第六周动手动脑
关于继承中的子类与父类的构造方法的使用
class Grandparent { public Grandparent() { System.out.println("GrandParent Created."); } public Grandparent(String string) { System.out.println("GrandParent Created.String:" + string); } } class Parent extends Grandparent { public Parent() { super("Hello.Grandparent."); System.out.println("Parent Created"); //super("Hello.Grandparent."); } } class Child extends Parent { public Child() { System.out.println("Child Created"); } } public class TestInherits { public static void main(String args[]) { Child c = new Child(); } }
运行结果:
GrandParent Created.
Parent Created
Child Created
从运行结果可以看出构造函数先运行父类再运行子类,并且通过修改上述代码可以看出super()只能在构造函数的第一行。
构造方法主要的作用就是初始化,初始化时需要先将父类的内容初始化再初始化自己的内容
final class 类名()是不可继承类,也就是所谓的“断子绝孙”类。
package one; public class ExplorationJDKSource { /** * @param args */ public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(new A()); } } class A{}
对该代码进行反汇编
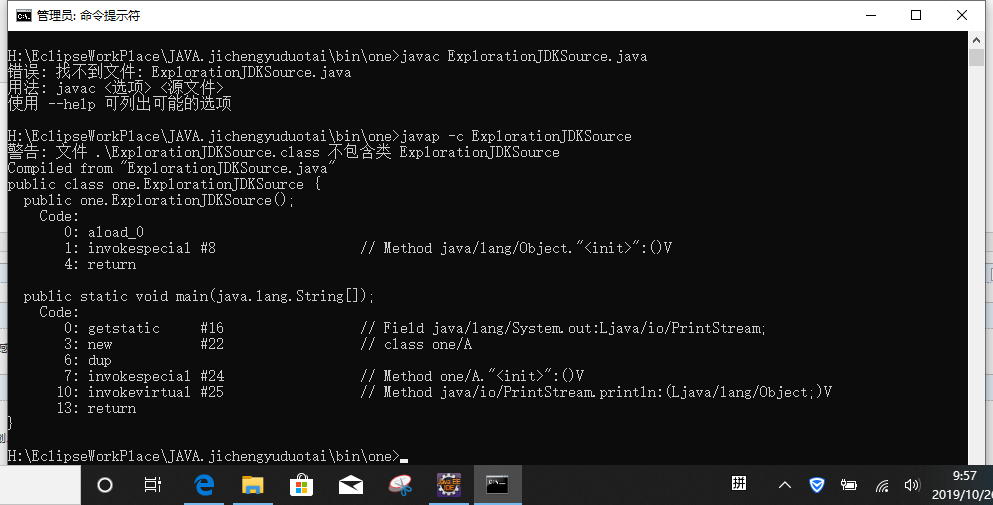
进入println的源代码:

进入valueOf源代码:

输出类 是输出的包名.类名@地址
package one; public class Fruit { public String toString() { return "Fruit toString."; } public static void main(String args[]) { Fruit f=new Fruit(); System.out.println("f="+f); // System.out.println("f="+f.toString()); } }
这段代码是该类覆盖了object父类的toString类
package one; public class text { public void show() { System.out.println("父类方法"); } }
package one; public class text1 extends text { public text1() { show(); } public void show() { //super.show(); System.out.println("这是子类"); } public static void main(String[] args) { new text1(); } }
上面两个代码是自己码的一个覆盖类,如果想要调用父类的被覆盖的类值能使用super.方法();的方法调用父类方法
package one; class Mammal{} class Dog extends Mammal {} class Cat extends Mammal{} public class TestCast { public static void main(String args[]) { Mammal m; Dog d=new Dog(); Cat c=new Cat(); m=d; //d=m; //d=(Dog)m; //d=c; //c=(Cat)m; } }
该代码运行时,
m=d;不会出错;
d=m;会出错;
d=(Dog)m;也会出错;
d=c;也会出错;
c=(Cat)m;也会出错;
总结上述内容,子类可以给父类赋值,父类给子类赋值会出错;
package one; public class ParentChildTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Parent parent=new Parent(); parent.printValue(); Child child=new Child(); child.printValue(); parent=child; parent.printValue(); parent.myValue++; parent.printValue(); ((Child)parent).myValue++; parent.printValue(); } } class Parent{ public int myValue=100; public void printValue() { System.out.println("Parent.printValue(),myValue="+myValue); } } class Child extends Parent{ public int myValue=200; public void printValue() { System.out.println("Child.printValue(),myValue="+myValue); } }
在子类与父类方法变量等相等时,父类对象调用父类方法 子类对象调用子类方法
子类对象在调用相同方法时 如果与父类方法同名则用“局部优先”原则,运行子类方法;
多态的好处就是可以在父类定义一个飞行的方法,然后子类可以根据自己的需要定义不同飞的方法和在何处飞等。
package zoo3; public class Zoo { public static void main(String args[]) { Feeder f = new Feeder("小李"); Animal[] ans = new Animal[16]; //饲养员小李喂养一只狮子 ans[0] = new Lion(); //饲养员小李喂养十只猴子 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { ans[1 + i] = new Monkey(); } //饲养员小李喂养5只鸽子 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { ans[11 + i] = new Pigeon(); } f.feedAnimals(ans); } } class Feeder { public String name; Feeder(String name) { this.name = name; } public void feedAnimals(Animal[] ans) { for (Animal an : ans) { an.eat(); } } } abstract class Animal { public abstract void eat(); } class Lion extends Animal { public void eat() { System.out.println("我不吃肉谁敢吃肉!"); } } class Monkey extends Animal { public void eat() { System.out.println("我什么都吃,尤其喜欢香蕉。"); } } class Pigeon extends Animal { public void eat() { System.out.println("我要减肥,所以每天只吃一点大米。"); } }
这种代码的优化可以使用一个而实例化所有类的对象






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:基于图像分类模型对图像进行分类
· go语言实现终端里的倒计时
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 25岁的心里话
· 闲置电脑爆改个人服务器(超详细) #公网映射 #Vmware虚拟网络编辑器
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· 零经验选手,Compose 一天开发一款小游戏!
· 一起来玩mcp_server_sqlite,让AI帮你做增删改查!!