Zigbee系列(路由机制)
参考文档:
ug103-02-fundamentals-zigbee.pdf section4 zigbe routing concepts
docs-05-3474-21-0csg-zigbee-specification.pdf 3.6.3 Routing
Broadcast Routing
Broadcast routing is a mechanism to send a message to all devices in a network. Network-level broadcast options exist to send to routers only or also to send to sleeping end devices. A broadcast message is repeated by all router-capable devices in the network three times to ensure delivery to all devices. While a broadcast is a reliable means of sending a message, it should be used sparingly because of the impact on network performance. Repeated broadcasts can limit any other traffic that may be occurring in the network.
Broadcasts are also not a reliable means of delivery to a sleeping device because the parent device is responsible for buffering the message for the sleeping child but may drop the message before the end device wakes to receive it.
广播地址:
|
0xffff |
All devices in PAN |
|
0xfffe |
Reserved |
|
0xfffd |
macRxOnWhenIdle = TRUE |
|
0xfffc |
All routers and coordinator |
|
0xfffb |
Low power routers only |
|
0xfff8 - 0xfffa |
Reserved |
|
Source Address |
Sequence Number |
Expiration Time |
||
|
broadcast initiator |
A countdown timer indicating the number of seconds until this |
|||
|
entry expires; the initial value is nwkNetworkBroadcastDeliveryTime. |
||||
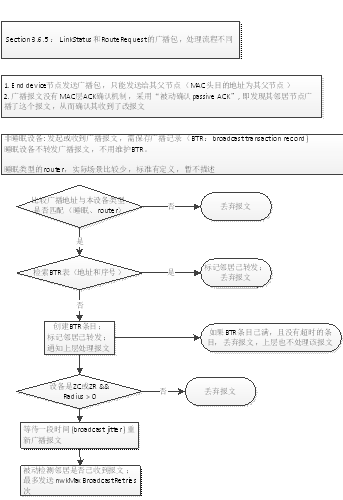
广播报文主要是通过BTR记录检测邻居节点是否已收到报文,如果邻居节点已收到报文,当前节点不再重发报文;如果未收到,重发nwkMaxBroadcastRetries次。
中间路由节点根据radius距离值,判断是否继续转发。
Multicast Routing
Multicast routing provides a one-to-many routing option. A multicast is used when one device wants to send a message to a group of devices, such as a light switch sending an on command to a bank of 10 lights. Under this mechanism, all the devices are joined into a multicast group. Only those devices that are members of the group will receive messages, although other devices will route these multicast messages. A multicast is a filtered limited broadcast. It should be used only as necessary in applications, because over-use of broadcast mechanisms can degrade network performance. A multicast message is never acknowledged.
-
只有数据帧使用多播,nwk command frame不使用多播。
-
多播详细可以由end device发起,多播报文不能发往睡眠类end device
Member Mode:成员类型多播(广播方式)
按照广播的方式,根据BTT广播记录表,广播报文。
节点接收到邻居发送的member mode多播报文,查询BTT记录。如果之前已处理过该报文,丢弃。
查询nwkGroupIDTable表,如果当前节点的groupID与报文的groupID匹配,通知上层处理该报文;
使用广播转发该报文,不需要使用passive ACK,经过nwkPassiveAckTimeout之后,重发报文,共发送nwkMaxBroadcastRetries次。
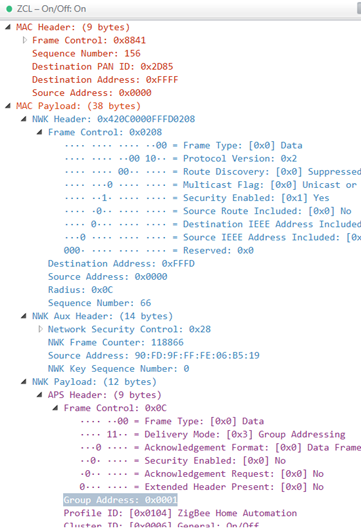
demo 抓包报文
发送原始报文:
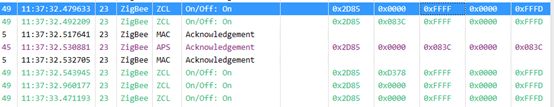
中间节点转发:
Non-Member Mode:非成员类型多播(单播方式)
检索路由表,查询groupID对应的下一跳地址,如果找到合法记录,发送(转发)报文。
如果没有记录,根据路由发现规则,建立新路由,单播转发报文。
查询nwkGroupIDTable表,如果当前节点的groupID与报文的groupID匹配,通知上层处理该报文;
直接发送
邻居节点不用查询路由表,报文直接发送。
2. Table Routing
Routes are formed when one node sends a route request to discover the path to another node. After a route is discovered between the two nodes, the source node sends its message to the first node in the route, as specified in the source node's routing table. Each intermediate node uses its own routing table to forward the message to the next node (that is hop) along the route until the message reaches its destination. If a route fails, a route error is sent back to the originator of the message who can then rediscover the route.
以A希望与D通信为例:
-
A发送路由请求(广播),B,C节点广播路由请求,并将到A的路由保存到自己的路由表中
-
D回应RouteReply,C、B根据自己的路由表,将报文转发到A
-
A通过下一跳B节点,将数据发送到D,
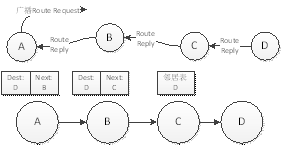

RouteTable 格式:
|
Destination Address |
status |
No Route cache |
Many-to-one |
Route record required |
GroupID flag |
Next-hop address |
|
0:ACTIVE |
A flag indicating that the destination address is a Group ID. |
The 16-bit network address of the next hop on the way to the destination. |
||||
The types of routing discussed below are:
• Table Routing
• Broadcast Routing
• Multicast Routing
• Many-to-One/Source Routing
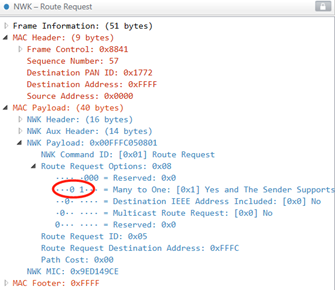
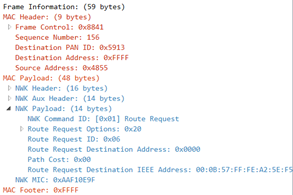
Many-To-One routing/Source routing
协调器发送Many-To-One route request广播报文,各子设备通过此报文获取到协调器的路由(接收到了上一节点转发的Route request)。
子设备有数据发往协调器时,先发送route record报文,协调器通过该报文获取到子设备的路由。
协调器发报文到子设备时,报文可以带上转发路径,路径中的各节点根据路径转发,称为source routing。
这种方式,可节省中间节点的内存,中间节点不需要大量的路由表条目。
High/Low RAM concentrator (协议文档中的memory constrained concentrator)
Nodes communicating with high RAM concentrators will continue to send in the route record packet with every inbound message until they receive their first source-routed packet from the concentrator that uses that recorded route. This source routed packet is what tells the node that the source route worked. The APS acknowledgement, if these are turned on, will count as this source routed packet. Also, this route-record suppression is even true for messages routed through this node. Thus, if outlier A sends to concentrator C via many-to-one route A-B-C, the first source routed message from C to B to A will cause B (and A) to stop sending route records up to the concentrator.
Please note,that if the concentrator is also the trust center, communication with the trust center will always be as if it were a low ram concentrator, so route records will always be sent in this case.
High Ram concentrator: 子设备持续发送route record,直到concentrator通过route record记录的路径发送了报文到子设备。报文包括APS ACK报文。
Low ram concentrarot:子设备每次单播一个报文,都发送route record。增加了网络中的数据量。

实际应用中,MTTO routing模式下,为了让concentrator快速恢复到子设备的路由,可以在发送MTTO route request报文后,触发子设备发送报文到concentrator。并且需要发送route record报文。(我们的实现方式:发送MTTO route request, 设置报文中的标记为Low Ram Concentrator,广播子设备的IEEE地址查询,子设备回应地址查询报文,发送route record, 协调器获取最新的路由路径)
MTTO Low Ram Concentrator:
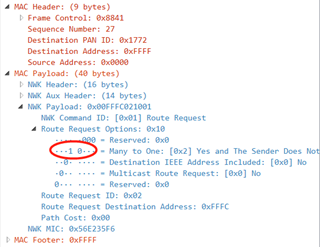
IEEE Address Request:

普通MTTO: