babylon.js 学习笔记(5)
前面我们画的小房子,基本上都是用内置的标准形状组合而成,但并非所有对象都这么简单,今天我们来画一个小汽车,汽车由多个零件组成,控制这些零件的缩放、位置、旋转,如果每个都单独用代码来修改position/roration/scaling,未免太复杂,幸好babylon.js中,对象有所谓的child/parent 关系。简单来说,如果A是B的parent,则对A的任何位置/缩放/旋转,其child也会同步受影响,但child可以在parent的基础上,再独立叠加新变化。有没有发现,这很符合遗传学,孩子必然长得象父母,但是又有些自己的特征。
一、理解 parent / child 关系
const createScene = () => {
const scene = new BABYLON.Scene(engine);
const camera = new BABYLON.ArcRotateCamera("camera", -Math.PI / 2.2, Math.PI / 2.5, 15, new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 0, 0));
camera.attachControl(canvas, true);
const light = new BABYLON.HemisphericLight("light", new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 1, 0));
//方块6个面的颜色
const faceColors = [];
faceColors[0] = BABYLON.Color3.Blue();
faceColors[1] = BABYLON.Color3.Teal()
faceColors[2] = BABYLON.Color3.Red();
faceColors[3] = BABYLON.Color3.Purple();
faceColors[4] = BABYLON.Color3.Green();
faceColors[5] = BABYLON.Color3.Yellow();
const boxParent = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateBox("Box", { faceColors: faceColors });
const boxChild = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateBox("Box", { size: 0.5, faceColors: faceColors });
//小方块是大方块的child
boxChild.setParent(boxParent);
//child的独立特征
boxChild.position.x = 0;
boxChild.position.y = 2;
boxChild.position.z = 0;
boxChild.rotation.x = Math.PI / 4;
boxChild.rotation.y = Math.PI / 4;
boxChild.rotation.z = Math.PI / 4;
//parent的位置变化,将影响child
boxParent.position.x = 2;
boxParent.position.y = 0;
boxParent.position.z = 0;
boxParent.rotation.x = 0;
boxParent.rotation.y = 0;
boxParent.rotation.z = -Math.PI / 4;
//辅助坐标轴,方便理解
const boxChildAxes = localAxes(1.5, scene);
boxChildAxes.parent = boxChild;
showAxis(5, scene);
return scene;
}
//坐标轴
const showAxis = (size, scene) => {
const makeTextPlane = (text, color, size) => {
const dynamicTexture = new BABYLON.DynamicTexture("DynamicTexture", 50, scene, true);
dynamicTexture.hasAlpha = true;
dynamicTexture.drawText(text, 5, 40, "bold 36px Arial", color, "transparent", true);
const plane = new BABYLON.Mesh.CreatePlane("TextPlane", size, scene, true);
plane.material = new BABYLON.StandardMaterial("TextPlaneMaterial", scene);
plane.material.backFaceCulling = false;
plane.material.specularColor = new BABYLON.Color3(0, 0, 0);
plane.material.diffuseTexture = dynamicTexture;
return plane;
};
const axisX = BABYLON.Mesh.CreateLines("axisX", [
new BABYLON.Vector3.Zero(), new BABYLON.Vector3(size, 0, 0), new BABYLON.Vector3(size * 0.95, 0.05 * size, 0),
new BABYLON.Vector3(size, 0, 0), new BABYLON.Vector3(size * 0.95, -0.05 * size, 0)
]);
axisX.color = new BABYLON.Color3(1, 0, 0);
const xChar = makeTextPlane("X", "white", size / 8);
xChar.position = new BABYLON.Vector3(0.9 * size, -0.05 * size, 0);
const axisY = BABYLON.Mesh.CreateLines("axisY", [
new BABYLON.Vector3.Zero(), new BABYLON.Vector3(0, size, 0), new BABYLON.Vector3(-0.05 * size, size * 0.95, 0),
new BABYLON.Vector3(0, size, 0), new BABYLON.Vector3(0.05 * size, size * 0.95, 0)
]);
axisY.color = new BABYLON.Color3(0, 1, 0);
const yChar = makeTextPlane("Y", "white", size / 8);
yChar.position = new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 0.9 * size, -0.05 * size);
const axisZ = BABYLON.Mesh.CreateLines("axisZ", [
new BABYLON.Vector3.Zero(), new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 0, size), new BABYLON.Vector3(0, -0.05 * size, size * 0.95),
new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 0, size), new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 0.05 * size, size * 0.95)
]);
axisZ.color = new BABYLON.Color3(0, 1, 1);
const zChar = makeTextPlane("Z", "white", size / 8);
zChar.position = new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 0.05 * size, 0.9 * size);
};
//小方块的坐标轴
localAxes = (size, scene) => {
const local_axisX = BABYLON.Mesh.CreateLines("local_axisX", [
new BABYLON.Vector3.Zero(), new BABYLON.Vector3(size, 0, 0), new BABYLON.Vector3(size * 0.95, 0.05 * size, 0),
new BABYLON.Vector3(size, 0, 0), new BABYLON.Vector3(size * 0.95, -0.05 * size, 0)
], scene);
local_axisX.color = new BABYLON.Color3(1, 0, 0);
local_axisY = BABYLON.Mesh.CreateLines("local_axisY", [
new BABYLON.Vector3.Zero(), new BABYLON.Vector3(0, size, 0), new BABYLON.Vector3(-0.05 * size, size * 0.95, 0),
new BABYLON.Vector3(0, size, 0), new BABYLON.Vector3(0.05 * size, size * 0.95, 0)
], scene);
local_axisY.color = new BABYLON.Color3(0, 1, 0);
const local_axisZ = BABYLON.Mesh.CreateLines("local_axisZ", [
new BABYLON.Vector3.Zero(), new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 0, size), new BABYLON.Vector3(0, -0.05 * size, size * 0.95),
new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 0, size), new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 0.05 * size, size * 0.95)
], scene);
local_axisZ.color = new BABYLON.Color3(0, 1, 1);
const local_origin = new BABYLON.TransformNode("local_origin");
local_axisX.parent = local_origin;
local_axisY.parent = local_origin;
local_axisZ.parent = local_origin;
return local_origin;
}
代码有点长,坐标轴的部分可以先不管,只看createScene即可。
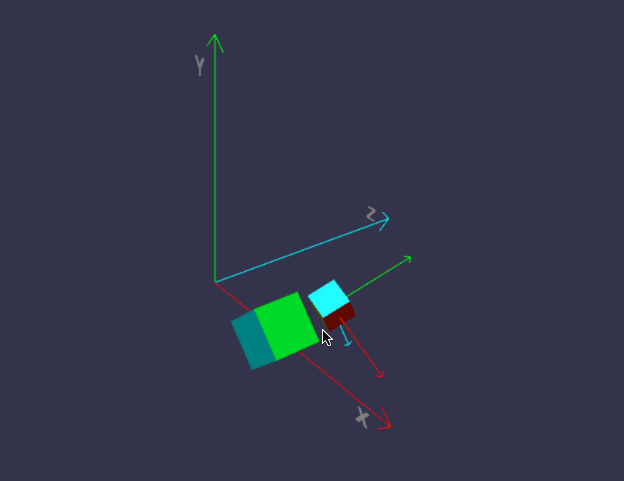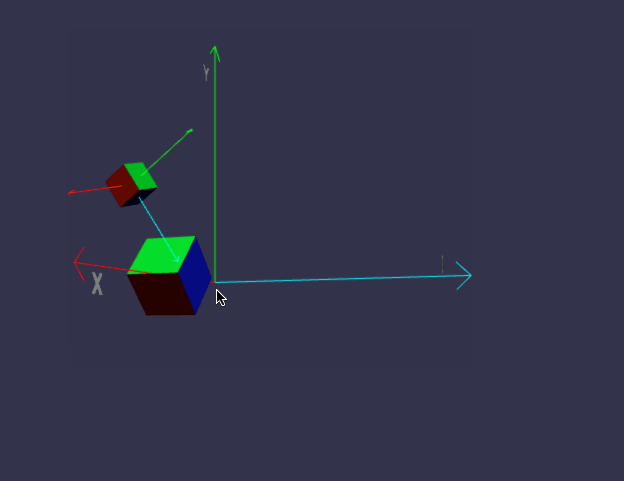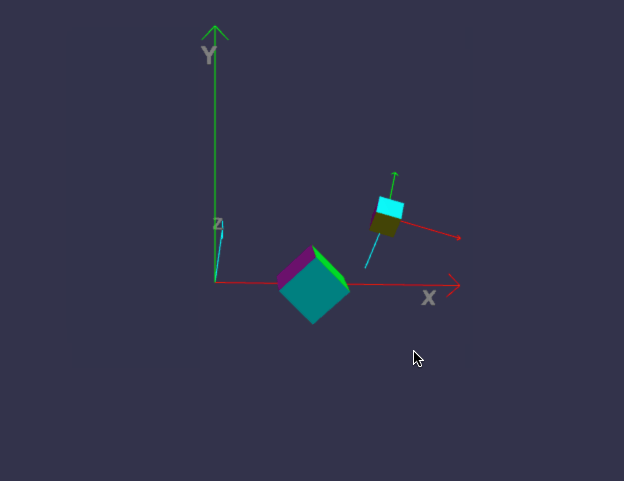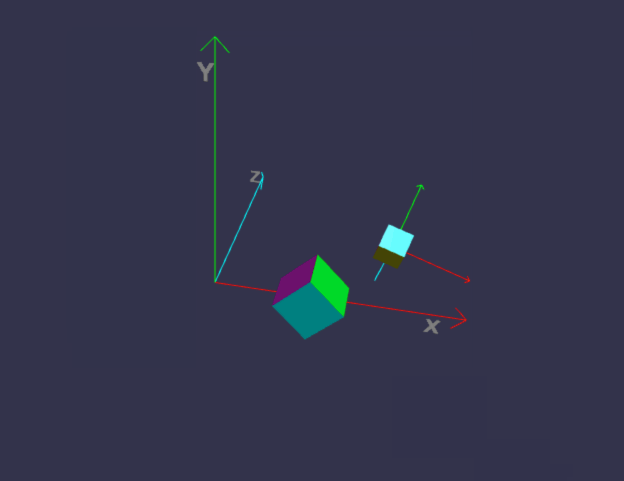
在线地址:https://yjmyzz.github.io/babylon_js_study/day05/01.html
二、理解 ExtrudePolygon
ExtrudePolygon方法可以画出一些不规则形状,比如下面:
const buildCar = () => {
//base
const outline = [
new BABYLON.Vector3(-0.3, 0, -0.1),
new BABYLON.Vector3(0.2, 0, -0.1),
]
//top
outline.push(new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 0, 0.1));
outline.push(new BABYLON.Vector3(-0.3, 0, 0.1));
//back formed automatically
const car = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.ExtrudePolygon("car", { shape: outline, depth: 0.2 });
return car;
}

在线地址:https://yjmyzz.github.io/babylon_js_study/day05/02.html
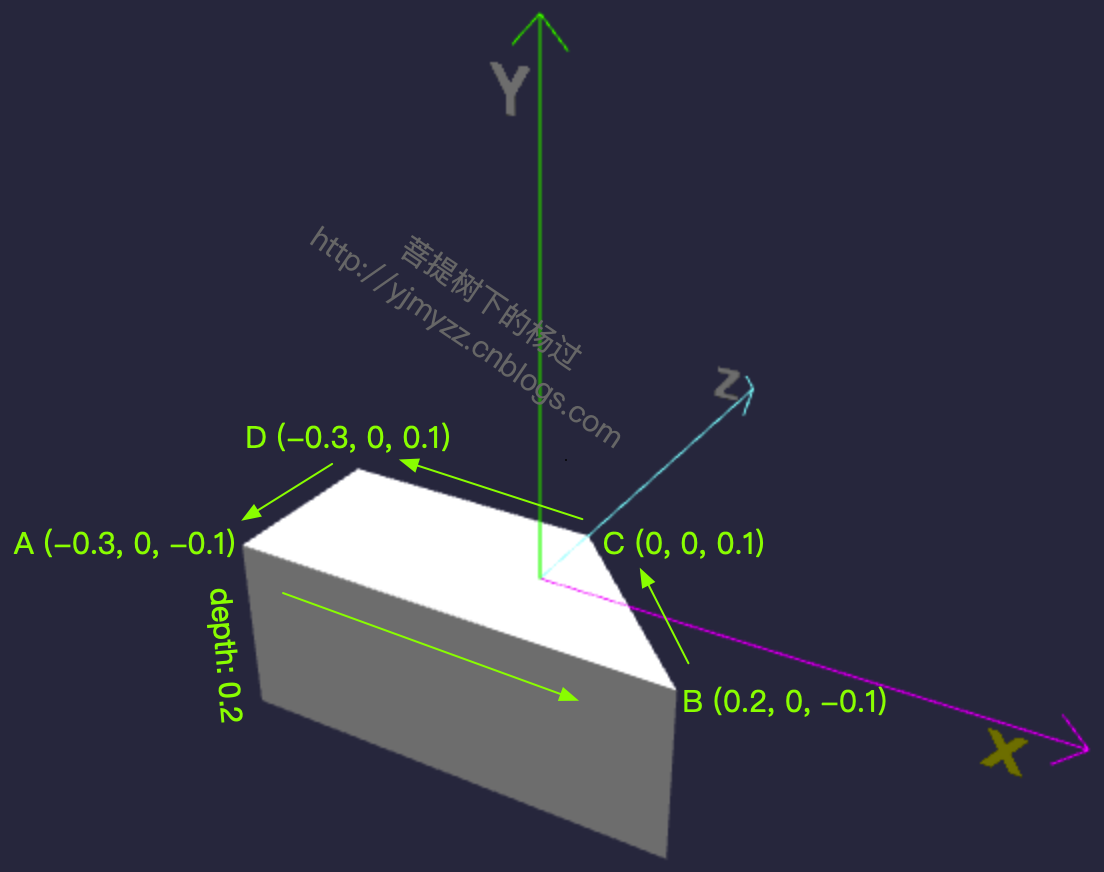
具体画的过程,可以结合下面的图理解:简单来说,A->B->C->D 先画出1个梯形,然后向下拉长,就得到了这个模型。
再完善一下,把车头及轮子加上
const createScene = () => {
const scene = new BABYLON.Scene(engine);
const camera = new BABYLON.ArcRotateCamera("camera", -Math.PI / 2, Math.PI / 2.5, 3, new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 0, 0));
camera.attachControl(canvas, true);
const light = new BABYLON.HemisphericLight("light", new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 1, 0));
//造车身
const car = buildCar();
//安装轮子
buildWheel(car);
showAxis(0.8, scene);
return scene;
}
//车身
const buildCar = () => {
//base
const outline = [
new BABYLON.Vector3(-0.3, 0, -0.1),
new BABYLON.Vector3(0.2, 0, -0.1),
]
//curved front
for (let i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
outline.push(new BABYLON.Vector3(0.2 * Math.cos(i * Math.PI / 40), 0, 0.2 * Math.sin(i * Math.PI / 40) - 0.1));
}
//top
outline.push(new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 0, 0.1));
outline.push(new BABYLON.Vector3(-0.3, 0, 0.1));
//back formed automatically
const car = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.ExtrudePolygon("car", { shape: outline, depth: 0.2 });
return car;
}
//轮子
const buildWheel = (car) => {
const wheelRB = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateCylinder("wheelRB", { diameter: 0.125, height: 0.05 })
wheelRB.parent = car;
wheelRB.position.z = -0.1;
wheelRB.position.x = -0.2;
wheelRB.position.y = 0.035;
const wheelRF = wheelRB.clone("wheelRF");
wheelRF.position.x = 0.1;
const wheelLB = wheelRB.clone("wheelLB");
wheelLB.position.y = -0.2 - 0.035;
const wheelLF = wheelRF.clone("wheelLF");
wheelLF.position.y = -0.2 - 0.035;
}

在线地址:https://yjmyzz.github.io/babylon_js_study/day05/03.html
最后再加上贴图:

const createScene = () => {
const scene = new BABYLON.Scene(engine);
const camera = new BABYLON.ArcRotateCamera("camera", -Math.PI / 2, Math.PI / 2.5, 3, new BABYLON.Vector3(0.2, -0.20, 1.5));
camera.attachControl(canvas, true);
const light = new BABYLON.HemisphericLight("light", new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 1, 0));
const car = buildCar();
car.rotation.x = -Math.PI / 2;
showAxis(0.6, scene);
return scene;
}
const buildCar = () => {
//base
const outline = [
new BABYLON.Vector3(-0.3, 0, -0.1),
new BABYLON.Vector3(0.2, 0, -0.1),
]
//curved front
for (let i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
outline.push(new BABYLON.Vector3(0.2 * Math.cos(i * Math.PI / 40), 0, 0.2 * Math.sin(i * Math.PI / 40) - 0.1));
}
//top
outline.push(new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 0, 0.1));
outline.push(new BABYLON.Vector3(-0.3, 0, 0.1));
//car face UVs
const faceUV = [];
faceUV[0] = new BABYLON.Vector4(0, 0.5, 0.38, 1);
faceUV[1] = new BABYLON.Vector4(0, 0, 1, 0.5);
faceUV[2] = new BABYLON.Vector4(0.38, 1, 0, 0.5);
//car material
const carMat = new BABYLON.StandardMaterial("carMat");
carMat.diffuseTexture = new BABYLON.Texture("../assets/img/car.png");
//back formed automatically
const car = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.ExtrudePolygon("car", { shape: outline, depth: 0.2, faceUV: faceUV, wrap: true });
car.material = carMat;
//wheel face UVs
const wheelUV = [];
wheelUV[0] = new BABYLON.Vector4(0, 0, 1, 1);
wheelUV[1] = new BABYLON.Vector4(0, 0.5, 0, 0.5);
wheelUV[2] = new BABYLON.Vector4(0, 0, 1, 1);
//car material
const wheelMat = new BABYLON.StandardMaterial("wheelMat");
wheelMat.diffuseTexture = new BABYLON.Texture("../assets/img/wheel.png");
const wheelRB = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateCylinder("wheelRB", { diameter: 0.125, height: 0.05, faceUV: wheelUV })
wheelRB.material = wheelMat;
wheelRB.parent = car;
wheelRB.position.z = -0.1;
wheelRB.position.x = -0.2;
wheelRB.position.y = 0.035;
const wheelRF = wheelRB.clone("wheelRF");
wheelRF.position.x = 0.1;
const wheelLB = wheelRB.clone("wheelLB");
wheelLB.position.y = -0.2 - 0.035;
const wheelLF = wheelRF.clone("wheelLF");
wheelLF.position.y = -0.2 - 0.035;
return car;
}

在线地址:https://yjmyzz.github.io/babylon_js_study/day05/04.html
三、轮子动画
既然是汽车,轮子肯定得转起来,可以借助Animation对象来实现
const createScene = () => {
const scene = new BABYLON.Scene(engine);
const camera = new BABYLON.ArcRotateCamera("camera", -Math.PI / 2, Math.PI / 2.5, 3, new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 0, 0));
camera.attachControl(canvas, true);
const light = new BABYLON.HemisphericLight("light", new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 1, 0));
const wheel = buildWheel();
wheelAnimation(scene, wheel);
showAxis(0.6, scene);
return scene;
}
//造轮子
const buildWheel = () => {
const wheelUV = [];
wheelUV[0] = new BABYLON.Vector4(0, 0, 1, 1);
wheelUV[1] = new BABYLON.Vector4(0, 0.5, 0, 0.5);
wheelUV[2] = new BABYLON.Vector4(0, 0, 1, 1);
const wheelMat = new BABYLON.StandardMaterial("wheelMat");
wheelMat.diffuseTexture = new BABYLON.Texture("../assets/img/wheel.png");
const wheelRB = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateCylinder("wheelRB", { diameter: 0.125, height: 0.05, faceUV: wheelUV })
wheelRB.material = wheelMat;
return wheelRB;
}
//轮子转动
const wheelAnimation = (scene, wheel) => {
//定义一个动画,每秒30帧,绕y轴转动
const animWheel = new BABYLON.Animation("wheelAnimation", "rotation.y",
30, BABYLON.Animation.ANIMATIONTYPE_FLOAT, BABYLON.Animation.ANIMATIONLOOPMODE_CYCLE);
//动画关键帧
const wheelKeys = [];
//起始帧
wheelKeys.push({
frame: 0,
value: 0
});
//截止帧(即:第30帧,转到360度)
wheelKeys.push({
frame: 30,
value: 2 * Math.PI
});
//设置关键帧
animWheel.setKeys(wheelKeys);
//将wheel与动画关联
wheel.animations = [];
wheel.animations.push(animWheel);
//开始动画,最后的true表示循环播放
scene.beginAnimation(wheel, 0, 30, true);
}
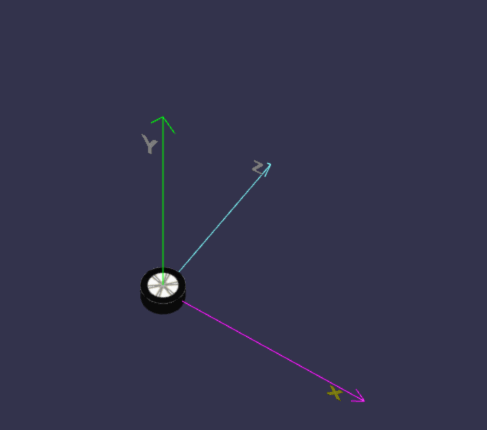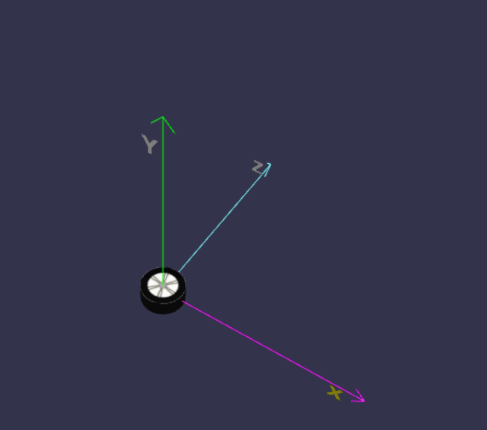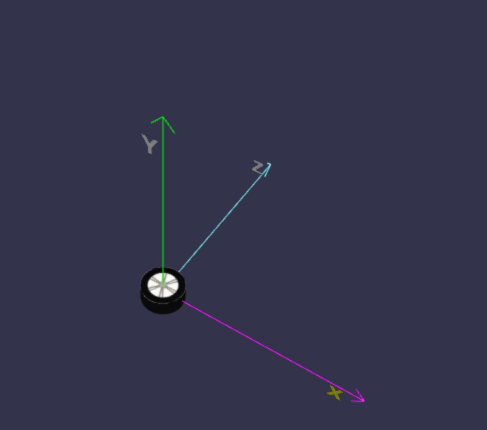
在线地址:https://yjmyzz.github.io/babylon_js_study/day05/05.html
把4个轮子都加上动画:
const createScene = () => {
const scene = new BABYLON.Scene(engine);
const camera = new BABYLON.ArcRotateCamera("camera", -Math.PI / 2, Math.PI / 2.5, 2, new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 0, 0));
camera.attachControl(canvas, true);
const light = new BABYLON.HemisphericLight("light", new BABYLON.Vector3(1, 1, 0));
const car = buildCar();
const wheels = buildWheels(car);
car.rotation.x = -Math.PI / 2;
wheelAnimation(scene, wheels);
showAxis(0.6, scene);
return scene;
}
const buildCar = () => {
//base
const outline = [
new BABYLON.Vector3(-0.3, 0, -0.1),
new BABYLON.Vector3(0.2, 0, -0.1),
]
//curved front
for (let i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
outline.push(new BABYLON.Vector3(0.2 * Math.cos(i * Math.PI / 40), 0, 0.2 * Math.sin(i * Math.PI / 40) - 0.1));
}
//top
outline.push(new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 0, 0.1));
outline.push(new BABYLON.Vector3(-0.3, 0, 0.1));
//car face UVs
const faceUV = [];
faceUV[0] = new BABYLON.Vector4(0, 0.5, 0.38, 1);
faceUV[1] = new BABYLON.Vector4(0, 0, 1, 0.5);
faceUV[2] = new BABYLON.Vector4(0.38, 1, 0, 0.5);
//car material
const carMat = new BABYLON.StandardMaterial("carMat");
carMat.diffuseTexture = new BABYLON.Texture("../assets/img/car.png");
//back formed automatically
const car = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.ExtrudePolygon("car", { shape: outline, depth: 0.2, faceUV: faceUV, wrap: true });
car.material = carMat;
return car;
}
const buildWheels = (car) => {
//wheel face UVs
const wheelUV = [];
wheelUV[0] = new BABYLON.Vector4(0, 0, 1, 1);
wheelUV[1] = new BABYLON.Vector4(0, 0.5, 0, 0.5);
wheelUV[2] = new BABYLON.Vector4(0, 0, 1, 1);
//car material
const wheelMat = new BABYLON.StandardMaterial("wheelMat");
wheelMat.diffuseTexture = new BABYLON.Texture("../assets/img/wheel.png");
const wheelRB = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateCylinder("wheelRB", { diameter: 0.125, height: 0.05, faceUV: wheelUV })
wheelRB.material = wheelMat;
wheelRB.parent = car;
wheelRB.position.z = -0.1;
wheelRB.position.x = -0.2;
wheelRB.position.y = 0.035;
const wheelRF = wheelRB.clone("wheelRF");
wheelRF.position.x = 0.1;
const wheelLB = wheelRB.clone("wheelLB");
wheelLB.position.y = -0.2 - 0.035;
const wheelLF = wheelRF.clone("wheelLF");
wheelLF.position.y = -0.2 - 0.035;
const wheels = [];
wheels.push(wheelRB);
wheels.push(wheelRF);
wheels.push(wheelLB);
wheels.push(wheelLF);
return wheels;
}
//轮子转动
const wheelAnimation = (scene, wheels) => {
//定义一个动画,每秒30帧,绕y轴转动
const animWheel = new BABYLON.Animation("wheelAnimation", "rotation.y",
30, BABYLON.Animation.ANIMATIONTYPE_FLOAT, BABYLON.Animation.ANIMATIONLOOPMODE_CYCLE);
//动画关键帧
const wheelKeys = [];
//起始帧
wheelKeys.push({
frame: 0,
value: 0
});
//截止帧(即:第30帧,转到360度)
wheelKeys.push({
frame: 30,
value: 2 * Math.PI
});
//设置关键帧
animWheel.setKeys(wheelKeys);
for (let i = 0; i < wheels.length; i++) {
//将wheel与动画关联
wheels[i].animations = [];
wheels[i].animations.push(animWheel);
//开始动画,最后的true表示循环播放
scene.beginAnimation(wheels[i], 0, 30, true);
}
}
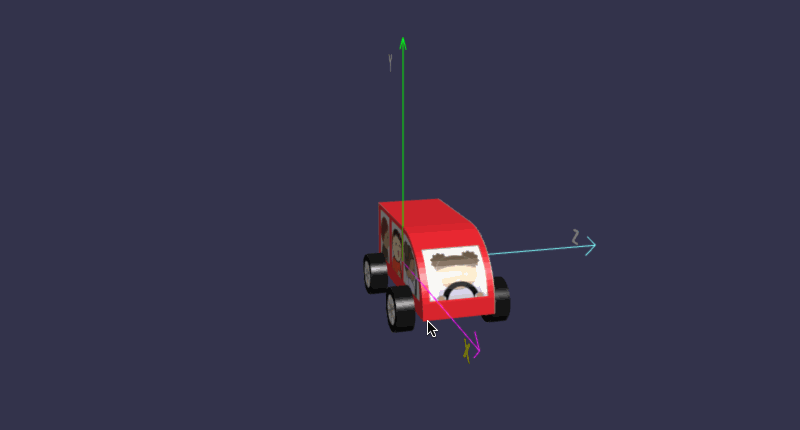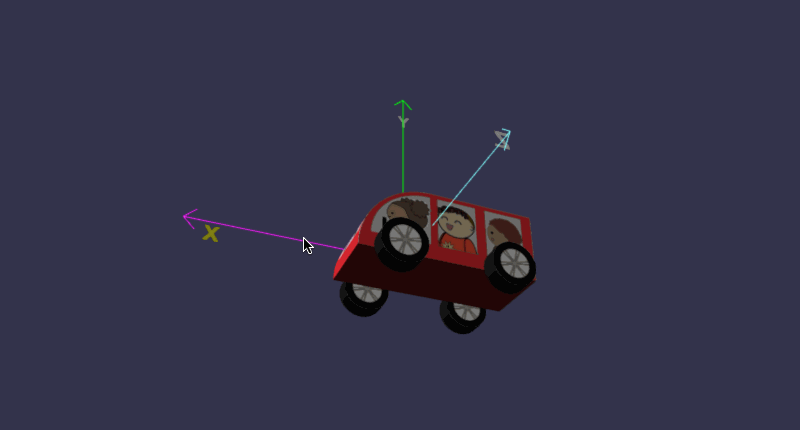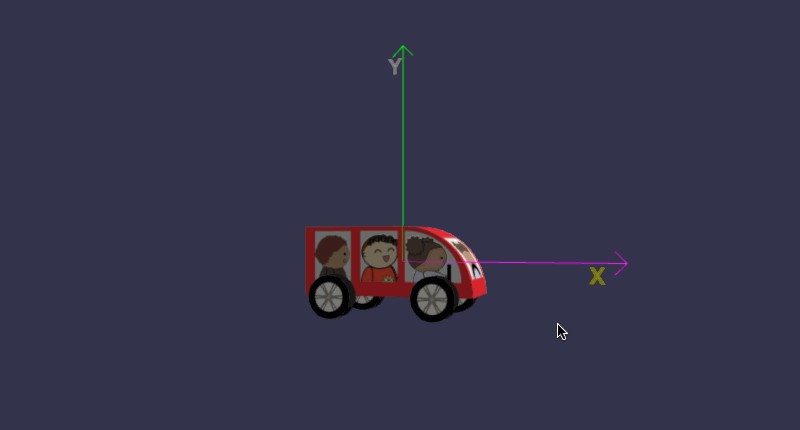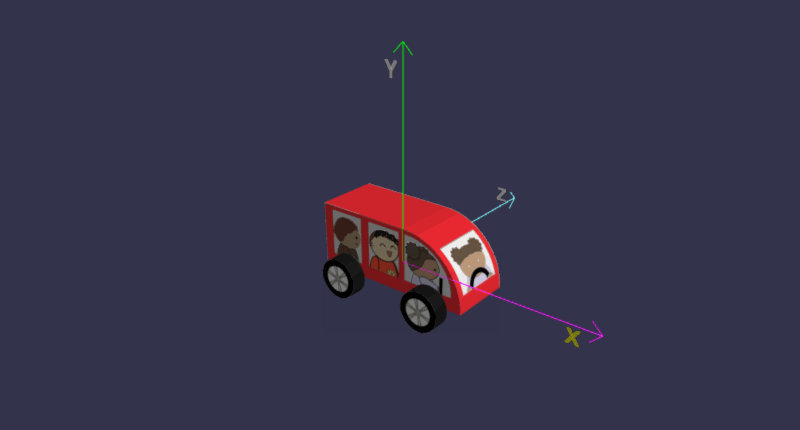
在线地址:https://yjmyzz.github.io/babylon_js_study/day05/06.html
参考文档:https://doc.babylonjs.com/features/introductionToFeatures/chap3/carmat
出处:http://yjmyzz.cnblogs.com
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文连接,否则保留追究法律责任的权利。

