java基础-迭代器(Iterator)与增强for循环
java基础-迭代器(Iterator)与增强for循环
作者:尹正杰
版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任。
一.Iterator迭代器概述
Java中提供了很多个集合,它们在存储元素时,采用的存储方式不同。我们需要取出这些集合中的元素,可通过一种通用的方式来完成。
Collection集合元素的通用获取方式:在取元素之前先要判断集合中有没有元素,如果有,就把这个元素取出来,继续在判断,如果还有就在取出来。一直把集合中所有的元素全部取出。这种取出方式专业术语称为迭代。换句话说,迭代是取出集合中元素的一种方式,因为Collection中有iterator方法,所以每一个子类集合对象都是迭代器对象。
二.迭代器的实现原理
其实集合中的迭代器就是获取结合中元素的方式。这是时候我们就不得不说一下Iterator接口了,经过查阅API文档发现它有三个抽象方法,如下:
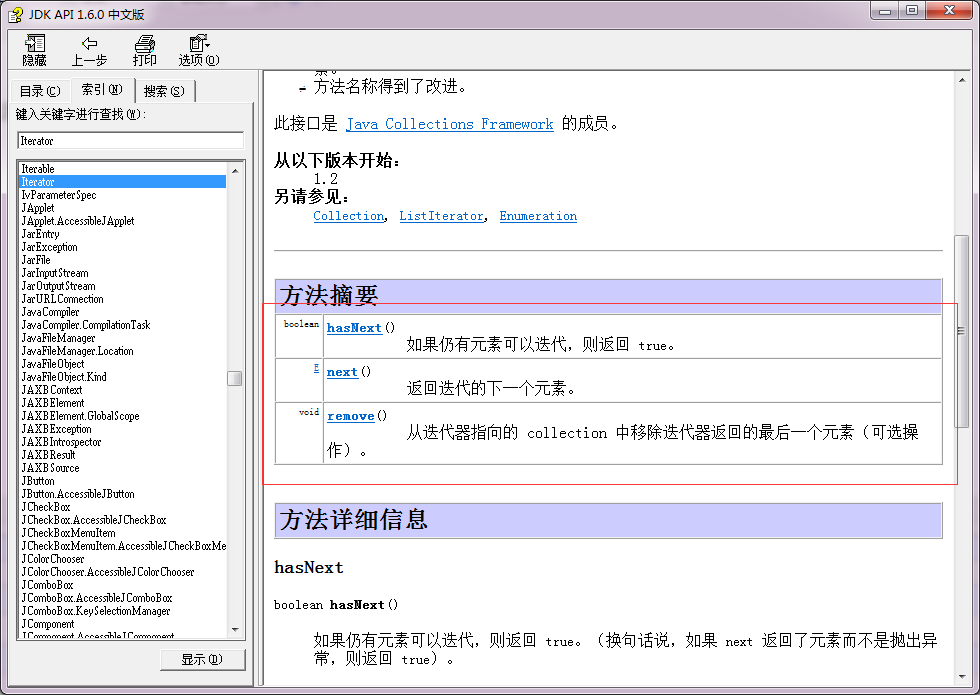
由于Iterator只是接口,不能被直接实例化,因此想要使用该接口就必须实现该接口的所有抽象方法,而我们学习的Collection接口也定影实现Iterator接口的抽象方法,即“iterator()”。因此只要是Collection的实现类就必须重写“iterator()”方法,最终返回“Iterator”接口实现类的对象(也就是可迭代对象),然后在调用hasNext()和next()方法来对集合进行迭代操作。
综上所述,我们可以总结为以下三点:
1>.迭代器不保证取出来元素的顺序和存入的顺序一致,“有序”是靠集合实例本身保证的;
2>.迭代器本身是一个接口,该方法返回的是一个迭代器实例对象,通常使用的是接口多态使用迭代器;
3>.迭代器中常用的两个方法是:
a>.boolean hasNext() : 用来判断结合中是否有下一个元素可以迭代,如果返回true,说明可以迭代。
b>.Object next() : 用来返回迭代的下一个元素,并把指针向后移动一位。
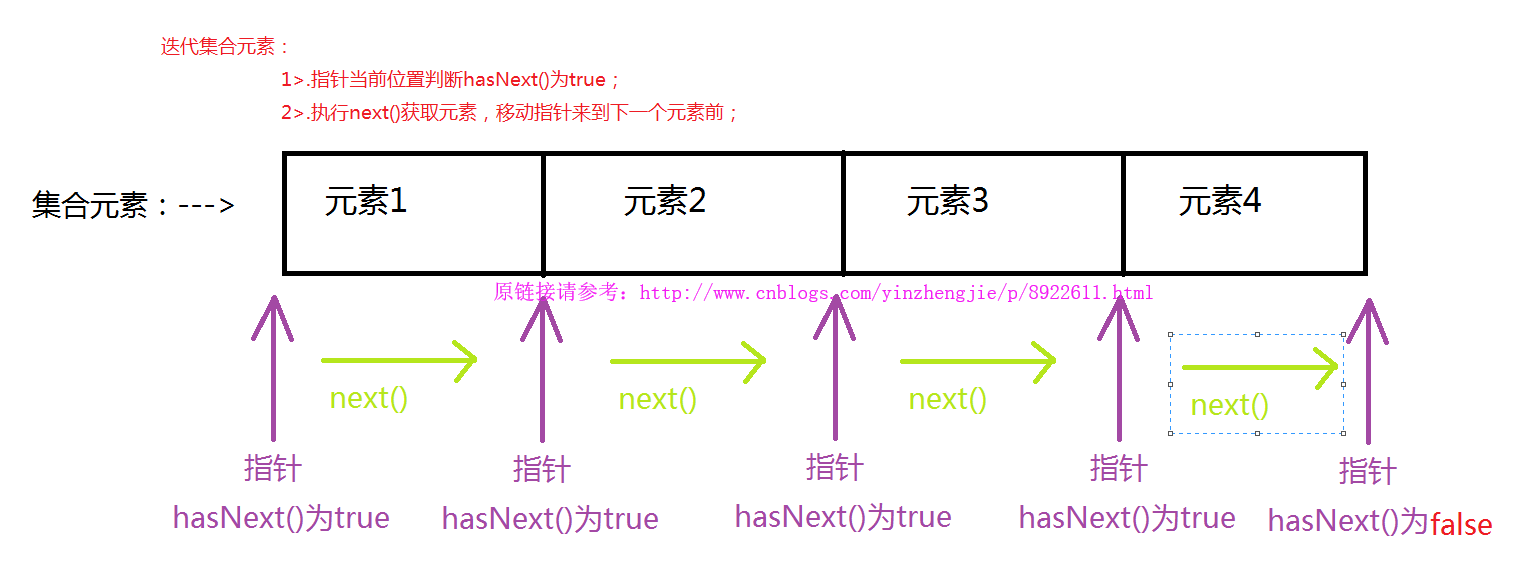
迭代器的执行过程,可以用张图来帮助大家理解,如下:
三.迭代器的代码实现
1 /* 2 @author :yinzhengjie 3 Blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/tag/Java%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/ 4 EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com 5 */ 6 7 package cn.org.yinzhengjie.note; 8 9 import java.util.ArrayList; 10 import java.util.Collection; 11 import java.util.Iterator; 12 13 public class IteratorDemo { 14 public static void main(String[] args) { 15 Collection<String> coll = new ArrayList<String>(); 16 coll.add("yinzhengjie"); 17 coll.add("尹正杰"); 18 coll.add("java"); 19 coll.add("python"); 20 coll.add("shell"); 21 coll.add("golang"); 22 23 //调用集合的方法iterator()获取出,Iterator接口的实现类的对象 24 Iterator<String> it1 = coll.iterator(); 25 26 System.out.println("第一种方式进行迭代:"); 27 //1>.用while循环遍历集合进行迭代 28 while(it1.hasNext()) { 29 System.out.println("\t"+it1.next()); 30 } 31 32 System.out.println("第二种方式进行迭代:"); 33 //2>.用for循环进行迭代(相对while循环更节省内存,因为it2是for局部遍历,而it1是main方法的变量) 34 for(Iterator<String> it2 = coll.iterator();it2.hasNext();) { 35 System.out.println("\t"+it2.next()); 36 } 37 38 System.out.println("第三种方式进行迭代:"); 39 //3>.用foreach循环(也叫增强for循环)继续迭代,需要JDK1.5版本以后才可以哟! 40 for (String string : coll) { 41 System.out.println("\t"+string); 42 } 43 } 44 } 45 46 47 /* 48 以上代码执行结果如下: 49 第一种方式进行迭代: 50 yinzhengjie 51 尹正杰 52 java 53 python 54 shell 55 golang 56 第二种方式进行迭代: 57 yinzhengjie 58 尹正杰 59 java 60 python 61 shell 62 golang 63 第三种方式进行迭代: 64 yinzhengjie 65 尹正杰 66 java 67 python 68 shell 69 golang 70 */
四.集合迭代过程中的转型
1 /* 2 @author :yinzhengjie 3 Blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/tag/Java%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/ 4 EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com 5 */ 6 7 package cn.org.yinzhengjie.note; 8 9 import java.util.ArrayList; 10 import java.util.Collection; 11 import java.util.Iterator; 12 13 public class IteratorDemo { 14 public static void main(String[] args) { 15 Collection<String> coll = new ArrayList<String>(); 16 coll.add("yinzhengjie"); 17 coll.add("尹正杰"); 18 coll.add("Java"); 19 20 Iterator it = coll.iterator(); 21 while(it.hasNext()){ 22 Object obj = it.next(); 23 if(obj instanceof String) { 24 String str = (String)obj; 25 System.out.println(str.length()); 26 } 27 } 28 } 29 } 30 31 32 /* 33 以上代码执行结果如下: 34 11 35 3 36 4 37 */
五.增强for循环遍历数组
增强for循环是JDK1.5以后出来的一个高级for循环,专门用来遍历数组和集合的,它的内部原理其实是一个Iterator迭代器,所以在遍历的过程中,不能对集合中的元素进行增删操作。JDK1.5版本后,出现新的接口,即“java.lang.Iterable”。只要实现“java.lang.Iterable”这个接口,就允许对象称为增强for循环(“foreach”语句,注意“foreach”并不是关键字哟!)的目标。
1 格式如下:
2 for( 数据类型 变量名:数组或这集合){
3 System.out.println(变量名);
4 }
如果只做遍历的话,推荐大家使用增强for循环, 因为for循环存在优点的同时也会存在缺点。
优点:代码少了,方便对容器遍历。
缺点:没有索引,不能操作容器里面的元素。
接下来我们用foreach来遍历数组和集合,代码如下:
1>.遍历数组
1 /* 2 @author :yinzhengjie 3 Blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/tag/Java%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/ 4 EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com 5 */ 6 7 package cn.org.yinzhengjie.note; 8 9 public class ForeachDemo { 10 public static void main(String[] args) { 11 12 String[] arr = {"yinzhengjie","org","cn"}; 13 for (String string : arr) { 14 System.out.println(string+"\t\t"+string.length()); 15 } 16 } 17 } 18 19 20 /* 21 以上代码执行结果如下: 22 yinzhengjie 11 23 org 3 24 cn 2 25 */
2>.遍历集合
1 /* 2 @author :yinzhengjie 3 Blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/tag/Java%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/ 4 EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com 5 */ 6 7 package cn.org.yinzhengjie.note; 8 9 import java.util.ArrayList; 10 import java.util.Collection; 11 12 class Student{ 13 private String name; 14 private int age; 15 public String getName() { 16 return name; 17 } 18 public void setName(String name) { 19 this.name = name; 20 } 21 public int getAge() { 22 return age; 23 } 24 public void setAge(int age) { 25 this.age = age; 26 } 27 public Student(String name, int age) { 28 super(); 29 this.name = name; 30 this.age = age; 31 } 32 public Student() { 33 super(); 34 } 35 //这里我们重写一下toString方法!方便System.out.pirntln在调用该对象的toString方法时不会去找Object的默认返回值。 36 public String toString() { 37 return this.name + "---" + this.age; 38 39 } 40 } 41 42 43 public class ForeachDemo { 44 public static void main(String[] args) { 45 //接口多态 46 Collection<Student> coll = new ArrayList<>(); 47 coll.add(new Student("yinzhengjie",18)); 48 coll.add(new Student("尹正杰",20)); 49 50 for (Student p : coll) { 51 System.out.println(p); 52 } 53 } 54 } 55 56 57 /* 58 以上代码执行结果如下: 59 yinzhengjie 11 60 org 3 61 cn 2 62 */
本文来自博客园,作者:尹正杰,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/p/8922611.html,个人微信: "JasonYin2020"(添加时请备注来源及意图备注,有偿付费)
当你的才华还撑不起你的野心的时候,你就应该静下心来学习。当你的能力还驾驭不了你的目标的时候,你就应该沉下心来历练。问问自己,想要怎样的人生。



