How2Kernel-Lab2
How2Kernel Lab2
0x1 assignment.c
Assignment module : Make changes to the assignment from lab1 using ioctl so that we can change the xor key
就是说修改一下Lab1的assignment.c用ioctl来实现一个可以修改key的模块。
偷个懒,直接使用作者实现的ioctl来写了,实现一个write来输入一个字符串转换成int赋值给key,一个read来读出现在的key。
贴代码:
/*
* Assignment module : Make changes to the assignment from lab1 using ioctl so that
* we can change the xor key
*/
#include <linux/module.h> /* Needed by all modules */
#include <linux/kernel.h> /* Needed for KERN_ALERT */
#include <linux/init.h> /* Needed for the macros */
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <asm/uaccess.h> /* for put_user */
#include <linux/string.h>
#define DEVICE_NAME "lab2" /* Dev name as it appears in /proc/devices */
#define BUF_LEN 80 /* Max length of the message from the device */
static int procfile_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file);
static int procfile_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *file);
static ssize_t procfile_read(struct file *file, char *buffer, size_t buffer_length, loff_t *offset);
static ssize_t procfile_write(struct file *file, const char *buffer, size_t count, loff_t *offset);
long procfile_ioctl(struct file *file, unsigned int ioctl_num, unsigned long ioctl_param);
enum
{
IOCTL_SET_MSG,
IOCTL_GET_MSG,
IOCTL_GET_NTH_BYTE
};
static int Major; /* Major number assigned to our device driver */
static int Device_Open = 0; /* Is device open?
* Used to prevent multiple access to device */
static char msg[BUF_LEN]; /* The msg the device will give when asked */
static char *msg_Ptr;
static int key = 13;
static char Message[BUF_LEN];
module_param(key, int, S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR | S_IRGRP | S_IROTH);
MODULE_PARM_DESC(key, "An integer");
static struct file_operations fops_struct =
{
.read = procfile_read,
.write = procfile_write,
.open = procfile_open,
.release = procfile_release,
.unlocked_ioctl = procfile_ioctl,
};
long procfile_ioctl(struct file *file, unsigned int ioctl_num, unsigned long ioctl_param)
{
int i;
char *temp;
char ch;
/*
* Switch according to the ioctl called
*/
switch (ioctl_num)
{
case IOCTL_SET_MSG:
/*
* Receive a pointer to a message (in user space) and set that
* to be the device's message. Get the parameter given to
* ioctl by the process.
*/
temp = ioctl_param;
/*
* Find the length of the message
*/
get_user(ch, temp);
for (i = 0; ch && i < BUF_LEN; i++, temp++)
get_user(ch, temp);
procfile_write(file, ioctl_param, i, 0);
break;
case IOCTL_GET_MSG:
break;
case IOCTL_GET_NTH_BYTE:
break;
}
return 0;
}
/*
* Called when a process tries to open the device file, like
* "cat /dev/xxx"
*/
static int procfile_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
static int counter = 0;
if (Device_Open)
return -EBUSY;
Device_Open++;
try_module_get(THIS_MODULE);
return 0;
}
/*
* Called when a process closes the device file.
*/
static int procfile_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
Device_Open--; /* We're now ready for our next caller */
/*
* Decrement the usage count, or else once you opened the file, you'll
* never get get rid of the module.
*/
module_put(THIS_MODULE);
return 0;
}
static ssize_t procfile_write(struct file *file, const char *buffer, size_t count, loff_t *offset)
{
int i;
int n;
unsigned char sign = 0;
memset(msg, 0, BUF_LEN);
for (i = 0; i < count && i < BUF_LEN; i++)
get_user(msg[i], buffer + i);
msg[i] = 0;
printk(KERN_INFO "msg is : %s\n", msg);
msg_Ptr = msg;
while (*msg_Ptr == ' ')
{
msg_Ptr++;
}
if (*msg_Ptr == '-')
{
sign = 1;
msg_Ptr++;
}
else if (*msg_Ptr == '+')
{
msg_Ptr++;
}
n = 0;
while ('0' <= *msg_Ptr && '9' >= *msg_Ptr)
{
n = n * 10 + *msg_Ptr++ - '0';
}
n = sign ? -n : n;
key = n;
printk(KERN_INFO "key is : %d\n", key);
/*
* Again, return the number of input characters used
*/
return i;
}
static ssize_t procfile_read(struct file *file, char *buffer, size_t buffer_length, loff_t *offset)
{
printk(KERN_INFO "key is : %d\n", key);
}
static int __init assignment_init(void)
{
Major = register_chrdev(0, DEVICE_NAME, &fops_struct);
if (Major < 0)
{
printk("Registering the character device failed with %d\n",
Major);
return Major;
}
printk(KERN_INFO "I was assigned major number %d. To talk to\n", Major);
printk(KERN_INFO "the driver, create a dev file with\n");
printk(KERN_INFO "'mknod /dev/lab2 c %d 0'.\n", Major);
printk(KERN_INFO "Try various minor numbers. Try to cat and echo to\n");
printk(KERN_INFO "the device file.\n");
printk(KERN_INFO "Remove the device file and module when done.\n");
return 0;
}
static void __exit assignment_exit(void)
{
/*
* Unregister the device
*/
unregister_chrdev(Major, DEVICE_NAME);
}
module_init(assignment_init);
module_exit(assignment_exit);
然后一个调用这个模块的demo:
/*
* ioctl.c - the process to use ioctl's to control the kernel module
*
* Until now we could have used cat for input and output. But now
* we need to do ioctl's, which require writing our own process.
*/
/*
* device specifics, such as ioctl numbers and the
* major device file.
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <fcntl.h> /* open */
#include <unistd.h> /* exit */
#define DEVICE_FILE_NAME "lab2"
void
ioctl_set_msg(int file_desc, char *message)
{
int ret_val;
ret_val = ioctl(file_desc, 0, message);
if (ret_val < 0) {
printf("ioctl_set_msg failed:%d\n", ret_val);
exit(-1);
}
}
/*
* Main - Call the ioctl functions
*/
int
main()
{
int file_desc;
file_desc = open(DEVICE_FILE_NAME, 0);
if (file_desc < 0) {
printf("Can't open device file: %s\n", DEVICE_FILE_NAME);
exit(-1);
}
char buf[100];
printf("Read byte : %d\n", read(0, buf, 100));
ioctl_set_msg(file_desc, buf);
close(file_desc);
}
模块加载之后需要mknod来创建一个字符设备文件。
sudo mknod lab2 c 240 0
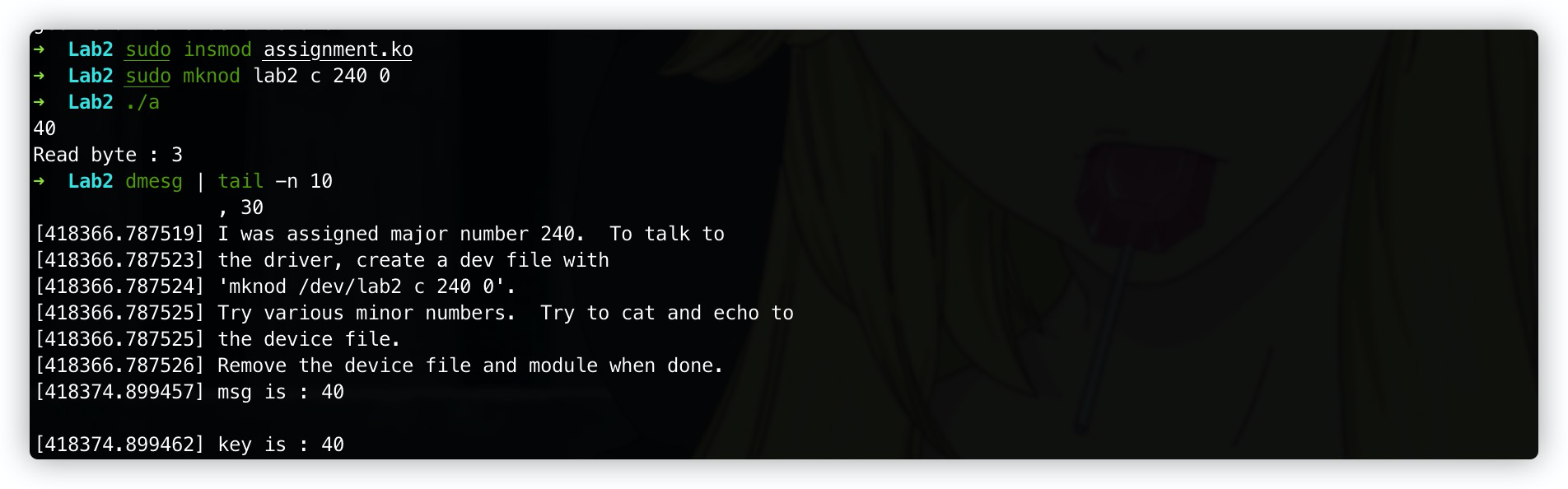
0x2 结果
还是先改一下Makefile
ifneq (${KERNELRELEASE},)
obj-m += ioctl.o
obj-m += chardev.o
obj-m += assignment.o
# Assignment module here
else
KERNEL_SOURCE := /lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build
#../kernel_source/linux-4.18.16/
PWD := $(shell pwd)
default:
# Compile for the same architecture as the host machine
$(MAKE) -C $(KERNEL_SOURCE) M=${PWD} modules
gcc -static -o demo demo.c
arm:
# Cross compile for arm64/aarch64 architecture - Cross compiler needed !!!
ARCH=arm64 CROSS_COMPILE=aarch64-linux-gnu- $(MAKE) -C $(KERNEL_SOURCE) M=${PWD} modules
clean:
# Cleans the Directory - removes all the files that were created
$(MAKE) -C $(KERNEL_SOURCE) M=${PWD} clean
rm demo
endif