算法练习(8)-判断单链表是否回文链表
在一些文学作品中,大家想必接触过回文诗,比如:“雾窗寒对遥天暮,暮天遥对寒窗雾”或“垂帘画阁画帘垂”,即:正着念反着念完全一样。回文单链表跟这个类似,比如:
0-1-2-1-0或0-1-1-0,很容易发现规律:可以找到一个对称轴,将链表分为前后二段,并且前后对折起来,完全重合。
为了方便,先定义单链表结构,以及一些工具类:

1 public class LinkNode { 2 public int val; 3 public LinkNode next; 4 5 public LinkNode(int val, LinkNode next) { 6 this.val = val; 7 this.next = next; 8 } 9 10 public LinkNode(int val) { 11 this.val = val; 12 } 13 }

1 /** 2 * @author yjmyzz@126.com 3 * @blog http://yjmyzz.cnblogs.com 菩提树下的杨过 4 */ 5 public class LinkNodeUtils { 6 7 /** 8 * 打印单链表 9 * 10 * @param head 11 */ 12 public static void print(LinkNode head) { 13 if (head == null) { 14 return; 15 } 16 while (head != null) { 17 System.out.print(head.val + (head.next != null ? " -> " : "\n")); 18 head = head.next; 19 } 20 } 21 22 /** 23 * 将数组填充到单链表 24 * 25 * @param arr 26 * @return 27 */ 28 public static LinkNode build(int[] arr) { 29 if (arr == null || arr.length <= 0) { 30 return null; 31 } 32 LinkNode head = new LinkNode(arr[0]); 33 LinkNode curr = head; 34 for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) { 35 LinkNode next = new LinkNode(arr[i]); 36 curr.next = next; 37 curr = next; 38 } 39 return head; 40 } 41 }
解法1:利用stack翻转,然后逐一对比
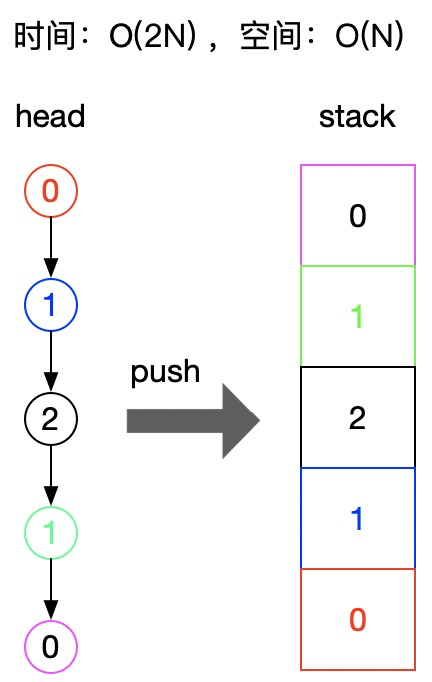
代码如下:

1 public static boolean isPalindromic(LinkNode head) { 2 if (head == null || head.next == null) { 3 return true; 4 } 5 LinkNode h = head; 6 Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>(); 7 while (head != null) { 8 stack.push(head.val); 9 head = head.next; 10 } 11 head = h; 12 while (head != null) { 13 if (stack.pop() != head.val) { 14 return false; 15 } 16 head = head.next; 17 } 18 return true; 19 }
思路很简单:将所有元素逐一压入栈,由于堆栈先进后出,这样相当于把链表反向,然后跟原链表逐一对比,即:正向与反向,检查所有元素是否重合。
测试:

1 public static void main(String[] args) { 2 LinkNode h1 = LinkNodeUtils.build(new int[]{0}); 3 LinkNode h2_1 = LinkNodeUtils.build(new int[]{0, 0}); 4 LinkNode h2_2 = LinkNodeUtils.build(new int[]{0, 1}); 5 LinkNode h3_1 = LinkNodeUtils.build(new int[]{0, 1, 0}); 6 LinkNode h3_2 = LinkNodeUtils.build(new int[]{0, 1, 1}); 7 LinkNode h4_1 = LinkNodeUtils.build(new int[]{0, 1, 1, 0}); 8 LinkNode h4_2 = LinkNodeUtils.build(new int[]{0, 1, 2, 3}); 9 LinkNode h4_3 = LinkNodeUtils.build(new int[]{0, 1, 2, 0}); 10 LinkNode h5_1 = LinkNodeUtils.build(new int[]{0, 1, 2, 1, 0}); 11 LinkNode h5_2 = LinkNodeUtils.build(new int[]{0, 1, 2, 3, 0}); 12 LinkNode h6_1 = LinkNodeUtils.build(new int[]{0, 1, 2, 2, 1, 0}); 13 LinkNode h6_2 = LinkNodeUtils.build(new int[]{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5}); 14 15 System.out.printf("\n" + isPalindromic(h1) + " \t "); 16 LinkNodeUtils.print(h1); 17 18 System.out.printf("\n" + isPalindromic(h2_1) + " \t "); 19 LinkNodeUtils.print(h2_1); 20 System.out.printf("\n" + isPalindromic(h2_2) + " \t "); 21 LinkNodeUtils.print(h2_2); 22 23 System.out.printf("\n" + isPalindromic(h3_1) + " \t "); 24 LinkNodeUtils.print(h3_1); 25 System.out.printf("\n" + isPalindromic(h3_2) + " \t "); 26 LinkNodeUtils.print(h3_2); 27 28 System.out.printf("\n" + isPalindromic(h4_1) + " \t "); 29 LinkNodeUtils.print(h4_1); 30 System.out.printf("\n" + isPalindromic(h4_2) + " \t "); 31 LinkNodeUtils.print(h4_2); 32 System.out.printf("\n" + isPalindromic(h4_3) + " \t "); 33 LinkNodeUtils.print(h4_3); 34 35 System.out.printf("\n" + isPalindromic(h5_1) + " \t "); 36 LinkNodeUtils.print(h5_1); 37 System.out.printf("\n" + isPalindromic(h5_2) + " \t "); 38 LinkNodeUtils.print(h5_2); 39 40 System.out.printf("\n" + isPalindromic(h6_1) + " \t "); 41 LinkNodeUtils.print(h6_1); 42 System.out.printf("\n" + isPalindromic(h6_2) + " \t "); 43 LinkNodeUtils.print(h6_2); 44 }
输出:

true 0 true 0 -> 0 false 0 -> 1 true 0 -> 1 -> 0 false 0 -> 1 -> 1 true 0 -> 1 -> 1 -> 0 false 0 -> 1 -> 2 -> 3 false 0 -> 1 -> 2 -> 0 true 0 -> 1 -> 2 -> 1 -> 0 false 0 -> 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 0 true 0 -> 1 -> 2 -> 2 -> 1 -> 0 false 0 -> 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5
解法2:转换成数组,首尾对比
既然能用堆栈,也能使用数组,如下图:
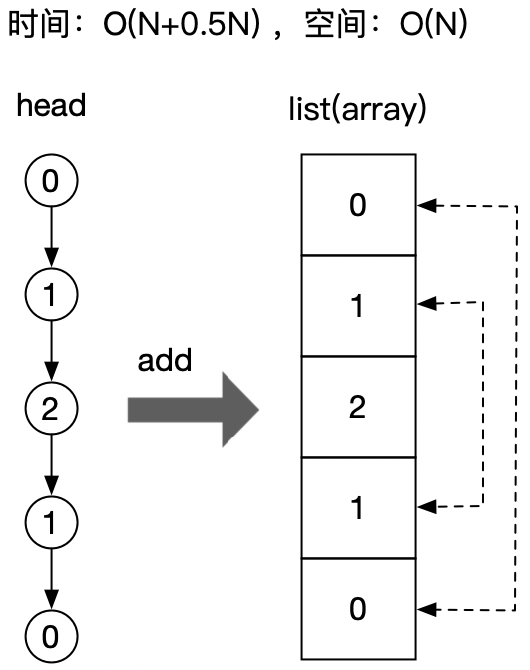
相对解法1,将链表转换成数组后,利用回文的特点,折半检查,循环次数能降一半,比解法1稍微快一点。

1 public static boolean isPalindromic2(LinkNode head) { 2 if (head == null || head.next == null) { 3 return true; 4 } 5 List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); 6 while (head != null) { 7 list.add(head.val); 8 head = head.next; 9 } 10 for (int i = 0; i < list.size() / 2; i++) { 11 if (!list.get(i).equals(list.get(list.size() - 1 - i))) { 12 return false; 13 } 14 } 15 return true; 16 }
解法3:前半段压入栈,然后跟下半段对比
前面的2种解法,额外空间复杂度都是O(N),但仔细想一下,既然是回文,前一半跟后一半是一样的,只需要将一半的元素压栈,再跟另一半对比就能知道结果,这样额外空间能省一半。
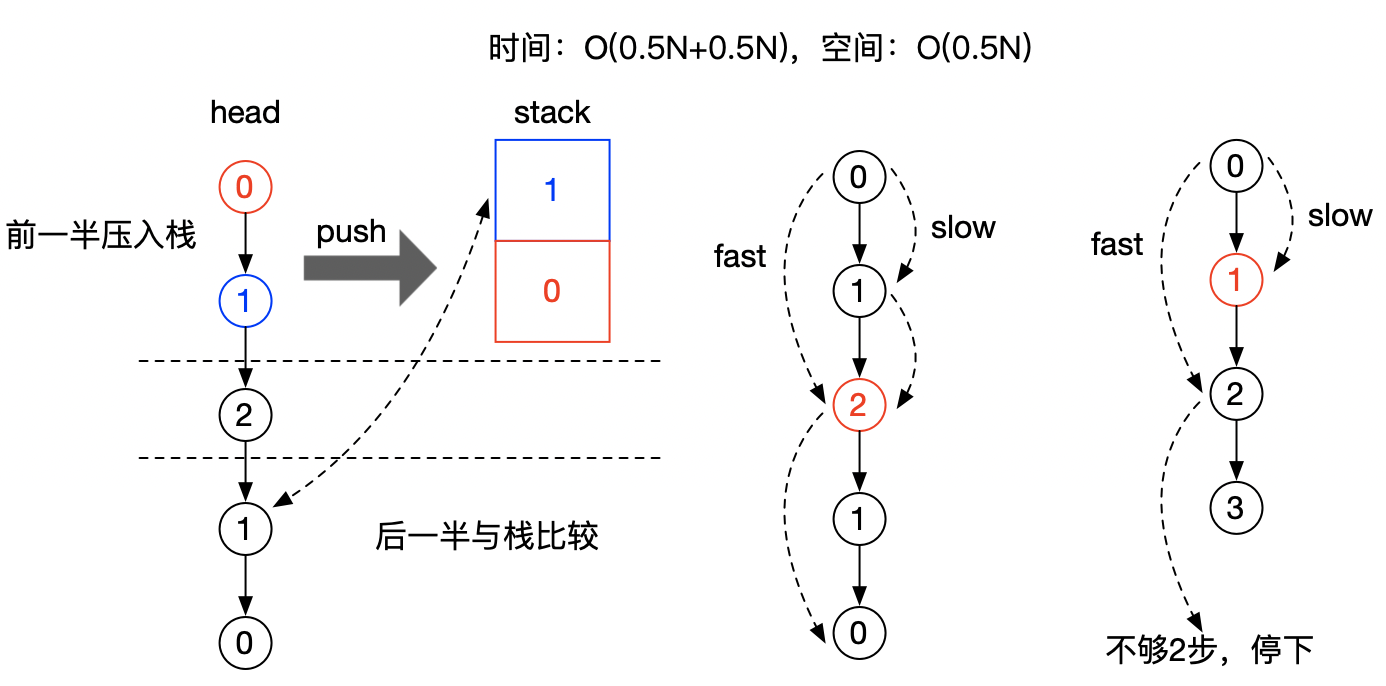
那么问题来了,怎么能正好将一半的元素压入堆栈?可以使用经典快慢指针,如上图,快指针1次走2步,慢指针1次走1步,这样fast走到尾时,slow指针刚好走到中间位置(或中间位置的前1个)

1 public static boolean isPalindromic3(LinkNode head) { 2 if (head == null || head.next == null) { 3 return true; 4 } 5 //2个元素的快速判断 6 if (head.next.next == null) { 7 return head.val == head.next.val; 8 } 9 LinkNode slow = head; 10 LinkNode fast = head; 11 Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>(); 12 while (fast.next != null) { 13 if (fast.next.next != null) { 14 stack.push(slow.val); 15 fast = fast.next.next; 16 slow = slow.next; 17 } else { 18 //fast在倒数第2个,不够向前跳2步的特殊处理 19 stack.push(slow.val); 20 break; 21 } 22 } 23 //此时,slow要么在中点,要么在中间的前1个位置,再向前走1步,到达下半段的第1个位置 24 slow = slow.next; 25 while (slow != null) { 26 if (slow.val != stack.pop()) { 27 return false; 28 } 29 slow = slow.next; 30 } 31 return true; 32 }
在借助额外空间的解法中,解法3是最好的版本。
解法4:后半段翻转,跟前半段对比,对比结束再将后半段还原
前面的解法,都需要借助额外的存储空间,如果链表元素非常多(比如:几千万个),就算只要1半,占用的空间也不少。能否实现额外空间复杂度O(1),也就是常数项,同时时间复杂度仍然在O(N)水平?
仔细想想,回文结构,前半段链表元素跟后半段是对称的。即:如果把后半段翻转过来,就跟前半段一样了。所以,只要把后半段单独拿出来,反转后再跟前半段对比,如果每个元素都一样,就是回文。不过要注意:这样会破坏原链表,所以在检查结束后,记得将后半段再翻转回来,跟前半段续接上,还原整个链表。
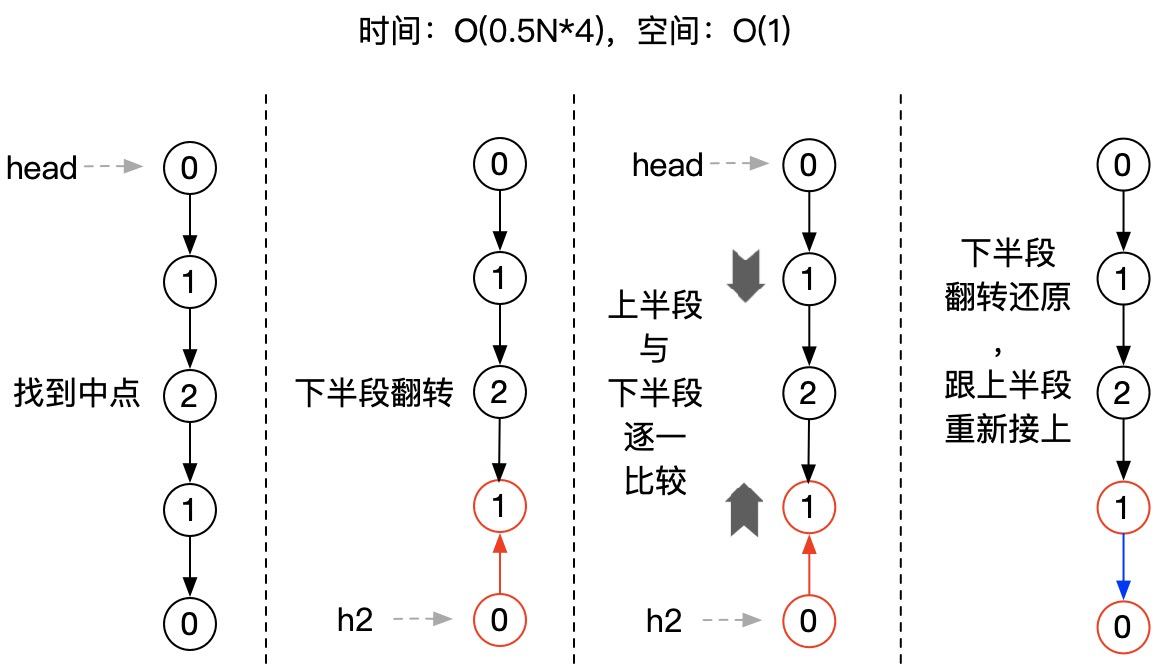

1 static LinkNode middleNode(LinkNode head) { 2 LinkNode slow = head; 3 LinkNode fast = head; 4 while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) { 5 slow = slow.next; 6 fast = fast.next.next; 7 } 8 return slow; 9 } 10 11 static LinkNode reverseList(LinkNode head) { 12 LinkNode newHead = null; 13 while (head != null) { 14 LinkNode next = head.next; 15 head.next = newHead; 16 newHead = head; 17 head = next; 18 } 19 return newHead; 20 } 21 22 public static boolean isPalindromic4(LinkNode head) { 23 if (head == null || head.next == null) { 24 //空链表或单个元素,也视为回文(相当于对称轴是自己) 25 return true; 26 } 27 //2个元素的快速判断 28 if (head.next.next == null) { 29 return head.val == head.next.val; 30 } 31 LinkNode mid = middleNode(head); 32 //后半段翻转 33 LinkNode h2 = reverseList(mid.next); 34 //保存下来,用于后面恢复 35 LinkNode newH2 = h2; 36 boolean isPalindromic = true; 37 while (h2 != null) { 38 if (h2.val != head.val) { 39 isPalindromic = false; 40 break; 41 } 42 h2 = h2.next; 43 head = head.next; 44 } 45 //后半段翻转回来,跟前面的接上 46 mid.next = reverseList(newH2); 47 return isPalindromic; 48 }
如果在面试过程中大家遇到这道题,能把这4种解法依次演进,给面试官讲清楚,相信一定会给面试官司留下好印象
出处:http://yjmyzz.cnblogs.com
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文连接,否则保留追究法律责任的权利。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号