目录
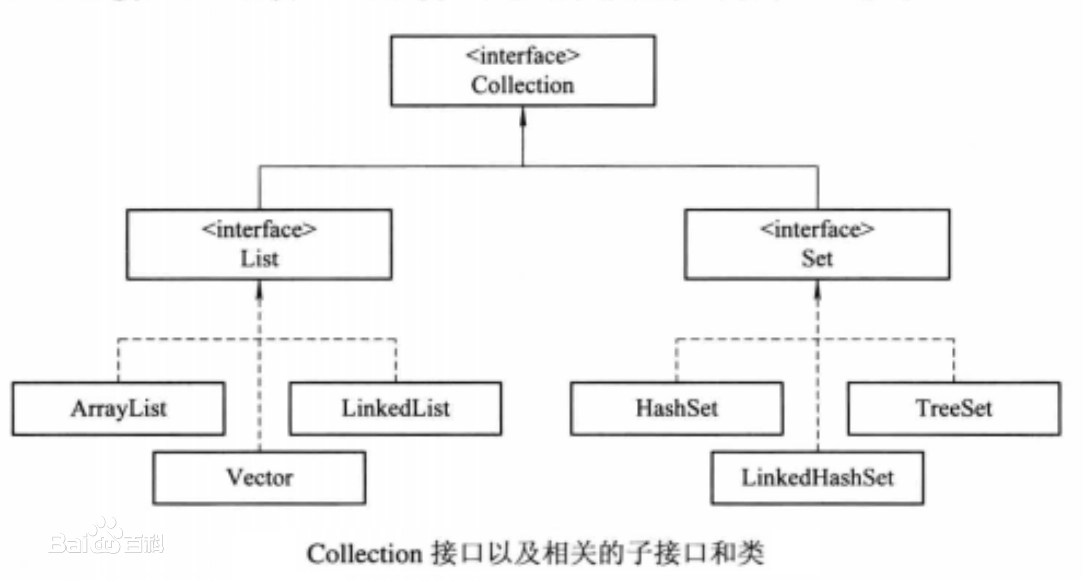
如前面提到的,Map接口与Collection接口不同,Map提供键到值的映射。Map接口提供三种Collection视图,允许以键集、值集或键一值映射关系集的形式查看某个映射的内容。Map接口及其相关类的关系如图所示
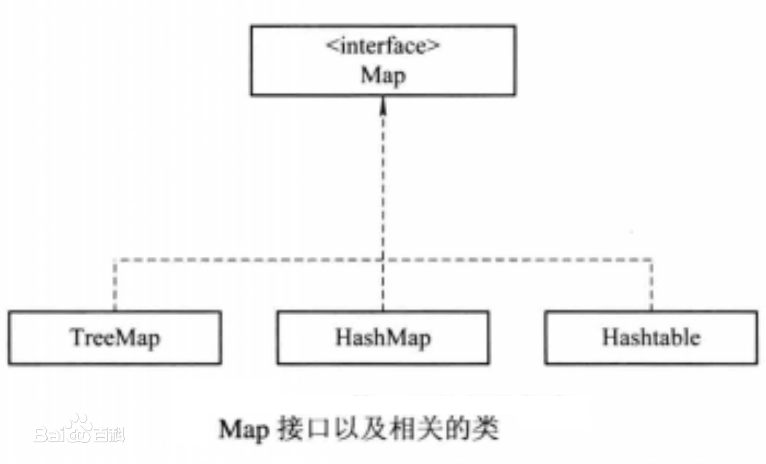
Java集合全览
ArrayList 是一个数组列表,相当于 动态数组。与数组相比,容量可以动态增长。它继承于AbstractList,实现了List, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable这些接口。ArrayList 允许空值和重复元素,当往 ArrayList 中添加的元素数量大于其底层数组容量时,其会通过扩容机制重新生成一个更大的数组。另外,由于 ArrayList 底层基于数组实现,所以其可以保证在 O(1) 复杂度下完成随机查找操作。其他方面,ArrayList 是非线程安全类,并发环境下,多个线程同时操作 ArrayList,会引发不可预知的错误。

ArrayList的继承关系
1 java.lang.Object 2 ↳ java.util.AbstractCollection<E> 3 ↳ java.util.AbstractList<E> 4 ↳ java.util.ArrayList<E> 5 6 public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E> 7 implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable {}
ArrayList与Collection关系:

ArrayList包含了两个重要对象:elementData 和 size。
- elementData 是 "Object [ ]类型的数组",保存了添加到ArrayList中的元素。实际上,elementData是个动态数组,我们能通过构造函数 ArrayList(int initialCapacity)来执行它的初始容量为initialCapacity;如果通过不含参数的构造函数ArrayList()来创建ArrayList,则elementData的容量默认是10。elementData数组的大小会根据ArrayList容量的增长而动态的增长,具体的增长方式,请参考源码分析中的ensureCapacity()函数。
- size则是动态数组的实际大小
1 private static final long serialVersionUID = 8683452581122892189L; 2 3 /** 4 * 默认初始化容量 5 */ 6 private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10; 7 8 /** 9 * 用于空实例的共享空数组实例。 10 */ 11 private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; 12 13 /** 14 * Shared empty array instance used for default sized empty instances. We 15 * distinguish this from EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA to know how much to inflate when 16 * first element is added. 17 * 用于默认大小的空实例的共享空数组实例。我们将其与EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA分开来,以了解添加第一个元素时要扩容多少。 18 * 即一个空数组实例 19 * - 当用户没有指定 ArrayList 的容量时,返回的是该数组,刚创建一个 ArrayList 时,其内数据量为 0. 20 * - 当用户第一次添加元素时,该数组会扩容,变成默认容量为 10(DEFAULT_CAPACITY)的一个数组 21 * - 与 EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA 的区别:DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA数组是默认返回的,而EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA是在指定容量为 0 时返回。 22 */ 23 private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; 24 25 /** 26 * The array buffer into which the elements of the ArrayList are stored. 27 * The capacity of the ArrayList is the length of this array buffer. Any 28 * empty ArrayList with elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA 29 * will be expanded to DEFAULT_CAPACITY when the first element is added. 30 存储ArrayList元素的数组缓冲区,ArrayList的容量是这个数组缓冲区的长度。当第一个元素被添加的时候,elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA 将被扩展成 DEFAULT_CAPACITY 31 * 当前数据对象存放地方,当前对象不参与序列化 32 * transient关键字代表临时数据,被修饰的变量不参与序列化 33 * 34 */ 35 transient Object[] elementData; // non-private to simplify nested class access 36 37 /** 38 * The size of the ArrayList (the number of elements it contains). 39 * 数组大小 40 * ArrayList实际存储的数据容量,当初始容量值小于0时抛出异常 41 * @serial 42 */ 43 private int size;
ArrayList 有三个构造方法 :
- 无参构造方法
- 构造空的具有特定初始容量值的ArrayList方法
- 构造一个包含指定集合元素的列表,按照集合的迭代器返回它们的顺序方法
注意下图中的注释Constructs an empty list with an initial capacity of ten 调用无参构造方法,默认构造一个容量为10的空list.
/** * Constructs an empty list with an initial capacity of ten. * *无参构造方法: *- 创建一个 空的 ArrayList,此时其内数组缓冲区 elementData = {}, 长度为 0 *- 当元素第一次被加入时,扩容至默认容量 10 */ public ArrayList() { this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; }
- 在知道将会向 ArrayList 插入多少元素的情况下
- 在有大量数据写入 时;一定要初始化指定长度
/** * Constructs an empty list with the specified initial capacity. * 创建一个初始容量的、空的ArrayList * * * @param initialCapacity initialCapacity 初始容量 * @throws IllegalArgumentException 当初始容量值非法(小于0)时抛出异常 * */ public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) { if (initialCapacity > 0) { this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity]; } else if (initialCapacity == 0) { this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; } else { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+ initialCapacity); } }
3.3.2.3 构造一个包含指定集合元素的列表,按照集合的迭代器返回它们的顺序
/** * Constructs a list containing the elements of the specified * collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's * iterator. 构造一个包含指定集合元素的列表,按照集合的迭代器返回它们的顺序 * @param c 要放入 ArrayList 中的集合,其内元素将会全部添加到新建的 ArrayList 实例中 * @throws NullPointerException 当参数 c 为 null 时抛出异常 */ public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) { //把集合传化成Object[]数组 elementData = c.toArray(); //转化后的数组长度赋给当前ArrayList的size,并判断是否为0 if ((size = elementData.length) != 0) { // c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652) // (see e.g. https://bugs.openjdk.java.net/browse/JDK-6260652) // jdk bug(Arrays内部实现的ArrayList的toArray()方法的行为与规范不一致) 15年修复; if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class) elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class); } else { // 替换空数组 this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; } }
JDK-6260652 (see e.g. https://bugs.openjdk.java.net/browse/JDK-6260652)
产生原因
1 public Object[] toArray() { 2 return a.clone(); 3 }
Arrays内部实现的ArrayList的toArray()方法的行为与规范不一致。根据JLS规范String[]的clone方法返回的也是String[]类型,所以toArray()方法返回的真实类型是String[],所以给toArray()[0]赋值时可能会导致类型不匹配的错误
jdk11中的Arrays内部实现的ArrayList的toArray()方法。所以调用copyOf()返回值类型为Object[]
1 @Override 2 public Object[] toArray() { 3 return Arrays.copyOf(a, a.length, Object[].class); 4 }
关于方法:Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class),就是根据class的类型来决定是new 还是反射去构造一个泛型数组,同时利用native函数,批量赋值元素至新数组中。
如下:
1 public static <T,U> T[] copyOf(U[] original, int newLength, Class<? extends T[]> newType) { 2 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") 3 //根据class的类型来决定是new 还是反射去构造一个泛型数组 4 T[] copy = ((Object)newType == (Object)Object[].class) 5 ? (T[]) new Object[newLength] 6 : (T[]) Array.newInstance(newType.getComponentType(), newLength); 7 //利用native函数,批量赋值元素至新数组中。 8 System.arraycopy(original, 0, copy, 0, 9 Math.min(original.length, newLength)); 10 return copy; 11 }
System.arraycopy
1 public static native void arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos, 2 Object dest, int destPos, 3 int length);
对于数组(线性表)结构,插入操作分为两种情况。一种是在元素序列尾部插入,另一种是在元素序列其他位置插入。ArrayList 的源码里也体现了这两种插入情况,如下:
1 /** 2 * This helper method split out from add(E) to keep method 3 * bytecode size under 35 (the -XX:MaxInlineSize default value), 4 * which helps when add(E) is called in a C1-compiled loop. 5 * (这个辅助方法是从add(E)方法分离而来的,为了保持方法字节码低于35,这将有助于add(E)方法调用C1编译循环) 6 */ 7 private void add(E e, Object[] elementData, int s) { 8 if (s == elementData.length) 9 elementData = grow(); 10 //将新元素插入序列尾部 11 elementData[s] = e; 12 size = s + 1; 13 } 14 15 16 17 18 /** 19 * Appends the specified element to the end of this list. 20 * 21 * @param e element to be appended to this list 22 * @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add}) 23 */ 24 public boolean add(E e) { 25 modCount++; 26 add(e, elementData, size); 27 return true; 28 } 29 30 /** 31 * Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this 32 * list. Shifts the element currently at that position (if any) and 33 * any subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their indices). 34 * 在此列表的指定位置插入指定的元素。将当前位于该位置的元素(如果有)和任何后续元素向右移动(在其索引中添加一个元素) 35 * @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted 36 * @param element element to be inserted 37 * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} 38 */ 39 public void add(int index, E element) { 40 rangeCheckForAdd(index); 41 modCount++; 42 final int s; 43 Object[] elementData; 44 if ((s = size) == (elementData = this.elementData).length) 45 elementData = grow(); 46 //将 index 及其之后的所有元素都向后移一位将 index 及其之后的所有元素都向后移一位 47 System.arraycopy(elementData, index, 48 elementData, index + 1, 49 s - index); 50 //将新元素插入至 index 处 51 elementData[index] = element; 52 size = s + 1; 53 }
如下图:
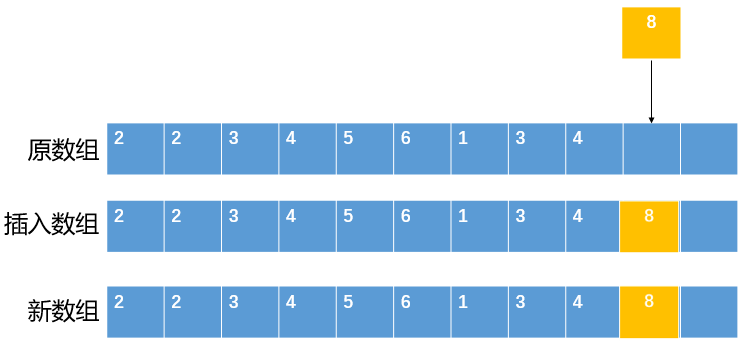
4.1.2 元素序列指定位置(假设该位置合理)插入
- 检查数组是否有足够空间
- 将 index 及其之后的所有元素向后移一位
- 将新元素插入至 index 处
如下图:
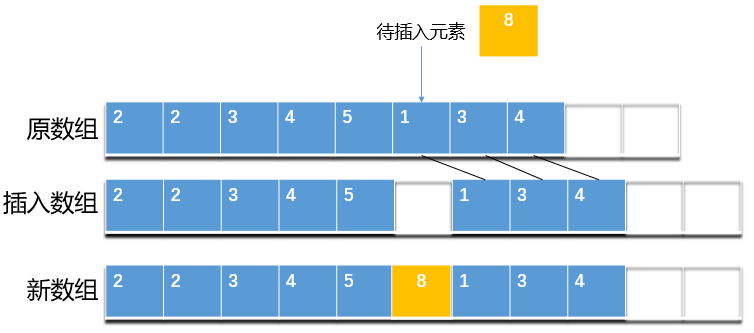
从上图可以看出,将新元素插入至序列指定位置,需要先将该位置及其之后的元素都向后移动一位,为新元素腾出位置。这个操作的时间复杂度为O(N),频繁移动元素可能会导致效率问题,特别是集合中元素数量较多时。在日常开发中,若非所需,我们应当尽量避免在大集合中调用第二个插入方法。
当数据结构中没有空余空间可供使用时,就需要进行扩容。在 ArrayList 中,当空间用完,其会按照原数组空间的1.5倍进行扩容。相关源码如下:
1 /** 扩容的入口方法 2 * Increases the capacity of this {@code ArrayList} instance, if 3 * necessary, to ensure that it can hold at least the number of elements 4 * specified by the minimum capacity argument. 5 *增加{@code ArrayList}实例的容量,如果必需的,以确保它至少可以容纳minimum capacity参数指定的元素数 6 * @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity 7 */ 8 public void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) { 9 if (minCapacity > elementData.length 10 && !(elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA 11 && minCapacity <= DEFAULT_CAPACITY)) { 12 modCount++; 13 grow(minCapacity); 14 } 15 } 16 17 18 /** 19 * The maximum size of array to allocate (unless necessary). 20 * 数组缓冲区最大存储容量 21 * Some VMs reserve some header words in an array. 22 * - 一些 VM 会在一个数组中存储某些数据--->为什么要减去 8 的原因 23 * Attempts to allocate larger arrays may result in 24 * OutOfMemoryError: Requested array size exceeds VM limit 25 *- 尝试分配这个最大存储容量,可能会导致 OutOfMemoryError(当该值 > VM 的限制时) 26 */ 27 private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8; 28 29 30 /** 31 * Increases the capacity to ensure that it can hold at least the 32 * number of elements specified by the minimum capacity argument. 33 * 增加容量确保至少可以容纳 minimum capacity 指定的元素数 34 * @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity 35 * @throws OutOfMemoryError if minCapacity is less than zero 36 */ 37 private Object[] grow(int minCapacity) { 38 return elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, 39 newCapacity(minCapacity)); 40 } 41 42 /** 扩容的核心方法 43 * Returns a capacity at least as large as the given minimum capacity. 44 * Returns the current capacity increased by 50% if that suffices. 45 * Will not return a capacity greater than MAX_ARRAY_SIZE unless 46 * the given minimum capacity is greater than MAX_ARRAY_SIZE. 47 * 返回至少等于给定最小值的容量。返回的是当前容量增加50%,如果够了,不会返回大于MAX_ARRAY_SIZE的容量,除非给定的最小容量大于MAX_ARRAY_SIZE 48 * @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity 49 * @throws OutOfMemoryError if minCapacity is less than zero 50 */ 51 private int newCapacity(int minCapacity) { 52 // overflow-conscious code 防止溢出代码 53 int oldCapacity = elementData.length; 54 int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1); //旧容量大小+在旧容量基础上增加50%(右移1位相当于除以2) 55 if (newCapacity - minCapacity <= 0) { 56 if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) 57 return Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity); // 58 if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow 59 throw new OutOfMemoryError(); 60 return minCapacity; 61 } 62 return (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE <= 0) // 判断扩容后的容量是否超过数组缓冲区最大存储容量MAX_ARRAY_SIZE 63 ? newCapacity 64 : hugeCapacity(minCapacity); //超过则进行大容量分配 65 } 66 67 /** 68 * 大容量分配,最大分配 Integer.MAX_VALUE 69 */ 70 private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) { 71 if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow 72 throw new OutOfMemoryError(); 73 //如果指定的最小容量超过 MAX_ARRAY_SIZE,则将数组容量扩容至 Integer.MAX_VALUE 74 return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) 75 ? Integer.MAX_VALUE 76 : MAX_ARRAY_SIZE; 77 }
不同于插入操作,ArrayList 没有无参删除方法。所以其只能删除指定位置的元素或删除指定元素,这样就无法避免移动元素(除非从元素序列的尾部删除)。代码如下:
1 /** 删除指定位置的元素 2 * Removes the element at the specified position in this list. 3 * Shifts any subsequent elements to the left (subtracts one from their 4 * indices). 5 * 6 * @param index the index of the element to be removed 7 * @return the element that was removed from the list 8 * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} 9 */ 10 public E remove(int index) { 11 Objects.checkIndex(index, size); 12 final Object[] es = elementData; 13 //返回被删除的元素值 14 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E oldValue = (E) es[index]; 15 fastRemove(es, index); 16 17 return oldValue; 18 } 19 20 /** 21 * 从列表中删除第一个出现的指定元素(如果存在)。 22 * 如果列表不包含元素,则不变。更准确地说,删除索引最低的元素 23 * Removes the first occurrence of the specified element from this list, 24 * if it is present. If the list does not contain the element, it is 25 * unchanged. More formally, removes the element with the lowest index 26 * {@code i} such that 27 * {@code Objects.equals(o, get(i))} 28 * (if such an element exists). Returns {@code true} if this list 29 * contained the specified element (or equivalently, if this list 30 * changed as a result of the call). 31 * 32 * @param o element to be removed from this list, if present 33 * @return {@code true} if this list contained the specified element 34 */ 35 public boolean remove(Object o) { 36 final Object[] es = elementData; 37 final int size = this.size; 38 int i = 0; 39 //遍历数组,查找要删除元素的位置 40 found: { 41 if (o == null) { 42 for (; i < size; i++) 43 if (es[i] == null) 44 break found; 45 } else { 46 for (; i < size; i++) 47 if (o.equals(es[i])) 48 break found; 49 } 50 return false; 51 } 52 fastRemove(es, i); 53 return true; 54 } 55 56 57 /** 58 * Private remove method that skips bounds checking and does not 59 * return the value removed. 60 */ 61 private void fastRemove(Object[] es, int i) { 62 modCount++; 63 final int newSize; 64 if ((newSize = size - 1) > i) 65 // 将 index + 1 及之后的元素向前移动一位,覆盖被删除值 66 System.arraycopy(es, i + 1, es, i, newSize - i); 67 // 将最后一个元素置空,并将 size 值减 1 68 es[size = newSize] = null; 69 }
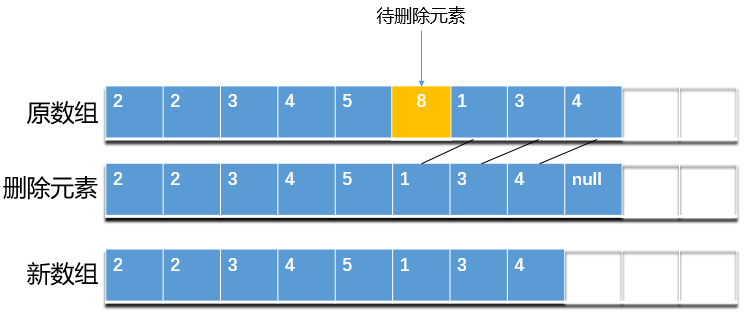
上面的删除方法并不复杂,这里以第一个删除方法为例,删除一个元素步骤如下:
- 获取指定位置 index 处的元素值
- 将 index + 1 及之后的元素向前移动一位
- 将最后一个元素置空,并将 size 值减 1
- 返回被删除值,完成删除操作
如下图:
假如在我们往 ArrayList 插入大量元素后,又删除很多元素,此时底层数组会空闲处大量的空间。因为 ArrayList 没有自动缩容机制,导致底层数组大量的空闲空间不能被释放,造成浪费。对于这种情况,ArrayList 也提供了相应的处理方法,如下:
1 /** 将数组容量缩小至元素数量,即将数组缓冲区大小调整到实际ArrayList 存储元素的大小 2 * Trims the capacity of this {@code ArrayList} instance to be the 3 * list's current size. An application can use this operation to minimize 4 * the storage of an {@code ArrayList} instance. 5 */ 6 public void trimToSize() { 7 modCount++; 8 //当实际大小 < 数组缓冲区大小时(如调用默认构造函数后,刚添加一个元素,此时element.length=10,而size=1) 9 //通过这一步,可以使得空间得到有效利用,不会出现资源浪费的情况 10 // 11 if (size < elementData.length) { 12 //注意这里的运算符优先级语法,执行顺序为elementData = ((size == 0) ? EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA : Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size)); 13 //先判断size是否为0,如果为0:实际存储为EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA,如果有数据就是Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size) 14 elementData = (size == 0) 15 ? EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA 16 : Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size); 17 } 18 }

可以使用 trimToSize () 手动触发 ArrayList 的缩容机制来释放多余的空间
ArrayList 实现了 RandomAccess 接口(该接口是个标志性接口),表明它具有快速随机访问的能力。ArrayList 底层基于数组实现,所以它可在常数阶的时间内完成随机访问,效率很高。对 ArrayList 进行遍历时,一般情况下,我们喜欢使用 foreach 循环遍历,但这并不是推荐的遍历方式。ArrayList 具有随机访问的能力,如果在一些效率要求比较高的场景下,更推荐下面这种方式:
1 for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) { 2 list.get(i); 3 }
ArrayList在使用下标的方式循环遍历的时候性能最好,通过下标可以直接取数据,速度最快。ArrayList在使用迭代器时,因为要通过ArrayList先生成指针,而指针无法直接取到对应的下标,因此在使用下标遍历时就需要计算对应的下面是哪个元素,从指针的头一步一步的走,所以效率就很低。因此效率就会低于下标方式,而foreach又是在迭代器基础上又进行了封装,因此效率会更低一点,但是会很接近迭代器。
在 Java 集合框架中,很多类都实现了快速失败机制。该机制被触发时,会抛出并发修改异常ConcurrentModificationException,这个异常大家在平时开发中多多少少应该都碰到过。关于快速失败机制,ArrayList 的注释里对此做了解释,这里引用一下:
The iterators returned by this class’s iterator() and
listIterator(int) methods are fail-fast
if the list is structurally modified at any time after the iterator is
created, in any way except through the iterator’s own
ListIterator remove() or ListIterator add(Object) methods,
the iterator will throw a ConcurrentModificationException. Thus, in the face of
concurrent modification, the iterator fails quickly and cleanly, rather
than risking arbitrary, non-deterministic behavior at an undetermined
time in the future.
上面注释大致意思是,ArrayList 迭代器中的方法都是均具有快速失败的特性,当遇到并发修改的情况时,迭代器会快速失败,以避免程序在将来不确定的时间里出现不确定的行为。
以上就是 Java 集合框架中引入快速失败机制的原因,并不难理解,这里不多说了。
遍历时删除是一个不正确的操作,即使有时候代码不出现异常,但执行逻辑也会出现问题。关于这个问题,阿里巴巴 Java 开发手册里也有所提及。这里引用一下:
【强制】不要在 foreach 循环里进行元素的 remove/add 操作。remove 元素请使用 Iterator 方式,如果并发操作,需要对 Iterator 对象加锁。
相关代码(稍作修改)如下:
1 List<String> a = new ArrayList<String>(); 2 a.add("1"); 3 a.add("2"); 4 for (String temp : a) { 5 System.out.println(temp); 6 if("1".equals(temp)){ 7 a.remove(temp); 8 } 9 } 10 }
相信有些朋友应该看过这个,并且也执行过上面的程序。上面的程序执行起来不会虽不会出现异常,但代码执行逻辑上却有问题,只不过这个问题隐藏的比较深。我们把 temp 变量打印出来,会发现只打印了数字1,2没打印出来。初看这个执行结果确实很让人诧异,不明原因。如果死抠上面的代码,我们很难找出原因,此时需要稍微转换一下思路。我们都知道 Java 中的 foreach 是个语法糖,编译成字节码后会被转成用迭代器遍历的方式。所以我们可以把上面的代码转换一下,等价于下面形式:
1 List<String> a = new ArrayList<>(); 2 a.add("1"); 3 a.add("2"); 4 Iterator<String> it = a.iterator(); 5 while (it.hasNext()) { 6 String temp = it.next(); 7 System.out.println("temp: " + temp); 8 if("1".equals(temp)){ 9 a.remove(temp); 10 } 11 }
这个时候,我们再去分析一下 ArrayList 的迭代器源码就能找出原因。
private class Itr implements Iterator<E> { int cursor; // index of next element to return int lastRet = -1; // index of last element returned; -1 if no such int expectedModCount = modCount; public boolean hasNext() { return cursor != size; } @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public E next() { // 并发修改检测,检测不通过则抛出异常 checkForComodification(); int i = cursor; if (i >= size) throw new NoSuchElementException(); Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData; if (i >= elementData.length) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); cursor = i + 1; return (E) elementData[lastRet = i]; } final void checkForComodification() { if (modCount != expectedModCount) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); }
// 省略不相关的代码 }
我们一步一步执行一下上面的代码,第一次进入 while 循环时,一切正常,元素 1 也被删除了。但删除元素 1 后,就无法再进入 while 循环,此时 it.hasNext() 为 false。原因是删除元素 1 后,元素计数器 size = 1,而迭代器中的 cursor 也等于 1,从而导致 it.hasNext() 返回false。归根结底,上面的代码段没抛异常的原因是,循环提前结束,导致 next 方法没有机会抛异常。不信的话,大家可以把代码稍微修改一下,即可发现问题:
List<String> a = new ArrayList<>(); a.add("1"); a.add("2"); a.add("3"); Iterator<String> it = a.iterator(); while (it.hasNext()) { String temp = it.next(); System.out.println("temp: " + temp); if("1".equals(temp)){ a.remove(temp); } }
以上是关于遍历时删除的分析,在日常开发中,我们要避免上面的做法。正确的做法使用迭代器提供的删除方法,而不是直接删除。
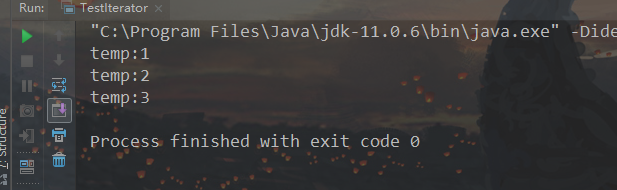
1 List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); 2 list.add("1"); 3 list.add("2"); 4 list.add("3"); 5 6 Iterator<String> itr = list.iterator(); 7 while (itr.hasNext()){ 8 String temp = itr.next(); 9 System.out.println("temp:"+temp); 10 if ("1".equals(temp)){ 11 itr.remove(); //使用iterator的remove方法 12 } 13 }
运行结果:
参考整理自以下出处:
https://www.cnblogs.com/yahooz/p/13283431.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/demo111/p/4823879.html
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_40949465/article/details/88663843


 posted on
posted on
