Java基础-Java中23种设计模式之常用的设计模式
Java基础-Java中23种设计模式之常用的设计模式
作者:尹正杰
版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任。
一.设计模式分类
设计模式是针对特定场景给出的专家级的解决方案。总的来说设计模式分为以下三大类:
1>.创建型模式
答:共五种,即工厂方法模式、抽象工厂模式、单例模式、建造者模式、原型模式。
2>.结构型模式
答:共七种,即适配器模式、装饰器模式、代理模式、外观模式、桥接模式、组合模式、享元模式。
3>.行为型模式
答:共十一种:策略模式、模板方法模式、观察者模式、迭代子模式、责任链模式、命令模式、备忘录模式、状态模式、访问者模式、中介者模式、解释器模式。
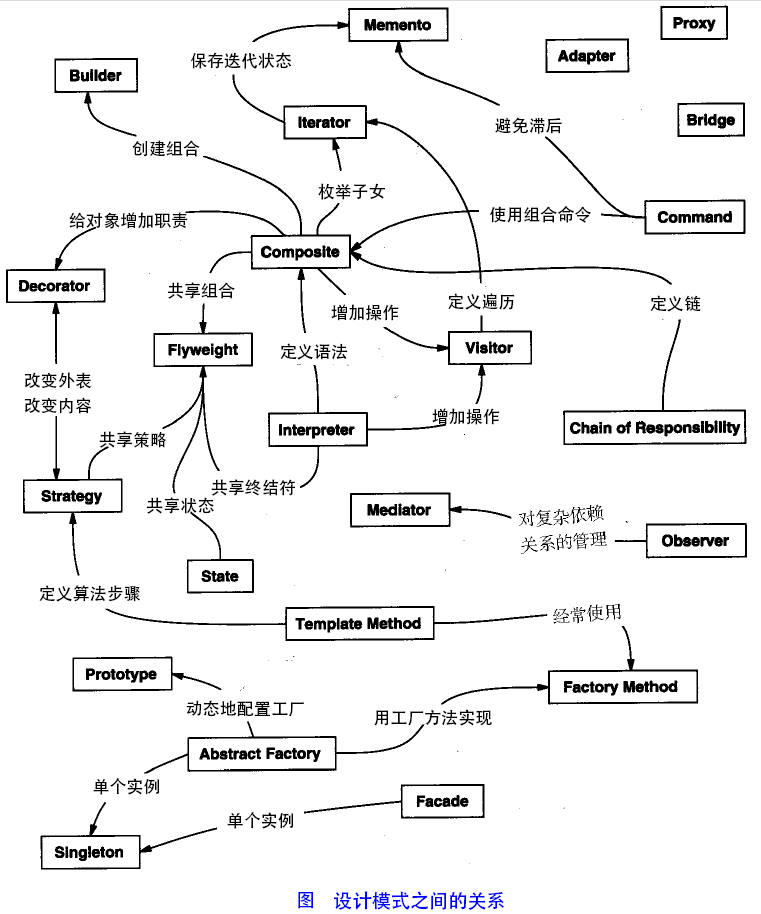
其实还有两类,并发型模式和线程池模式。用一个图片来整体描述一下:(下图引用自:https://blog.csdn.net/doymm2008/article/details/13288067)
二.设计模式的六大原则
1>.开闭原则(Open Close Principle)
答:开闭原则就是说对扩展开放,对修改关闭。在程序需要进行拓展的时候,不能去修改原有的代码,实现一个热插拔的效果。所以一句话概括就是:为了使程序的扩展性好,易于维护和升级。想要达到这样的效果,我们需要使用接口和抽象类。
2>.里氏代换原则(Liskov Substitution Principle)
答:里氏代换原则(Liskov Substitution Principle LSP)面向对象设计的基本原则之一。 里氏代换原则中说,任何基类可以出现的地方,子类一定可以出现。 LSP是继承复用的基石,只有当衍生类可以替换掉基类,软件单位的功能不受到影响时,基类才能真正被复用,而衍生类也能够在基类的基础上增加新的行为。里氏代换原则是对“开-闭”原则的补充。实现“开-闭”原则的关键步骤就是抽象化。而基类与子类的继承关系就是抽象化的具体实现,所以里氏代换原则是对实现抽象化的具体步骤的规范。—— From Baidu 百科
3>.依赖倒转原则(Dependence Inversion Principle)
答:这个是开闭原则的基础,具体内容:真对接口编程,依赖于抽象而不依赖于具体。
4>.接口隔离原则(Interface Segregation Principle)
答:这个原则的意思是:使用多个隔离的接口,比使用单个接口要好。还是一个降低类之间的耦合度的意思,从这儿我们看出,其实设计模式就是一个软件的设计思想,从大型软件架构出发,为了升级和维护方便。所以上文中多次出现:降低依赖,降低耦合。
5>.迪米特法则(最少知道原则)(Demeter Principle)
答:为什么叫最少知道原则,就是说:一个实体应当尽量少的与其他实体之间发生相互作用,使得系统功能模块相对独立。
6>.合成复用原则(Composite Reuse Principle)
答:原则是尽量使用合成/聚合的方式,而不是使用继承。
三.单例模式(Singleton)
1>.什么是单例模式
单例对象(Singleton)是一种常用的设计模式。在Java应用中,单例对象能保证在一个JVM中,该对象只有一个实例存在。这样的模式有几个好处:
第一:某些类创建比较频繁,对于一些大型的对象,这是一笔很大的系统开销。
第二:省去了new操作符,降低了系统内存的使用频率,减轻垃圾回收(GC)机制压力。
第三:有些类如交易所的核心交易引擎,控制着交易流程,如果该类可以创建多个的话,系统完全乱了。(比如一个军队出现了多个司令员同时指挥,肯定会乱成一团),所以只有使用单例模式,才能保证核心交易服务器独立控制整个流程。
单利模式是非常简单的一种设计模式,它大致分为两种:即懒汉式和饿汉式。
2>.懒汉式
1 /* 2 @author :yinzhengjie 3 Blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/tag/Java%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/ 4 EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com 5 */ 6 package cn.org.yinzhengjie.java.singletonMode; 7 8 public class GarbageBox { 9 10 //定义一个GarbageBox的引用变量 11 private static GarbageBox instance = null ; 12 13 //私有构造方法,防止被实例化 14 private GarbageBox(){ 15 } 16 17 //定义获取实例的方法 18 public static GarbageBox getInstance(){ 19 //先判断instance是否为空,如果不为空就直接返回instance对象 20 if(instance != null){ 21 return instance ; 22 } 23 //通过同步代码块的方式进行加锁 24 synchronized (GarbageBox.class){ 25 //仍需要判断instance是否为空,目的是为了防止多个线程产生不同的对象! 26 if(instance == null){ 27 instance = new GarbageBox() ; 28 } 29 } 30 return instance; 31 } 32 33 public void sayHello(){ 34 System.out.println("Hello Wold,My name is yinzhengjie !"); 35 } 36 }

1 /* 2 @author :yinzhengjie 3 Blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/tag/Java%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/ 4 EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com 5 */ 6 package cn.org.yinzhengjie.java.singletonMode; 7 8 public class Demo { 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 GarbageBox instance = GarbageBox.getInstance(); 11 instance.sayHello(); 12 } 13 } 14 15 16 /* 17 以上代码输出结果如下: 18 Hello Wold,My name is yinzhengjie ! 19 */
3>.饿汉式
1 /* 2 @author :yinzhengjie 3 Blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/tag/Java%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/ 4 EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com 5 */ 6 package cn.org.yinzhengjie.java.singletonMode; 7 8 public class GarbageBox { 9 //直接在成员变量中定义GarbageBox对象 10 private static GarbageBox instance = new GarbageBox(); 11 12 //直接就将该对象返回给调用者 13 public static GarbageBox getInstance() { 14 return instance; 15 } 16 17 public void sayHello() { 18 System.out.println("Hello Wold,My name is yinzhengjie !"); 19 } 20 }

1 /* 2 @author :yinzhengjie 3 Blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/tag/Java%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/ 4 EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com 5 */ 6 package cn.org.yinzhengjie.java.singletonMode; 7 8 public class Demo { 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 GarbageBox instance = GarbageBox.getInstance(); 11 instance.sayHello(); 12 } 13 } 14 15 16 /* 17 以上代码输出结果如下: 18 Hello Wold,My name is yinzhengjie ! 19 */
四.装饰者模式
1>.什么是装饰者模式
答:顾名思义,装饰模式就是给一个对象增加一些新的功能,而且是动态的,要求装饰对象和被装饰对象实现同一个接口,装饰对象持有被装饰对象的实例。
2>.装饰器模式的应用场景
第一:需要扩展一个类的功能。
第二:动态的为一个对象增加功能,而且还能动态撤销。(继承不能做到这一点,继承的功能是静态的,不能动态增删。)
装饰者模式在Java中的I/O流中应用的非常广泛!缺点:产生过多相似的对象,不易排错!
3>.实现代码

1 /* 2 @author :yinzhengjie 3 Blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/tag/Java%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/ 4 EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com 5 */ 6 package cn.org.yinzhengjie.java.decorativePattern; 7 8 public class Worker { 9 String Name; 10 int Age ; 11 12 public Worker(String name, int age) { 13 Name = name; 14 Age = age; 15 } 16 17 public Worker() { } 18 19 public void EarnMoney() { 20 System.out.printf("%s 开始挣钱啦!",this.Name); 21 try { 22 Thread.sleep(5000); //此处模拟挣钱需要花费的时间 23 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 24 e.printStackTrace(); 25 } 26 System.out.println("打工完毕"); 27 } 28 29 public String getName() { 30 return Name; 31 } 32 33 public void setName(String name) { 34 Name = name; 35 } 36 37 public int getAge() { 38 return Age; 39 } 40 41 public void setAge(int age) { 42 Age = age; 43 } 44 }
1 /* 2 @author :yinzhengjie 3 Blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/tag/Java%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/ 4 EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com 5 */ 6 package cn.org.yinzhengjie.java.decorativePattern; 7 8 public class WrappedWorker extends Worker { 9 private Worker worker; 10 11 public WrappedWorker( Worker worker) { 12 this.worker = worker; 13 } 14 15 16 //新增功能,给Worker的EarnMoney方法添加计时功能! 17 public void EarnMoney() { 18 long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); 19 worker.EarnMoney(); 20 long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); 21 System.out.printf("调用Worker的EarnMoney方法共计用时为:%d\n",(end - start)); 22 } 23 }

1 /* 2 @author :yinzhengjie 3 Blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/tag/Java%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/ 4 EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com 5 */ 6 package cn.org.yinzhengjie.java.decorativePattern; 7 8 public class Demo { 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 Worker yinzhengjie = new Worker("yinzhengjie", 18); 11 WrappedWorker yzj = new WrappedWorker(yinzhengjie); 12 yzj.EarnMoney(); 13 } 14 }
五.工厂(factory)模式
1>.什么是工厂模式
工厂方法模式分为以下三种:
第一:普通工厂模式,就是建立一个工厂类,对实现了同一接口的一些类进行实例的创建。
第二:多个工厂方法模式,是对普通工厂方法模式的改进,在普通工厂方法模式中,如果传递的字符串出错,则不能正确创建对象,而多个工厂方法模式是提供多个工厂方法,
第三:静态工厂方法模式,将上面的多个工厂方法模式里的方法置为静态的,不需要创建实例,直接调用即可。
2>.普通工厂模式

1 /* 2 @author :yinzhengjie 3 Blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/tag/Java%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/ 4 EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com 5 */ 6 package cn.org.yinzhengjie.java.factory; 7 8 public interface Animal { 9 public void eat(); 10 }

1 /* 2 @author :yinzhengjie 3 Blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/tag/Java%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/ 4 EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com 5 */ 6 package cn.org.yinzhengjie.java.factory; 7 8 public class Cat implements Animal { 9 public void eat() { 10 System.out.println("猫吃鱼!"); 11 } 12 }

1 /* 2 @author :yinzhengjie 3 Blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/tag/Java%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/ 4 EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com 5 */ 6 package cn.org.yinzhengjie.java.factory; 7 8 public class Dog implements Animal { 9 public void eat() { 10 System.out.println("狗吃肉!"); 11 } 12 }
1 /* 2 @author :yinzhengjie 3 Blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/tag/Java%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/ 4 EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com 5 */ 6 package cn.org.yinzhengjie.java.factory; 7 8 public class AnimalFactory { 9 public Animal produce(String type){ 10 if (type.equals("cat")){ 11 return new Cat(); 12 }else if (type.equals("dog")){ 13 return new Dog(); 14 }else { 15 System.out.println("输入的类型不匹配"); 16 return null; 17 } 18 } 19 }

1 /* 2 @author :yinzhengjie 3 Blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/tag/Java%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/ 4 EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com 5 */ 6 package cn.org.yinzhengjie.java.factory; 7 8 public class Demo { 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 AnimalFactory animal = new AnimalFactory(); 11 Animal cat = animal.produce("cat"); 12 Animal dog = animal.produce("dog"); 13 cat.eat(); 14 dog.eat(); 15 } 16 }
3>.多个工厂方法模式

1 /* 2 @author :yinzhengjie 3 Blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/tag/Java%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/ 4 EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com 5 */ 6 package cn.org.yinzhengjie.java.factory; 7 8 public interface Animal { 9 public void eat(); 10 }

1 /* 2 @author :yinzhengjie 3 Blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/tag/Java%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/ 4 EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com 5 */ 6 package cn.org.yinzhengjie.java.factory; 7 8 public class Cat implements Animal { 9 public void eat() { 10 System.out.println("猫吃鱼!"); 11 } 12 }

1 /* 2 @author :yinzhengjie 3 Blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/tag/Java%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/ 4 EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com 5 */ 6 package cn.org.yinzhengjie.java.factory; 7 8 public class Dog implements Animal { 9 public void eat() { 10 System.out.println("狗吃肉!"); 11 } 12 }
1 /* 2 @author :yinzhengjie 3 Blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/tag/Java%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/ 4 EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com 5 */ 6 package cn.org.yinzhengjie.java.factory; 7 8 /** 9 * 多个工厂方法模式是对普通工厂方法模式的改进,在普通工厂方法模式中,如果传递的字符串出错,则不能正确创建对象,而多个工 10 * 厂方法模式是提供多个工厂方法,分别创建对象。 11 */ 12 public class AnimalFactory { 13 public Animal produceCat(){ 14 return new Cat(); 15 } 16 17 public Animal produceDog(){ 18 return new Dog(); 19 } 20 }

1 /* 2 @author :yinzhengjie 3 Blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/tag/Java%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/ 4 EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com 5 */ 6 package cn.org.yinzhengjie.java.factory; 7 8 public class Demo { 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 AnimalFactory animal = new AnimalFactory(); 11 Animal cat = animal.produceCat(); 12 Animal dog = animal.produceDog(); 13 cat.eat(); 14 dog.eat(); 15 } 16 } 17 18 19 /* 20 以上代码执行结果如下: 21 猫吃鱼! 22 狗吃肉! 23 */
4>.静态工厂方法模式

1 /* 2 @author :yinzhengjie 3 Blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/tag/Java%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/ 4 EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com 5 */ 6 package cn.org.yinzhengjie.java.factory; 7 8 public interface Animal { 9 public void eat(); 10 }

1 /* 2 @author :yinzhengjie 3 Blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/tag/Java%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/ 4 EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com 5 */ 6 package cn.org.yinzhengjie.java.factory; 7 8 public class Cat implements Animal { 9 public void eat() { 10 System.out.println("猫吃鱼!"); 11 } 12 }

1 /* 2 @author :yinzhengjie 3 Blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/tag/Java%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/ 4 EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com 5 */ 6 package cn.org.yinzhengjie.java.factory; 7 8 public class Dog implements Animal { 9 public void eat() { 10 System.out.println("狗吃肉!"); 11 } 12 }
1 /* 2 @author :yinzhengjie 3 Blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/tag/Java%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/ 4 EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com 5 */ 6 package cn.org.yinzhengjie.java.factory; 7 8 /** 9 * 静态工厂方法模式是将的多个工厂方法模式里的方法置为静态的,不需要创建实例,直接调用即可。 10 */ 11 public class AnimalFactory { 12 public static Animal produceCat(){ 13 return new Cat(); 14 } 15 16 public static Animal produceDog(){ 17 return new Dog(); 18 } 19 }

1 /* 2 @author :yinzhengjie 3 Blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/tag/Java%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/ 4 EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com 5 */ 6 package cn.org.yinzhengjie.java.factory; 7 8 public class Demo { 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 Animal cat = AnimalFactory.produceCat(); 11 Animal dog = AnimalFactory.produceDog(); 12 13 cat.eat(); 14 dog.eat(); 15 } 16 } 17 18 19 /* 20 以上代码执行结果如下: 21 猫吃鱼! 22 狗吃肉! 23 */
总体来说,凡是出现了大量的产品需要创建,并且具有共同的接口时,可以通过工厂方法模式进行创建。在以上的三种模式中,第一种如果传入的字符串有误,不能正确创建对象,第三种相对于第二种,不需要实例化工厂类,所以,大多数情况下,我们会选用第三种——静态工厂方法模式。
六.适配器
1>.什么是适配器
2>.
3>.
七.动态代理模式
1>.什么是动态代理模式
我们知道装饰者模式可以静态装饰一个类,通过装饰者模式可以给被装饰者添加附加功能,但是如果添加的功能特别多,你需要不断的继承这个类,这样可能会导致类的暴增!为了解决这个问题,引入了与装饰者类功能相似的动态代理模式。动态代理模式的核心就是代理器实现接口的方法,实现类也实现接口的方法。用户在调用接口的功能时,是通过代理器来访问的,而代理器则只需要调用实现目标类对象即可,并在代理器的invoke方法中添加相应的业务逻辑即可!画了一个草图如下:

2>.动态代理的应用场景
如果已有的方法在使用的时候需要对原有的方法进行改进,此时有两种办法:
第一:修改原有的方法来适应。这样违反了“对扩展开放,对修改关闭”的原则。
第二:就是采用一个代理类调用原有的方法,且对产生的结果进行控制。这种方法就是代理模式。
使用代理模式,可以将功能划分的更加清晰,有助于后期维护!
3>.动态代理案例展示
假设有两个接口,分别为WelcomeService和WelcomeService2,有一个实现类WelcomeServiceImpl,它实现了WelcomeService和WelcomeService2这两个接口。现在我们需要通过动态代理模式来统计实现这两个接口中每个方法的执行时间。具体代码如下:

1 /* 2 @author :yinzhengjie 3 Blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/tag/Java%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/ 4 EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com 5 */ 6 package cn.org.yinzhengjie.proxy; 7 8 /** 9 * 代理接口 10 */ 11 public interface WelcomeService { 12 public void sayHell(); 13 }

1 /* 2 @author :yinzhengjie 3 Blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/tag/Java%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/ 4 EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com 5 */ 6 package cn.org.yinzhengjie.proxy; 7 8 public interface WelcomeService2 { 9 public abstract void eat(); 10 public abstract void work(); 11 }

1 /* 2 @author :yinzhengjie 3 Blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/tag/Java%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/ 4 EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com 5 */ 6 package cn.org.yinzhengjie.proxy; 7 8 /** 9 * 目标类 10 */ 11 public class WelcomeServiceImpl implements WelcomeService,WelcomeService2{ 12 public void sayHell() { 13 System.out.println("hi ,I'm Yinzhengjie !!!"); 14 } 15 16 public void eat() { 17 System.out.println("I like food !"); 18 } 19 20 public void work() { 21 System.out.println("I'm a programmer"); 22 } 23 }
1 /* 2 @author :yinzhengjie 3 Blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/tag/Java%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/ 4 EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com 5 */ 6 package cn.org.yinzhengjie.proxy; 7 8 import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler; 9 import java.lang.reflect.Method; 10 import java.lang.reflect.Proxy; 11 12 public class ProxyDemo { 13 public static void main(String[] args) { 14 15 //目标对象 16 final WelcomeServiceImpl target = new WelcomeServiceImpl() ; 17 18 //系统类加载器 19 ClassLoader loader = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader() ; 20 21 //代理接口集合 22 Class[] inters = { 23 WelcomeService.class, 24 WelcomeService2.class 25 } ; 26 27 //处理器 28 InvocationHandler h = new InvocationHandler() { 29 //proxy表示被代理的对象,method表示被代理对象的方法,args表示被代理对象的方法中的参数 30 public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { 31 //附加行为,即统计每个方法的执行时间! 32 long start = System.nanoTime(); 33 //调用目标对象的方法, 34 Object ret = method.invoke(target , args) ; 35 long end = System.nanoTime(); 36 System.out.printf("执行该方法用时为:[%d]纳秒\n",(end-start)); 37 //返回目标对象方法的返回值 38 return ret; 39 } 40 } ; 41 42 //得到代理对象obj 43 Object obj = Proxy.newProxyInstance(loader, inters, h); 44 //由于代理对象也实现了WelcomeService和WelcomeService2接口,因此我们只需要向下转型就可以调用各个接口对应的方法!同时也会触发附加计时功能! 45 WelcomeService ws = (WelcomeService)obj; 46 WelcomeService2 ws2 = (WelcomeService2)obj; 47 //调用各个接口的方法 48 ws.sayHell(); 49 ws2.work(); 50 ws2.eat(); 51 } 52 } 53 54 /* 55 以上代码执行结果如下: 56 hi ,I'm Yinzhengjie !!! 57 执行该方法用时为:[188156]纳秒 58 I'm a programmer 59 执行该方法用时为:[30720]纳秒 60 I like food ! 61 执行该方法用时为:[25920]纳秒 62 */
八.池化模式
九.
十.
Java中的设计模式有很多种,我就举例十中装饰者模式,在多的我也用不到了。如果你觉得上面的几种设计模式很简单,并且对其它的设计模式很感兴趣,可参考:https://blog.csdn.net/doymm2008/article/details/13288067。接下来我们利用上面已经学到的模式编写我们自己的数据源吧(DataSource)。
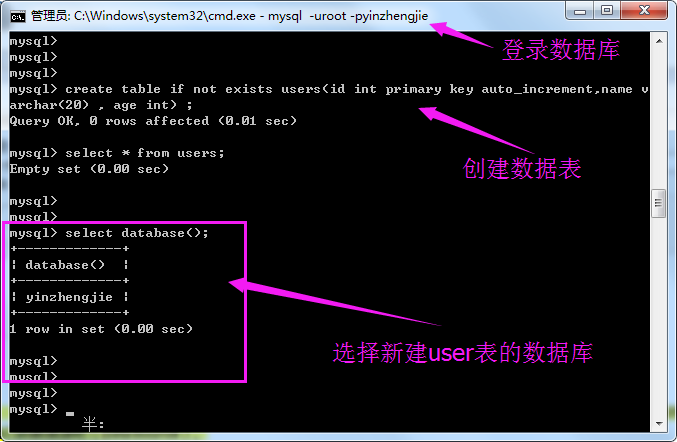
1>.实验环境(新建表)
2>.Java代码如下

1 /* 2 @author :yinzhengjie 3 Blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/tag/Java%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/ 4 EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com 5 */ 6 package cn.org.yinzhengjie.datasource; 7 8 import java.sql.*; 9 import java.util.Map; 10 import java.util.Properties; 11 import java.util.concurrent.Executor; 12 13 /** 14 * 连接适配器 15 */ 16 public abstract class MyConnectionAdaptor implements Connection{ 17 public Statement createStatement() throws SQLException { 18 return null; 19 } 20 21 public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql) throws SQLException { 22 return null; 23 } 24 25 public CallableStatement prepareCall(String sql) throws SQLException { 26 return null; 27 } 28 29 public String nativeSQL(String sql) throws SQLException { 30 return null; 31 } 32 33 public void setAutoCommit(boolean autoCommit) throws SQLException { 34 35 } 36 37 public boolean getAutoCommit() throws SQLException { 38 return false; 39 } 40 41 public void commit() throws SQLException { 42 43 } 44 45 public void rollback() throws SQLException { 46 47 } 48 49 public void close() throws SQLException { 50 51 } 52 53 public boolean isClosed() throws SQLException { 54 return false; 55 } 56 57 public DatabaseMetaData getMetaData() throws SQLException { 58 return null; 59 } 60 61 public void setReadOnly(boolean readOnly) throws SQLException { 62 63 } 64 65 public boolean isReadOnly() throws SQLException { 66 return false; 67 } 68 69 public void setCatalog(String catalog) throws SQLException { 70 71 } 72 73 public String getCatalog() throws SQLException { 74 return null; 75 } 76 77 public void setTransactionIsolation(int level) throws SQLException { 78 79 } 80 81 public int getTransactionIsolation() throws SQLException { 82 return 0; 83 } 84 85 public SQLWarning getWarnings() throws SQLException { 86 return null; 87 } 88 89 public void clearWarnings() throws SQLException { 90 91 } 92 93 public Statement createStatement(int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency) throws SQLException { 94 return null; 95 } 96 97 public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency) throws SQLException { 98 return null; 99 } 100 101 public CallableStatement prepareCall(String sql, int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency) throws SQLException { 102 return null; 103 } 104 105 public Map<String, Class<?>> getTypeMap() throws SQLException { 106 return null; 107 } 108 109 public void setTypeMap(Map<String, Class<?>> map) throws SQLException { 110 111 } 112 113 public void setHoldability(int holdability) throws SQLException { 114 115 } 116 117 public int getHoldability() throws SQLException { 118 return 0; 119 } 120 121 public Savepoint setSavepoint() throws SQLException { 122 return null; 123 } 124 125 public Savepoint setSavepoint(String name) throws SQLException { 126 return null; 127 } 128 129 public void rollback(Savepoint savepoint) throws SQLException { 130 131 } 132 133 public void releaseSavepoint(Savepoint savepoint) throws SQLException { 134 135 } 136 137 public Statement createStatement(int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency, int resultSetHoldability) throws SQLException { 138 return null; 139 } 140 141 public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency, int resultSetHoldability) throws SQLException { 142 return null; 143 } 144 145 public CallableStatement prepareCall(String sql, int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency, int resultSetHoldability) throws SQLException { 146 return null; 147 } 148 149 public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int autoGeneratedKeys) throws SQLException { 150 return null; 151 } 152 153 public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int[] columnIndexes) throws SQLException { 154 return null; 155 } 156 157 public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, String[] columnNames) throws SQLException { 158 return null; 159 } 160 161 public Clob createClob() throws SQLException { 162 return null; 163 } 164 165 public Blob createBlob() throws SQLException { 166 return null; 167 } 168 169 public NClob createNClob() throws SQLException { 170 return null; 171 } 172 173 public SQLXML createSQLXML() throws SQLException { 174 return null; 175 } 176 177 public boolean isValid(int timeout) throws SQLException { 178 return false; 179 } 180 181 public void setClientInfo(String name, String value) throws SQLClientInfoException { 182 183 } 184 185 public void setClientInfo(Properties properties) throws SQLClientInfoException { 186 187 } 188 189 public String getClientInfo(String name) throws SQLException { 190 return null; 191 } 192 193 public Properties getClientInfo() throws SQLException { 194 return null; 195 } 196 197 public Array createArrayOf(String typeName, Object[] elements) throws SQLException { 198 return null; 199 } 200 201 public Struct createStruct(String typeName, Object[] attributes) throws SQLException { 202 return null; 203 } 204 205 public void setSchema(String schema) throws SQLException { 206 207 } 208 209 public String getSchema() throws SQLException { 210 return null; 211 } 212 213 public void abort(Executor executor) throws SQLException { 214 215 } 216 217 public void setNetworkTimeout(Executor executor, int milliseconds) throws SQLException { 218 219 } 220 221 public int getNetworkTimeout() throws SQLException { 222 return 0; 223 } 224 225 public <T> T unwrap(Class<T> iface) throws SQLException { 226 return null; 227 } 228 229 public boolean isWrapperFor(Class<?> iface) throws SQLException { 230 return false; 231 } 232 }

1 /* 2 @author :yinzhengjie 3 Blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/tag/Java%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/ 4 EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com 5 */ 6 package cn.org.yinzhengjie.datasource; 7 8 import javax.sql.DataSource; 9 import java.io.PrintWriter; 10 import java.sql.Connection; 11 import java.sql.SQLException; 12 import java.sql.SQLFeatureNotSupportedException; 13 import java.util.logging.Logger; 14 15 /** 16 * 数据源适配器 17 */ 18 public abstract class MyDataSourceAdaptor implements DataSource { 19 public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException { 20 return null; 21 } 22 23 public Connection getConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException { 24 return null; 25 } 26 27 public <T> T unwrap(Class<T> iface) throws SQLException { 28 return null; 29 } 30 31 public boolean isWrapperFor(Class<?> iface) throws SQLException { 32 return false; 33 } 34 35 public PrintWriter getLogWriter() throws SQLException { 36 return null; 37 } 38 39 public void setLogWriter(PrintWriter out) throws SQLException { 40 41 } 42 43 public void setLoginTimeout(int seconds) throws SQLException { 44 45 } 46 47 public int getLoginTimeout() throws SQLException { 48 return 0; 49 } 50 51 public Logger getParentLogger() throws SQLFeatureNotSupportedException { 52 return null; 53 } 54 }

1 /* 2 @author :yinzhengjie 3 Blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/tag/Java%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/ 4 EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com 5 */ 6 package cn.org.yinzhengjie.datasource; 7 8 import java.sql.Connection; 9 import java.sql.DriverManager; 10 import java.sql.SQLException; 11 import java.util.LinkedList; 12 13 /** 14 * 单模模式实现连接池 15 */ 16 public class ConnectionPool { 17 18 private static ConnectionPool instance ; 19 20 private LinkedList<Connection> idles = new LinkedList<Connection>() ; 21 22 private LinkedList<Connection> busies = new LinkedList<Connection>() ; 23 24 //最大连接数 25 private static int MAX = 3 ; 26 27 //最小连接数 28 private static int MIN = 2 ; 29 30 private String user = "root" ; 31 private String pass = "yinzhengjie" ; 32 private String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:5200/yinzhengjie" ; 33 34 private ConnectionPool(){ 35 try { 36 Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); 37 initPool() ; 38 } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { 39 e.printStackTrace(); 40 } 41 } 42 43 /** 44 * 初始化连接池 , 开启min连接数 45 */ 46 private void initPool() { 47 for(int i = 0 ; i < MIN ; i ++){ 48 Connection conn = openNewConnection() ; 49 idles.add(conn) ; 50 } 51 } 52 53 /** 54 * 55 */ 56 public static ConnectionPool getInstance(){ 57 if(instance != null){ 58 return instance ; 59 } 60 61 synchronized (ConnectionPool.class){ 62 if(instance == null){ 63 instance = new ConnectionPool() ; 64 } 65 } 66 return instance ; 67 } 68 69 /** 70 * 开启新连接 71 */ 72 private Connection openNewConnection(){ 73 try { 74 Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url , user ,pass) ; 75 return new MyConnection(conn , this) ; 76 } catch (SQLException e) { 77 e.printStackTrace(); 78 } 79 return null ; 80 } 81 82 83 /** 84 * 将连接释放回池子中 85 */ 86 public synchronized void backToPool(MyConnection myConnection) { 87 busies.remove(myConnection) ; 88 idles.add(myConnection) ; 89 this.notifyAll(); 90 } 91 92 /** 93 * 从连接池中获取连接 94 */ 95 public synchronized Connection getConnection() { 96 //有可用连接 97 if(!idles.isEmpty()){ 98 Connection conn = idles.remove(0) ; 99 busies.add(conn) ; 100 return conn ; 101 } 102 //没有到达最大值 103 if(busies.size() < MAX){ 104 Connection conn = openNewConnection(); 105 busies.add(conn) ; 106 return conn ; 107 } 108 109 while(idles.isEmpty()){ 110 try { 111 this.wait(); 112 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 113 e.printStackTrace(); 114 } 115 } 116 Connection conn = idles.remove(0); 117 busies.add(conn); 118 return conn; 119 } 120 }

1 /* 2 @author :yinzhengjie 3 Blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/tag/Java%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/ 4 EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com 5 */ 6 package cn.org.yinzhengjie.datasource; 7 8 import java.sql.Connection; 9 import java.sql.PreparedStatement; 10 import java.sql.SQLException; 11 12 /** 13 * 连接使用适配器和装饰模式 14 */ 15 public class MyConnection extends MyConnectionAdaptor{ 16 17 private Connection conn ; 18 19 private ConnectionPool pool ; 20 21 public MyConnection(Connection conn , ConnectionPool pool ){ 22 this.conn = conn ; 23 this.pool = pool ; 24 } 25 26 public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql) throws SQLException { 27 return conn.prepareStatement(sql); 28 } 29 30 public void setAutoCommit(boolean autoCommit) throws SQLException { 31 conn.setAutoCommit(autoCommit); 32 } 33 34 public void commit() throws SQLException { 35 conn.commit(); 36 } 37 38 public void rollback() throws SQLException { 39 conn.rollback(); 40 } 41 42 public void close() throws SQLException { 43 pool.backToPool(this) ; 44 } 45 46 public void setTransactionIsolation(int level) throws SQLException { 47 conn.setTransactionIsolation(level); 48 } 49 }

1 /* 2 @author :yinzhengjie 3 Blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/tag/Java%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/ 4 EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com 5 */ 6 package cn.org.yinzhengjie.datasource; 7 8 import java.sql.Connection; 9 import java.sql.SQLException; 10 11 /** 12 * 自定义数据源 13 */ 14 public class MyDataSource extends MyDataSourceAdaptor{ 15 private ConnectionPool pool ; 16 17 public MyDataSource(){ 18 pool = ConnectionPool.getInstance() ; 19 } 20 21 public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException { 22 return pool.getConnection() ; 23 } 24 25 26 }
1 /* 2 @author :yinzhengjie 3 Blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/tag/Java%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/ 4 EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com 5 */ 6 package cn.org.yinzhengjie.datasource; 7 8 import java.sql.Connection; 9 import java.sql.PreparedStatement; 10 import java.sql.SQLException; 11 12 /** 13 * 执行以下代码之前,需要启动MySQL,并在yinzhengjie数据下创建user表,否则会抛异常哟!创建表的SQL语句如下: 14 * create table if not exists users(id int primary key auto_increment,name varchar(20) , age int) ; 15 */ 16 public class MyDataSoureApp { 17 static int i = 0 ; 18 public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException { 19 final MyDataSource ds = new MyDataSource(); 20 21 for(i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i ++){ 22 new Thread(){ 23 public void run() { 24 try { 25 Connection conn = ds.getConnection(); 26 String sql = "insert into users(name ,age) values(?,?)"; 27 PreparedStatement ppst = conn.prepareStatement(sql); 28 ppst.setString(1, "yinzhengjie" + i); 29 ppst.setInt(2, i + 10); 30 ppst.executeUpdate(); 31 ppst.close(); 32 conn.close(); 33 } catch (Exception e) { 34 e.printStackTrace(); 35 } 36 37 } 38 }.start(); 39 40 } 41 } 42 }
3>.测试结果

本文来自博客园,作者:尹正杰,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/p/9250870.html,个人微信: "JasonYin2020"(添加时请备注来源及意图备注,有偿付费)
当你的才华还撑不起你的野心的时候,你就应该静下心来学习。当你的能力还驾驭不了你的目标的时候,你就应该沉下心来历练。问问自己,想要怎样的人生。







【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· 阿里最新开源QwQ-32B,效果媲美deepseek-r1满血版,部署成本又又又降低了!
· 开源Multi-agent AI智能体框架aevatar.ai,欢迎大家贡献代码
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· AI技术革命,工作效率10个最佳AI工具