javafx-框架篇
javafx 学习,第一章,框架篇#
为什么要开 gui 这个坑呢?单纯的就是学 Java 漏洞头有点晕,想换个口味,主要目的就是想着可以做一个 poc/exp 工具。
接着为什么要用 Javafx 而不用 swing 呢?因为俺乐意。.
新建 maven 项目#
首先新建一个 maven 项目,我选的 jdk 是 Java8,因为 Java8 自带 javafx,接着新建一个类名为 GuiDemo,继承 Application 类,代码如下:
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
public class GuiDemo extends Application {
@Override
public void start(Stage primaryStage) throws Exception {
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
launch(args);
}
}
上面继承的 Application 类是抽象类,必须重写 start 方法,我们 gui 的东西都在 start 方法里面写。然后就是一个 main 方法.
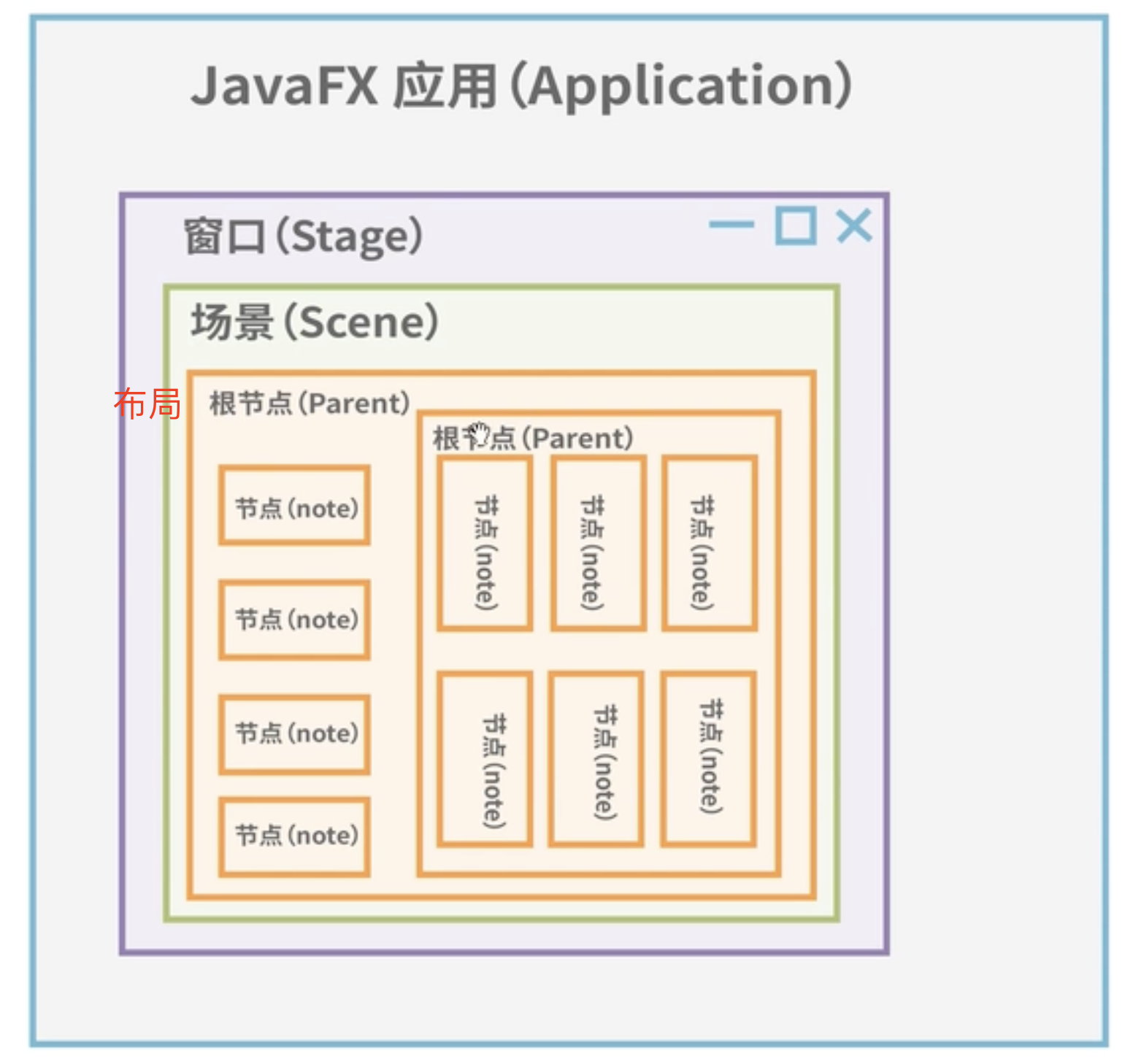
javafx 架构#
一个窗口/舞台(stage)只能有一个场景(scene),一个场景里可以放根节点(一般都是布局(Pane)),布局(Pane)可以相互嵌套,布局里面存放节点,比如:label、button 等
代码运行顺序:main 方法--》Application 的 launch()方法--》start 方法
代码示例:
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.control.Label;
import javafx.scene.layout.BorderPane;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
public class GuiDemo extends Application { //创建一个GuiDemo类,GuiDemo继承Application类
@Override
public void start(Stage primaryStage) throws Exception {
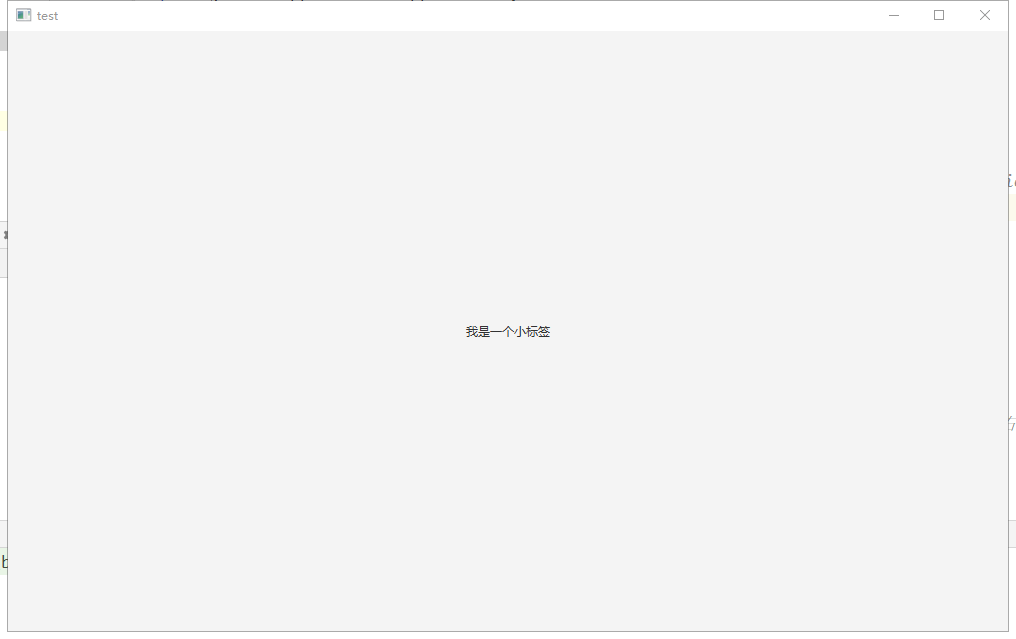
//标签
Label label = new Label("我是一个小标签");
//布局
BorderPane borderPane = new BorderPane(label);//borderPane布局会把场景分成上下左右中,默认放在中间
//场景
Scene scene = new Scene(borderPane, 1000, 600);
//主要的舞台/窗口
primaryStage.setTitle("test");
/*窗口设置场景*/
primaryStage.setScene(scene);
primaryStage.show();
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
launch(args);
}
}
运行结果:
接着细细来看
Javafx 的 Stage#
Stage 类是一个窗口/舞台
常用方法:
/*主要的舞台/窗口*/
primaryStage.setTitle("HelloJavaFX");
/*设置icon*/
primaryStage.getIcons().add(new Image("images/icon.png"));
/*窗口设置场景*/
primaryStage.setScene(scene);
primaryStage.show();
关闭窗口时确认框:
primaryStage.setOnCloseRequest(event -> {
event.consume();
Alert alert = new Alert(Alert.AlertType.CONFIRMATION);
alert.setTitle("退出程序");
alert.setHeaderText(null);
alert.setContentText("确认退出程序?");
Optional<ButtonType> result = alert.showAndWait();
if(result.get()==ButtonType.OK){
Platform.exit();
}
});
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.application.Platform;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.control.Alert;
import javafx.scene.control.ButtonType;
import javafx.scene.control.Label;
import javafx.scene.layout.BorderPane;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
import java.util.Optional;
public class GuiDemo extends Application { //创建一个GuiDemo类,GuiDemo继承Application类
@Override
public void start(Stage primaryStage) throws Exception {
//标签
Label label = new Label("我是一个小标签");
//布局
BorderPane borderPane = new BorderPane(label);//borderPane布局会把场景分成上下左右中,默认放在中间
//场景
Scene scene = new Scene(borderPane, 1000, 600);
//主要的舞台/窗口
primaryStage.setTitle("test");
/*窗口设置场景*/
primaryStage.setScene(scene);
primaryStage.setOnCloseRequest(event -> {
event.consume();
Alert alert = new Alert(Alert.AlertType.CONFIRMATION);
alert.setTitle("退出程序");
alert.setHeaderText(null);
alert.setContentText("确认退出程序?");
Optional<ButtonType> result = alert.showAndWait();
if (result.get() == ButtonType.OK) {
Platform.exit();
}
});
primaryStage.show();
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
launch(args);
}
}
javafx 的 Scene#
Scene scene = new Scene(borderPane,1000,600);//在一个场景放入一个节点树的根节点(布局),然后是宽高
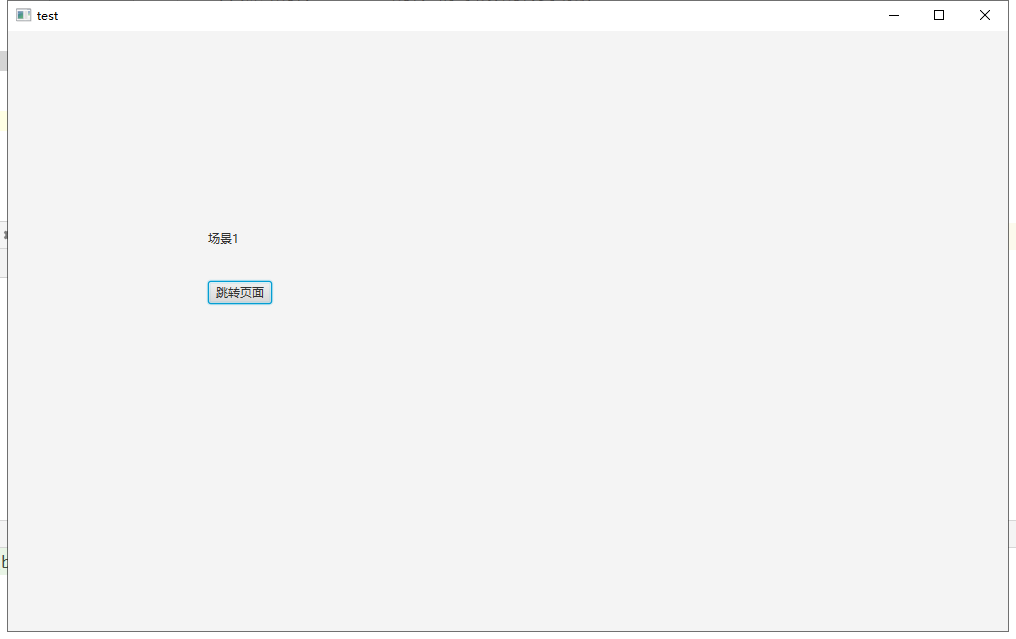
例子,实现点击按钮跳转场景
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.application.Platform;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.control.Alert;
import javafx.scene.control.Button;
import javafx.scene.control.ButtonType;
import javafx.scene.control.Label;
import javafx.scene.layout.AnchorPane;
import javafx.scene.layout.BorderPane;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
import java.util.Optional;
public class GuiDemo extends Application { //创建一个GuiDemo类,GuiDemo继承Application类
@Override
public void start(Stage primaryStage) throws Exception {
//标签
Label label1 = new Label("场景1");
label1.setLayoutX(200);
label1.setLayoutY(200);
//按钮
Button button1 = new Button("跳转页面");
button1.setLayoutX(200);
button1.setLayoutY(250);
//标签
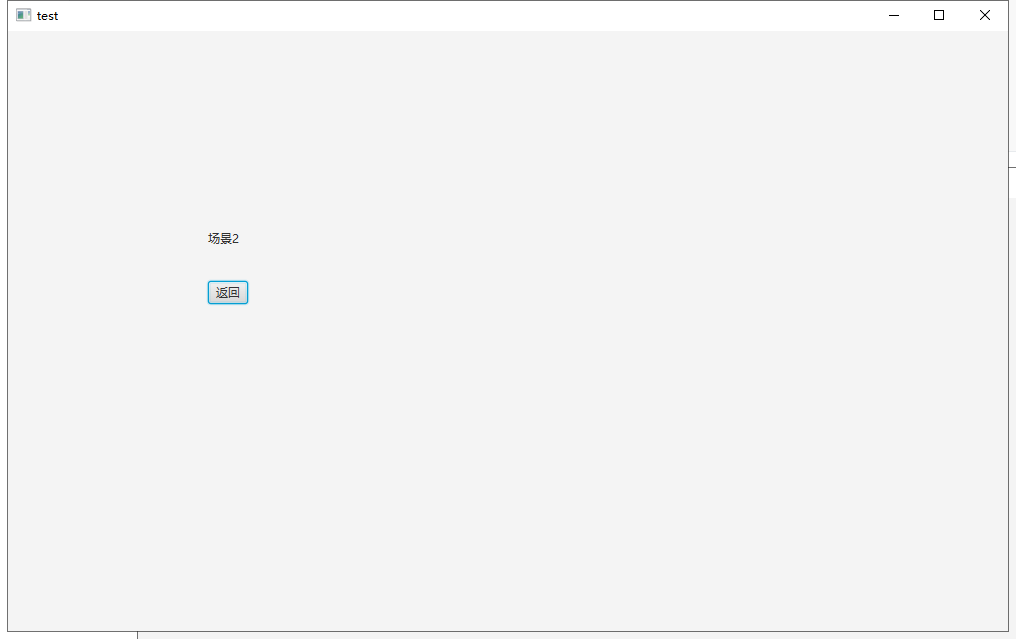
Label label2 = new Label("场景2");
label2.setLayoutX(200);
label2.setLayoutY(200);
//按钮
Button button2 = new Button("返回");
button2.setLayoutX(200);
button2.setLayoutY(250);
//布局1
AnchorPane pane1 = new AnchorPane();
pane1.getChildren().addAll(label1, button1);
//布局2
AnchorPane pane2 = new AnchorPane();
pane2.getChildren().addAll(label2, button2);
//场景
Scene scene1 = new Scene(pane1, 1000, 600);
Scene scene2 = new Scene(pane2, 1000, 600);
//点击跳转button1-跳转 的时候,跳转到场景2
button1.setOnAction(event -> {
primaryStage.setScene(scene2);
});
//点击按钮2 button2-返回 的时候,返回到场景1
button2.setOnAction(event -> {
primaryStage.setScene(scene1);
});
//主要的舞台/窗口
primaryStage.setTitle("test");
primaryStage.setScene(scene1);//这里相当于默认场景是场景1
/*窗口设置场景*/
primaryStage.show();
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
launch(args);
}
}
javafx 的 Pane#
Pane
布局的父类,使用坐标定位,类似绝对布局,子控件使用layoutX,layoutY定位
BorderPane边框布局
将界面分割成上中下,中间部分又分成左中右,一共五部分,通过<top><left><center><right><bottom>来设置内容。
HBox 水平布局
将控件水平排列,不换行。
VBox 垂直布局
将控件垂直排列,不换行。
FlowPane 流式布局
默认水平排列,排满一行之后会换行,提供属性设置水平还是垂直
GridPane 网格布局
类似HTML的table布局,按表格分布,可以合并单元格, columnConstraints定义列,rowConstraints定义行。
AnchorPane 锚点布局
类似相对布局,可以指定子控件在布局的左下角等位置,可设置相对距离
ScrollPane 滚动布局
提供滚动内容。
StackPane 堆栈布局
所有子控件叠加在一起,可单独指定某个子控件位置。
TilePane 磁贴布局
把所有子控件放在一个网格中,每格大小一样,节点可以按水平或垂直排列,排到边界处会自动换行。
DialogPane 对话布局
弹窗。
javafx 的 Note#
/*标签*/
Label label = new Label("场景1");
label.setLayoutX(200);
label.setLayoutY(200);
label.setStyle("-fx-background-color: blue;-fx-border-color: red;-fx-border-width: 2px");
/*设置节点的长宽*/
label.setPrefWidth(200);
label.setPrefHeight(50);
/*设置节点内容居中*/
label.setAlignment(Pos.CENTER);
/*设置透明度*/
label.setOpacity(0.5);
javafx 事件驱动#
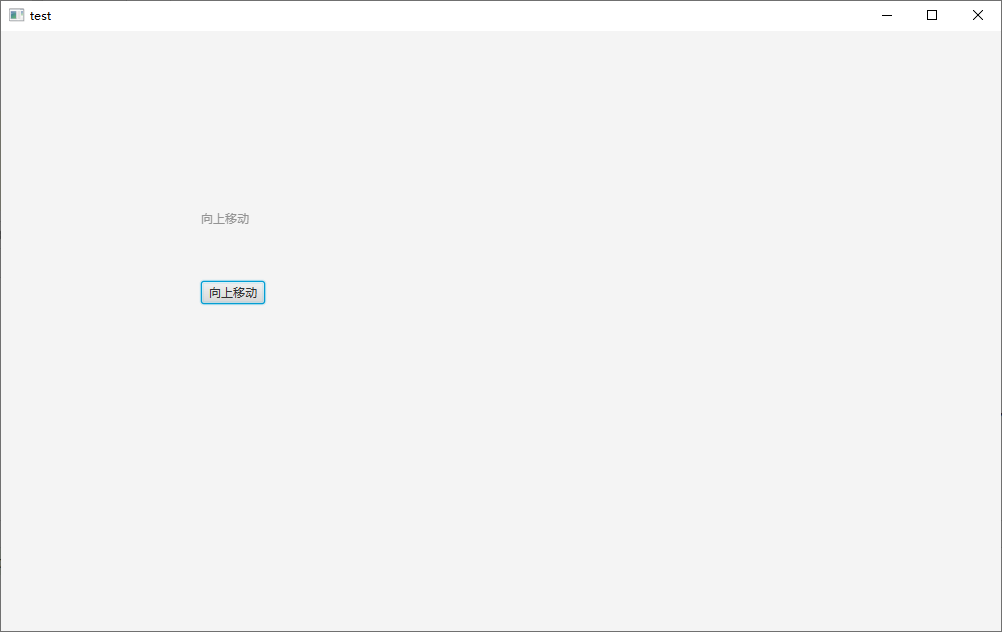
例子如下:设置点击鼠标 label 向上,按键盘向下,label 向下
鼠标点击时间:setOnAction 方法,该方法的参数需要 EventHandler<ActionEvent>() 对象
键盘释放事件:setOnKeyReleased 方法,需要 EventHandler<KeyEvent>() 对象
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.event.ActionEvent;
import javafx.event.EventHandler;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.control.*;
import javafx.scene.input.KeyCode;
import javafx.scene.input.KeyEvent;
import javafx.scene.layout.AnchorPane;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
public class GuiDemo extends Application {//创建一个GuiDemo类,GuiDemo继承Application类
@Override
public void start(Stage primaryStage) throws Exception {
//标签
Label label1 = new Label("向上移动");
label1.setLayoutX(200);
label1.setLayoutY(200);
label1.setOpacity(0.5);
//按钮
Button button1 = new Button("向上移动");
button1.setLayoutX(200);
button1.setLayoutY(250);
//布局1
AnchorPane pane1 = new AnchorPane();
pane1.getChildren().addAll(label1, button1);
//场景
Scene scene1 = new Scene(pane1, 1000, 600);
//设置按钮鼠标点击事件
button1.setOnAction(new EventHandler<ActionEvent>() {
@Override
public void handle(ActionEvent event) {
label1.setLayoutY(label1.getLayoutY() - 10);
}
});
//设置场景键盘事件
scene1.setOnKeyReleased(new EventHandler<KeyEvent>() {
@Override
public void handle(KeyEvent event) {
/*获取键盘事件*/
KeyCode code = event.getCode();
/*判断是不是向下*/
if (code.equals(code.DOWN)) {
label1.setLayoutY(label1.getLayoutY() + 10);
}
}
});
//主要的舞台/窗口
primaryStage.setTitle("test");
primaryStage.setScene(scene1);
/*窗口设置场景*/
primaryStage.show();
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
launch(args);
}
}
那么如何把项目打包成一个 jar 文件呢?#
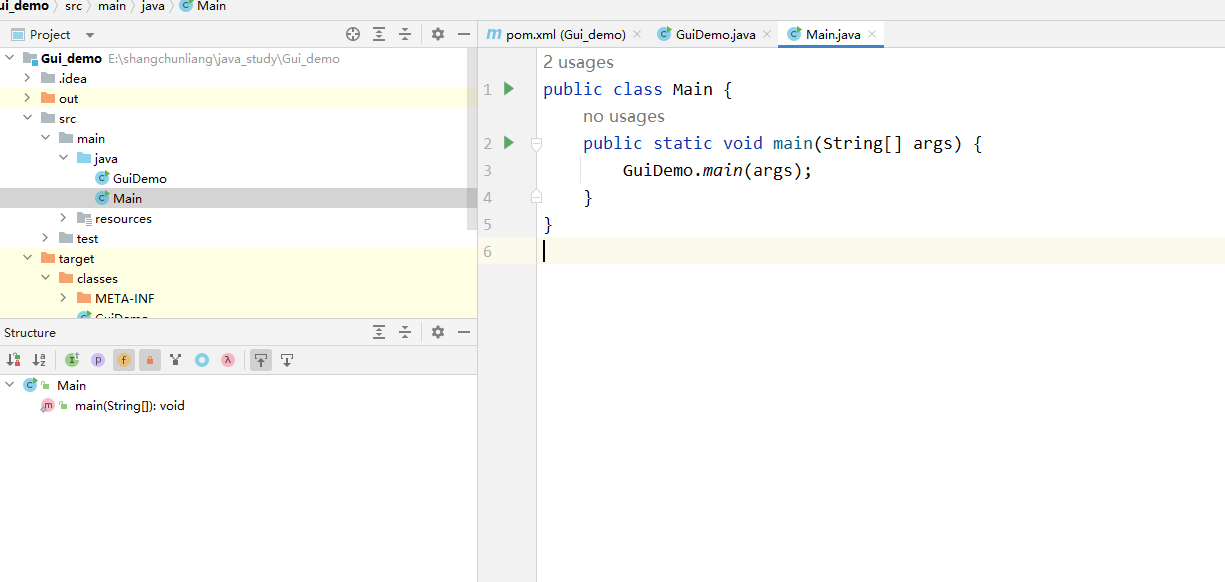
首先需要创建一个 main 类,作为入口
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
GuiDemo.main(args);
}
}
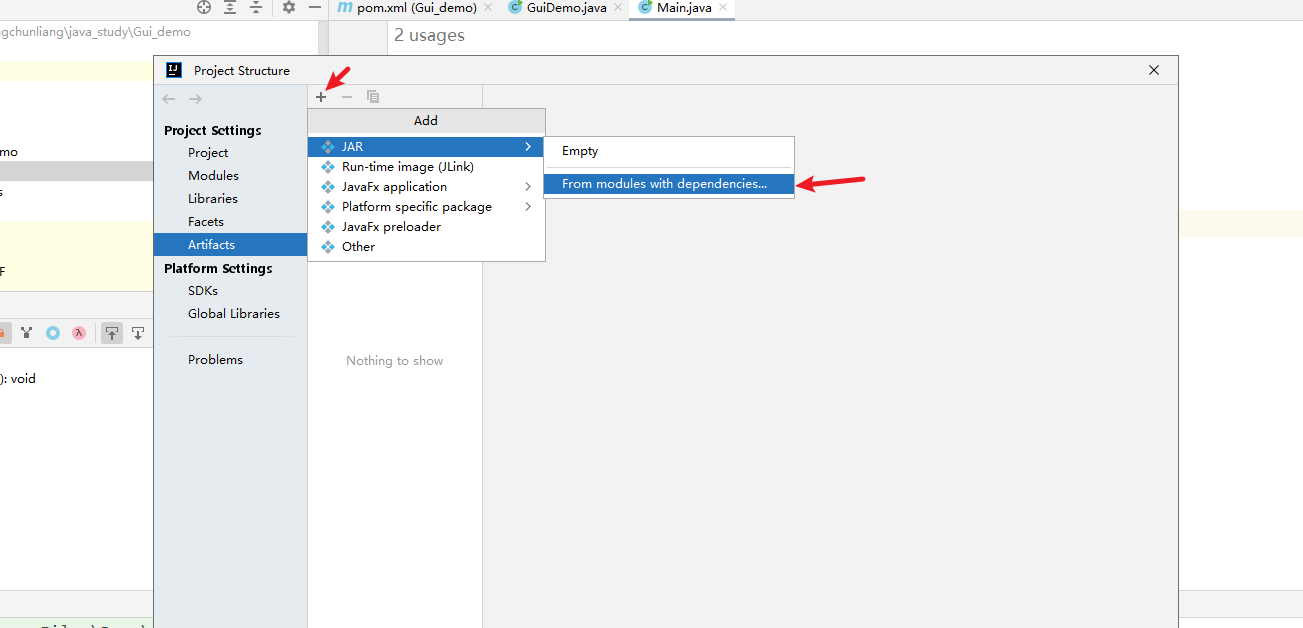
点击 Project Structure
其他默认即可
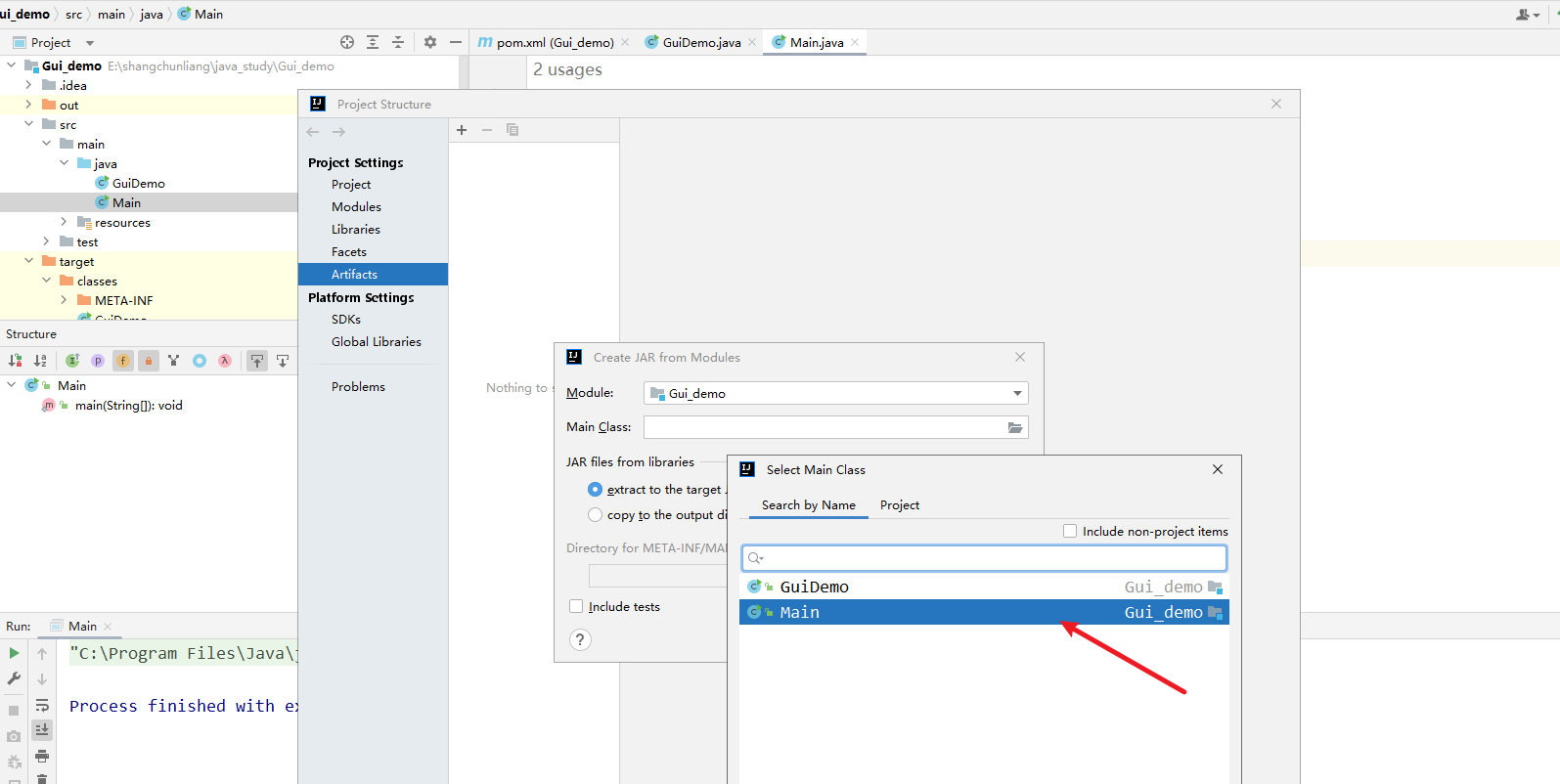
接着点击 build——》Build Artifacts ,点击 build 即可
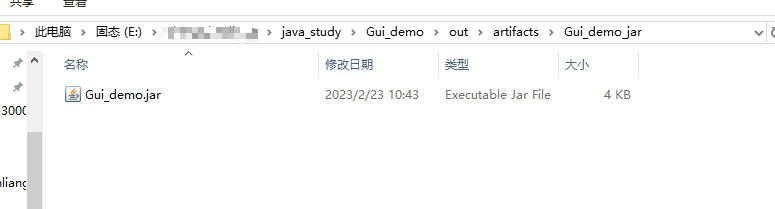
build 完后,在项目的 \out\artifacts\Gui_demo_jar
运行方式鼠标双击或者 java -jar xxx.jar 即可。








【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 全程不用写代码,我用AI程序员写了一个飞机大战
· DeepSeek 开源周回顾「GitHub 热点速览」
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· MongoDB 8.0这个新功能碉堡了,比商业数据库还牛
· .NET10 - 预览版1新功能体验(一)