Java基础-时间复杂度计算方式
Java基础-时间复杂度计算方式
作者:尹正杰
版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任。
时间复杂度通常是衡量算法的优劣的,衡量算法的时间严格来讲是很难衡量的,由于不同的机器性能不用环境都会造成不同的执行时间。
一.什么是时间复杂度
1>.什么是时间频度
算法的执行时间和语句的执行次数成正比,因此通过计算执行测试来推断执行时间。算法中语句执行次数称为语句频度或时间频度,记为T(n),n是问题的规模,T是Time。
2>.什么是
当时间频度的通常操作重复执行的次数是问题规模n的某个函数,用T(n)表示,若有某个辅助函数f(n),存在一个正常数c使得f(n) * c >= T(n)恒成立。记作T(n)=O(f(n)),称O(f(n)) 为算法的渐进时间复杂度,简称时间复杂度。换句话说,只要计算一下语句的执行次数和n之间的关就可以了,去除系数部分,低阶项部分,就是时间复杂度的值了。
举个例子,在公式:“xxx = 3N^3 + 2n^2 + 5n”中,其中“2n^2”和“5n”相对于“3N^3 ”来说,属于低阶项部分,我们将其去除,在看“3N^3"中,”3“为系数部分,我们将其也去除,因此只剩下“N^3 ”啦!这个时候我们就说“xxx”的时间复杂度为“O(n^3)”。
二.
1>.
时间复杂度为:无论数组长度n为多少,代码执行一次。因此,时间复杂度为O(1)。实现代码如下:
1 /* 2 @author :yinzhengjie 3 Blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/tag/Java%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/ 4 EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com 5 */ 6 package cn.org.yinzhengjie.java.timeComplexity; 7 8 public class Demo { 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 String[] names = {"尹正杰","yinzhengjie","YinZhengJie"}; 11 String firstElement = getFirstElement(names); 12 System.out.println(firstElement); 13 } 14 15 public static String getFirstElement(String[] names){ 16 //无论数组的长度n为多少,代码只执行一次。 17 return names[0]; 18 } 19 } 20 21 /* 22 以上代码输出结果如下: 23 尹正杰 24 */
1 /* 2 @author :yinzhengjie 3 Blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/tag/Java%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/ 4 EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com 5 */ 6 package cn.org.yinzhengjie.java.timeComplexity; 7 8 public class Demo { 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 String[] names = {"尹正杰","yinzhengjie","YinZhengJie"}; 11 printArray(5); 12 } 13 14 public static void printArray(int n){ 15 for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++){ 16 //执行一次。 17 System.out.println("尹正杰(yinzhengjie)") ; 18 } 19 } 20 } 21 22 /* 23 以上代码输出结果如下: 24 尹正杰(yinzhengjie) 25 尹正杰(yinzhengjie) 26 尹正杰(yinzhengjie) 27 尹正杰(yinzhengjie) 28 尹正杰(yinzhengjie) 29 */
打印语句执行次数:n * n = n^2,因此时间复杂度是O(n^2)。
1 /* 2 @author :yinzhengjie 3 Blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/tag/Java%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/ 4 EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com 5 */ 6 package cn.org.yinzhengjie.java.timeComplexity; 7 8 public class Demo { 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 printArray(9); 11 } 12 13 public static void printArray(int n){ 14 for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++){ 15 for(int j = 1 ; j <= i ; j ++){ 16 //打印语句的执行次数n * n次。 17 System.out.printf("%d x %d = %d\t",j,i,(j*i)); 18 } 19 System.out.println(); 20 } 21 } 22 } 23 24 /* 25 以上代码输出结果如下: 26 1 x 1 = 1 27 1 x 2 = 2 2 x 2 = 4 28 1 x 3 = 3 2 x 3 = 6 3 x 3 = 9 29 1 x 4 = 4 2 x 4 = 8 3 x 4 = 12 4 x 4 = 16 30 1 x 5 = 5 2 x 5 = 10 3 x 5 = 15 4 x 5 = 20 5 x 5 = 25 31 1 x 6 = 6 2 x 6 = 12 3 x 6 = 18 4 x 6 = 24 5 x 6 = 30 6 x 6 = 36 32 1 x 7 = 7 2 x 7 = 14 3 x 7 = 21 4 x 7 = 28 5 x 7 = 35 6 x 7 = 42 7 x 7 = 49 33 1 x 8 = 8 2 x 8 = 16 3 x 8 = 24 4 x 8 = 32 5 x 8 = 40 6 x 8 = 48 7 x 8 = 56 8 x 8 = 64 34 1 x 9 = 9 2 x 9 = 18 3 x 9 = 27 4 x 9 = 36 5 x 9 = 45 6 x 9 = 54 7 x 9 = 63 8 x 9 = 72 9 x 9 = 81 35 */
4>
冒泡排序是经典的排序算法是每次比较相邻的两个元素进行对调,进行多轮,知道数列有序。
1 /* 2 @author :yinzhengjie 3 Blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/tag/Java%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/ 4 EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com 5 */ 6 package cn.org.yinzhengjie.java.timeComplexity; 7 8 public class Demo { 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 char[] arr = {'i','f','c','b','d','g','e','a','h'}; 11 printArray(arr); 12 bubbleSort(arr); 13 printArray(arr); 14 } 15 //进行冒泡排序 16 public static void bubbleSort(char[] arr){ 17 //外层比较n-1次 18 for(int i = 0 ; i < arr.length - 1 ; i ++){ 19 //比较n-1-i次 20 for(int j = 0 ; j < arr.length -1 - i ; j ++){ 21 char temp = arr[j] ; 22 if(arr[j] > arr[j + 1]){ 23 arr[j] = arr[j + 1] ; 24 arr[j + 1] = temp ; 25 } 26 } 27 } 28 } 29 //遍历数组 30 public static void printArray(char[] arr){ 31 for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { 32 char c = arr[i]; 33 System.out.print(c+" "); 34 } 35 System.out.println(); 36 } 37 38 } 39 40 /* 41 以上代码输出结果如下: 42 i f c b d g e a h 43 a b c d e f g h i 44 */
1 /* 2 @author :yinzhengjie 3 Blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/tag/Java%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/ 4 EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com 5 */ 6 package cn.org.yinzhengjie.java.timeComplexity; 7 8 public class Demo { 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 char[] arr = {'i','f','c','b','d','g','e','a','h'}; 11 printArray(arr); 12 bubbleSort(arr); 13 printArray(arr); 14 } 15 //进行冒泡排序 16 public static void bubbleSort(char[] arr){ 17 //外层比较n-1次 18 for(int i = 0 ; i < arr.length - 1 ; i ++){ 19 boolean flag = true ; 20 //比较n-1-i次 21 for(int j = 0 ; j < arr.length -1 - i ; j ++){ 22 char temp = arr[j] ; 23 if(arr[j] > arr[j + 1]){ 24 //发生交换,就设置标志位为false,即数列无序。 25 flag = false ; 26 arr[j] = arr[j + 1] ; 27 arr[j + 1] = temp ; 28 } 29 } 30 //判断如果是数列有序,则终止循环。 31 if(flag){ 32 break ; 33 } 34 } 35 } 36 //遍历数组 37 public static void printArray(char[] arr){ 38 for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { 39 char c = arr[i]; 40 System.out.print(c+" "); 41 } 42 System.out.println(); 43 } 44 45 } 46 47 /* 48 以上代码输出结果如下: 49 i f c b d g e a h 50 a b c d e f g h i 51 */
设置标志位flag=1,表示整个数列已经有序,就不需要再排序了,在里层循环中,如果发现没有进行过数据交换,就所说数列已经有序。在最好情况下,就是数列本身已经有序,只需要执行外层的n-1次循环即可,因此复杂度为O(n)。
折半查找也叫二分查找,是高效的查找方式,前提条件是数列需要时有序数列。实现代码如下:
1 /* 2 @author :yinzhengjie 3 Blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/tag/Java%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/ 4 EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com 5 */ 6 package cn.org.yinzhengjie.java.timeComplexity; 7 8 public class Demo { 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 char[] arr = {'a','b','c','d','e','f','g'}; 11 int tag = 'n'; 12 int res = halfSearch(arr, tag); 13 System.out.println(res); 14 tag = 'd'; 15 int res2 = halfSearch(arr, tag); 16 System.out.println(res2); 17 18 } 19 //进行冒泡排序 20 public static int halfSearch(char[] arr, int tag){ 21 int min = arr[0] ; 22 int max = arr[0] ; 23 int mid = arr[arr.length/2] ; 24 for( min = 0 , max = arr.length - 1 ; min <= max ; ){ 25 mid = (min + max) / 2 ; 26 //命中了 27 if(arr[mid] == tag){ 28 return mid ; 29 } 30 //落在右侧范围 31 else if(arr[mid] < tag){ 32 min = mid + 1 ; 33 } 34 //落在左侧范围 35 else{ 36 max = mid - 1 ; 37 } 38 } 39 return -1; 40 } 41 } 42 43 /* 44 以上代码输出结果如下: 45 -1 46 3 47 */
折半查找的最好的时间复杂度为n(1),就是第一次折半时就恰好找到我们想要的值,当然,最坏时间复杂度为:以2为底,n的对数。即”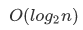 ”
”
6>.
哈希map是java中最重要的集合之一,设计非常巧妙,使用通过数组+链表方式组合实现,哈希的目的是让对象在空间内尽可能分散。那么HashMap的时间复杂度是多少呢?
如果hashmap的每个桶内的元素个数最多不会超过一个常数C,当增加元素时,不断增加桶的数量,而保证每个桶内的元素量固定,因此就可以保证最快的查询速度,则时间复杂度就是O(C*n^2),去掉系数部分就是O(n^0) = O(1);
如果在最坏的情况下就是所有元素进入同一个桶,导致给桶内的链条非常长,则检索数据时,时间复杂度为:O(n);
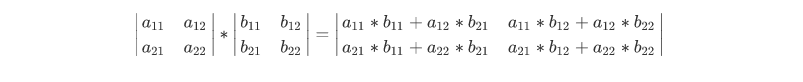
例如:
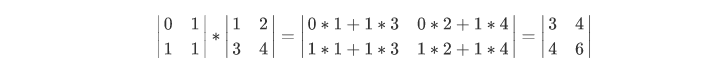
方阵乘法的代码如下:
1 /* 2 @author :yinzhengjie 3 Blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/tag/Java%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/ 4 EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com 5 */ 6 package cn.org.yinzhengjie.java.timeComplexity; 7 8 public class Demo { 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 int[][] a = { 11 {0,1}, 12 {1,1} 13 } ; 14 int[][] b = { 15 {1,2}, 16 {3,4} 17 } ; 18 19 mulmatrix(a,b); 20 21 } 22 /** 23 * 两个n阶方阵的乘积 24 * @param a 25 * @param b 26 * @return 27 */ 28 public static void mulmatrix(int[][] a , int[][] b){ 29 int n = a.length ; 30 int[][] r = new int[n][n] ; 31 // 32 for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++){ 33 for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) { 34 for (int k = 0; k < n; k++) { 35 r[i][j] = r[i][j] + (a[i][k] * b[k][j] ) ; 36 } 37 } 38 } 39 40 for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++){ 41 for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) { 42 System.out.print(r[i][j] + "\t"); 43 } 44 System.out.println(); 45 } 46 } 47 } 48 49 /* 50 以上代码输出结果如下: 51 3 4 52 4 6 53 */
本文来自博客园,作者:尹正杰,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/p/9245140.html,个人微信: "JasonYin2020"(添加时请备注来源及意图备注,有偿付费)
当你的才华还撑不起你的野心的时候,你就应该静下心来学习。当你的能力还驾驭不了你的目标的时候,你就应该沉下心来历练。问问自己,想要怎样的人生。





