逻辑回归 | 使用 sklearn.linear_model.LogisticRegression 预测不同职业的人优惠券使用情况
逻辑回归:
是一种广义的线性回归分析模型
逻辑回归针对的目标变量是类别型的,参数估值上,采用最大似然法。
分类问题可以转换成概率的都是逻辑回归的常见场景,如:
会不会逾期(风控)
会不会是流失客户(会员运营)
会不会点击(CTR预估、推荐系统、搜索)
优点:模型简单、可解释性强
缺点:不能做特征交叉
代码演示
需求:探究不同职业的人使用优惠券的可能
1 数据预处理
注意:剔除异常值、处理缺失值,排除共线性问题
1.1 本文数据预览
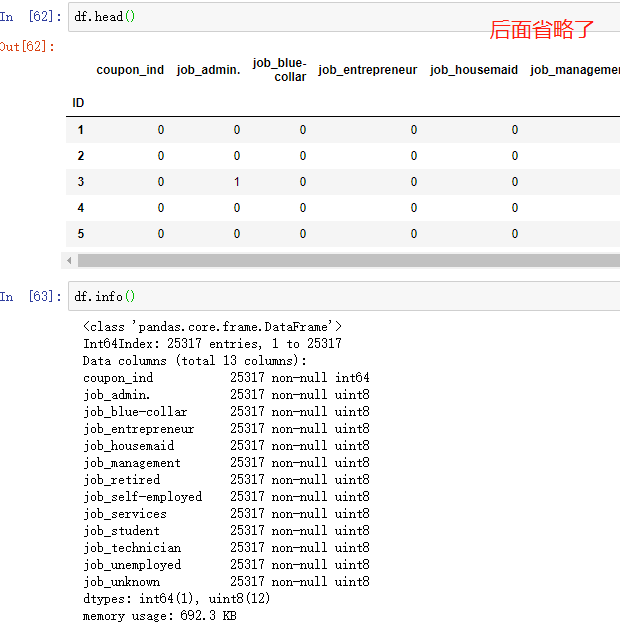
1.2 过采样处理样本不均衡问题处理
1.2.1 选定自变量 因变量
x = df[['job_admin.', 'job_blue-collar', 'job_entrepreneur', 'job_housemaid', 'job_management', 'job_retired', 'job_self-employed', 'job_services', 'job_student', 'job_technician', 'job_unemployed', 'job_unknown']] y = df['coupon_ind']
1.2.2 查看是否均衡,发现样本不均衡
也可以使用 df.coupon_ind.value_counts() 来查看
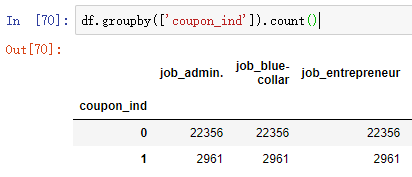
1.2.3 进行过采样处理
from imblearn.over_sampling import SMOTE smo = SMOTE(random_state=11) x, y= smo.fit_sample(x, y)
2 划分训练集、测试集
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split( x, y, test_size=0.3, random_state=11)
3 逻辑回归模型
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression lr = LogisticRegression() lr.fit(x_train, y_train)
# 回归系数
lr.coef_
# 截距
lr.intercept_
4模型评估
4.1 使用模型进行预测
y_pred_train = lr.predict(x_train)
y_pred_test = lr.predict(x_test)
4.2 查看得分
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score accuracy_score(y_train, y_pred_train)
4.3 查看召回率
from sklearn.metrics import auc, roc_curve fpr, tpr, _ = roc_curve(y_train, y_pred_train) roc_auc = auc(fpr,tpr) roc_auc



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号