目录
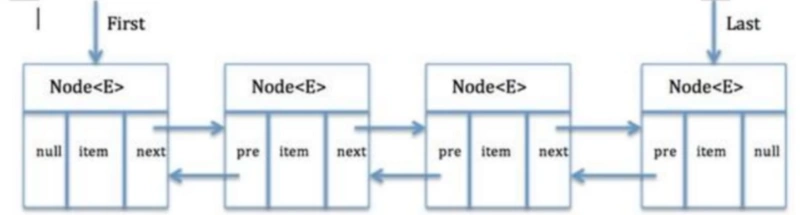
LinkedList本质上是一个双向链表。
那么什么是链表呢?链表原先是C/C++的概念,是一种线性的存储结构,意思是将要存储的数据存在一个存储单元里面,这个存储单元里面除了存放有待存储的数据以外,还存储有其下一个存储单元的地址(下一个存储单元的地址是必要的,有些存储结构还存放有其前一个存储单元的地址),每次查找数据的时候,通过某个存储单元中的下一个存储单元的地址寻找其后面的那个存储单元。
而LinkedList是双向链表,在list中的每个元素,在存储自身元素外,还额外存储了其前一个和后一个元素的地址,所以 也就可以很方便地根据当前元素获取到其前后的元素。链表的尾部元素的后一个节点是链表的头节点;而链表的头结点前一个节点则是则是链表的尾节点。
由于LinkedList的底层是双向链表,因此其顺序访问的效率非常高,而随机访问的效率就比较低了,因为通过索引去访问的时候,首先会比较索引值和链表长度的1/2,若前者大,则从链表尾开始寻找,否则从链表头开始寻找,这样就把双向链表与索引值联系起来了。

总结:
public class LinkedList<E>
extends AbstractSequentialList<E>
implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
- LinkedList<E>:说明它支持泛型。
-
extends AbstractSequentialList<E>
- AbstractSequentialList 继承自AbstractList,但AbstractSequentialList 只支持按次序访问,而不像 AbstractList 那样支持随机访问。这是LinkedList随机访问效率低的原因之一。
-
implements
- List<E>:说明它支持集合的一般操作。
- Deque<E>:Deque,Double ended queue,双端队列。LinkedList可用作队列或双端队列就是因为实现了它。
- Cloneable:表明其可以调用clone()方法来返回实例的field-for-field拷贝。
- java.io.Serializable:表明该类是可以序列化的。
与ArrayList对比
LinkedList并没有实现RandomAccess,而实现RandomAccess表明其支持快速(通常是固定时间)随机访问。此接口的主要目的是允许一般的算法更改其行为,从而在将其应用到随机或连续访问列表时能提供良好的性能。这是LinkedList随机访问效率低的原因之一。
// LinkedList节点个数 transient int size = 0; /** * Pointer to first node. * //指向头节点的指针 */ transient Node<E> first; /** * Pointer to last node. * 指向尾节点的指针 */ transient Node<E> last;
//私有内部类Node,用来存储集合中的元素
// Node作为LinkedList的底层数据结构,关联了前驱节点,后续节点和值
private static class Node<E> {
E item; //节点的值
Node<E> next; //当前节点的后一个节点的引用(可以理解为指向当前节点的后一个节点的指针)
Node<E> prev; //当前节点的前一个节点的引用(可以理解为指向当前节点的前一个节点的指针)
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
/** * Constructs an empty list. * 构造一个空链表 */ public LinkedList() { } /** * Constructs a list containing the elements of the specified * collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's * iterator. * 构造一个包含指定集合元素的链表,按照集合的迭代器返回它们的顺序 * * @param c 要放入链表中的集合 * @throws NullPointerException 当前参数c为null时抛出异常 */ public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) { this(); addAll(c); }
通过addFirst() 方法调用私有方法linkFirst (E e):在链表头部位置插入元素
/** * Inserts the specified element at the beginning of this list. * * @param e the element to add */ public void addFirst(E e) { linkFirst(e); } /** * Links e as first element. * 在表头添加指定元素e 即链接头节点 */ private void linkFirst(E e) { final Node<E> f = first; //将头结点赋给f节点 final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(null, e, f); //新建节点,节点的prev为null,next指针指向头节点f(原来的头节点变成了第二个) first = newNode; //更新first节点,将新建节点newNode赋给头节点 if (f == null) //如果f为空,表示原来的linkdeList就为空,更新last节点为新节点,此时头尾元素都是e last = newNode; else //否则把f的prev设置为newNode,即将原来的头节点f的前置指针指向新的头节点newNode f.prev = newNode; size++; //元素总数自增 modCount++; //修改次数自增 }
通过add (E e)或者addLast (E e) 方法调用私有方法linkLast (E e) 来在链表尾部位置插入元素e
步骤:
- 先用一个变量l指向尾结点,
- 创建新结点
- 尾结点指向新的结点
- 判断原来的尾结点(变量l指向的结点)是否为空,
- 如果为空说明是个空链表,将头结点指向新的结点;
- 原来的尾结点不为空,将原来尾结点(l指向的结点)的prev指向新的结点
/** * Appends the specified element to the end of this list. * * <p>This method is equivalent to {@link #addLast}. * * @param e element to be appended to this list * @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add}) */ public boolean add(E e) { linkLast(e); return true; } /** * Appends the specified element to the end of this list. * * <p>This method is equivalent to {@link #add}. * * @param e the element to add */ public void addLast(E e) { linkLast(e); } /** * Links e as last element. * 在表尾插入指定元素e 即链接尾节点 */ void linkLast(E e) { final Node<E> l = last; //将尾节点赋给l节点 final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null); //新建节点,节点的prev指向l节点,next指针为null last = newNode; //更新last节点,将新建节点newNode赋给尾节点 if (l == null) //如果l为空,表示原来的linkedList为空,更新first节点为新节点,此时头尾元素都是e first = newNode; else l.next = newNode; //否则把l的next设置为newNode,即将原来的尾节点l的后置指针指向新的节点 size++; //元素总数自增 modCount++; //修改次数自增 }
通过add(int index,E element) 方法调用linkBefore (E e, Node<E> succ)来在非空节点succ之前插入元素e
/** * Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this list. * Shifts the element currently at that position (if any) and any * subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their indices). * 在指定位置添加元素 * * @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted * @param element element to be inserted * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} */ public void add(int index, E element) { checkPositionIndex(index); if (index == size) linkLast(element); else linkBefore(element, node(index)); //非尾部插入情况 } /** * Inserts element e before non-null Node succ. * 在指定节点succ之前插入指定元素e,指定节点succ不为null */ void linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) { // assert succ != null; final Node<E> pred = succ.prev; //获得指定节点的的前继节点 final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ); //新建节点newNode,前置指针指向pred,后置指针指向succ succ.prev = newNode; //更新succ节点的前继节点为新节点 if (pred == null) //如果succ的前一个节点为空,表示该节点插入在头节点之前,更新first节点 first = newNode; else pred.next = newNode; //否则直接将pred的后置指针指向newNode即可 size++; //元素总数自增 modCount++; //修改次数自增 }
addAll(Collection<? extends E> c)
步骤:
- 检查index范围是否在size之内
- toArray()方法把集合的数据存到对象数组中
- 得到插入位置的前驱和后继节点
- 遍历数据,将数据插入到指定位置的节点之前
/** 调用addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) 完成集合的添加 * Inserts all of the elements in the specified collection into this * list, starting at the specified position. Shifts the element * currently at that position (if any) and any subsequent elements to * the right (increases their indices). The new elements will appear * in the list in the order that they are returned by the * specified collection's iterator. * * @param index index at which to insert the first element * from the specified collection * @param c collection containing elements to be added to this list * @return {@code true} if this list changed as a result of the call * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} * @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null */ public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) { //插入指定集合到链表的指定位置 checkPositionIndex(index); //1、检查index范围是否在size之内 Object[] a = c.toArray(); //2、toArray()方法把集合的数据存到对象数组中 int numNew = a.length; if (numNew == 0) return false; Node<E> pred, succ; //3、获得插入位置的前驱节点和后继节点 if (index == size) { //如果插入位置为链表尾部,则前驱节点为last,后继节点为null succ = null; pred = last; } else { //否则,调用node()方法得到index上的节点赋给succ,再得到前驱节点 succ = node(index); pred = succ.prev; } for (Object o : a) { //4、遍历数组中每个元素并将数据插入 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) o; Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, null); //创建新节点 if (pred == null) //如果插入位置在链表头部 first = newNode; //更新头节点 else pred.next = newNode; //否则将前驱节点的后置指针指向新建节点 pred = newNode; //最后把新建节点作为前驱节点,继续循环,以便后续新节点的添加 } if (succ == null) { //如果插入位置是链表的尾部 last = pred; //更新last指针 } else { pred.next = succ; //构建双向链表,新建节点插入到succ[index位置上的节点]之前 succ.prev = pred; //将succ的前置指针指向index位置上的节点 } size += numNew; modCount++; return true; }
get (int index)
/** * Returns the element at the specified position in this list. * * @param index index of the element to return * @return the element at the specified position in this list * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} */ public E get(int index) { checkElementIndex(index); //检查index范围是否在size之内 return node(index).item; //调用node(index)去找到index对应的node然后返回它的值 } /** * Returns the (non-null) Node at the specified element index. * 返回在指定索引处的非空元素 */ Node<E> node(int index) { // assert isElementIndex(index); if (index < (size >> 1)) { //下标小于长度的一半,从头开始遍历 Node<E> x = first; for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) x = x.next; return x; } else { //下标大于长度的一半,从尾开始遍历 Node<E> x = last; for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--) x = x.prev; return x; } }
获取头节点 (index = 0) 数据方法:
区别:getFirst(),element(),peek(),peekFirst()这四个获取头节点方法的区别在于对链表为空时的处理,是抛出异常还是返回null
getFirst()和 element()方法在链表为空时,抛出异常
element()方法内部使用getFirst()实现。两者在链表为空时,抛出NoSuchElementException
peek()和peekFirst()在链表为空时返回null
/** * Returns the first element in this list. * 返回链表中头节点的值 * @return the first element in this list * @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty */ public E getFirst() { final Node<E> f = first; if (f == null) throw new NoSuchElementException(); return f.item; } /** * Retrieves, but does not remove, the head (first element) of this list. * 获取链表头节点的值,头节点为空抛出异常 * @return the head of this list * @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty * @since 1.5 */ public E element() { return getFirst(); } /** * Retrieves, but does not remove, the head (first element) of this list. * 返回队列的头节点的值,如果头节点为空则返回null * @return the head of this list, or {@code null} if this list is empty * @since 1.5 */ public E peek() { final Node<E> f = first; return (f == null) ? null : f.item; } /** * Retrieves, but does not remove, the first element of this list, * or returns {@code null} if this list is empty. * 返回队列的头节点的值,如果头节点为空则返回null * @return the first element of this list, or {@code null} * if this list is empty * @since 1.6 */ public E peekFirst() { final Node<E> f = first; return (f == null) ? null : f.item; }
获取尾节点(index = -1)数据方法:
/** * Returns the last element in this list. * 返回链表中的尾节点的值 * @return the last element in this list * @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty */ public E getLast() { final Node<E> l = last; if (l == null) throw new NoSuchElementException(); return l.item; } /** * Retrieves, but does not remove, the last element of this list, * or returns {@code null} if this list is empty. * 返回队列中的尾节点的值,如果尾节点为空则返回null * @return the last element of this list, or {@code null} * if this list is empty * @since 1.6 */ public E peekLast() { final Node<E> l = last; return (l == null) ? null : l.item; }
通过remove ( ),removeFirst(),pop() 方法调用unlinkFirst (Node<E> f)来删除头节点,并返回被删除的头节点的值
/** * Retrieves and removes the head (first element) of this list. * * @return the head of this list * @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty * @since 1.5 */ public E remove() { return removeFirst(); } /** * Pops an element from the stack represented by this list. In other * words, removes and returns the first element of this list. * * <p>This method is equivalent to {@link #removeFirst()}. * * @return the element at the front of this list (which is the top * of the stack represented by this list) * @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty * @since 1.6 */ public E pop() { return removeFirst(); } /** * Retrieves and removes the first element of this list, * or returns {@code null} if this list is empty. * * @return the first element of this list, or {@code null} if * this list is empty * @since 1.6 */ public E pollFirst() { final Node<E> f = first; return (f == null) ? null : unlinkFirst(f); } public E removeFirst() { final Node<E> f = first; if (f == null) throw new NoSuchElementException(); //链表为空则抛出异常 return unlinkFirst(f); } /** * Unlinks non-null first node f. * 删除头节点,并返回被删除头节点的值 */ private E unlinkFirst(Node<E> f) { // assert f == first && f != null; final E element = f.item; //定义element,保存头节点的值 final Node<E> next = f.next; //保存头节点指向的下一个节点 f.item = null; //将头节点f的元素值置为空 f.next = null; // help GC //将头节点的next置为空 first = next; //更新头节点first if (next == null) //如果next为null,则将尾节点置为null last = null; else next.prev = null; //否则将next的前置指针指向null size--; //元素总数自减 modCount++; //修改次数自增 return element; //返回被删除节点的元素值 }
通过removeLast ( ),pollLast ( ) 方法调用unlinkLast来删除尾节点
区别:removeLast()在链表为空时将抛出NoSuchElementException,而pollLast()方法返回null
/** * Retrieves and removes the last element of this list, * or returns {@code null} if this list is empty. * * @return the last element of this list, or {@code null} if * this list is empty * @since 1.6 */ public E pollLast() { final Node<E> l = last; return (l == null) ? null : unlinkLast(l); } /** * Removes and returns the last element from this list. * * @return the last element from this list * @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty */ public E removeLast() { final Node<E> l = last; if (l == null) throw new NoSuchElementException(); return unlinkLast(l); } /** * Unlinks non-null last node l. * 删除尾节点,并返回被删除节点的元素值 */ private E unlinkLast(Node<E> l) { // assert l == last && l != null; final E element = l.item; //定义element,保存尾节点的元素值 final Node<E> prev = l.prev; //保存尾节点指向的上一个节点 l.item = null; //将尾节点l的元素值置空 l.prev = null; // help GC //将尾节点的prev置为空 last = prev; //更新尾节点last if (prev == null) //如果prev为null,则将头节点置为null first = null; else prev.next = null; //否则将prev的后置指针置为null size--; //元素总数自减 modCount++; //修改次数自增 return element; //返回被删除节点的元素值 }
通过remove(Obejct o)unlink(Node<E> x)删除指定节点,返回指定元素的值:
/** * Removes the first occurrence of the specified element from this list, * if it is present. If this list does not contain the element, it is * unchanged. More formally, removes the element with the lowest index * {@code i} such that * {@code Objects.equals(o, get(i))} * (if such an element exists). Returns {@code true} if this list * contained the specified element (or equivalently, if this list * changed as a result of the call). * * @param o element to be removed from this list, if present * @return {@code true} if this list contained the specified element */ public boolean remove(Object o) { if (o == null) { for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { if (x.item == null) { unlink(x); return true; } } } else { for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { if (o.equals(x.item)) { unlink(x); return true; } } } return false; } /** * Unlinks non-null node x. * 删除指定节点,返回指定元素的值 */ E unlink(Node<E> x) { // assert x != null; final E element = x.item; //保存节点的值 final Node<E> next = x.next; //获得后继节点 final Node<E> prev = x.prev; //获得前驱节点 if (prev == null) { first = next; //如果删除的是头节点,让头节点指向该节点的后继节点 } else { prev.next = next; //否则将前驱节点的后置指针指向后继节点 x.prev = null; } if (next == null) { last = prev; //如果删除的是尾节点,让尾节点指向该节点的前驱节点 } else { next.prev = prev; //否则将后继节点的前置指针指向前驱节点 x.next = null; } x.item = null; //将指点删除节点的元素置为null size--; modCount++; return element; }
根据对象得到索引的方法
indexOf(Object o)
/** 正向遍历链表,返回指定元素第一次出现时的索引。如果元素没有出现,返回-1 * Returns the index of the first occurrence of the specified element * in this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element. * More formally, returns the lowest index {@code i} such that * {@code Objects.equals(o, get(i))}, * or -1 if there is no such index. * * @param o element to search for * @return the index of the first occurrence of the specified element in * this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element */ public int indexOf(Object o) { int index = 0; if (o == null) { //从头节点开始遍历 for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { if (x.item == null) return index; index++; } } else { for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { if (o.equals(x.item)) return index; index++; } } return -1; }
lastIndexOf(Object o)
/** 逆向遍历链表,返回指定元素第一次出现时的索引。如果元素没有出现,返回-1 * Returns the index of the last occurrence of the specified element * in this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element. * More formally, returns the highest index {@code i} such that * {@code Objects.equals(o, get(i))}, * or -1 if there is no such index. * * @param o element to search for * @return the index of the last occurrence of the specified element in * this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element */ public int lastIndexOf(Object o) { int index = size; if (o == null) { //从尾节点开始遍历 for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) { index--; if (x.item == null) return index; } } else { for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) { index--; if (o.equals(x.item)) return index; } } return -1; }
contains(Object o)
/** 判断链表是否包含指定对象o * Returns {@code true} if this list contains the specified element. * More formally, returns {@code true} if and only if this list contains * at least one element {@code e} such that * {@code Objects.equals(o, e)}. * * @param o element whose presence in this list is to be tested * @return {@code true} if this list contains the specified element */ public boolean contains(Object o) { return indexOf(o) >= 0; }
set(int index,E element)
/** * Replaces the element at the specified position in this list with the * specified element. * 替换指定索引处的元素为指定元素element,并返回原先索引处的元素值 * @param index index of the element to replace * @param element element to be stored at the specified position * @return the element previously at the specified position * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} */ public E set(int index, E element) { checkElementIndex(index); Node<E> x = node(index); E oldVal = x.item; x.item = element; return oldVal; }
转为数组: (没有参数)
/** 遍历LinkedList中的每个节点,把值添加到数组中 * Returns an array containing all of the elements in this list * in proper sequence (from first to last element). * * <p>The returned array will be "safe" in that no references to it are * maintained by this list. (In other words, this method must allocate * a new array). The caller is thus free to modify the returned array. * * <p>This method acts as bridge between array-based and collection-based * APIs. * * @return an array containing all of the elements in this list * in proper sequence */ public Object[] toArray() { Object[] result = new Object[size]; int i = 0; for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) result[i++] = x.item; return result; }
转为数组:(参数为数组)
/** * */ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) { if (a.length < size) //如果数组a的长度小于集合的大小的话,通过反射创建一个和集合同样大小的数组 a = (T[])java.lang.reflect.Array.newInstance( a.getClass().getComponentType(), size); int i = 0; Object[] result = a; for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) //接着把集合中的所有元素添加到数组中 result[i++] = x.item; if (a.length > size) //数组长度大于集合中元素个数,则把a[size]置为null a[size] = null; return a; }
LinkedList提供了两种迭代器,一种是返回Iterator,另一种返回ListIterator。
1.返回ListIterator迭代器:
public ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index) { checkPositionIndex(index); return new ListItr(index); }
2.返回Iterator迭代器:
public Iterator<E> descendingIterator() { return new DescendingIterator(); }
以上参考整理自以下出处:
https://blog.csdn.net/m0_37884977/article/details/80467658
https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000019197171
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_39723544/article/details/82286271


 posted on
posted on
