Java基础-异常(Exception)处理
Java基础-异常(Exception)处理
作者:尹正杰
版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任。
一.异常的概述
什么是异常?Java代码在运行时期发生的问题就是异常。在Java中,把异常信息封装成了一个类。当出现了问题时,就会创建异常类对象,并抛出异常相关信息(如异常信息出现的位置,原因等)。
二.异常的继承体系
在Java中使用Exception类来描述异常。Exception类及其子类是Throwable的一种形式,它指出了合理应用程序想要捕获的异常条件。查看Java的API文档我们可以发现Exception有继承关系,它的父类是Throwable。Throwable是Java语言中所有错误或异常的超类。另外,在异常Exception类中,有一个子类要特殊说明一下,RuntimeException子类,RuntimeException及其它的子类只能在Java程序运行过程中出现。
我们再来观察Throwable类,能够发现与异常Exception平级的有一个Error,它是Throwable的子类,它用来表示Java程序中可能会产生的严重错误。解决办法只有一个,修改代码避免Error错误的产生。下面是一个Error异常的案例:
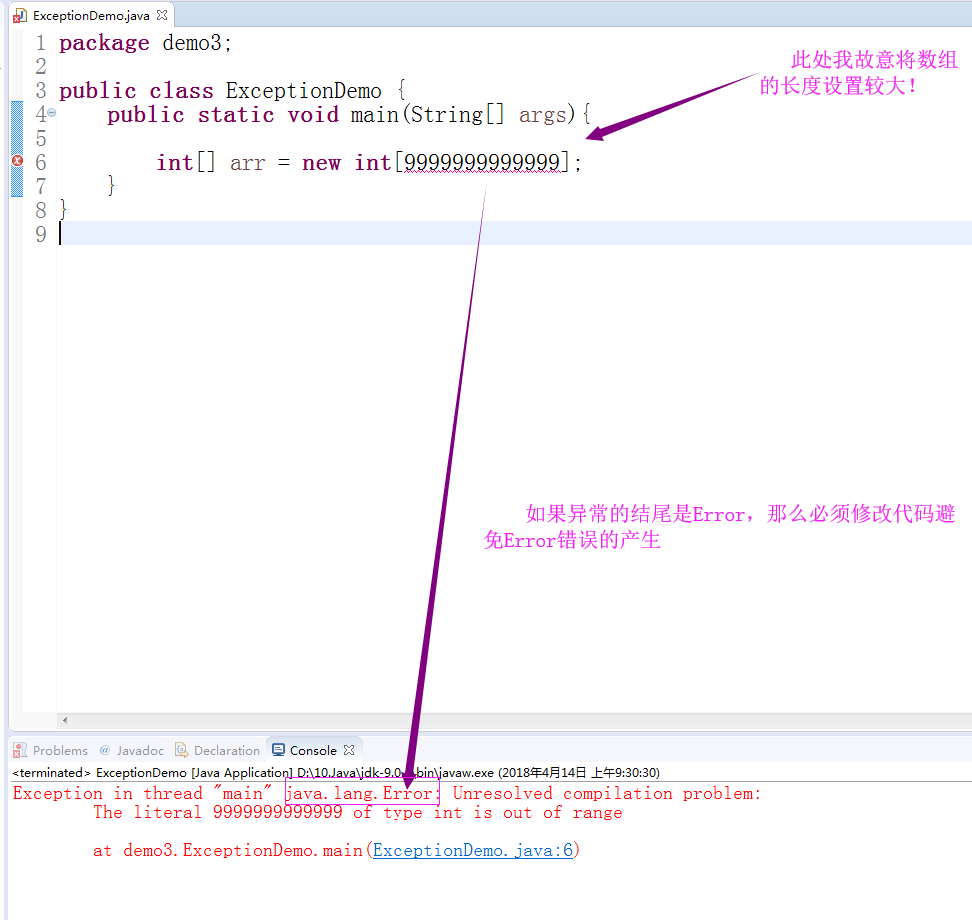
综上所述,异常继承体系可以大致做以下简要分类,此处并未列出全部的异常,请以Java的API文档为标准,下图只是为了方便记忆:

三.异常对象的产生原因和处理方式
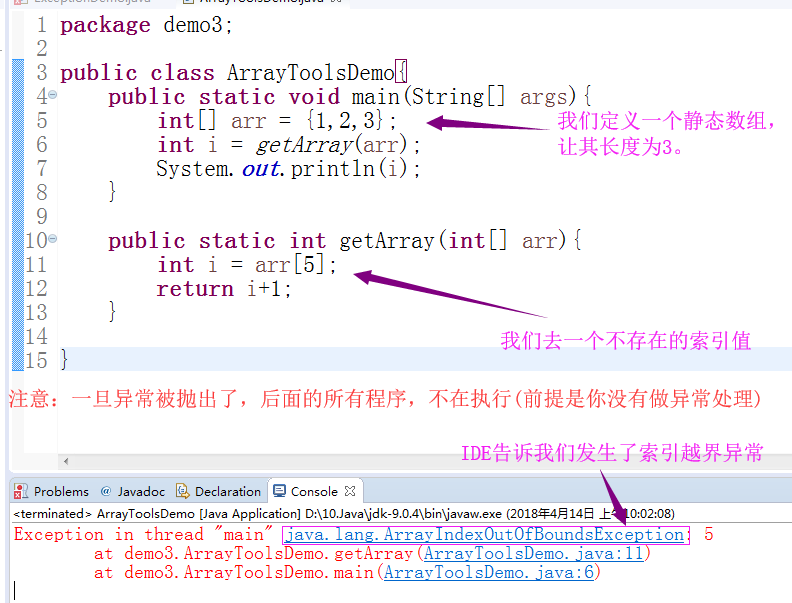
我们看见上面的代码是有异常抛出的,那么异常究竟是怎么抛出的呢?其实他大致分为以下几个步骤:
1>.JVM检测到异常
通过上面的学习,我们知道异常的祖宗其实就是Throwable类,在这个类下面很多个子类已经提前定义好了。在代码运行的时候,JVM是完全有能力检测到出现的异常信息(比如:ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException)。
2>.JVM创建异常对象
当JVM虚拟机检测到异常后,首先会创建异常对象(比如:new java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 5)。
3>.将异常抛给方的调用者
当创建好异常后,首先JVM虚拟机会检测程序手否对这种类型的异常有相应的处理方式,如果有,则按照业务逻辑执行,如果没有,就会将异常的对象进行抛出,最终会抛给方法的调用者。
4>.调用者继续抛出异常
从上面的代码中可以看到,getAway方法的调用者是main函数,因此会把异常抛给main方法,JVM虚拟机又会在main方法查找是否有异常处理的方式,如果没有对数组越界异常进行处理就将异常对象(java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 5)继续向上抛出,也就是main方法的调用者。而main方法运行在栈内存中,实际上是抛给了JVM虚拟机啦。
5>.JVM虚拟机收到异常后的事情
其实JVM虚拟机(最终异常的处理者)收到异常后,做了两件事情:
a>.将异常信息的内容输出,让程序员进行排错;
b>.杀死抛出异常的进程(也就是结束main方法);
四.方法内部抛出对象关键字(throw)
在编写程序时,我们必须要考虑程序出现问题的情况。比如,在定义方法时,方法需要接受参数。那么,当调用方法使用接受到的参数时,首选需要先对参数数据进行合法判断,数据若不合法,就应该告诉调用者,传递合法的数据进来。这时需要使用抛出异常的方式来告诉调用者。在Java中,提供了一个throw关键字,它用来抛出一个指定的异常对象。那么,抛出一个异常具体如何操作呢?
1 /* 2 @author :yinzhengjie 3 Blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/tag/Java%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/ 4 EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com 5 */ 6 7 public class ExceptionDemo{ 8 public static void main(String[] args){ 9 int[] arr = null; 10 // int[] arr1 = {}; 11 int i = getArray(arr); 12 System.out.println(i); 13 } 14 15 //对数组的最后索引*2,返回 16 public static int getArray(int[] arr){ 17 //对方法参数进行合法性的判断,进行判断是不是null 18 if(arr == null){ 19 //通过关键字throw抛出异常的形式,告诉调用者。 20 throw new RuntimeException("传递的数组不存在"); 21 } 22 23 24 //对数组进行判断,判断数组中是否储存在元素。 25 if(arr.length == 0){ 26 //以抛出异常的形式,告诉调用者,数组中没有元素 27 throw new RuntimeException("传递的是空数组"); 28 }else{ 29 int i = arr[arr.length-1]; 30 return i*2; 31 } 32 } 33 } 34 35 36 /* 37 以上代码执行结果如下: 38 Exception in thread "main" java.lang.RuntimeException: 传递的数组不存在 39 at ExceptionDemo.getArray(ExceptionDemo.java:20) 40 at ExceptionDemo.main(ExceptionDemo.java:11) 41 */ 42 43 44
五.异常方法声明关键字(throws)
throws用于在方法的声明上,标明此方法可能出现异常的类型,让调用者自己处理。换句话说,调用了一个抛出异常的方法,调用者就必须处理,若不处理,就会编译失败。
1 /* 2 @author :yinzhengjie 3 Blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/tag/Java%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/ 4 EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com 5 */ 6 7 public class ExceptionDemo{ 8 //main方法将异常抛给了JVM虚拟机。 9 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ 10 // int[] arr1 = null; 11 int[] arr2 = {}; 12 int i = getArray(arr2); 13 System.out.println(i); 14 } 15 16 //对数组的最后索引*2,通过throws关键字声明抛出的异常,调用者必须处理,否则编译失败! 17 public static int getArray(int[] arr) throws Exception{ 18 //对方法参数进行合法性的判断,进行判断是不是null 19 if(arr == null){ 20 //通过关键字throw抛出异常的形式,告诉调用者。 21 throw new Exception("传递的数组不存在"); 22 } 23 24 25 //对数组进行判断,判断数组中是否储存在元素。 26 if(arr.length == 0){ 27 //以抛出异常的形式,告诉调用者,数组中没有元素 28 throw new Exception("传递的是空数组"); 29 }else{ 30 int i = arr[arr.length-1]; 31 return i*2; 32 } 33 } 34 } 35 36 37 /* 38 以上代码执行结果如下: 39 Exception in thread "main" java.lang.Exception: 传递的是空数组 40 at ExceptionDemo.getArray(ExceptionDemo.java:28) 41 at ExceptionDemo.main(ExceptionDemo.java:12) 42 */ 43 44 45
六.Java中的异常处理方式
1>.异常处理格式
1 try{
2 被检测的代码;
3 可能出现异常的代码;
4 }catch(异常类名变量){
5 异常的处理方式;
6 循环,判断,调用方法,变量
7 }finally{
8 必须要执行的代码;
9 }
2>.try...异常处理

1 /* 2 @author :yinzhengjie 3 Blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/tag/Java%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/ 4 EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com 5 */ 6 7 public class ExceptionDemo{ 8 //main方法进行处理异常 9 public static void main(String[] args){ 10 int[] arr = null; 11 try{ 12 int i = getArray(arr); 13 System.out.println(i); 14 }catch(NullPointerException e) { 15 System.out.println(e); 16 } 17 System.out.println("Game Over!"); 18 } 19 20 //创建异常对象并抛出 21 public static int getArray(int[] arr) throws NullPointerException{ 22 //对方法参数进行合法性的判断,进行判断是不是null 23 if(arr == null){ 24 //手动抛出异常,抛出空指针异常 25 throw new NullPointerException("传递的数组不存在"); 26 } 27 28 //对数组的索引进行判断 29 if(arr.length < 3){ 30 //手动抛出异常,抛出数组的索引越界异常 31 throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("数组没有下标为3的索引"); 32 } 33 return arr[3]+1; 34 } 35 } 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 /* 43 以上代码执行结果如下: 44 java.lang.NullPointerException: 传递的数组不存在 45 Game Over! 46 47 48 */ 49 50 51
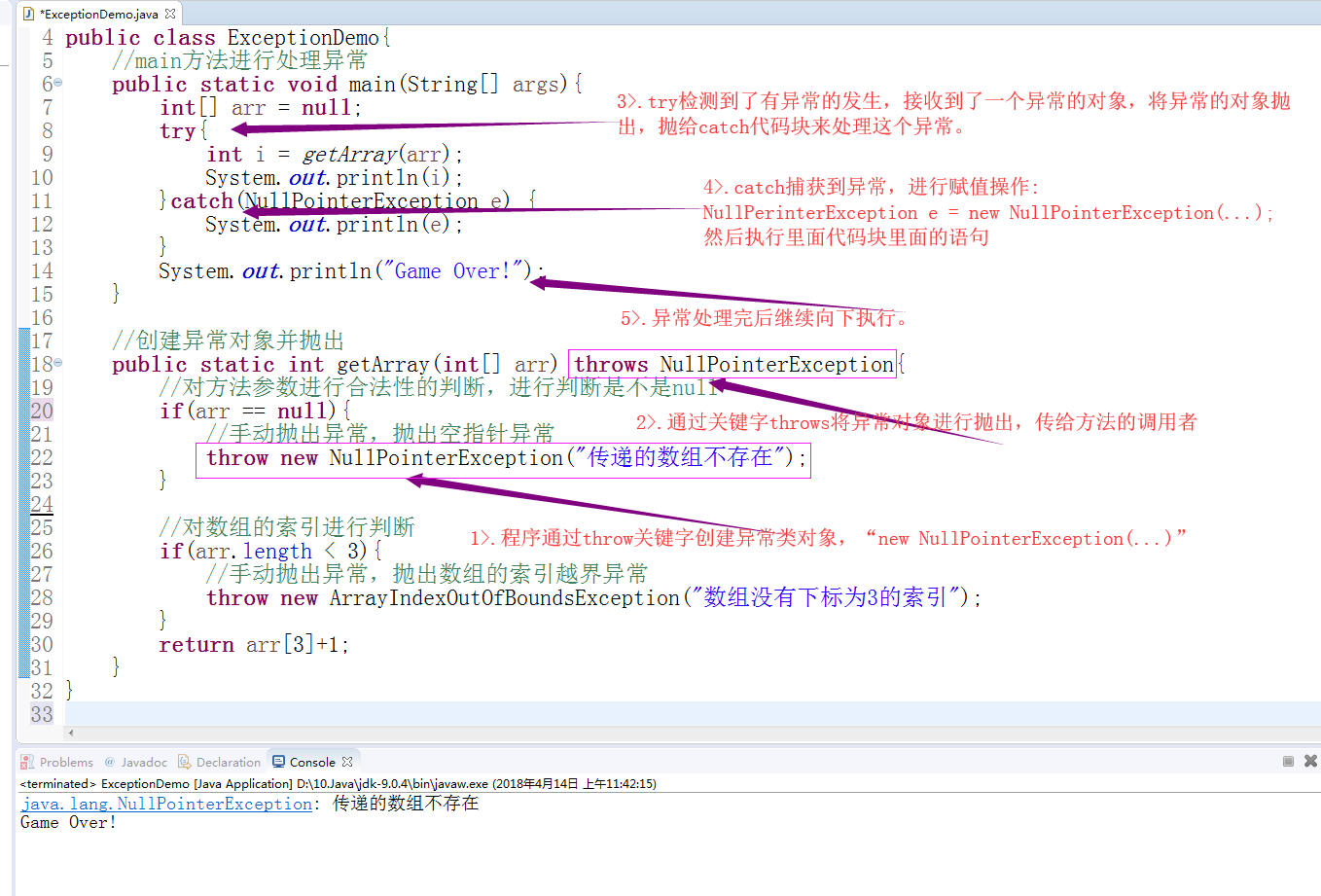
3>.异常多catch处理
平级异常,抛出的异常类之间,没有继承关系。上下级关系的异常,越高级的父类越应该写在下面。
1 /* 2 @author :yinzhengjie 3 Blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/tag/Java%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/ 4 EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com 5 */ 6 7 public class ExceptionDemo{ 8 //main方法进行处理异常 9 public static void main(String[] args){ 10 int[] arr = new int[0]; 11 try{ 12 int i = getArray(arr); 13 System.out.println(i); 14 }catch(NullPointerException e) { 15 System.out.println(e); 16 }catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) { 17 System.out.println(e); 18 }catch(Exception e){ //Exception应该放在最后一个catch,因为它包含上面2种异常。 19 System.out.println(e); 20 } 21 System.out.println("Game Over!"); 22 } 23 24 //可以抛出多个异常 25 public static int getArray(int[] arr) throws NullPointerException,ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException{ 26 //对方法参数进行合法性的判断,进行判断是不是null 27 if(arr == null){ 28 //手动抛出异常,抛出空指针异常 29 throw new NullPointerException("传递的数组不存在"); 30 } 31 32 //对数组的索引进行判断 33 if(arr.length < 3){ 34 //手动抛出异常,抛出数组的索引越界异常 35 throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("数组没有下标为3的索引"); 36 } 37 return arr[3]+1; 38 } 39 } 40 41 42 43 44 /* 45 以上代码执行结果如下: 46 java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 数组没有下标为3的索引 47 Game Over! 48 */
4>.finnal代码块
finally中的代码块无论程序是否有异常,程序都必须执行里面的代码(除非你在来到finally之前就用System.exit(0)退出程序啦!)。它一般用来释放IO资源,比如关闭文件或者关闭数据库的链接等等。
1 /* 2 @author :yinzhengjie 3 Blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/tag/Java%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/ 4 EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com 5 */ 6 7 public class ExceptionDemo{ 8 //main方法进行处理异常 9 public static void main(String[] args){ 10 int[] arr = new int[0]; 11 try { 12 function(100); 13 }catch(Exception e){ 14 System.out.println(e); 15 }finally { 16 System.out.println("必须要执行的代码!"); 17 } 18 System.out.println("Game Over!"); 19 } 20 21 //创建异常对象并抛出 22 public static void function(int a) throws Exception{ 23 if(a == 0) { 24 throw new Exception(); 25 }else { 26 System.out.println(a); 27 } 28 } 29 } 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 /* 37 以上代码执行结果如下: 38 100 39 必须要执行的代码! 40 Game Over! 41 */
5>.运行时期异常的特点
异常分为编译异常和运行时异常。
a>.编译异常
调用了抛出异常的方法(抛出编译异常需要在方法上用关键字throws声明异常),不处理的话就会编译不通过。处理方式有两种,第一种就是用try语句进行处理,或者是用throws语句丢给调用者去处理。

1 /* 2 @author :yinzhengjie 3 Blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/tag/Java%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/ 4 EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com 5 */ 6 7 public class ExceptionDemo{ 8 //main方法进行处理异常 9 public static void main(String[] args){ 10 int[] arr = new int[0]; 11 try { 12 function(100); 13 }catch(Exception e){ 14 System.out.println(e); 15 }finally { 16 System.out.println("必须要执行的代码!"); 17 } 18 System.out.println("Game Over!"); 19 } 20 21 //抛出编译异常需要在方法上用关键字throws声明异常 22 public static void function(int a) throws Exception{ 23 //创建编译异常 24 throw new Exception(); 25 } 26 } 27 28 29 30 31 /* 32 以上代码执行结果如下: 33 java.lang.Exception 34 必须要执行的代码! 35 Game Over! 36 37 */
b>.运行时期异常
抛出的异常是RuntimeException类,或者是他的子类。方法内部抛出的异常是运行异常,在方法声明上,不需要throws语句。不仅如此,运行时异常我们也不需要去用try语句或者throws语句去处理。

1 /* 2 @author :yinzhengjie 3 Blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/tag/Java%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/ 4 EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com 5 */ 6 7 public class ExceptionDemo{ 8 //main方法进行处理异常 9 public static void main(String[] args){ 10 //调用者,不需要处理异常 11 function(100); 12 } 13 //运行时异常可以不用在方法上用关键字throws声明。 14 public static void function(int a){ 15 //创建运行时异常 16 throw new RuntimeException(); 17 } 18 }
c>.运行异常的设计原因
运行异常,在编译的时候不能察觉出来,如果发生了运行异常,程序人员停止程序修改源代码。运行异常一旦发生,后面的代码没有执行的意义。比如我们看下面一段代码,估计身为老司机的你一眼就看出问题了,但是在编译的时候就不死活不报错,一旦你运行就会崩溃。
1 /* 2 @author :yinzhengjie 3 Blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/tag/Java%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/ 4 EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com 5 */ 6 7 8 public class ExceptionDemo{ 9 public static void main(String[] args){ 10 int[] arr = {1,2,3}; 11 function(arr); 12 } 13 14 public static void function(int[] arr){ 15 /* 此处我们对数组的第六个元素进行操作,但是如果传入的数组长度不到6, 16 *则继续向下执行代码就没有任何意义,程序员应该修改以下的代码逻辑性! 17 */ 18 if(arr[5] > 100) { 19 arr[5] = arr[5]/10; 20 }else { 21 arr[5] = arr[5]/3; 22 } 23 } 24 }
d>.运行异常的案例
定义一个方法,计算一个圆形面积。传递参数为负数时可以完成计算,但是违反了真实情况,因此我们可以将传入的数据进行判断,如果不符合现实情况就让程序崩溃掉,让调用者传入合法的数据信息,我们举一个简单的案例(求圆形的面积,你可以补充求周长来练习):
1 /* 2 @author :yinzhengjie 3 Blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/tag/Java%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/ 4 EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com 5 */ 6 7 8 public class ExceptionDemo{ 9 public static void main(String[] args){ 10 //传入一个负数去求面积,会导致程序崩溃 11 double d = getArea(-1); 12 System.out.printf("圆形的面积是:%f\n",d); 13 } 14 15 //定义方法,计算圆形的面积 16 public static double getArea(double r){ 17 //当传入的半径是非正数时,就让程序崩溃掉! 18 if(r <= 0) { 19 throw new RuntimeException("圆形不存在"); 20 } 21 return r*r*Math.PI; 22 23 } 24 } 25 26 27 28 /* 29 以上代码执行结果如下: 30 Exception in thread "main" java.lang.RuntimeException: 圆形不存在 31 at ExceptionDemo.getArea(ExceptionDemo.java:19) 32 at ExceptionDemo.main(ExceptionDemo.java:11) 33 34 */
6>.方法重写时候异常的处理
继承后,在子类重写父类方法的时候,异常处理结论:
a>.父类的方法如果抛出异常,子类重写后可以不抛出异常,也可以不抛出异常,但是,如果子类要抛,抛出的异常不能大于父类的异常(都指的是继承关系);
b>.父类的方法没有异常抛出,子类重写后也不能抛出异常;

1 /* 2 @author :yinzhengjie 3 Blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/tag/Java%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/ 4 EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com 5 */ 6 7 8 public class ExceptionDemo{ 9 public static void main(String[] args){ 10 11 } 12 } 13 14 class Father{ 15 public void function()throws Exception{ 16 17 } 18 } 19 20 class Son extends Father{ 21 //子类可以抛出异常也可以不抛出异常Exception 22 public void function(){ 23 24 } 25 }

1 /* 2 @author :yinzhengjie 3 Blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/tag/Java%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/ 4 EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com 5 */ 6 7 8 public class ExceptionDemo{ 9 public static void main(String[] args){ 10 11 } 12 } 13 14 class Father{ 15 public void function(){ 16 17 } 18 } 19 20 class Son extends Father{ 21 //子类可以抛出异常也可以不抛出异常Exception 22 public void function(){ 23 24 } 25 }
七.自定义异常
1>.Throwable类常用的方法
a>.String getMessage() :对异常信息的详细描述。
b>.String toString() :对异常信息的简短描述。
c>.void printStackTrace() :将异常信息追踪到标准的错误流,也是JVM虚拟机默认调用的方式,因为它的异常信息最详细。
1 /* 2 @author :yinzhengjie 3 Blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/tag/Java%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/ 4 EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com 5 */ 6 7 8 public class ExceptionDemo{ 9 public static void main(String[] args){ 10 try { 11 function(); 12 }catch(Exception e) { 13 System.out.println(e.getMessage()); 14 System.out.println(e.toString()); 15 e.printStackTrace(); //JVM默认调用的就是这个方法,异常信息最全。 16 } 17 18 } 19 20 21 public static void function() throws Exception{ 22 throw new Exception("异常啦!"); 23 } 24 25 } 26 27 28 29 /* 30 以上代码执行结果如下: 31 异常啦! 32 java.lang.Exception: 异常啦! 33 java.lang.Exception: 异常啦! 34 at ExceptionDemo.function(ExceptionDemo.java:22) 35 at ExceptionDemo.main(ExceptionDemo.java:11) 36 */
2>.自定义异常
1 /* 2 @author :yinzhengjie 3 Blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/tag/Java%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/ 4 EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com 5 */ 6 7 8 //自定义异常类 9 class MyException extends RuntimeException{ 10 11 MyException(String message){ 12 super(message); 13 } 14 } 15 16 public class ExceptionDemo{ 17 public static void main(String[] args){ 18 try{ 19 test(); 20 }catch(MyException e){ 21 System.out.println(e.getMessage()); 22 //.... 23 } 24 } 25 26 public static void test() throws MyException { 27 throw new MyException("发生自定义异常!"); 28 } 29 } 30 31 32 33 /* 34 以上代码执行结果如下: 35 发生自定义异常! 36 */
本文来自博客园,作者:尹正杰,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/p/8825696.html,个人微信: "JasonYin2020"(添加时请备注来源及意图备注,有偿付费)
当你的才华还撑不起你的野心的时候,你就应该静下心来学习。当你的能力还驾驭不了你的目标的时候,你就应该沉下心来历练。问问自己,想要怎样的人生。




