
import queue
q=queue.PriorityQueue()
#put进入一个元组,元组的第一个元素是优先级(通常是数字,也可以是非数字之间的比较),数字越小优先级越高
q.put((20,'a'))
q.put((10,'b'))
q.put((30,'c'))
print(q.get())
print(q.get())
print(q.get())
'''
结果(数字越小优先级越高,优先级高的优先出队):
(10, 'b')
(20, 'a')
(30, 'c')
'''
十四、Python标准模块--concurrent.futures
https://docs.python.org/dev/library/concurrent.futures.html
#1 介绍
concurrent.futures模块提供了高度封装的异步调用接口
ThreadPoolExecutor:线程池,提供异步调用
ProcessPoolExecutor: 进程池,提供异步调用
Both implement the same interface, which is defined by the abstract Executor class.
#2 基本方法
#submit(fn, *args, **kwargs) 异步提交任务
#map(func, *iterables, timeout=None, chunksize=1) 取代for循环submit的操作
#shutdown(wait=True) 相当于进程池的pool.close()+pool.join()操作wait=True,等待池内所有任务执行完毕回收完资源后才继续wait=False,立即返回,并不
会等待池内的任务执行完毕但不管wait参数为何值,整个程序都会等到所有任务执行完毕submit和map必须在shutdown之前
#result(timeout=None) 取得结果
#add_done_callback(fn) 回调函数
栗子:
#ProcessPoolExecutor #介绍 The ProcessPoolExecutor class is an Executor subclass that uses a pool of processes to execute calls asynchronously. ProcessPoolExecutor uses the multiprocessing module, which allows it to side-step the Global Interpreter Lock but also means that only picklable objects can be executed and returned. class concurrent.futures.ProcessPoolExecutor(max_workers=None, mp_context=None) An Executor subclass that executes calls asynchronously using a pool of at most max_workers processes. If max_workers is None or not given, it will default to the number of processors on the machine. If max_workers is lower or equal to 0, then a ValueError will be raised. #用法 from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor,ProcessPoolExecutor import os,time,random def task(n): print('%s is runing' %os.getpid()) time.sleep(random.randint(1,3)) return n**2 if __name__ == '__main__': executor=ProcessPoolExecutor(max_workers=3) futures=[] for i in range(11): future=executor.submit(task,i) futures.append(future) executor.shutdown(True) print('+++>') for future in futures: print(future.result())
#ThreadPoolExecutor #介绍 ThreadPoolExecutor is an Executor subclass that uses a pool of threads to execute calls asynchronously. class concurrent.futures.ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=None, thread_name_prefix='') An Executor subclass that uses a pool of at most max_workers threads to execute calls asynchronously. Changed in version 3.5: If max_workers is None or not given, it will default to the number of processors on the machine, multiplied by 5, assuming that ThreadPoolExecutor is often used to overlap I/O instead of CPU work and the number of workers should be higher than the number of workers for ProcessPoolExecutor. New in version 3.6: The thread_name_prefix argument was added to allow users to control the threading.Thread names for worker threads created by the pool for easier debugging. #用法 与ProcessPoolExecutor相同
#map的用法 from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor,ProcessPoolExecutor import os,time,random def task(n): print('%s is runing' %os.getpid()) time.sleep(random.randint(1,3)) return n**2 if __name__ == '__main__': executor=ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=3) # for i in range(11): # future=executor.submit(task,i) executor.map(task,range(1,12)) #map取代了for+submit
#回调函数 from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor,ProcessPoolExecutor from multiprocessing import Pool import requests import json import os def get_page(url): print('<进程%s> get %s' %(os.getpid(),url)) respone=requests.get(url) if respone.status_code == 200: return {'url':url,'text':respone.text} def parse_page(res): res=res.result() print('<进程%s> parse %s' %(os.getpid(),res['url'])) parse_res='url:<%s> size:[%s]\n' %(res['url'],len(res['text'])) with open('db.txt','a') as f: f.write(parse_res) if __name__ == '__main__': urls=[ 'https://www.baidu.com', 'https://www.python.org', 'https://www.openstack.org', 'https://help.github.com/', 'http://www.sina.com.cn/' ] # p=Pool(3) # for url in urls: # p.apply_async(get_page,args=(url,),callback=pasrse_page) # p.close() # p.join() p=ProcessPoolExecutor(3) for url in urls: p.submit(get_page,url).add_done_callback(parse_page) #parse_page拿到的是一个future对象obj,需要用obj.result()拿到结果


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号