MyBatis 源码篇-DataSource
本章介绍 MyBatis 提供的数据源模块,为后面与 Spring 集成做铺垫,从以下三点出发:
- 描述 MyBatis 数据源模块的类图结构;
- MyBatis 是如何集成第三方数据源组件的;
- PooledConnection 设计初衷猜想;
类图结构
MyBatis 数据源部分的代码在 datasource 目录下。
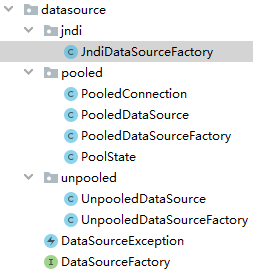
提供了三种类型的数据源实现:unpooled(没有连接池)、pooled(MyBatis 自身实现的连接池)、jndi(依赖 JNDI 服务)
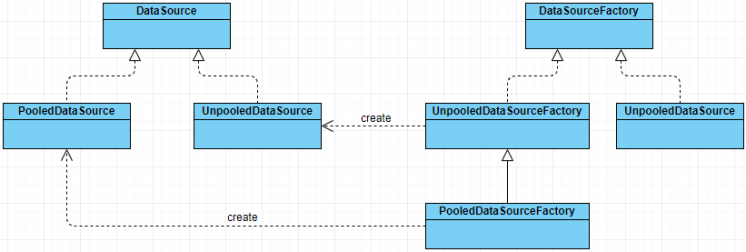
MyBatis 提供了两个 javax.sql.DataSource 接口实现,分别是 PooledDataSource 和 UnpooledDataSource。MyBatis 使用不同的 DataSourceFactory 接口实现创建不同类型的 DataSource。这是工厂方法的典型应用。
MyBatis 数据源的配置方式参考官方文档:https://mybatis.org/mybatis-3/zh/configuration.html#environments
MyBatis 数据源类的具体描述参考《MyBatis 技术内幕》的 2.6 章,这里只简单介绍各个类的主要作用。
- UnpooledDataSourceFactory 类用于创建 UnpooledDataSource 对象,并初始化 UnpooledDataSourceFactory.dataSource 字段,UnpooledDataSourceFactory.setProperties() 方法会完成对 UnpooledDataSource 对象的配置。
- PooledDataSourceFactory 继承了 UnpooledDataSourceFactory,但并没有覆盖 setProperties() 方法和 getDataSource() 方法。两者唯一的区别是 PooledDataSourceFactory 的构造函数会将其 dataSource 字段初始化为 PooledDataSource 对象。
- UnpooledDataSource 实现了 javax.sql.DataSource 接口中定义的 getConnection() 方法及其重载方法,用于获取数据库连接。每次通过 UnpooledDataSource.getConnection() 方法获取数据库连接时都会创建一个新连接。
- PooledDataSource 实现了简易数据库连接池的功能,它创建新数据库连接的功能是依赖其中封装的 UnpooledDataSource 对象实现的。PooledDataSource 并不会直接管理 java.sql.Connection 对象,而是管理 PooledConnection 对象。
- PooledConnection 中封装了真正的数据库连接对象(java.sql.Connection)以及其代理对象,这里的代理对象是通过 JDK 动态代理产生的。
- PoolState 是用于管理 PooledConnection 对象状态的组件,它通过两个 List 集合分别管理空闲状态的连接和活跃状态的连接。
集成第三方框架
MyBatis 数据源模块集成第三方数据源组件比较简单,只需要添加对应的工厂实现类,新的数据源就可以被 MyBatis 使用,不必修改已有的代码。工厂方法模式符合“开-闭”原则。
比如我们要引入 C3P0 数据源,只需要新增工厂实现类:
public class C3P0DataSourceFactory extends UnpooledDataSourceFactory { public C3P0DataSourceFactory() { this.dataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource(); } }
在 MyBatis 配置文件中添加相应的数据源配置:
<dataSource type="org.myproject.C3P0DataSourceFactory"> <property name="driver" value="org.postgresql.Driver"/> <property name="url" value="jdbc:postgresql:mydb"/> <property name="username" value="postgres"/> <property name="password" value="root"/> </dataSource>
这样我们就可以在我们的项目中使用新的数据源了。
在 MyBatis 加载配置文件的时候,会解析配置文件,根据 dataSource 节点配置的内容生成相应的工厂类对象。XMLConfigBuilder#dataSourceElement 源码如下所示:
private DataSourceFactory dataSourceElement(XNode context) throws Exception { if (context != null) { String type = context.getStringAttribute("type"); Properties props = context.getChildrenAsProperties(); // 根据type属性中配置的类路径生成对应的数据源工厂类 DataSourceFactory factory = (DataSourceFactory) resolveClass(type).newInstance(); // 为数据源设置配置的属性 factory.setProperties(props); return factory; } throw new BuilderException("Environment declaration requires a DataSourceFactory."); }
PooledConnection 设计初衷猜想
PooledConnection 的实现如下:
class PooledConnection implements InvocationHandler { private static final String CLOSE = "close"; private static final Class<?>[] IFACES = new Class<?>[] { Connection.class }; private final int hashCode; private final PooledDataSource dataSource; private final Connection realConnection; private final Connection proxyConnection; private long checkoutTimestamp; private long createdTimestamp; private long lastUsedTimestamp; private int connectionTypeCode; private boolean valid; /* * Constructor for SimplePooledConnection that uses the Connection and PooledDataSource passed in * * @param connection - the connection that is to be presented as a pooled connection * @param dataSource - the dataSource that the connection is from */ public PooledConnection(Connection connection, PooledDataSource dataSource) { this.hashCode = connection.hashCode(); this.realConnection = connection; this.dataSource = dataSource; this.createdTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis(); this.lastUsedTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis(); this.valid = true; // 创建代理对象 this.proxyConnection = (Connection) Proxy.newProxyInstance(Connection.class.getClassLoader(), IFACES, this); } /* * Getter for the *real* connection that this wraps * * @return The connection */ public Connection getRealConnection() { return realConnection; } /* * Getter for the proxy for the connection * * @return The proxy */ public Connection getProxyConnection() { return proxyConnection; } /* * Required for InvocationHandler implementation. * * @param proxy - not used * @param method - the method to be executed * @param args - the parameters to be passed to the method * @see java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler#invoke(Object, java.lang.reflect.Method, Object[]) */ @Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { String methodName = method.getName(); if (CLOSE.hashCode() == methodName.hashCode() && CLOSE.equals(methodName)) { dataSource.pushConnection(this); return null; } else { try { if (!Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) { // issue #579 toString() should never fail // throw an SQLException instead of a Runtime checkConnection(); } return method.invoke(realConnection, args); } catch (Throwable t) { throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t); } } } ...... }
PooledConnection 类中封装了真正的数据库连接对象(java.sql.Connection)以及其代理对象。PooledDataSource.getConnection() 方法获取的是 proxyConnection 对象,代码实现如下所示。
@Override public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException { return popConnection(dataSource.getUsername(), dataSource.getPassword()).getProxyConnection(); } @Override public Connection getConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException { return popConnection(username, password).getProxyConnection(); }
PooledConnection 类为什么要这么设计?一般要强化 Connection 类,添加一些我们自定义的功能,我们会采用装饰器模式,为什么要使用动态代理呢?
因为直接采用装饰器模式,有点麻烦,我们需要把 Connection 类中所有需要用到的方法都要在 PooledConnection 类中暴露出去,说白了就是要重写一遍,比较麻烦,而采用动态代理模式,所有的方法调用都会转到 invoke() 方法执行,我们只需要对特定的方法做一下处理就行,比如这里只对 Connection 的 close() 方法做了特殊处理,其他方法都直接执行 Connection 类中方法。



