#MybatisPuls基础入门:
MybatisPuls基础入门:
介绍:使用maven搭建
一、环境搭建---配置文件(存放在resources 文件夹下)
1).applicationConetext.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:mybatis-spring="http://mybatis.org/schema/mybatis-spring"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://mybatis.org/schema/mybatis-spring http://mybatis.org/schema/mybatis-spring-1.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-4.0.xsd">
<!-- 数据源 -->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:db.properties"/>
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driver}"></property>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.url}"></property>
<property name="user" value="${jdbc.username}"></property>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 事务管理器 -->
<bean id="dataSourceTransactionManager"
class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 基于注解的事务管理 -->
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="dataSourceTransactionManager"/>
<!-- 配置SqlSessionFactoryBean
Mybatis提供的: org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean
MP提供的:com.baomidou.mybatisplus.spring.MybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean
-->
<bean id="sqlSessionFactoryBean" class="com.baomidou.mybatisplus.spring.MybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean">
<!-- 数据源 -->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
<property name="configLocation" value="classpath:mybatis-config.xml"></property>
<!-- 别名处理 修改地方1 实体类路径-->
<property name="typeAliasesPackage" value="com.web.pojo"></property>
<!--
注入全局MP策略配置
mp 本身存在 globalConfig ,但我们也需要自己引入
-->
<property name="globalConfig" ref="globalConfiguration"></property>
</bean>
<!--
定义MybatisPlus的全局策略配置
需要注入到 bean 中才能起作用
-->
<bean id ="globalConfiguration" class="com.baomidou.mybatisplus.entity.GlobalConfiguration">
<!--
在2.3版本以后,dbColumnUnderline 默认值就是true
mp 给出了 下划线和驼峰命名 的解决方法
例如 : 数据库 : list_name 实体类 listName
-->
<property name="dbColumnUnderline" value="true"></property>
<!--
全局的主键策略
相当于所有的实体类的自增策略是 Type.Auto
-->
<property name="idType" value="0"></property>
<!--
全局的表前缀策略配置 修改地方三 数据库表名前缀
默认访问的数据库的表示 该前缀 + 实体类名称 = 数据库表名
-->
<property name="tablePrefix" value="tbl_"></property>
</bean>
<!--
配置mybatis 扫描mapper接口的路径
-->
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
<!-- 修改地方二 mapper接口 -->
<property name="basePackage" value="com.web.mapper"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
2)jdbc.properties
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/fenbushi
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=520
3)log4j.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE log4j:configuration SYSTEM "log4j.dtd">
<log4j:configuration xmlns:log4j="http://jakarta.apache.org/log4j/">
<appender name="STDOUT" class="org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender">
<param name="Encoding" value="UTF-8" />
<layout class="org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout">
<param name="ConversionPattern" value="%-5p %d{MM-dd HH:mm:ss,SSS} %m (%F:%L) \n" />
</layout>
</appender>
<logger name="java.sql">
<level value="debug" />
</logger>
<logger name="org.apache.ibatis">
<level value="info" />
</logger>
<root>
<level value="debug" />
<appender-ref ref="STDOUT" />
</root>
</log4j:configuration>
4).mybatis-config.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
</configuration>
二、环境搭建---所需要依赖
<dependencies>
<!-- mp依赖
mybatisPlus 会自动的维护Mybatis 以及MyBatis-spring相关的依赖
-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus</artifactId>
<version>2.3</version>
</dependency>
<!--junit 测试-->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.9</version>
</dependency>
<!-- log4j 日志记录 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>1.2.17</version>
</dependency>
<!-- c3p0 数据库连接池-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.mchange</groupId>
<artifactId>c3p0</artifactId>
<version>0.9.5.2</version>
</dependency>
<!-- mysql -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.37</version>
</dependency>
<!-- spring -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>4.3.10.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-orm</artifactId>
<version>4.3.10.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
二、创建数据库表和实体类
1.tbl_user表
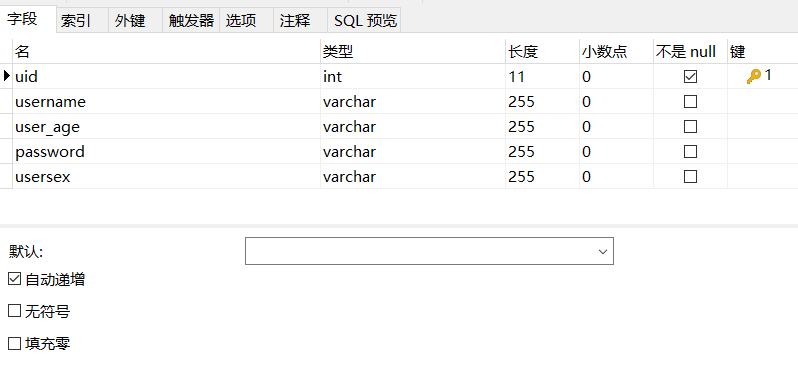
注:配置文件中添加了全局前缀策略,使用的好处是使用MP的CRUD 实体类可以不用指定对应的操作的表
操作的表 = 前缀 + 实体类名
<property name="tablePrefix" value="tbl_"></property>
2.实体类
public class User {
/**
* TableId
* value:表示 主键的列名,如果数据库表中的列名等于实体类的名称可以省略
* type:主键自增
*
* */
@TableId(value = "uid",type = IdType.AUTO)
private Integer uid;
private String username;
private String userAge;
private String usersex;
private String password;
}
注:该配置文件开启了 下划线转驼峰命名的配置,所以该实体类中的 userAge 对应数据库表名中的 user_age,(如果操作的mp依赖是2.3版本以上的则自动默认是开启的);
<property name="dbColumnUnderline" value="true"></property>
3.创建mapper接口并实现 BaseMapper<>
BaseMapper中提供了大部分该对象的CRUD的方法
public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper<User> {}
三、操作
1.在测试类中设置成员属性
// 读取配置文
private ApplicationContext ioc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//获取bean容器中的 userMapper接口
private UserMapper userMapper = ioc.getBean("userMapper",UserMapper.class);
2.查看是否连接上数据库
@Test
public void testDataScoure(){
// 获取配置文件中的datasource
DataSource ds = ioc.getBean("dataSource",DataSource.class);
// 查看时否连接上
System.out.println(ds);
try {
// 连接信息
Connection connection = ds.getConnection();
System.out.println(connection);
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
1.添加:insert
// 添加一个 班级信息
@Test
public void insertClazz(){
User user = new User();
user.setUsername("土豆");
user.setPassword("123");
user.setUserAge("23");
Integer insert = usermapperMapper.insert(user);
System.out.println("影响条数:"+ insert);
System.out.println("主键id:"+ user.getUid());
}
2.添加:insertAllColumn
// 添加一个 班级信息
@Test
public void insertClazz(){
User user = new User();
user.setUsername("黄瓜");
user.setPassword("123");
user.setUserAge("23");
Integer insert = usermapperMapper.insertAllColumn(user);
System.out.println("影响条数:"+ insert);
}
总结一:
- insert:方法中自带非空判断,没有属性的属性不会添加。且如果数据不全,能添加到数据库但是没有返回值。
- insertAllColumn:添加的时候没有非空半段,会将所有的属性都添加到数据库。
- 除了查询每个方法都会返回数据库中影响的条数,添加还会放回出添加到数据库的字段并将该值赋值到添加的类中。
3.修改 updateById通过id进行修改
@Test
public void update(){
User user =new User();
user.setUid(1);
user.setPassword("123");
user.setUsername("小花");
Integer update = userMapper.updateById(user);
System.out.println("影响条数:" + update);
}
该方法具有非空判断,只会修改属性不为空的字段
4.修改 updateAllColumnById 覆盖式修改
@Test
public void updateColumn(){
User user =new User();
user.setId(1);
user.setPassword("123");
user.setUsername("土豆");
Integer update = userMapper.updateAllColumnById(user);
System.out.println("影响条数:" + update);
}
这个方法相当于覆盖,如果部分属性没有值,这个方法执行后数据库的这些属性将会变为空值
5.通过id 查询数据
/**
* 查询方法 selectById
* */
@Test
public void selectById(){
User user = userMapper.selectById(1);
System.out.println("id为1 的记录 :" + user);
}
6. selectOne :通过实体类中非空属性进行查询
/**
* 查询 selectOne
*
* */
@Test
public void selectOne(){
User user1 = new User();
user1.setUsername("赵小花");
User user2 = userMapper.selectOne(user1);
System.out.println("id为1 的记录 :" + user2);
}
注:如果实体类中的属性不为空,则会默认为查询的一个条件
坑:如果查询的时候某些属性都是有许多相同的,查询的时候会报错。因为该方法只能返回条数据
7. selectBatchIds :通过id集合查询数据(参数为集合类型)
/**
* 查询 selectBatchIds
*
* 通过id 集合查询数据
* */
@Test
public void selectByIds(){
List<Integer> ids = new ArrayList<Integer>();
ids.add(1);
ids.add(2);
List<User> users = userMapper.selectBatchIds(ids);
System.out.println("id为1 的记录 :" + users);
}
8. selectByMap :map集合封装的数据查询数据(参数为map集合)
/**
*map集合封装的数据查询数据(参数为map集合)
*
* */
@Test
public void selectMap(){
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<String,Object>();
map.put("username","赵小花");
map.put("user_age","25");
map.put("password","123");
List<User> users = userMapper.selectByMap(map);
System.out.println("查询结果:" + users);
}
注:map中的主键对应的数据库表中的字段,不是实体类中的属性
Wrapper的实现了类有 EntityMapper 和 Condition
9.selectList 条件构造器查询数据
/**
* 条件构造器 条件查询
*
* 降序查询数据
*
* */
@Test
public void selectByWrapper1(){
List<User> users = userMapper.selectList(
new EntityWrapper<User>().eq("password", "123")
// 两者存起一就好好 推荐使用第一个
// .orderDesc(Arrays.asList(new String[] {"user_age"})) // orderDesc 和 orderAsc 的参数都是 集合可以借助Arrays完成数据操作
.orderBy("user_age") // 默认的是升序 不是降序 可以使用 last 注入自定义的sql 语句
.last("desc limit 1,3")// last 表示 在sql后面拼接sql语句 这样就无法防止sql注入
);
System.out.println(users);
}
10.selectList: Condition条件构造
/**
* 条件构造器 条件查询
*
* 降序查询数据
*
* */
@Test
public void selectByWrapper1(){
List<User> users = userMapper.selectList(
Condition.create().eq("password", "123")
// 两者存起一就好好 推荐使用第一个
// .orderDesc(Arrays.asList(new String[] {"user_age"})) // orderDesc 和 orderAsc 的参数都是 集合可以借助Arrays完成数据操作
.orderBy("user_age") // 默认的是升序 不是降序 可以使用 last 注入自定义的sql 语句
.last("desc limit 1,3")// last 表示 在sql后面拼接sql语句 这样就无法防止sql注入
);
System.out.println(users);
}
总结 :Condition 和EntityWarpper 的不同之处在于
- Condition是通过 create()方法创建出来的
- EntityWarpper是需要new出来的
11.selectPage: 条件+分页查询
/**
* 条件构造器 分页条件查询
*
* 需求 性别为男 姓名为 xxx的用户 年龄在 11 到 25之间的用户信息
* 每页显示 2条数据
*
* */
@Test
public void selectByWrapper2(){
List<User> users = userMapper.selectPage(new Page<User>(1, 2),
new EntityWrapper<User>().between("user_age", "11","25")
.eq("usersex", "男")
.eq("username", "张三"));
System.out.println(users);
}
12.update: 条件构造器记性修改
/**
* 条件构造器 条件查询
* 修改密码为 123,姓名为张三 或 姓名包含五的人的密码为6666
*
* */
@Test
public void updateWrapper(){
User user = new User();
user.setPassword("6666");
Integer update = userMapper.update(user, new EntityWrapper<User>().eq("password", "123")
.eq("username", "张三")
.or() // 后面又是 条件组合
.like("username", "五"));
System.out.println("影响条数:" + update);
}
13.update: 条件构造器记性修改
/**
* 条件构造器 条件查询
* (修改密码为 123,姓名为张三 )或 (姓名包含五密码为111得人),人的密码为6666
*
* */
@Test
public void updateWrapper(){
User user = new User();
user.setPassword("6666");
Integer update = userMapper.update(user, new EntityWrapper<User>().eq("password", "123")
.eq("username", "张三")
.orNew() // 后面又是 条件组合
.like("username", "五")
.eq("username","111"));
System.out.println("影响条数:" + update);
}
小结:
- or()表示的是这个条件和前面的条件是平级关系
- orNew()表示的是后面的是后者的另一个条件(条件组合)
14.deleteById:通过id删除信息
/**
* 删除 deleteById(Id)
*
* */
@Test
public void deleteById(){
Integer integer = userMapper.deleteById(1);
System.out.println("影响条数:" + integer);
}
15. deleteBatchIds:通过id的集合删除数据(查询相似)
/**
* 删除 deleteBatchIds(List supper)
* ids 的集合
* */
@Test
public void deleteBatchIds(){
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
list.add(2);
list.add(4);
Integer integer = userMapper.deleteBatchIds(list);
System.out.println("影响条数:" + integer);
}
16.deleteMap删除 (和selectMap使用相似)
/**
* 删除 deleteByMap(Map supper)
* map中的主键仍然是数据库表的字段
* */
@Test
public void deleteByMap(){
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
map.put("usernmame","张三");
map.put("password","123");
Integer integer = userMapper.deleteByMap(map);
System.out.println("影响条数:" + integer);
}
17.delete:条件构造删除
/**
* 条件构造器 条件删除
*删除年龄等于 23 或姓名包含五的数据
*
* */
@Test
public void deleteWrapper(){
Integer delete = userMapper.delete( new EntityWrapper<User>().eq("password", "123")
.eq("user_age", "23")
.orNew() // 后面又是 条件组合
.like("username", "五"));
System.out.println("影响条数:" + delete);
}



