数据采集作业3
作业①:
要求:指定一个网站,爬取这个网站中的所有的所有图片,例如:中国气象网(http://www.weather.com.cn)。使用scrapy框架分别实现单线程和多线程的方式爬取。务必控制总页数(学号尾数2位)、总下载的图片数量(尾数后3位)等限制爬取的措施。
输出信息: 将下载的Url信息在控制台输出,并将下载的图片存储在images子文件中,并给出截图。
item.py
import scrapy
class work1_Item(scrapy.Item):
img_url = scrapy.Field()
settings.py:
# Scrapy settings for Practical_work3 project
#
# For simplicity, this file contains only settings considered important or
# commonly used. You can find more settings consulting the documentation:
#
# https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/settings.html
# https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/downloader-middleware.html
# https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/spider-middleware.html
BOT_NAME = 'Practical_work3'
SPIDER_MODULES = ['Practical_work3.spiders']
NEWSPIDER_MODULE = 'Practical_work3.spiders'
# UA伪装
# Crawl responsibly by identifying yourself (and your website) on the user-agent
USER_AGENT = 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/117.0.0.0 Safari/537.36 Edg/117.0.2045.47'
# Obey robots.txt rules
ROBOTSTXT_OBEY = False
# 去除赘余的日志信息
LOG_LEVEL = 'ERROR'
ITEM_PIPELINES = {
'Practical_work3.pipelines.work1_Pipeline': 300,
'Practical_work3.pipelines.work2_Pipeline': 200,
'Practical_work3.pipelines.work3_Pipeline': 100
}
# Configure maximum concurrent requests performed by Scrapy (default: 16)
#CONCURRENT_REQUESTS = 32
# Configure a delay for requests for the same website (default: 0)
# See https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/settings.html#download-delay
# See also autothrottle settings and docs
#DOWNLOAD_DELAY = 3
# The download delay setting will honor only one of:
#CONCURRENT_REQUESTS_PER_DOMAIN = 16
#CONCURRENT_REQUESTS_PER_IP = 16
# Disable cookies (enabled by default)
#COOKIES_ENABLED = False
# Disable Telnet Console (enabled by default)
#TELNETCONSOLE_ENABLED = False
# Override the default request headers:
#DEFAULT_REQUEST_HEADERS = {
# 'Accept': 'text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8',
# 'Accept-Language': 'en',
#}
# Enable or disable spider middlewares
# See https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/spider-middleware.html
#SPIDER_MIDDLEWARES = {
# 'Practical_work3.middlewares.PracticalWork3SpiderMiddleware': 543,
#}
# Enable or disable downloader middlewares
# See https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/downloader-middleware.html
#DOWNLOADER_MIDDLEWARES = {
# 'Practical_work3.middlewares.PracticalWork3DownloaderMiddleware': 543,
#}
# Enable or disable extensions
# See https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/extensions.html
#EXTENSIONS = {
# 'scrapy.extensions.telnet.TelnetConsole': None,
#}
# Configure item pipelines
# See https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/item-pipeline.html
#ITEM_PIPELINES = {
# 'Practical_work3.pipelines.PracticalWork3Pipeline': 300,
#}
# Enable and configure the AutoThrottle extension (disabled by default)
# See https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/autothrottle.html
#AUTOTHROTTLE_ENABLED = True
# The initial download delay
#AUTOTHROTTLE_START_DELAY = 5
# The maximum download delay to be set in case of high latencies
#AUTOTHROTTLE_MAX_DELAY = 60
# The average number of requests Scrapy should be sending in parallel to
# each remote server
#AUTOTHROTTLE_TARGET_CONCURRENCY = 1.0
# Enable showing throttling stats for every response received:
#AUTOTHROTTLE_DEBUG = False
# Enable and configure HTTP caching (disabled by default)
# See https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/downloader-middleware.html#httpcache-middleware-settings
#HTTPCACHE_ENABLED = True
#HTTPCACHE_EXPIRATION_SECS = 0
#HTTPCACHE_DIR = 'httpcache'
#HTTPCACHE_IGNORE_HTTP_CODES = []
#HTTPCACHE_STORAGE = 'scrapy.extensions.httpcache.FilesystemCacheStorage'
pipelines.py:
单线程
# Define your item pipelines here
#
# Don't forget to add your pipeline to the ITEM_PIPELINES setting
# See: https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/item-pipeline.html
# useful for handling different item types with a single interface
import threading
from itemadapter import ItemAdapter
import urllib.request
import os
import pathlib
import pymysql
from Practical_work3.items import work1_Item
from Practical_work3.items import work2_Item
from Practical_work3.items import work3_Item
class work1_Pipeline:
count = 0
desktopDir = str(pathlib.Path.home()).replace('\\','\\\\') + '\\Desktop'
threads = []
def open_spider(self,spider):
picture_path=self.desktopDir+'\\images'
if os.path.exists(picture_path): # 判断文件夹是否存在
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(picture_path, topdown=False):
for name in files:
os.remove(os.path.join(root, name)) # 删除文件
for name in dirs:
os.rmdir(os.path.join(root, name)) # 删除文件夹
os.rmdir(picture_path) # 删除文件夹
os.mkdir(picture_path) # 创建文件夹
单线程
def process_item(self, item, spider):
url = item['img_url']
print(url)
img_data = urllib.request.urlopen(url=url).read()
img_path = self.desktopDir + '\\images\\' + str(self.count)+'.jpg'
with open(img_path, 'wb') as fp:
fp.write(img_data)
self.count = self.count + 1
return item
多线程:
# Define your item pipelines here
#
# Don't forget to add your pipeline to the ITEM_PIPELINES setting
# See: https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/item-pipeline.html
# useful for handling different item types with a single interface
import threading
from itemadapter import ItemAdapter
import urllib.request
import os
import pathlib
import pymysql
from Practical_work3.items import work1_Item
from Practical_work3.items import work2_Item
from Practical_work3.items import work3_Item
class work1_Pipeline:
count = 0
desktopDir = str(pathlib.Path.home()).replace('\\','\\\\') + '\\Desktop'
threads = []
def open_spider(self,spider):
picture_path=self.desktopDir+'\\images'
if os.path.exists(picture_path): # 判断文件夹是否存在
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(picture_path, topdown=False):
for name in files:
os.remove(os.path.join(root, name)) # 删除文件
for name in dirs:
os.rmdir(os.path.join(root, name)) # 删除文件夹
os.rmdir(picture_path) # 删除文件夹
os.mkdir(picture_path) # 创建文件夹
# 多线程
def process_item(self, item, spider):
if isinstance(item,work1_Item):
url = item['img_url']
print(url)
T=threading.Thread(target=self.download_img,args=(url,))
T.setDaemon(False)
T.start()
self.threads.append(T)
return item
def download_img(self,url):
img_data = urllib.request.urlopen(url=url).read()
img_path = self.desktopDir + '\\images\\' + str(self.count)+'.jpg'
with open(img_path, 'wb') as fp:
fp.write(img_data)
self.count = self.count + 1
def close_spider(self,spider):
for t in self.threads:
t.join()
spider.py:
import scrapy
from Practical_work3.items import work1_Item
class Work1Spider(scrapy.Spider):
name = 'work1'
# allowed_domains = ['www.weather.com.cn']
start_urls = ['http://www.weather.com.cn/']
def parse(self, response):
data = response.body.decode()
selector=scrapy.Selector(text=data)
img_datas = selector.xpath('//a/img/@src')
for img_data in img_datas:
item = work1_Item()
item['img_url'] = img_data.extract()
yield item
run.py
from scrapy import cmdline
cmdline.execute("scrapy crawl work1".split())
结果如下:
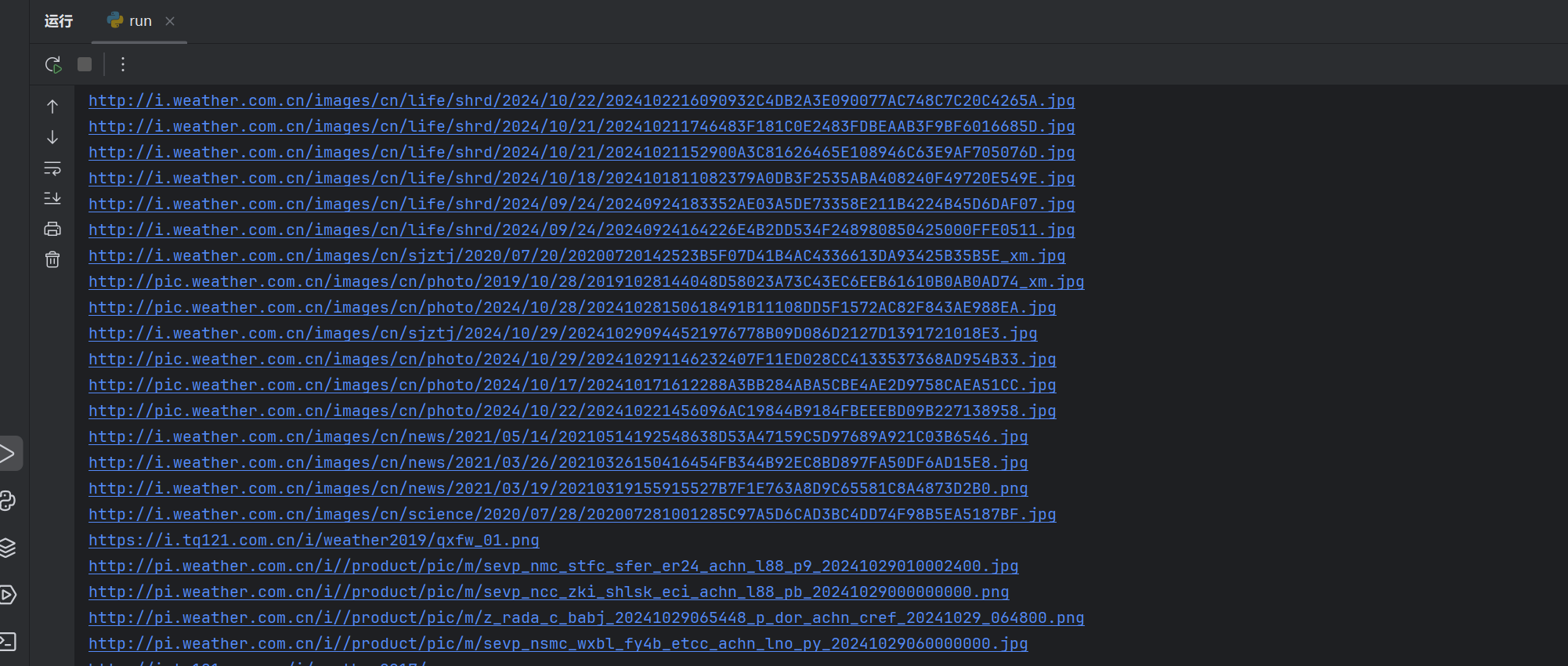
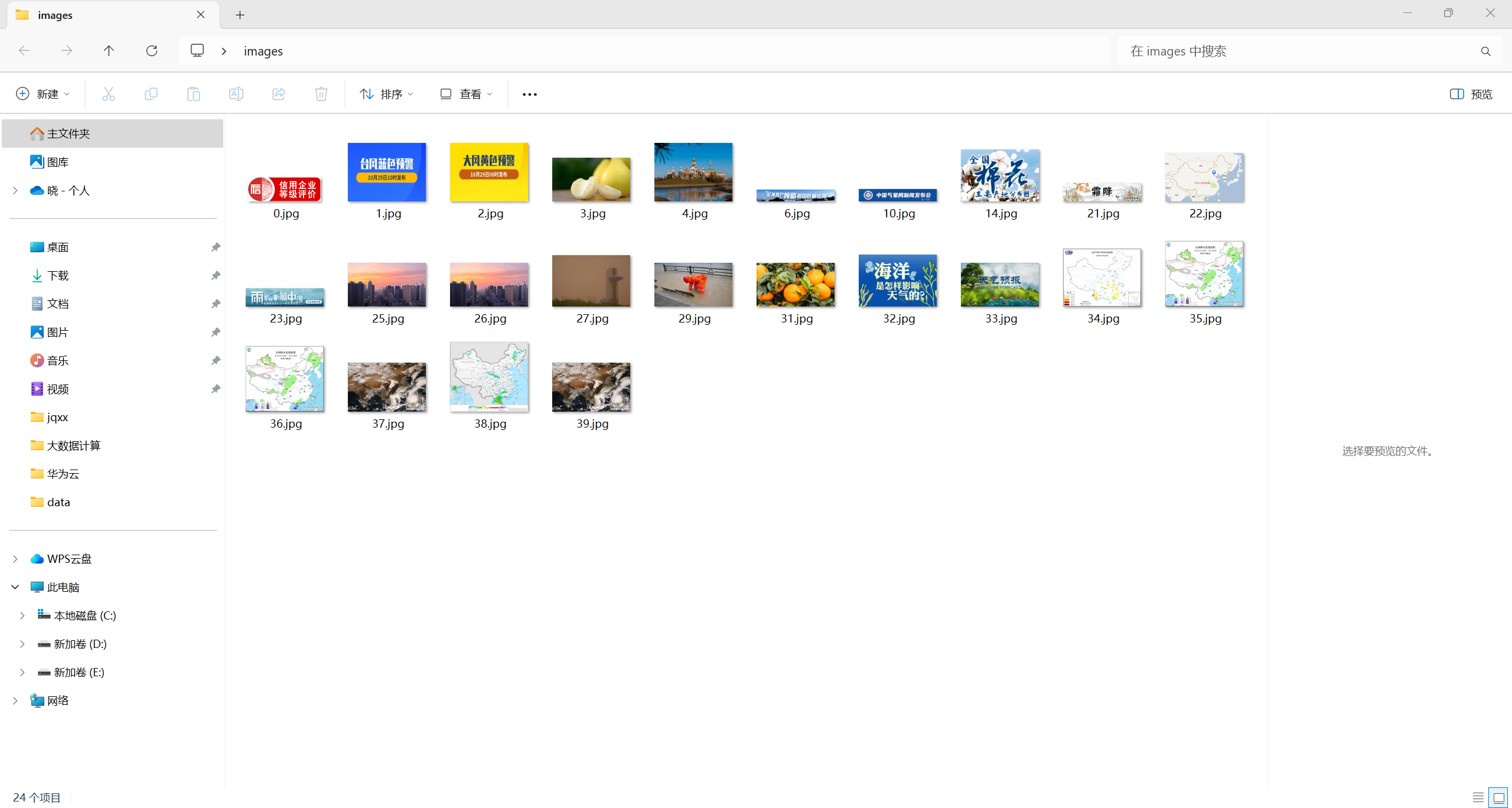
(2)心得体会
- 多线程相比单线程,效率高了不少,一开始直接在管道类实现多线程,后面发现也可以在setting.py里设置多线程,只需要修改CONCURRENT_REQUESTS的值即可
- scrapy框架初上手,了解了该框架的基本用法
- 自动生成的allowed_domains列表,指允许访问的域名,一般不使用
作业②
-
要求:熟练掌握 scrapy 中 Item、Pipeline 数据的序列化输出方法;使用scrapy框架+Xpath+MySQL数据库存储技术路线爬取股票相关信息。
-
候选网站:东方财富网:https://www.eastmoney.com/
-
输出信息:MySQL数据库存储和输出格式如下:
-
表头英文命名例如:序号id,股票代码:bStockNo……,由同学们自行定义设计
-
序号 股票代码 股票名称 最新报价 涨跌幅 涨跌额 成交量 振幅 最高 最低 今开 昨收 1 688093 N世华 28.47 10.92 26.13万 7.6亿 22.34 32.0 28.08 30.20 17.55 2……
item.py
import scrapy
class work2_Item(scrapy.Item):
f2 = scrapy.Field()
f3 = scrapy.Field()
f4 = scrapy.Field()
f5 = scrapy.Field()
f6 = scrapy.Field()
f7 = scrapy.Field()
f12 = scrapy.Field()
f14 = scrapy.Field()
f15 = scrapy.Field()
f16 = scrapy.Field()
f17 = scrapy.Field()
f18 = scrapy.Field()
pipeline.py
import pymysql
from Practical_work3.items import work2_Item
class work2_Pipeline:
def open_spider(self, spider):
"""
在爬虫开始时执行的方法。
尝试连接到 MySQL 数据库,创建游标对象,删除名为'stock'的表(如果存在),
然后创建一个新的'stock'表用于存储数据。
参数:
spider:当前正在运行的爬虫对象。
"""
try:
# 连接到 MySQL 数据库,指定主机地址、用户名、密码、端口号、字符集和数据库名称
self.db = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', user='root', passwd='114514', port=3306, charset='utf8', database='scrapy')
# 创建游标对象,用于执行 SQL 语句
self.cursor = self.db.cursor()
# 如果存在名为'stock'的表,则删除它
self.cursor.execute('DROP TABLE IF EXISTS stock')
# 创建新的'stock'表,定义了多个字段,包括数值类型和字符串类型,其中'id'字段为主键
sql = """CREATE TABLE stock(Latest_quotation Double,Chg Double,up_down_amount Double,turnover Double,transaction_volume Double,
amplitude Double,id varchar(12) PRIMARY KEY,name varchar(32),highest Double, lowest Double,today Double,yesterday Double)"""
self.cursor.execute(sql)
except Exception as e:
# 如果出现异常,打印错误信息
print(e)
def process_item(self, item, spider):
"""
在爬虫处理每个项目时执行的方法。
如果项目是'work2_Item'类型,则将项目中的数据插入到'stock'表中。
参数:
item:当前正在处理的项目对象。
spider:当前正在运行的爬虫对象。
返回:
返回处理后的项目对象,以便后续的管道继续处理。
"""
if isinstance(item, work2_Item):
# 构建 SQL 插入语句,将项目中的数据插入到'stock'表中
sql = """INSERT INTO stock VALUES (%f,%f,%f,%f,%f,%f,"%s","%s",%f,%f,%f,%f)""" % (item['f2'], item['f3'], item['f4'], item['f5'], item['f6'],
item['f7'], item['f12'], item['f14'], item['f15'], item['f16'], item['f17'], item['f18'])
# 执行 SQL 插入语句
self.cursor.execute(sql)
# 提交事务,确保数据被真正插入到数据库中
self.db.commit()
return item
def close_spider(self, spider):
"""
在爬虫结束时执行的方法。
关闭数据库游标和数据库连接,释放资源。
参数:
spider:当前正在运行的爬虫对象。
"""
self.cursor.close()
self.db.close()
self.db.close()
spider.py
import scrapy
import re
import json
from Practical_work3.items import work2_Item
class Work2Spider(scrapy.Spider):
name = 'work2'
# allowed_domains = ['25.push2.eastmoney.com']
start_urls = ['http://25.push2.eastmoney.com/api/qt/clist/get?cb=jQuery1124021313927342030325_1696658971596&pn=1&pz=20&po=1&np=1&ut=bd1d9ddb04089700cf9c27f6f7426281&fltt=2&invt=2&wbp2u=|0|0|0|web&fid=f3&fs=m:0+t:6,m:0+t:80,m:1+t:2,m:1+t:23,m:0+t:81+s:2048&fields=f2,f3,f4,f5,f6,f7,f12,f14,f15,f16,f17,f18&_=1696658971636']
def parse(self, response):
"""
爬虫的解析方法,用于处理下载的响应。
参数:
response:下载的响应对象。
以下是方法中的主要步骤:
1. 解码响应主体内容,获取数据字符串。
2. 创建一个 work2_Item 对象,用于存储提取的数据。
3. 使用正则表达式提取特定格式的数据。
4. 遍历提取的数据,将其转换为字典格式,并将数据存储到 item 中。
5. 最后,使用 yield 返回 item,将数据传递给后续的管道处理。
"""
data = response.body.decode()
item = work2_Item()
data = re.compile('"diff":\[(.*?)\]', re.S).findall(data)
columns = {'f2': '最新价', 'f3': '涨跌幅(%)', 'f4': '涨跌额', 'f5': '成交量', 'f6': '成交额', 'f7': '振幅(%)', 'f12': '代码', 'f14': '名称', 'f15': '最高', 'f16': '最低', 'f17': '今开', 'f18': '昨收'}
for one_data in re.compile('\{(.*?)\}', re.S).findall(data[0]):
data_dic = json.loads('{' + one_data + '}')
for k, v in data_dic.items():
item[k] = v
yield item
结果如下:
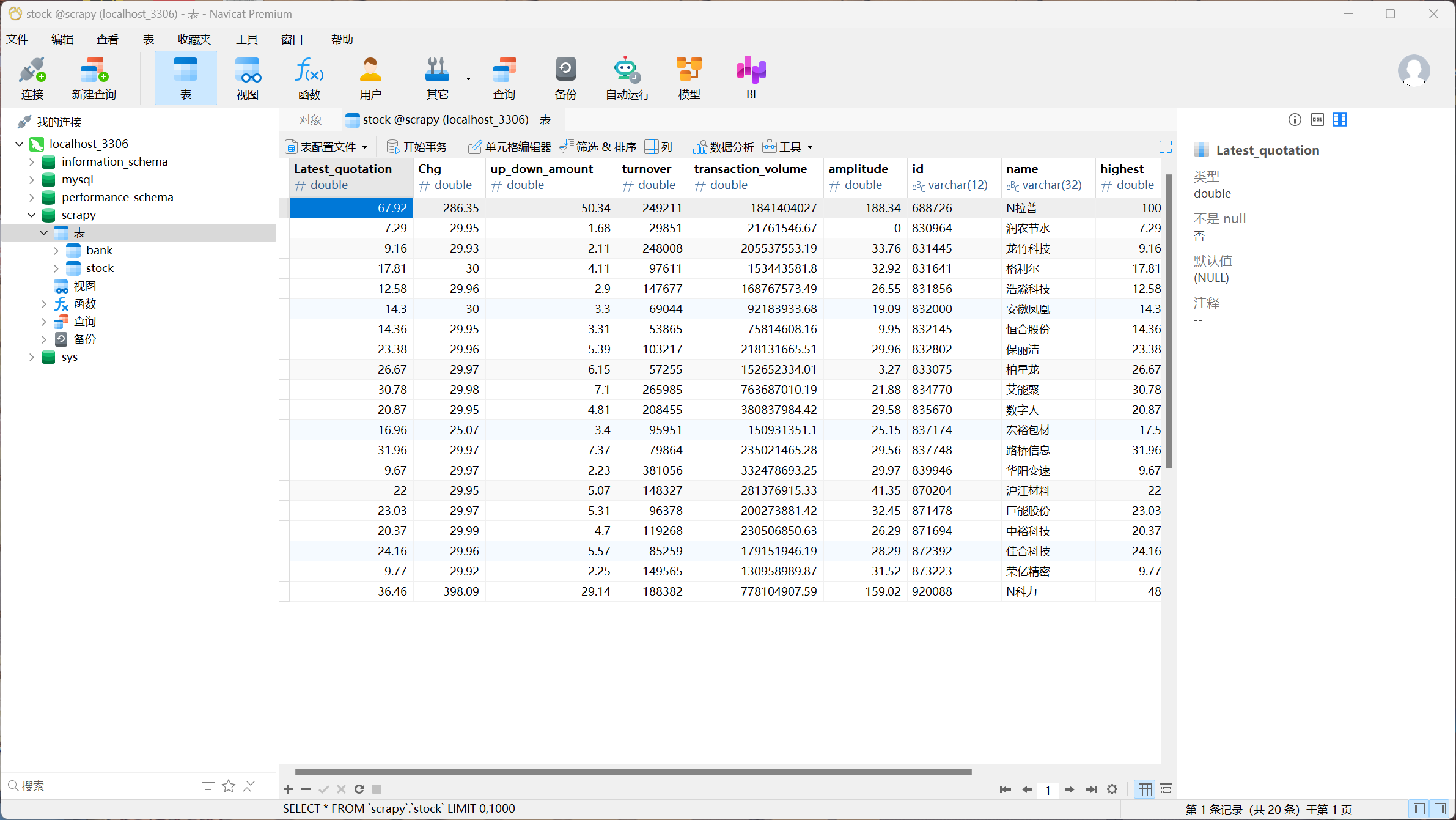
(2)心得体会
(1)mysql初上手,了解了python怎么连接mysql数据库
(2)由于该网址的数据是动态加载的,scrapy也只能爬取静态的网页,最终还是通过抓包的方式直接获得数据
作业③:
要求:熟练掌握 scrapy 中 Item、Pipeline 数据的序列化输出方法;使用scrapy框架+Xpath+MySQL数据库存储技术路线爬取外汇网站数据。
- 候选网站:****中国银行网:https://www.boc.cn/sourcedb/whpj/
- 输出信息:
| Currency | TBP | CBP | TSP | CSP | Time |
| ---------------- | ---------- | ---------- | ---------- | ---------- | ------------ |
| 阿联酋迪拉姆 | 198.58 | 192.31 | 199.98 | 206.59 | 11:27:14 |
item.py
import scrapy
class work3_Item(scrapy.Item):
name = scrapy.Field()
price1 = scrapy.Field()
price2 = scrapy.Field()
price3 = scrapy.Field()
price4 = scrapy.Field()
price5 = scrapy.Field()
date = scrapy.Field()
pipelines.py
import pymysql
from Practical_work3.items import work3_Item
class work3_Pipeline:
def open_spider(self,spider):
try:
self.db = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', user='root', passwd='114514', port=3306,charset='utf8',database='scrapy')
self.cursor = self.db.cursor()
self.cursor.execute('DROP TABLE IF EXISTS bank')
sql = """CREATE TABLE bank(Currency varchar(32),p1 varchar(17),p2 varchar(17),p3 varchar(17),p4 varchar(17),p5 varchar(17),Time varchar(32))"""
self.cursor.execute(sql)
except Exception as e:
print(e)
def process_item(self, item, spider):
if isinstance(item,work3_Item):
sql = 'INSERT INTO bank VALUES ("%s","%s","%s","%s","%s","%s","%s")' % (item['name'],item['price1'],item['price2'],
item['price3'],item['price4'],item['price5'],item['date'])
self.cursor.execute(sql)
self.db.commit()
return item
def close_spider(self,spider):
self.cursor.close()
self.db.close()
spider.py
import scrapy
from Practical_work3.items import work3_Item
class Work3Spider(scrapy.Spider):
name = 'work3'
# allowed_domains = ['www.boc.cn']
start_urls = ['https://www.boc.cn/sourcedb/whpj/']
def parse(self, response):
data = response.body.decode()
selector=scrapy.Selector(text=data)
data_lists = selector.xpath('//table[@align="left"]/tr')
for data_list in data_lists:
datas = data_list.xpath('.//td')
if datas != []:
结果如下:
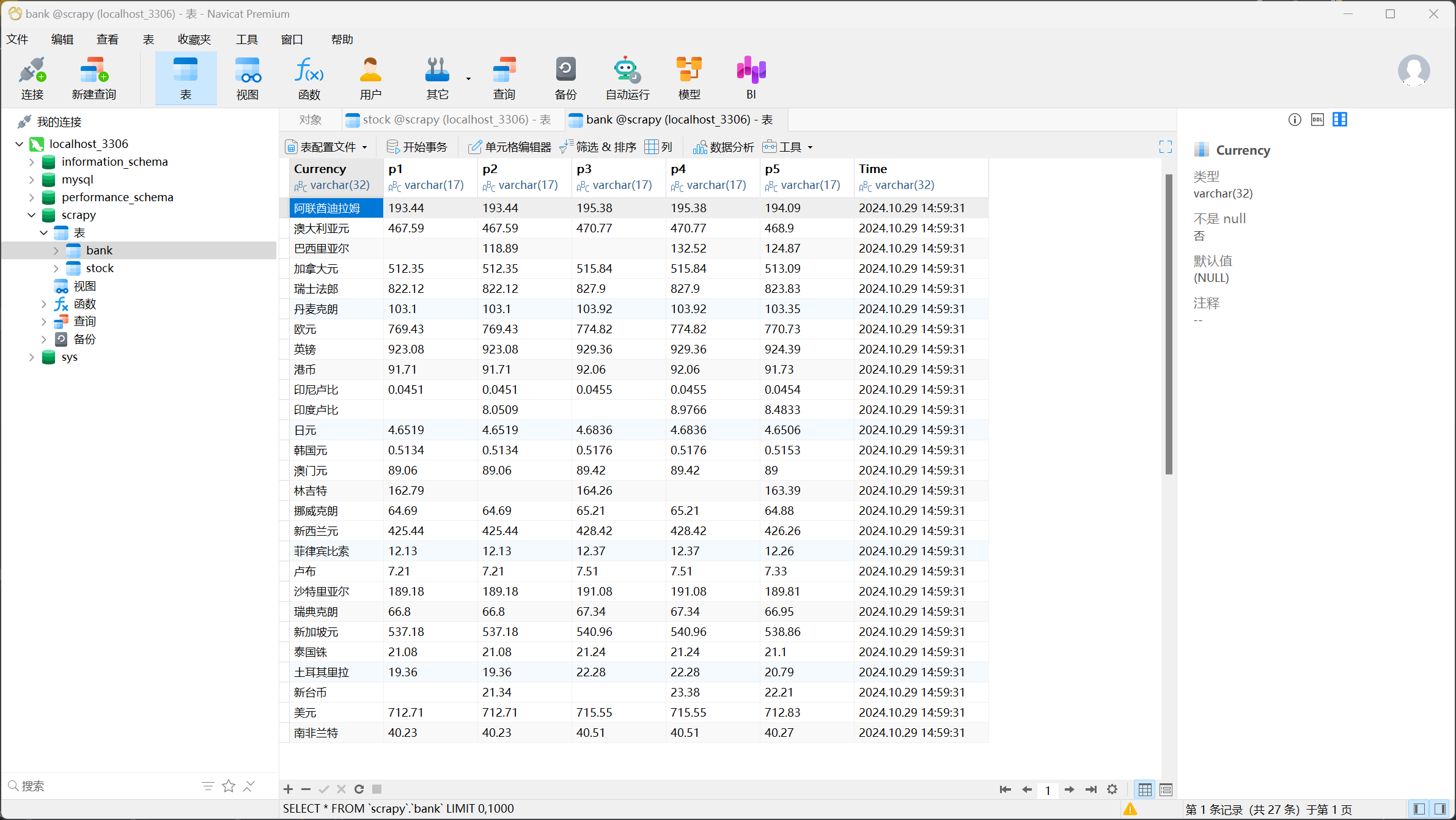
(2)心得体会
一开始xpath是直接在浏览器上复制下来的,结果却爬不到数据,一开始还以为该网址的数据也是动态加载的,结果并不是。尝试了半天,最后将相应的网页源码直接打印出来,然后查找,发现相应的源码少了tbody标签,将该层标签去掉之后便顺利爬取到数据。后面了解到浏览器显示的tbody标签是浏览器自行加上去的,xpath表达式中最好不要有tbody标签。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号